Hibernate入门
Hibernate
主流 ORM 框架 Object Relation Mapping 对象关系映射,将⾯向对象映射成⾯向关系。
如何使用
- 导入相关依赖
- 创建 Hibernate 配置文件
- 创建实体类
- 创建实体类关系映射文件
- 实体关系映射文件注册到 Hibernate 的配置文件
- 调用 Hibernate API 完成操作
- pom.xml 中需要配置 resource
具体操作
1、创建 Maven 工程,pom.xml
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-core</artifactId>
<version>5.4.27.Final</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.oracle</groupId>
<artifactId>ojdbc6</artifactId>
<version>11.2.0.4.0-atlassian-hosted</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.javassist</groupId>
<artifactId>javassist</artifactId>
<version>3.27.0-GA</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13</version
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-simple</artifactId>
<version>1.7.25</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2、创建hibernate.cfg.xml
核心配置:session-factory
SessionFactory:针对单个数据库映射经过编译的内存镜像文件,将数据库转换为一个java可以识别的镜像文件。
构件 SessionFactory 非常耗费资源,所以通常一个工程只需要创建一个 SessionFactory。
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='UTF-8'?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<!-- 数据源配置 -->
<property name="connection.driver_class">oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver</property>
<property name="connection.url">jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:orcl</property>
<property name="connection.username">system</property>
<property name="connection.password">123456</property>
<!--方言-->
<property name="dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.Oracle10gDialect</property>
<!--可选项打印sql语句-->
<property name="show_sql">true</property>
<!--格式化SQL语句-->
<property name="format_sql">true</property>
<!--是否自动生成数据表-->
<property name="hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto"/>
<!--加载映射文件-->
<mapping resource="mapper/Electronic.hbm.xml"/>
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>
3、创建实体类
package com.hua.hibernate.pojo;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.StringJoiner;
/**
* @author xiaohuashen
* @date 2021/1/4 10:51
*/
public class Electronic implements Serializable {
private Integer elId;
private String elType;
private Integer price;
private Date elDate;
public Integer getElId() {
return elId;
}
public Electronic setElId(Integer elId) {
this.elId = elId;
return this;
}
public String getElType() {
return elType;
}
public Electronic setElType(String elType) {
this.elType = elType;
return this;
}
public Integer getPrice() {
return price;
}
public Electronic setPrice(Integer price) {
this.price = price;
return this;
}
public Date getElDate() {
return elDate;
}
public Electronic setElDate(Date elDate) {
this.elDate = elDate;
return this;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return new StringJoiner(", ", Electronic.class.getSimpleName() + "[", "]")
.add("elId=" + elId)
.add("elType='" + elType + "'")
.add("price=" + price)
.add("elDate=" + elDate)
.toString();
}
}
4、创建实体关系映射文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-mapping package="com.hua.hibernate.pojo">
<class name="Electronic" table="Electronic">
<!--映射主键-->
<id name="elId" column="El_ID">
<!--指定主键生成策略-->
<generator class="increment"/>
</id>
<!--映射非主键-->
<property name="elType" column="El_TYPE"/>
<property name="price" column="El_PRICE"/>
<property name="elDate" column="El_DATE"/>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
5、实体关系映射文件注册到 Hibernate 的配置文件中 hibernate.cfg.xml。
<!--加载映射文件-->
<mapping resource="mapper/Electronic.hbm.xml"/>
6、使用Hibernate API 完成数据操作
import com.hua.hibernate.pojo.Electronic;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
import org.hibernate.query.Query;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.List;
//创建Configuration
private final Configuration configuration = new Configuration().configure();
//获取SessionFactory
private final SessionFactory sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory();
//获取Session
private final Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
//创建事务
private final Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction();
//实体类
Electronic electronic = new Electronic();
@Test
public void insert() {
electronic.setElId(1001);
electronic.setElType("CDMA-1");
electronic.setPrice(666);
try {
electronic.setElDate(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd").parse("2021-11-25"));
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
session.save(electronic);
transaction.commit();
session.close();
}
@Test
public void update() {
electronic = session.get(Electronic.class, 1);
session.update(electronic);
transaction.commit();
System.out.println("成功");
session.close();
}
}
7、pom.xml 中需要配置 resource。
<build>
<!-- 编译配置文件-->
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/java</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
</includes>
</resource>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resources</directory>
</resource>
</resources>
</build>
级联操作
1、一对多关系
客户和订单:每个客户可以购买多个产品,⽣成多个订单,但是⼀个订单只能属于⼀个客户,所以客户是⼀,订单是多。
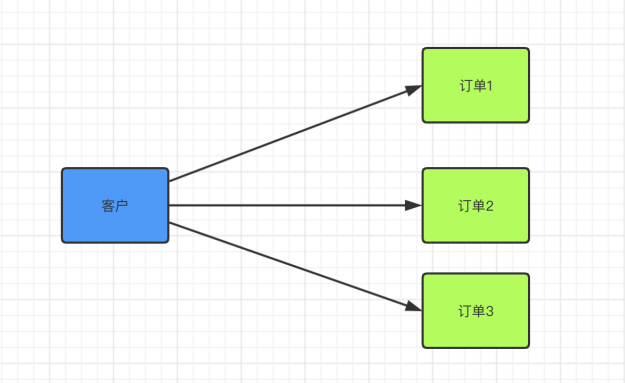
数据库中⼀的⼀⽅是主表,多的⼀⽅时候从表,通过主外键关系来维护。
⾯向对象中
package com.hua.hibernate.pojo;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.StringJoiner;
/**
* 顾客实体类
* @author xiaohuashen
* @date 2021/1/7 16:16
*/
public class Customer implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String name;
/**
* 一个顾客有多个订单
*/
private Set<Orders> orders;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public Customer setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
return this;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public Customer setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
return this;
}
public Set<Orders> getOrders() {
return orders;
}
public Customer setOrders(Set<Orders> orders) {
this.orders = orders;
return this;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return new StringJoiner(", ", Customer.class.getSimpleName() + "[", "]")
.add("id=" + id)
.add("name='" + name + "'")
.add("orders=" + orders)
.toString();
}
}
package com.hua.hibernate.pojo;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.StringJoiner;
/**
* 订单实体类
* @author xiaohuashen
* @date 2021/1/7 16:20
*/
public class Orders implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Customer customer;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public Orders setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
return this;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public Orders setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
return this;
}
public Customer getCustomer() {
return customer;
}
public Orders setCustomer(Customer customer) {
this.customer = customer;
return this;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return new StringJoiner(", ", Orders.class.getSimpleName() + "[", "]")
.add("id=" + id)
.add("name='" + name + "'")
.add("customer=" + customer)
.toString();
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Orders orders = (Orders) o;
return id.equals(orders.id) && Objects.equals(name, orders.name) && Objects.equals(customer, orders.customer);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(id, name, customer);
}
}
2、多对的关系
学生选课:一门课程可以被多个学生选择,一个学生可以选择多门课程,学生是多,课程也是多。
数据库中是通过两个一对多关系来维护的,学生和课程都是主表,额外增加一张中间表作为从表,两张主表和中间表都是一对多关系。
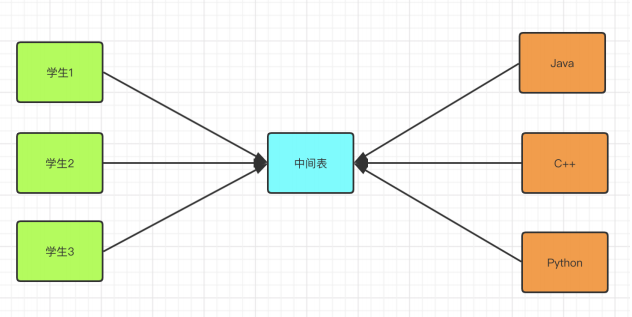
java面向对象代码
package com.hua.hibernate.pojo;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* 账户实体类
* @author xiaohuashen
* @date 2021/1/7 16:15
*/
public class Account implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String name;
/**
* 一个学生多个课程
*/
private Set<Course> courses;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public Account setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
return this;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public Account setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
return this;
}
public Set<Course> getCourses() {
return courses;
}
public Account setCourses(Set<Course> courses) {
this.courses = courses;
return this;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) {
return true;
}
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) {
return false;
}
Account account = (Account) o;
return id.equals(account.id) && Objects.equals(name, account.name) && Objects.equals(courses, account.courses);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(id, name, courses);
}
}
package com.hua.hibernate.pojo;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* 课程实体类
* @author xiaohuashen
* @date 2021/1/7 16:25
*/
public class Course implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String name;
/**
* 一个课程多个学生
*/
private Set<Account> accounts;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public Course setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
return this;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public Course setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
return this;
}
public Set<Account> getAccounts() {
return accounts;
}
public Course setAccounts(Set<Account> accounts) {
this.accounts = accounts;
return this;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) {
return true;
}
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) {
return false;
}
Course course = (Course) o;
return id.equals(course.id) && Objects.equals(name, course.name) && Objects.equals(accounts, course.accounts);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(id, name, accounts);
}
}
java 和数据库对于这两种关系的体现完全是两种不同的方式,Hibernate 框架的作用就是将这两种方式进行转换和映射。
Hibernate 实现一对多
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-mapping package="com.hua.hibernate.pojo">
<class name="Customer" table="CUSTOMER">
<!--映射主键-->
<id name="id" column="ID">
<!--指定主键生成策略-->
<generator class="increment"/>
</id>
<!--映射非主键-->
<property name="name" column="Name"/>
<set name="orders" table="ORDERS">
<key column="CID"/>
<one-to-many class="Orders"/>
</set>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
- set标签来配置实体类中集合 orsers
- name 实体类属性名
- table 表名
- key 外键
- one-to-many 与集合泛型的实体类对应
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-mapping package="com.hua.hibernate.pojo">
<class name="Orders" table="ORDERS">
<!--映射主键-->
<id name="id" column="ID">
<!--指定主键生成策略-->
<generator class="increment"/>
</id>
<!--映射非主键-->
<property name="name" column="Name"/>
<many-to-one name="customer" class="Customer" column="CID"/>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
- many-to-one 配置实体类对应的对象属性
- name 属性名
- class 属性对应的类
- column 外键
需要在 HIbernate 配置文件中进行注册绑定
<!--加载映射文件-->
<mapping resource="mapper/Customer.hbm.xml"/>
<mapping resource="mapper/Orders.hbm.xml"/>
一对多
Hibernate API
import com.hua.hibernate.pojo.Customer;
import com.hua.hibernate.pojo.Electronic;
import com.hua.hibernate.pojo.Orders;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
import org.hibernate.query.Query;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.List;
public class MyTest {
//创建Configuration
private final Configuration configuration = new Configuration().configure();
//获取SessionFactory
private final SessionFactory sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory();
//获取Session
private final Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
//创建事务
private final Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction();
/**
* 一对多处理
*/
@Test
public void test1(){
//创建 Customer
Customer customer = new Customer();
customer.setName("张三");
//创建 Orders
Orders orders = new Orders();
orders.setName("订单1");
//建⽴关联关系
orders.setCustomer(customer);
session.save(orders);
session.save(customer);
//事务提交
transaction.commit();
session.close();
}
}
多对多
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-mapping package="com.hua.hibernate.pojo">
<class name="Account" table="ACCOUNT">
<!--映射主键-->
<id name="id" column="ID">
<!--指定主键生成策略-->
<generator class="increment"/>
</id>
<!--映射非主键-->
<property name="name" column="NAME"/>
<set name="courses" table="ACCOUNT_COURSE" cascade="all" inverse="true">
<key column="AID"/>
<many-to-many class="Course" column="CID"/>
</set>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-mapping package="com.hua.hibernate.pojo">
<class name="Course" table="COURSE">
<!--映射主键-->
<id name="id" column="ID">
<!--指定主键生成策略-->
<generator class="increment"/>
</id>
<!--映射非主键-->
<property name="name" column="NAME"/>
<set name="accounts" table="ACCOUNT_COURSE" inverse="true">
<key column="CID"/>
<many-to-many class="Account" column="AID"/>
</set>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
- name 实体类对应的集合属性名
- table 第三张表的表名也就是中间表
- key 外键
- many-to-many 与集合泛型的实体类对应
- column 属性与中间表的外键字段对应
- Oracle 数据库的主键是不会自增的 不加 inverse 是会报无法把 null 插入到id的 mysql 数据库中是不需要添加的
注册 HIbernate 配置文件
<mapping resource="mapper/Account.hbm.xml"/>
<mapping resource="mapper/Course.hbm.xml"/>
Hibernate API
import com.hua.hibernate.pojo.*;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
import org.hibernate.query.Query;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
public class MyTest {
//创建Configuration
private final Configuration configuration = new Configuration().configure();
//获取SessionFactory
private final SessionFactory sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory();
//获取Session
private final Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
//创建事务
private final Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction();
/**
* 多对多处理
*/
@Test
public void test6(){
Account account =new Account();
account.setName("张三");
Course course = new Course();
course.setName("java");
Set<Course> courses = new HashSet<>();
courses.add(course);
account.setCourses(courses);
session.save(account);
transaction.commit();
session.close();
}
}
Hibernate 延迟加载
延迟加载、惰性加载、懒加载
使⽤延迟加载可以提⾼程序的运⾏效率,Java 程序与数据库交互的频次越低,程序运⾏的效率就越⾼, 所以我们应该尽量减少 Java 程序与数据库的交互次数,Hibernate 延迟加载就很好的做到了这⼀点。
客户和订单,当我们查询客户对象时,因为有级联设置,所以会将对应的订单信息⼀并查询出来,这样 就需要发送两条 SQL 语句,分别查询客户信息和订单信息。
延迟加载的思路是:当我们查询客户的时候,如果没有访问订单数据,只发送⼀条 SQL 语句查询客户信 息,如果需要访问订单数据,则发送两条 SQLL。
延迟加载可以看作是⼀种优化机制,根据具体的需求,⾃动选择要执⾏的 SQL 语句数量。
一对多
1、查询 Customer,对 orders 进⾏延迟加载设置,在 customer.hbm.xml 进⾏设置,延迟加载默认开 启。
<set name="orders" table="ORDERS" lazy="true">
<key column="CID"/>
<one-to-many class="Orders"/>
</set>
2、查询 Customer
import com.hua.hibernate.pojo.*;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
import org.hibernate.query.Query;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
public class MyTest {
//创建Configuration
private final Configuration configuration = new Configuration().configure();
//获取SessionFactory
private final SessionFactory sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory();
//获取Session
private final Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
//创建事务
private final Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction();
@Test
public void test7(){
Customer customer = session.get(Customer.class,1);
System.out.println(customer);
session.close();
}
注意这边直接运行是会报错 原因是一对多处理有无限递归 我们只需要把实体类里面的 ToString 顾客和订单的集合删除就好了
@Override
public String toString() {
return new StringJoiner(", ", Orders.class.getSimpleName() + "[", "]")
.add("id=" + id)
.add("name='" + name + "'")
.toString();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return new StringJoiner(", ", Customer.class.getSimpleName() + "[", "]")
.add("id=" + id)
.add("name='" + name + "'")
.toString();
}
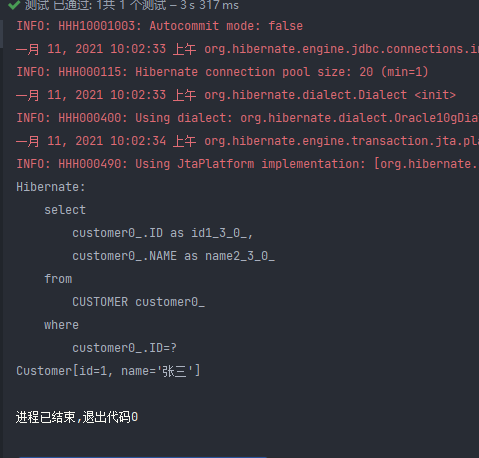
这个时候 lazy 改成 false 看结果
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-mapping package="com.hua.hibernate.pojo">
<class name="Customer" table="CUSTOMER">
<!--映射主键-->
<id name="id" column="ID">
<!--指定主键生成策略-->
<generator class="increment"/>
</id>
<!--映射非主键-->
<property name="name" column="NAME"/>
<set name="orders" table="ORDERS" lazy="false">
<key column="CID"/>
<one-to-many class="Orders"/>
</set>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
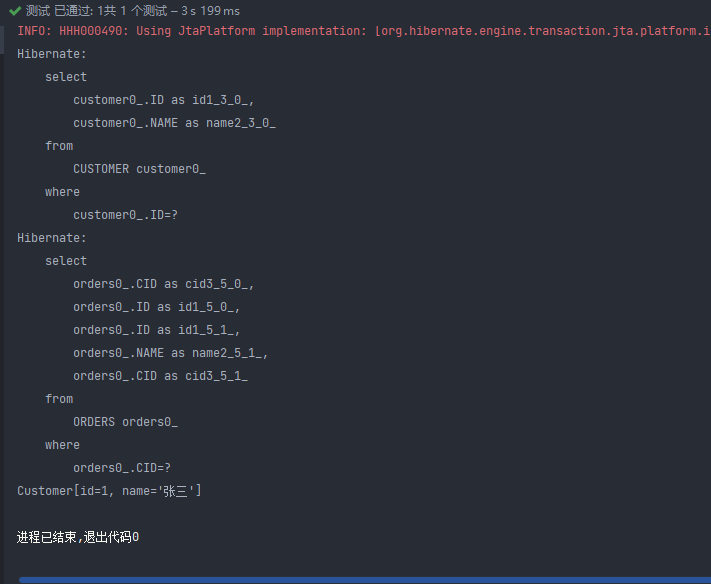
由上可见关闭延迟加载是会多一条 select 语句的 我们是没有去查询 orders 表的 关闭了延迟加载 Hibernate 是会去查询全部与表关联的数据,延迟加载可以动态的执行我们想要的结果从而减少性能消耗。
@Test
public void test7(){
Customer customer = session.get(Customer.class,1);
System.out.println(customer.getOrders());
session.close();
}
}
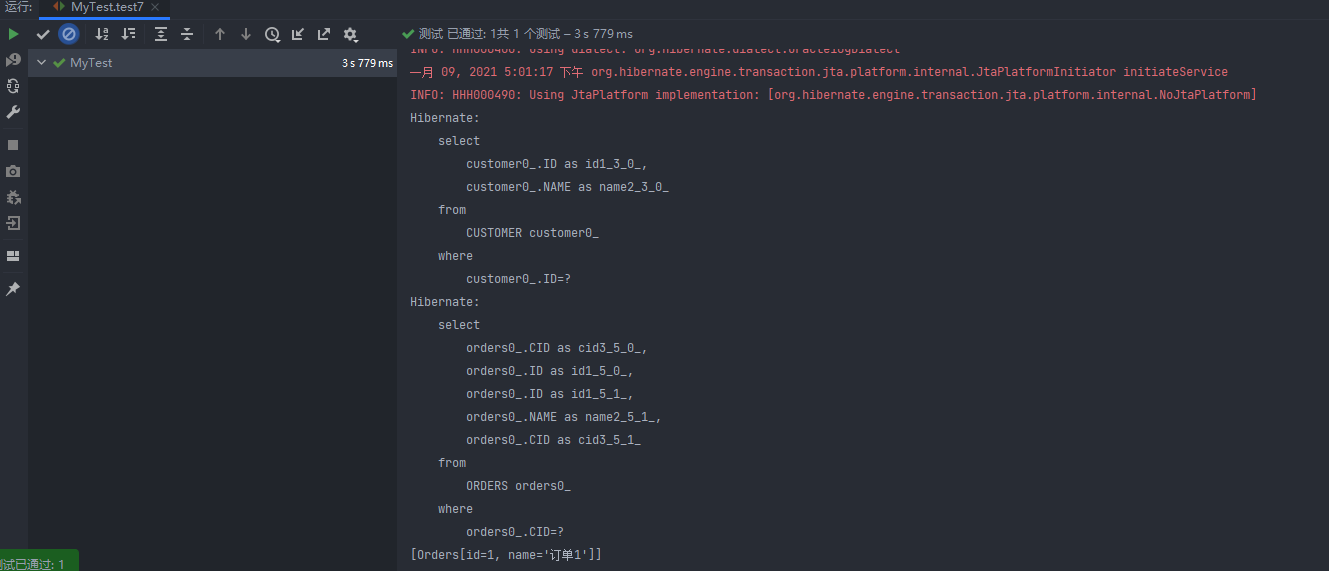
lazy 除了可以设置 true 和 false 之外,还可以设置 extra,extra 是⽐ true 更加懒惰的⼀种加载⽅式, 或者说是更加智能的⼀种加载⽅式,通过例⼦看区别:
查询 Customer 对象,打印该对象对应的 orders 集合的⻓度
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-mapping package="com.hua.hibernate.pojo">
<class name="Customer" table="CUSTOMER">
<!--映射主键-->
<id name="id" column="ID">
<!--指定主键生成策略-->
<generator class="increment"/>
</id>
<!--映射非主键-->
<property name="name" column="NAME"/>
<set name="orders" table="ORDERS" lazy="extra">
<key column="CID"/>
<one-to-many class="Orders"/>
</set>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
@Test
public void test7(){
Customer customer = session.get(Customer.class,1);
System.out.println(customer.getOrders().size());
session.close();
}
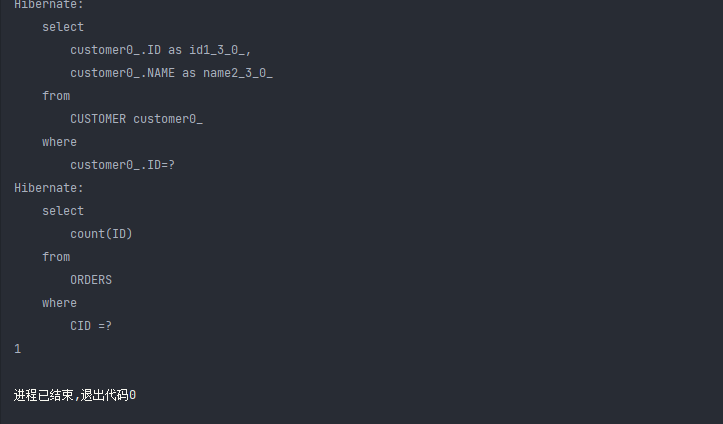
也可以通过 Orders 来设置 Customer 的延迟加载,orders.hbm.xml 中进⾏设置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-mapping package="com.hua.hibernate.pojo">
<class name="Orders" table="ORDERS">
<!--映射主键-->
<id name="id" column="ID">
<!--指定主键生成策略-->
<generator class="increment"/>
</id>
<!--映射非主键-->
<property name="name" column="NAME"/>
<many-to-one name="customer" class="Customer" column="CID" lazy="proxy"/>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
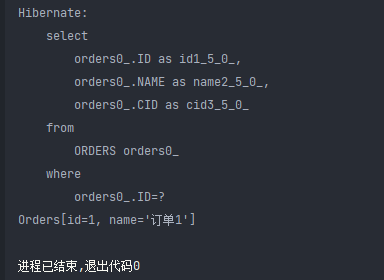
@Test
public void test7(){
Orders orders= session.get(Orders.class,1);
System.out.println(orders);
session.close();
}
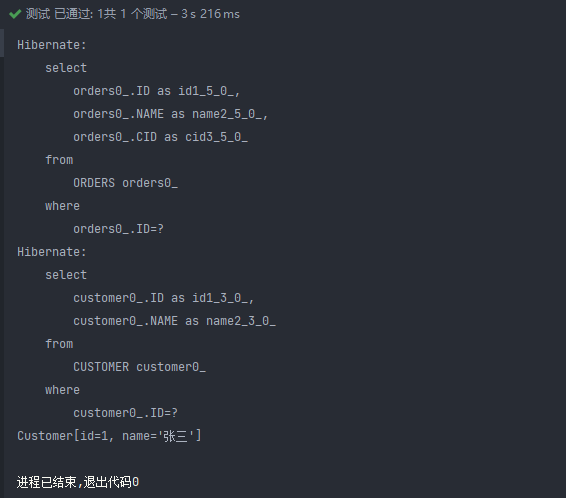
@Test
public void test7(){
Orders orders= session.get(Orders.class,1);
System.out.println(orders.getCustomer());
session.close();
}
no-proxy:当调⽤⽅法需要访问 customer 的成员变量时,发送 SQL 语句查询 Customer,否则不查 询。
proxy:⽆论调⽤⽅法是否需要访问 customer 的成员变量,都会发送 SQL 语句查询 Customer。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号