Java大作业 PTA题目集4、5、6总结Blog
Java大作业 PTA题目集4、5、6总结Blog
一、前言
知识点:聚合设计、渐进式图形继承设计、正则表达式、Java的“链表”等数据结构、集合框架应用
题量:很大
难度:很难
二、设计与分析
7-2 日期问题面向对象设计(聚合一) (35 分)
参考题目7-2的要求,设计如下几个类:DateUtil、Year、Month、Day,其中年、月、日的取值范围依然为:year∈[1900,2050] ,month∈[1,12] ,day∈[1,31] , 设计类图如下:
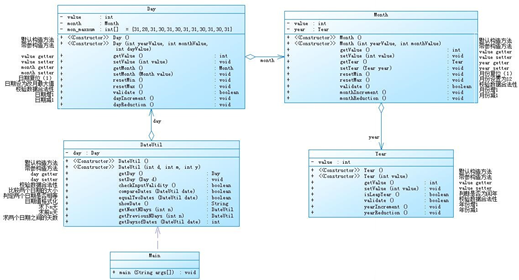
应用程序共测试三个功能:
求下n天
求前n天
求两个日期相差的天数
注意:严禁使用Java中提供的任何与日期相关的类与方法,并提交完整源码,包括主类及方法(已提供,不需修改)
输入格式:
有三种输入方式(以输入的第一个数字划分[1,3]):
1 year month day n //测试输入日期的下n天
2 year month day n //测试输入日期的前n天
3 year1 month1 day1 year2 month2 day2 //测试两个日期之间相差的天数
输出格式:
当输入有误时,输出格式如下: Wrong Format
当第一个数字为1且输入均有效,输出格式如下:
year-month-day
当第一个数字为2且输入均有效,输出格式如下:
year-month-day
当第一个数字为3且输入均有效,输出格式如下:
天数值
输入样例1:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
3 2014 2 14 2020 6 14
结尾无空行
输出样例1:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
2312
结尾无空行
输入样例2:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
2 1935 2 17 125340
结尾无空行
输出样例2:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
1591-12-17
结尾无空行
输入样例3:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
1 1999 3 28 6543
结尾无空行
输出样例3:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
2017-2-24
结尾无空行
输入样例4:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
0 2000 5 12 30
结尾无空行
输出样例4:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Wrong Format
结尾无空行
【解题报告】
写完程序后,想要测试三个功能点的正确性,可以参考Java8中的LocalDateTime类中的相关方法(在提交代码中不允许使用): 例如:
LocalDateTime today = LocalDateTime.now();//定义对象
//LocalDateTime today = LocalDateTime.of(2000,2,12);//定义对象
System.out.println(today.plusDays(10));//当前日期后十天
System.out.println(today.plusDays(-10));//当前日期前十天
注意,在使用Period求两个日期之间相差天数时,Period只能求同月日期的相差天数,因此要采用如下方法
System.out.println(LocalDate.now().toEpochDay() - LocalDate.now().minusDays(5).toEpochDay());
【源码】
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 public class Main{ 3 public static void main(String[] args){ 4 Scanner input =new Scanner(System.in); 5 int option=input.nextInt(); 6 if (option==1) { 7 int y1 = input.nextInt(); 8 int m1 = input.nextInt(); 9 int d1 = input.nextInt(); 10 int n1 = input.nextInt(); 11 DateUtil date1 = new DateUtil(y1, m1, d1); 12 boolean Vali=date1.validate(y1,m1,d1); 13 if (Vali == false) { 14 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 15 16 } 17 date1.NextNDays(n1); 18 } 19 else if (option==2) { 20 int y2 = input.nextInt(); 21 int m2 = input.nextInt(); 22 int d2 = input.nextInt(); 23 int n2 = input.nextInt(); 24 DateUtil date2 = new DateUtil(y2, m2, d2); 25 boolean Vali2= date2.validate(y2,m2,d2); 26 if (!Vali2) { 27 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 28 } 29 date2.PreviousNDays(n2); 30 31 } 32 else if (option==3) { 33 int y3 = input.nextInt(); 34 int m3 = input.nextInt(); 35 int d3 = input.nextInt(); 36 int y4 = input.nextInt(); 37 int m4 = input.nextInt(); 38 int d4 = input.nextInt(); 39 DateUtil date3 = new DateUtil(y3, m3, d3); 40 boolean Vali3=date3.validate(y3, m3, d3); 41 boolean Vali4=date3.validate(y4, m4, d4); 42 if (!Vali3 || !date3.validate(y4, m4, d4)) 43 { 44 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 45 46 } 47 date3.DaysofDates(y4, m4, d4); 48 49 } 50 else if (option!=1 || option!=2 || option !=3) 51 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 52 53 } 54 55 } 56 57 58 class Year{ 59 int yearValue=0; 60 61 Year(int yeardezhi){ 62 this.yearValue=yeardezhi; 63 } 64 boolean isLeapYear(int value){ 65 if(value%4==0&&value%100!=0||value%400==0) 66 return true; 67 else 68 return false; 69 } 70 void yearIncrement() { 71 yearValue+=1; 72 } 73 void yearReduction() { 74 yearValue-=1; 75 } 76 } 77 class Month extends Year{ 78 int monthValue; 79 Month(int yearValue,int monthValue){ 80 super(yearValue); 81 this.monthValue=monthValue; 82 } 83 84 } 85 class Day extends Month{ 86 int dayValue; 87 /* Day(){}*/ 88 Day(int yearValue,int monthValue,int dayValue){ 89 super(yearValue, monthValue); 90 this.dayValue=dayValue; 91 } 92 boolean validate(int yearValue,int monthValue,int dayValue){ 93 int[] month={31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; 94 if(isLeapYear(yearValue)==true) 95 month[1]=29; 96 if(yearValue<1900||yearValue>2050||monthValue<1||monthValue>12||dayValue<1||dayValue>31||dayValue>month[monthValue-1]) 97 return false; 98 else 99 return true; 100 } 101 102 } 103 class DateUtil extends Day{ 104 /* DateUtil(){}*/ 105 DateUtil(int yearValue,int monthValue,int dayValue){ 106 super(yearValue, monthValue, dayValue); 107 } 108 void NextNDays(int n){ 109 int[] month={31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; 110 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { 111 if(isLeapYear(yearValue)==true) 112 month[1]=29; 113 else 114 month[1]=28; 115 if(dayValue==month[monthValue-1]){ 116 if(monthValue==12) { 117 yearValue+=1; 118 monthValue=1; 119 dayValue=1; 120 } 121 else{ 122 monthValue+=1; 123 dayValue=1; 124 } 125 } 126 else 127 dayValue+=1; 128 } 129 System.out.println(yearValue+"-"+monthValue+"-"+dayValue); 130 } 131 void PreviousNDays(int n){ 132 int[] month={31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; 133 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { 134 if(isLeapYear(yearValue)==true) 135 month[1]=29; 136 else 137 month[1]=28; 138 if(dayValue==1){ 139 if(monthValue==1) { 140 yearValue-=1; 141 monthValue=12; 142 dayValue=31; 143 } 144 else{ 145 monthValue-=1; 146 dayValue=month[monthValue-1]; 147 } 148 } 149 else 150 dayValue-=1; 151 } 152 System.out.println(yearValue+"-"+monthValue+"-"+dayValue); 153 } 154 void DaysofDates(int x,int y,int z){ 155 int[] month={31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; 156 int temp; 157 int i; 158 if(yearValue>x) { 159 temp=yearValue; 160 yearValue=x; 161 x=temp; 162 } 163 if(monthValue>y) { 164 temp=monthValue; 165 monthValue=y; 166 y=temp; 167 } 168 if(dayValue>z) { 169 temp=dayValue; 170 dayValue=z; 171 z=temp; 172 } 173 for(i=0;;i++) { 174 if(isLeapYear(yearValue)==true) 175 month[1]=29; 176 else 177 month[1]=28; 178 if(yearValue==x&&monthValue==y&&dayValue==z) 179 break; 180 if(dayValue==month[monthValue-1]){ 181 if(monthValue==12) { 182 yearValue+=1; 183 monthValue=1; 184 dayValue=1; 185 } 186 else{ 187 monthValue+=1; 188 dayValue=1; 189 } 190 } 191 else 192 dayValue+=1; 193 } 194 System.out.println(i); 195 } 196 } 197 class fact{ 198 double fact(int n ) 199 { 200 double result = 0; 201 if (n!=0) 202 { 203 result=fact(n-1)*n; 204 return result; 205 } 206 if (n==0) 207 return 1; 208 return result; 209 } 210 211 double factsum( int n ) 212 { 213 int i; 214 double summary=0; 215 if (n!=0) 216 for (i=1;i<=n;i++) 217 { 218 summary=summary+fact(i); 219 } return summary; 220 221 222 } 223 }
【类图】
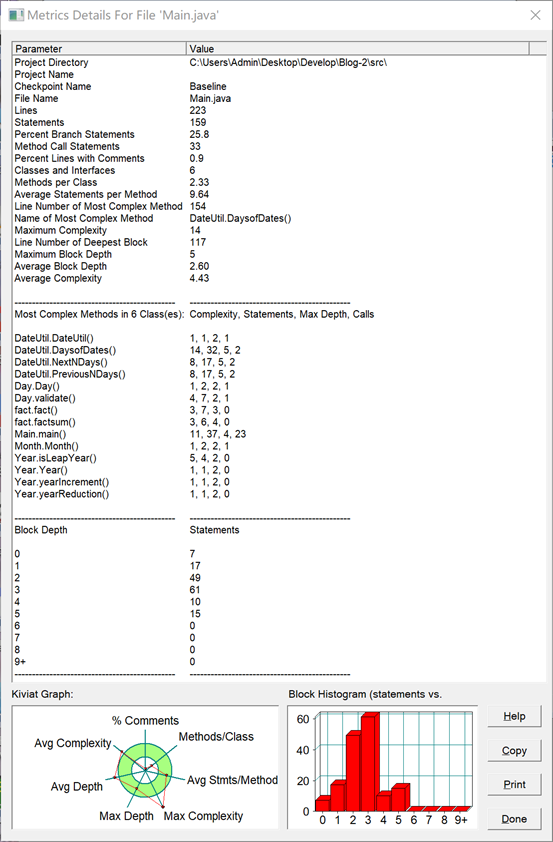
【SourceMonitor源码分析】
7-5 日期问题面向对象设计(聚合二) (40 分)
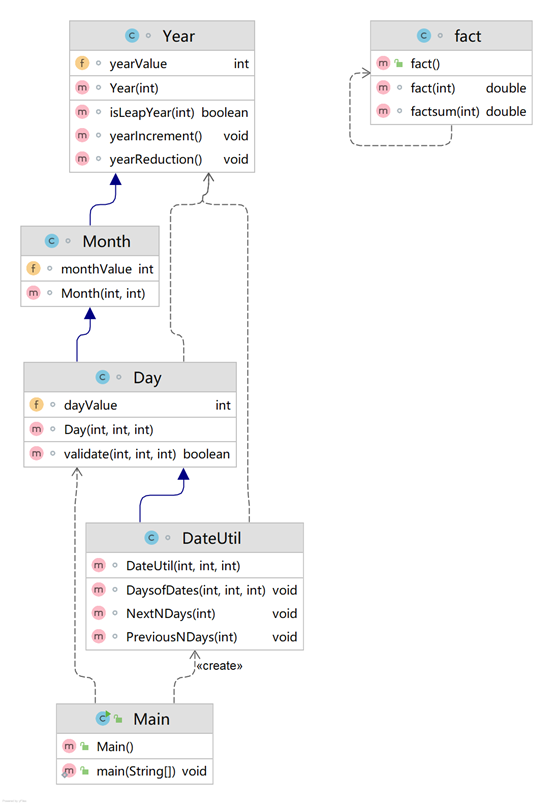
参考题目7-3的要求,设计如下几个类:DateUtil、Year、Month、Day,其中年、月、日的取值范围依然为:year∈[1820,2020] ,month∈[1,12] ,day∈[1,31] , 设计类图如下:
应用程序共测试三个功能:
求下n天
求前n天
求两个日期相差的天数
注意:严禁使用Java中提供的任何与日期相关的类与方法,并提交完整源码,包括主类及方法(已提供,不需修改)
输入格式:
有三种输入方式(以输入的第一个数字划分[1,3]):
1 year month day n //测试输入日期的下n天
2 year month day n //测试输入日期的前n天
3 year1 month1 day1 year2 month2 day2 //测试两个日期之间相差的天数
输出格式:
当输入有误时,输出格式如下: Wrong Format
当第一个数字为1且输入均有效,输出格式如下:
year1-month1-day1 next n days is:year2-month2-day2
当第一个数字为2且输入均有效,输出格式如下:
year1-month1-day1 previous n days is:year2-month2-day2
当第一个数字为3且输入均有效,输出格式如下:
The days between year1-month1-day1 and year2-month2-day2 are:值
输入样例1:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
3 2014 2 14 2020 6 14
结尾无空行
输出样例1:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
The days between 2014-2-14 and 2020-6-14 are:2312
结尾无空行
输入样例2:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
2 1834 2 17 7821
结尾无空行
输出样例2:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
1834-2-17 previous 7821 days is:1812-9-19
结尾无空行
输入样例3:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
1 1999 3 28 6543
结尾无空行
输出样例3:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
1999-3-28 next 6543 days is:2017-2-24
结尾无空行
输入样例4:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
0 2000 5 12 30
结尾无空行
输出样例4:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Wrong Format
结尾无空行
【解题报告】
写完程序后,想要测试三个功能点的正确性,可以参考Java8中的LocalDateTime类中的相关方法(在提交代码中不允许使用): 例如:
LocalDateTime today = LocalDateTime.now();//定义对象
//LocalDateTime today = LocalDateTime.of(2000,2,12);//定义对象
System.out.println(today.plusDays(10));//当前日期后十天
System.out.println(today.plusDays(-10));//当前日期前十天
注意,在使用Period求两个日期之间相差天数时,Period只能求同月日期的相差天数,因此要采用如下方法:
System.out.println(LocalDate.now().toEpochDay() - LocalDate.now().minusDays(5).toEpochDay());
【源码】
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 public class Main2 { 3 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 6 int year = 0; 7 int month = 0; 8 int day = 0; 9 int choice = input.nextInt(); 10 if (choice == 1) { // test getNextNDays method 11 int m = 0; 12 year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 13 month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 14 day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 15 16 17 DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day); 18 if (!date.checkInputValidity()) { 19 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 20 System.exit(0); 21 } 22 23 m = input.nextInt(); 24 25 if (m < 0) { 26 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 27 System.exit(0); 28 } 29 30 System.out.print(date.showDate() + " next " + m + " days is:"); 31 System.out.println(date.getNextNDays(m).showDate()); 32 } else if (choice == 2) { // test getPreviousNDays method 33 int n = 0; 34 year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 35 month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 36 day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 37 38 DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day); 39 40 if (!date.checkInputValidity()) { 41 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 42 System.exit(0); 43 } 44 45 n = input.nextInt(); 46 47 if (n < 0) { 48 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 49 System.exit(0); 50 } 51 52 System.out.print(date.showDate() + " previous " + n + " days is:"); 53 System.out.println(date.getPreviousNDays(n).showDate()); 54 } else if (choice == 3) { // test getDaysofDates method 55 year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 56 month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 57 day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 58 59 int anotherYear = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 60 int anotherMonth = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 61 int anotherDay = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 62 63 DateUtil fromDate = new DateUtil(year, month, day); 64 DateUtil toDate = new DateUtil(anotherYear, anotherMonth, anotherDay); 65 66 if (fromDate.checkInputValidity() && toDate.checkInputValidity()) { 67 System.out.println("The days between " + fromDate.showDate() + " and " + toDate.showDate() + " are:" 68 + fromDate.getDaysofDates(toDate)); 69 } else { 70 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 71 System.exit(0); 72 } 73 } else { 74 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 75 System.exit(0); 76 } 77 78 } 79 80 } 81 class DateUtil { 82 Year year; 83 Month month; 84 Day day; 85 int mon_maxnum[] = {31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; 86 public DateUtil(){ 87 88 } 89 90 public DateUtil(int y, int m, int d){ 91 this.day = new Day(d); 92 this.month = new Month(m); 93 this.year = new Year(y); 94 95 } 96 public Year getYear() { 97 int flag=1; 98 int count=0; 99 while (flag==1){ 100 Year newYear=year; 101 count++; 102 if (count==100){ 103 count=0; 104 break; 105 } 106 } 107 return year; 108 } 109 public void setYear(Year year) { 110 int flag=1; 111 int count=0; 112 while (flag==1){ 113 Year newYear=year; 114 count++; 115 if (count==100){ 116 count=0; 117 break; 118 } 119 } 120 this.year = year; 121 } 122 public Month getMonth() { 123 int flag=1; 124 int count=0; 125 int cnt=0; 126 while (flag==1){ 127 cnt++; 128 count++; 129 if (count==100){ 130 cnt=cnt-count; 131 count=0; 132 break; 133 } 134 } 135 return month; 136 } 137 public void setMonth(Month month) { 138 int flag=1; 139 int count=0; 140 int cnt=0; 141 while (flag==1){ 142 cnt++; 143 count++; 144 if (count==100){ 145 cnt=cnt-count; 146 count=0; 147 break; 148 } 149 } 150 this.month = month; 151 } 152 public Day getDay() { 153 int flag=1; 154 int count=0; 155 int cnt=0; 156 while (flag==1){ 157 cnt++; 158 count++; 159 if (count==100){ 160 cnt=cnt-count; 161 count=0; 162 break; 163 } 164 } 165 return day; 166 } 167 public void setDay(Day day) { 168 int flag=1; 169 int count=0; 170 int cnt=0; 171 while (flag==1){ 172 cnt++; 173 count++; 174 if (count==100){ 175 cnt=cnt-count; 176 count=0; 177 break; 178 } 179 } 180 this.day = day; 181 } 182 public void setDayMin() { 183 this.day.value=1; 184 int flag=1; 185 int count=0; 186 int cnt=0; 187 while (flag==1){ 188 cnt++; 189 count++; 190 if (count==100){ 191 cnt=cnt-count; 192 count=0; 193 break; 194 } 195 } 196 } 197 public void setDatMax() { 198 if(this.year.isLeapYear()) 199 mon_maxnum[1]++; 200 this.day.value=mon_maxnum[this.month.value-1]; 201 int flag=1; 202 int count=0; 203 int cnt=0; 204 while (flag==1){ 205 cnt++; 206 count++; 207 if (count==100){ 208 cnt=cnt-count; 209 count=0; 210 break; 211 } 212 } 213 } 214 215 public boolean checkInputValidity(){//检测输入的年、月、日是否合法 216 int flag=1; 217 int count=0; 218 int cnt=0; 219 while (flag==1){ 220 cnt++; 221 count++; 222 if (count==100){ 223 cnt=cnt-count; 224 count=0; 225 break; 226 } 227 } 228 if(this.year.isLeapYear()) 229 mon_maxnum[1]++; 230 if(this.year.validate()&&this.month.validate()&&this.day.value>=1&&this.day.value<=mon_maxnum[this.month.value-1]) 231 return true; 232 return false; 233 } 234 235 public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date){//比较当前日期与date的大小(先后) 236 if (date.year.value<this.year.value) 237 return false; 238 239 else if (date.year.value==this.year.value 240 &&date.month.value<this.month.value) 241 return false; 242 243 if (date.year.value==this.year.value 244 &&date.month.value==this.month.value 245 &&date.day.value<this.day.value) 246 return false; 247 248 return true; 249 } 250 251 public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date){//判断两个日期是否相等 252 if (this.getDay().getValue()==date.getDay().getValue() 253 && this.getYear().getValue()==date.getYear().getValue() 254 && this.getMonth().getValue()==date.getMonth().getValue()) 255 return true; 256 257 return false; 258 } 259 260 public String showDate(){//以“year-month-day”格式返回日期值 261 262 return this.getYear().getValue()+"-"+this.getMonth().getValue()+"-"+this.getDay().getValue(); 263 264 } 265 266 public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n){//取得year-month-day的下n天日期 267 int arr[] = {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; 268 int year=0, month=0, day=0; 269 int rest = restday(this); 270 int flag=1; 271 int count=0; 272 int cnt=0; 273 while (flag==1){ 274 cnt++; 275 count++; 276 if (count==100){ 277 cnt=cnt-count; 278 count=0; 279 break; 280 } 281 } 282 if (rest>n) {//本年 283 year=this.getYear().getValue(); 284 int mday = arr[this.getMonth().getValue()]; 285 if (this.getYear().isLeapYear()&&this.getMonth().getValue()==2) { 286 mday++; 287 } 288 289 mday=mday-this.getDay().getValue();//本月剩余的日期 290 if (mday>=n) { //本月 291 month = this.getMonth().getValue(); 292 day = this.getDay().getValue()+n; 293 } 294 else{ //其他月 295 n=n-mday; 296 month = 1+this.getMonth().getValue(); 297 int k = month; 298 while(n-arr[k]>0 && k<=12){ 299 n =n- arr[k]; 300 month++; 301 k++; 302 } 303 day = n; 304 } 305 } 306 else { 307 n=n-rest; 308 year = 1+this.getYear().getValue()+1-1; 309 int y = 365; 310 if (new Year(year).isLeapYear()) { 311 y++; 312 } 313 while(n-y>0){ 314 n=n-y; 315 year++; 316 y=365; 317 if (new Year(year).isLeapYear()) 318 y++; 319 } 320 int k = 1; 321 while(n-arr[k]>0&&k<=12){ 322 n = n-arr[k]; 323 k++; 324 } 325 month = k; 326 day = n; 327 } 328 329 // System.out.println(this.showDate()+" next "+n+" days is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+day); 330 331 return new DateUtil(year, month, day); 332 } 333 334 public int restday(DateUtil d) { 335 int n = 0; 336 int arr[] = {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; 337 for (int i = d.getMonth().getValue()+1; i <=12; i++) { 338 n+=arr[i]; 339 } 340 n+=arr[d.getMonth().getValue()]-d.getDay().getValue(); 341 if(d.getYear().isLeapYear()&&d.getMonth().getValue()<=2) 342 n++; 343 return n; 344 } 345 346 public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n){//取得year-month-day的前n天日期 347 int arr[] = {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; 348 int year=0, month=0, day=0; 349 int rest = 365-restday(this); 350 if (this.getYear().isLeapYear()) { 351 rest++; 352 } 353 if (rest>n) {//本年 354 year=this.getYear().getValue(); 355 int mday=this.getDay().getValue();//本月剩余的日期 356 if (mday>n) { //本月 357 month = this.getMonth().getValue(); 358 day = mday-n; 359 } 360 else{ //其他月 361 n-=mday; 362 month = this.getMonth().getValue()-1; 363 if (month==0) { 364 month = 12; 365 year=this.getYear().getValue()-1; 366 } 367 int k = month; 368 while(n-arr[k]>0&&k>=0){ 369 n -= arr[k]; 370 month--; 371 k--; 372 } 373 day = arr[k]-n; 374 if (new Year(year).isLeapYear()&&month==2) { 375 day++; 376 } 377 } 378 } 379 else { 380 n-=rest; 381 year = this.getYear().getValue()-1; 382 int y = 365; 383 if (new Year(year).isLeapYear()) { 384 y++; 385 } 386 while(n-y>0){ 387 n-=y; 388 year--; 389 y=365; 390 if (new Year(year).isLeapYear()) 391 y++; 392 } 393 int k = 12; 394 while(n-arr[k]>0&&k>=0){ 395 n -= arr[k]; 396 k--; 397 } 398 month = k; 399 day = arr[k]-n; 400 if (new Year(year).isLeapYear()&&month==2) { 401 day++; 402 } 403 } 404 // System.out.println(this.showDate()+" previous "+n+" days is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+day); 405 return new DateUtil(year, month, day); 406 } 407 408 409 public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date){ 410 DateUtil pred = this; 411 DateUtil nextd = date; 412 if (this.equalTwoDates(date)) { 413 return 0; 414 } 415 else if (!this.compareDates(date)) { 416 pred = date; 417 nextd = this; 418 } 419 int arr[] = {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; 420 int i,j,d = 0; 421 for(i=pred.getYear().getValue()+1;i<nextd.getYear().getValue();i++) { 422 d=d+365; 423 if(new Year(i).isLeapYear()) 424 d++; 425 } 426 if (pred.getYear().getValue()!=nextd.getYear().getValue()) { 427 for(j=pred.getMonth().getValue()+1;j<=12;j++) 428 d=d+arr[j]; 429 d+=arr[pred.getMonth().getValue()]-pred.getDay().getValue(); 430 for(j=1;j<nextd.getMonth().getValue();j++) 431 d+=arr[j]; 432 d+=nextd.getDay().getValue(); 433 if(pred.getYear().isLeapYear()&&pred.getMonth().getValue()<=2) 434 d++; 435 if (nextd.getYear().isLeapYear()&&nextd.getMonth().getValue()>2) { 436 d++; 437 } 438 } 439 else if(pred.getYear().getValue()==nextd.getYear().getValue()&&pred.getMonth().getValue()!=nextd.getMonth().getValue()){ 440 for(j=pred.getMonth().getValue()+1;j<=nextd.getMonth().getValue()-1;j++) 441 d+=arr[j]; 442 d+=arr[pred.getMonth().getValue()]-pred.getDay().getValue(); 443 d+=nextd.getDay().getValue(); 444 if(pred.getYear().isLeapYear()&&pred.getMonth().getValue()<=2) 445 d++; 446 } 447 else if(pred.getYear().getValue()==nextd.getYear().getValue()&&pred.getMonth().getValue()==nextd.getMonth().getValue()){ 448 d=nextd.getDay().getValue()-pred.getDay().getValue(); 449 } 450 return d; 451 } 452 453 454 } 455 class Day{ 456 int value; 457 public Day() { 458 459 } 460 public Day(int value) { 461 this.value = value; 462 } 463 public int getValue() { 464 return value; 465 } 466 public void setValue(int value) { 467 this.value = value; 468 } 469 public void dayIncrement() { 470 value++; 471 } 472 public void dayReduction() { 473 value--; 474 } 475 } 476 class Month{ 477 int value; 478 public Month() { 479 480 } 481 public Month(int value) { 482 this.value = value; 483 } 484 public int getValue() { 485 return value; 486 } 487 public void setValue(int value) { 488 this.value = value; 489 } 490 public void resetMin() { 491 value=1; 492 } 493 public void resetMax() { 494 value=12; 495 } 496 public boolean validate() { 497 if(1<=this.value&&12>=this.value) 498 return true; 499 return false; 500 } 501 public void monthIncrement() { 502 value++; 503 } 504 public void monthReduction() { 505 value--; 506 } 507 } 508 class Year{ 509 int value; 510 public Year() { 511 512 } 513 public Year(int value) { 514 this.value = value; 515 } 516 public int getValue() { 517 return value; 518 } 519 public void setValue(int value) { 520 this.value = value; 521 } 522 public boolean isLeapYear(){//判断year是否为闰年 523 boolean y1 = value%4 == 0; 524 boolean y2 = value%100 != 0; 525 boolean y3 = value%400 == 0; 526 527 if((y1&&y2)||y3) 528 return true; 529 else 530 return false; 531 } 532 public boolean validate() { 533 if(this.value<=2020&&this.value>=1820) 534 return true; 535 return false; 536 } 537 public void yearIncrement() { 538 value++; 539 } 540 public void yearReduction() { 541 value--; 542 } 543 }
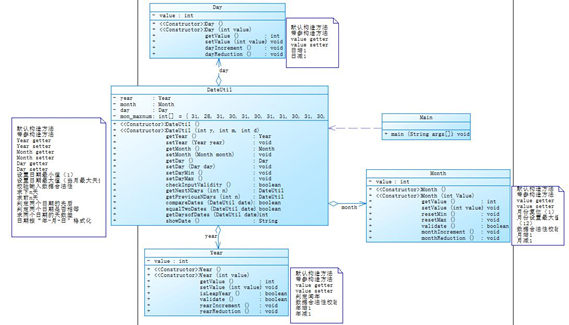
【类图】
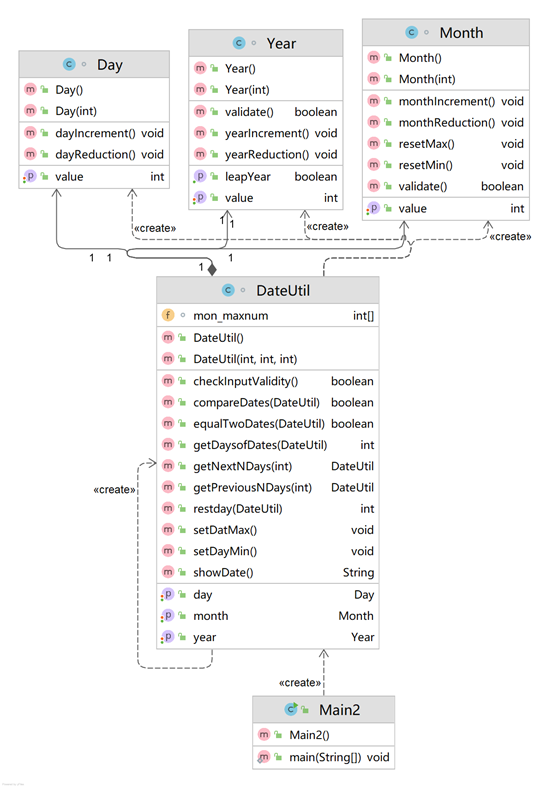
【SourceMonitor源码分析】
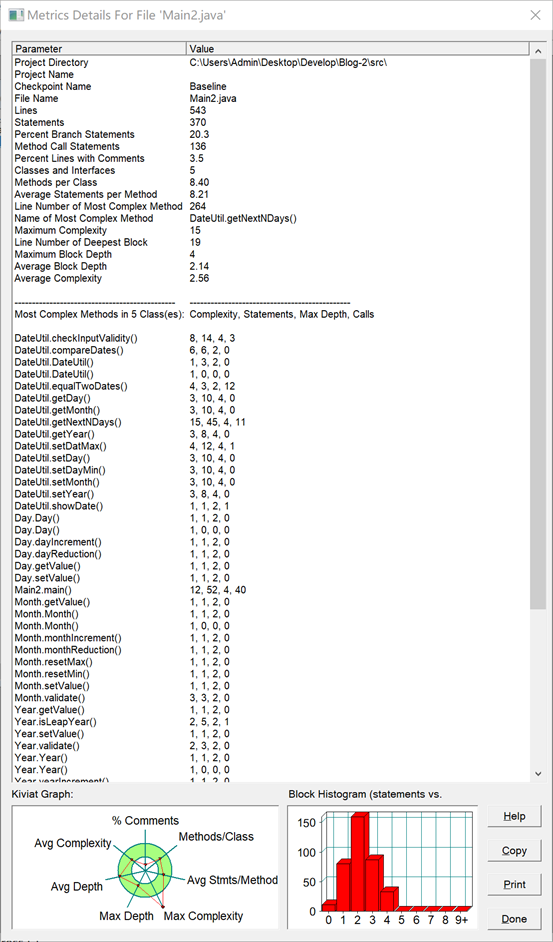
【两种日期类聚合设计的优劣比较】
7-2
优点:结构清晰,在功能类里使用的方法较少,条理清楚明晰,容易阅读和理解。
缺点:功能类无法直接调用每项类,意图调用某类需要先调用前序类,耗费了不必要的时间和计算机的资源;
对代码的圈复杂度分析发现:在功能类及主类中的复杂度很高,这种类型的聚合虽然看起来结构清晰容易理解,能将月日年的各种判断在各自的类中直接完成,但是调用起来十分冗杂繁琐,需要一层层的进行调用,降低了程序运行的效率。
7-4
优点:聚合设计在功能类中集成了很多方法,但是该类型聚合设计可以直接对月日年进行调用,实现题目给出的类图更为简单;
从圈复杂度分析:聚合二中的圈复杂度相对较低,侧面说明聚合二的执行效率更高。
综上所述,聚合二的结构合理且执行效率更高。
7-3 图形继承 (15 分)
编写程序,实现图形类的继承,并定义相应类对象并进行测试。
类Shape,无属性,有一个返回0.0的求图形面积的公有方法public double getArea();//求图形面积
类Circle,继承自Shape,有一个私有实型的属性radius(半径),重写父类继承来的求面积方法,求圆的面积
类Rectangle,继承自Shape,有两个私有实型属性width和length,重写父类继承来的求面积方法,求矩形的面积
类Ball,继承自Circle,其属性从父类继承,重写父类求面积方法,求球表面积,此外,定义一求球体积的方法public double getVolume();//求球体积
类Box,继承自Rectangle,除从父类继承的属性外,再定义一个属性height,重写父类继承来的求面积方法,求立方体表面积,此外,定义一求立方体体积的方法public double getVolume();//求立方体体积
注意:
每个类均有构造方法,且构造方法内必须输出如下内容:Constructing 类名
每个类属性均为私有,且必须有getter和setter方法(可用Eclipse自动生成)
输出的数值均保留两位小数
主方法内,主要实现四个功能(1-4): 从键盘输入1,则定义圆类,从键盘输入圆的半径后,主要输出圆的面积; 从键盘输入2,则定义矩形类,从键盘输入矩形的宽和长后,主要输出矩形的面积; 从键盘输入3,则定义球类,从键盘输入球的半径后,主要输出球的表面积和体积; 从键盘输入4,则定义立方体类,从键盘输入立方体的宽、长和高度后,主要输出立方体的表面积和体积;
假如数据输入非法(包括圆、矩形、球及立方体对象的属性不大于0和输入选择值非1-4),系统输出Wrong Format
输入格式:
共四种合法输入
1 圆半径
2 矩形宽、长
3 球半径
4 立方体宽、长、高
输出格式:
按照以上需求提示依次输出
输入样例1:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
1 1.0
结尾无空行
输出样例1:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Constructing Shape
Constructing Circle
Circle's area:3.14
结尾无空行
输入样例2:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
4 3.6 2.1 0.01211
结尾无空行
输出样例2:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Constructing Shape
Constructing Rectangle
Constructing Box
Box's surface area:15.26
Box's volume:0.09
结尾无空行
输入样例3:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
2 -2.3 5.110
结尾无空行
输出样例2:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Wrong Format
结尾无空行
【解题报告】
1. 尽量使代码可复用,例如使用this及super关键字
2. 观察构造方法链的调用过程
3. 保留小数格式可采用String.format
4. 重写方法建议使用标注@Override
5. 思考继承可以为程序结构带来什么不一样的特性
【源码】
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 public class Main3{ 3 public static void main(String[] args){ 4 Scanner input =new Scanner(System.in); 5 double mianji; 6 double tiji; 7 int n=input.nextInt(); 8 if(n==1){ 9 Shape yuanxing=new Shape(); 10 double r=input.nextDouble(); 11 if(r<=0) 12 { for (int cnt=0;cnt<=100;cnt++); 13 System.out.println("Wrong Format");} 14 else { 15 for (int cnt=0;cnt<=100;cnt++); 16 yuanxing.getConstructing(); 17 Circle circle=new Circle(); 18 circle.setRadius(r); 19 circle.getConstructing(); 20 for (int cnt=0;cnt<=100;cnt++); 21 mianji=circle.getArea(); 22 System.out.println("Circle's area:"+String.format("%.2f",mianji)); 23 for (int cnt=0;cnt<=100;cnt++); 24 } 25 } 26 else if(n==2){ 27 Shape juxing=new Shape(); 28 double l=input.nextDouble(); 29 for (int cnt=0;cnt<=100;cnt++); 30 double d=input.nextDouble(); 31 for (int cnt=0;cnt<=100;cnt++); 32 if(l<=0||d<=0) 33 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 34 else { 35 juxing.getConstructing(); 36 Rectangle rectangle=new Rectangle(); 37 for (int cnt=0;cnt<=100;cnt++); 38 rectangle.setLength(l); 39 rectangle.setWidth(d); 40 for (int cnt=0;cnt<=100;cnt++); 41 rectangle.getConstructing(); 42 mianji=rectangle.getArea(); 43 System.out.print("Rectangle's area:"+String.format("%.2f",mianji)); 44 } 45 } 46 else if(n==3){ 47 Shape qiu=new Shape(); 48 double r=input.nextDouble(); 49 if(r<=0) 50 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 51 else { 52 for (int cnt=0;cnt<=100;cnt++); 53 qiu.getConstructing(); 54 Ball ball=new Ball(); 55 ball.setRadius(r); 56 ball.getConstructing(); 57 mianji=ball.getArea(); 58 for (int cnt=0;cnt<=100;cnt++); 59 tiji=ball.getVolume(); 60 System.out.println("Ball's surface area:"+String.format("%.2f",mianji)); 61 System.out.print("Ball's volume:"+String.format("%.2f",tiji)); 62 for (int cnt=0;cnt<=100;cnt++); 63 } 64 } 65 else if(n==4){ 66 Shape changfangti=new Shape(); 67 double l=input.nextDouble(); 68 double d=input.nextDouble(); 69 double h=input.nextDouble(); 70 if(l<=0||d<=0||h<=0) 71 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 72 else { 73 changfangti.getConstructing(); 74 Box box=new Box(); 75 box.setLength(l); 76 box.setWidth(d); 77 box.setHeight(h); 78 box.getConstructing(); 79 mianji=box.getArea(); 80 tiji=box.getVolume(); 81 System.out.println("Box's surface area:"+String.format("%.2f",mianji)); 82 System.out.print("Box's volume:"+String.format("%.2f",tiji)); 83 } 84 } 85 else{ 86 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 87 } 88 } 89 } 90 class Shape{ 91 Shape(){ 92 } 93 void getConstructing(){ 94 System.out.println("Constructing Shape"); 95 } 96 public double getArea(){ 97 double primary = 0.0; 98 return primary; 99 } 100 } 101 102 class Circle extends Shape{ 103 private double radius; 104 void getConstructing(){ 105 System.out.println("Constructing Circle"); 106 } 107 public double getArea(){ 108 double result ; 109 result = 3.14*Math.pow(getRadius(),2); 110 return result; 111 } 112 public double getRadius() { 113 double result ; 114 result = this.radius; 115 return result; 116 } 117 public void setRadius(double radius) { 118 double init; 119 init = radius; 120 this.radius = init; 121 this.radius = radius; 122 } 123 } 124 125 class Rectangle extends Shape{ 126 private double length; 127 private double width; 128 void getConstructing(){ 129 System.out.println("Constructing Rectangle"); 130 } 131 public double getArea(){ 132 double result; 133 result = getLength()*getWidth(); 134 return result 135 ; 136 } 137 public double getLength() { 138 return length; 139 } 140 public void setLength(double length) { 141 this.length = length; 142 } 143 public double getWidth() { 144 for (int cnt=1;cnt<=100;cnt++); 145 double result; 146 result = width; 147 return result; 148 } 149 public void setWidth(double width) { 150 this.width = width; 151 } 152 } 153 class Ball extends Circle{ 154 void getConstructing(){ 155 System.out.println("Constructing Circle"); 156 System.out.println("Constructing Ball"); 157 } 158 public double getArea(){ 159 double result; 160 result = 4*3.14*Math.pow(getRadius(),2); 161 return result ; /*getRadius()*getRadius();*/ 162 } 163 public double getVolume(){ 164 double result; 165 result = (double) 4/3*3.14*Math.pow(getRadius(),3) ; /*getRadius()*getRadius()*getRadius();*/ 166 return result; 167 } 168 } 169 170 class Box extends Rectangle{ 171 double height; 172 public double getHeight() { 173 return height; 174 } 175 public void setHeight(double height) { 176 this.height = height; 177 } 178 void getConstructing(){ 179 System.out.println("Constructing Rectangle"); 180 System.out.println("Constructing Box"); 181 } 182 public double getArea(){ 183 double result; 184 result = (getLength()*getWidth()+getLength()*height+getWidth()*height)*2; 185 return result; 186 } 187 public double getVolume(){ 188 double result; 189 result =getLength()*getWidth()*height; 190 return result; 191 } 192 }
【类图】
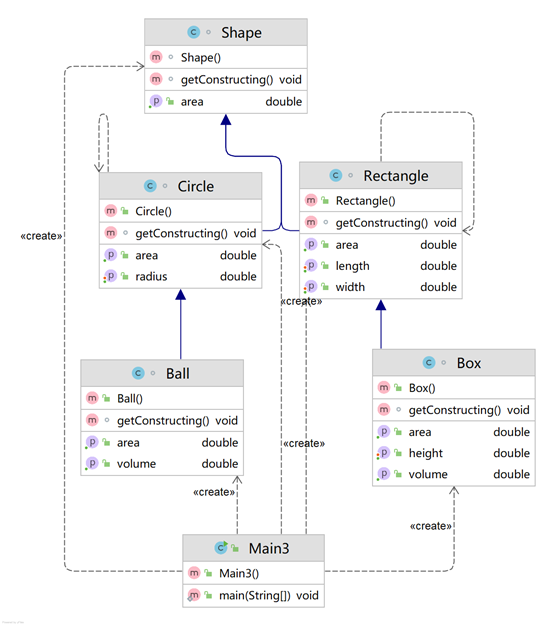
【SourceMonitor源码分析】
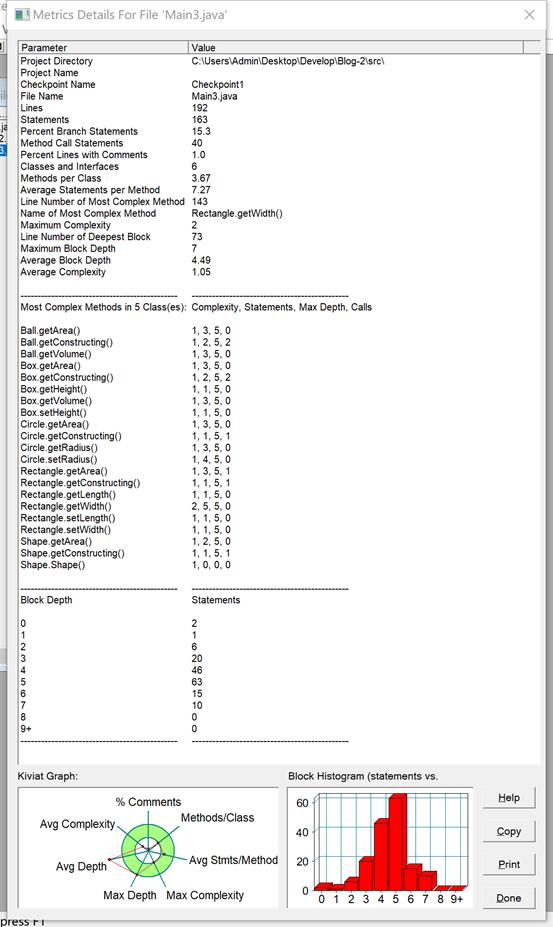
7-5 图形继承与多态 (50 分)
掌握类的继承、多态性及其使用方法。具体需求参见作业指导书。
输入格式:
从键盘首先输入三个整型值(例如a b c),分别代表想要创建的Circle、Rectangle及Triangle对象的数量,然后根据图形数量继续输入各对象的属性值(均为实型数),数与数之间可以用一个或多个空格或回车分隔。
输出格式:
如果图形数量非法(小于0)或图形属性值非法(数值小于0以及三角形三边关系),则输出Wrong Format。
如果输入合法,则正常输出,输出内容如下(输出格式见输入输出示例):
各个图形的面积;
所有图形的面积总和;
排序后的各个图形面积;
再次所有图形的面积总和。
输入样例1:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
1 1 1 2.3 3.2 3.2 6.5 3.2 4.2
结尾无空行
输出样例1:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Original area:
16.62 10.24 5.68
Sum of area:32.54
Sorted area:
5.68 10.24 16.62
Sum of area:32.54
结尾无空行
输入样例2:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
0 2 2 2.3 2.5 56.4 86.5 64.3 85.6 74.6544 3.2 6.1 4.5
结尾无空行
输出样例2:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Original area:
5.75 4878.60 2325.19 7.00
Sum of area:7216.54
Sorted area:
5.75 7.00 2325.19 4878.60
Sum of area:7216.54
结尾无空行
输入样例3:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
0 0 1 3 3 6
结尾无空行
输出样例3:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Wrong Format
结尾无空行
【解题报告】
1. 深入理解继承与多态的原理及用法
2. ArrayList常用方法及和数组的关系
3. 泛型的应用
4. Arrays及Collections的简单应用
** 必须使用面向对象的封装性、继承性及多态性解题,否则一律判定为0分。**
【源码】
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 import java.util.ArrayList; 3 public class Main { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 6 ArrayList<Shape> w=new ArrayList<>(); 7 int num1,num2,num3,i=0,j=0,judge=1; 8 double sum=0; 9 num1=input.nextInt(); 10 num2=input.nextInt(); 11 num3=input.nextInt(); 12 13 for (i = 0; i < num1; i++) { 14 double radius = input.nextDouble(); 15 w.add(new Circle(radius)); 16 17 if(w.get(i).validate()) 18 19 { 20 } 21 else 22 judge=0; 23 } 24 for (i = 0; i < num2; i++) { 25 double width = input.nextDouble(); 26 double length = input.nextDouble(); 27 w.add(new Rectangle(width, length)); 28 29 } 30 for (i = 0; i < num3; i++) { 31 double side1 = input.nextDouble(); 32 double side2 = input.nextDouble(); 33 double side3 = input.nextDouble(); 34 w.add(new Triangle(side1, side2, side3)); 35 } 36 int summary=num1+num2+num3; 37 for (i = 0; i < summary; i++) { 38 if (w.get(i).validate()) 39 { 40 } 41 else 42 { 43 judge = 0; 44 } 45 } 46 if(num1==0 && num2==0 && num3==0) 47 { 48 judge=1; 49 } 50 int flag0=0; 51 if (num1>=0 && num2>=0 && num3>=0) 52 flag0=1; 53 else 54 flag0=0; 55 if (judge == 1 && (flag==1)) { 56 System.out.println("Original area:"); 57 for (i = 0; i < num1; i++) { 58 System.out.print(String.format("%.2f", w.get(i).getArea()) + " "); 59 } 60 int sum2=num1+num2; 61 for (i = num1; i < sum2; i++) { 62 63 System.out.print(String.format("%.2f", w.get(i).getArea()) + " "); 64 } 65 for (i = sum2 ; i < summary; i++) { 66 67 System.out.print(String.format("%.2f", w.get(i).getArea()) + " "); 68 } 69 System.out.println(); 70 for (i = 0; i < summary; i++) { 71 sum = sum+w.get(i).getArea(); 72 } 73 System.out.println("Sum of area:" + String.format("%.2f", sum)); 74 sort(w); 75 System.out.println("Sorted area:"); 76 for (i = 0; i < summary; i++) { int flag6=1; 77 78 System.out.print(String.format("%.2f", w.get(i).getArea()) + " "); 79 } 80 System.out.println(); 81 sum=0; 82 for (i = 0; i < summary; i++) { 83 sum =sum + w.get(i).getArea(); 84 } 85 System.out.println("Sum of area:" + String.format("%.2f", sum)); 86 } else { 87 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 88 } 89 } 90 public static ArrayList<Shape> sort(ArrayList<Shape> w){ 91 int i=0,j=0; 92 double a=0,b=0,t=0; 93 Shape g; 94 for (i = 0; i < w.size(); i++) { 95 for (j = 0; j < w.size() - 1-i; j++) { 96 if (w.get(j).getArea() >= w.get(j + 1).getArea()) { 97 g = w.get(j); 98 w.set(j, w.get(j + 1)); 99 w.set(j + 1, g); 100 } 101 } 102 } 103 return w; 104 } 105 } 106 107 class Circle extends Shape{ 108 @Override 109 public double getArea(){ 110 double s; 111 s=Math.PI*radius*radius; 112 return s; 113 } 114 Shape shape; 115 Circle(){ 116 } 117 double radius; 118 Circle(double radius) 119 { 120 this.radius=radius; 121 } 122 @Override 123 public boolean validate(){ 124 if(radius>0) 125 return true; 126 else 127 return false; 128 } 129 } 130 abstract class Shape{ 131 Shape(){ 132 } 133 abstract public double getArea(); 134 abstract public boolean validate(); 135 } 136 class Triangle extends Shape{ 137 Shape shape; 138 Triangle(){ 139 } 140 double side1; 141 double side2; 142 double side3; 143 @Override 144 public boolean validate() 145 { 146 if(side1+side2<=side3||side1+side3<=side2||side2+side3<=side1) 147 { 148 return false; 149 } 150 if(side1-side2>=side3||side1-side3>=side2||side2-side3>=side1) 151 { 152 return false; 153 } 154 return true; 155 } 156 Triangle(double side1,double side2,double side3) 157 { 158 this.side1=side1; 159 this.side2=side2; 160 this.side3=side3; 161 } 162 @Override 163 public double getArea(){ 164 double p=(side1+side2+side3)/2; 165 double s=Math.sqrt(p*(p-side1)*(p-side2)*(p-side3)); 166 return s; 167 } 168 } 169 class Rectangle extends Shape{ 170 Shape shape; 171 Rectangle(){ 172 } 173 double width; 174 double length; 175 Rectangle(double width,double length) 176 { 177 this.width=width; 178 this.length=length; 179 } 180 @Override 181 public boolean validate(){ 182 if(width>0&&length>0) 183 return true; 184 else 185 return false; 186 } 187 @Override 188 public double getArea(){ 189 double s; 190 s=width*length; 191 return s; 192 } 193 }
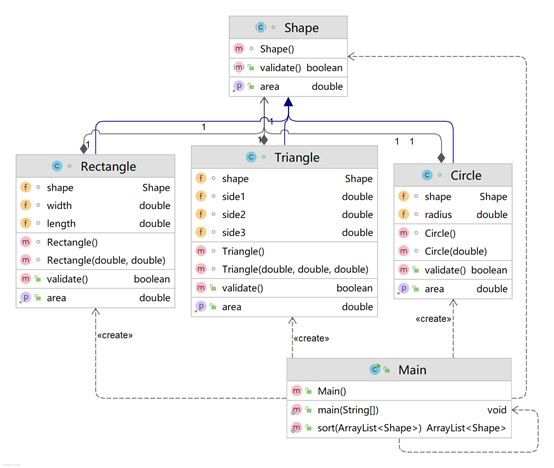
【类图】
【SourceMonitor源码分析】

7-6 实现图形接口及多态性 (30 分)
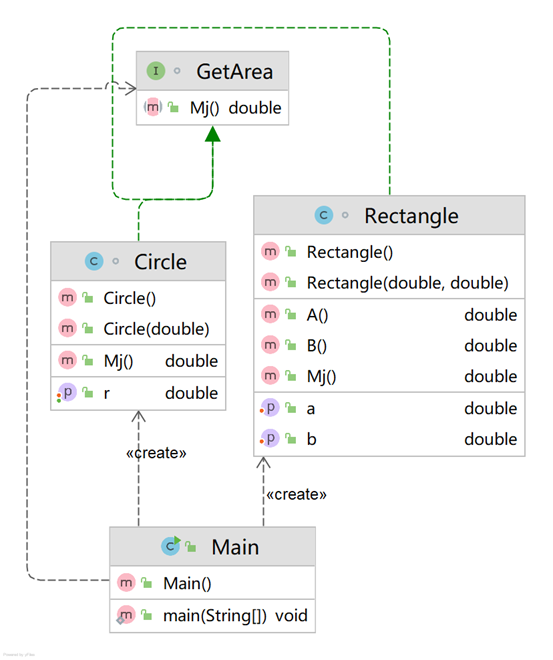
编写程序,使用接口及类实现多态性,类图结构如下所示:
其中:
GetArea为一个接口,无属性,只有一个GetArea(求面积)的抽象方法;
Circle及Rectangle分别为圆类及矩形类,分别实现GetArea接口
要求:在Main类的主方法中分别定义一个圆类对象及矩形类对象(其属性值由键盘输入),使用接口的引用分别调用圆类对象及矩形类对象的求面积的方法,直接输出两个图形的面积值。(要求只保留两位小数)
输入格式:
从键盘分别输入圆的半径值及矩形的宽、长的值,用空格分开。
输出格式:
如果输入的圆的半径值及矩形的宽、长的值非法(≤0),则输出Wrong Format
如果输入合法,则分别输出圆的面积和矩形的面积值(各占一行),保留两位小数。
输入样例1:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
2 3.6 2.45
结尾无空行
输出样例1:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
12.57
8.82
结尾无空行
输入样例2:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
9 0.5 -7.03
结尾无空行
输出样例2:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Wrong Format
结尾无空行
【解题报告】
必须实现类的封装性、继承性和多态性,否则本题不得分。
【源码】
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 interface GetArea{ 3 public double Mj(); 4 } 5 class Circle implements GetArea{ 6 private double r; 7 public Circle(){ 8 } 9 10 public Circle(double r){ 11 this.r=r; 12 13 } 14 15 public double getR(){ 16 17 return r; 18 } 19 20 public void setR(double r){ 21 this.r = r; 22 23 } 24 25 public double Mj(){ 26 return Math.PI*r*r; 27 } 28 } 29 30 class Rectangle implements GetArea{ 31 private double a,b; 32 33 public Rectangle(){ 34 } 35 36 public Rectangle(double a, double b){ 37 this.a=a; 38 this.b=b; 39 } 40 41 public double A(){ 42 43 return a; 44 } 45 public double B(){ 46 47 return b; 48 } 49 public void setA(double a){ 50 51 this.a=a; 52 } 53 public void setB(double b){ 54 55 this.b=b; 56 } 57 public double Mj(){ 58 59 return a*b; 60 } 61 } 62 63 public class Main{ 64 public static void main(String[] args){ 65 Scanner x = new Scanner(System.in); 66 double n1,n2,n3; 67 double num1,num2; 68 n1=x.nextDouble(); 69 n2=x.nextDouble(); 70 n3=x.nextDouble(); 71 72 if( n1<=0 || n2<=0 || n3<=0 ){//合法检测 73 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 74 System.exit(0); 75 } 76 GetArea Circle_Area=new Circle(n1); 77 GetArea Square_Area=new Rectangle(n2,n3); 78 num1=Circle_Area.Mj(); 79 num2=Square_Area.Mj(); 80 System.out.printf("%.2f\n",num1); 81 System.out.printf("%.2f\n",num2); 82 } 83 }
【类图】
【SourceMonitor源码分析】
【三种渐进式图形继承设计的思路与技术运用(封装、继承、多态、接口等)】
class Circle、Rectangle、Triangle继承与class Shape。
采用的是抽象类定义、实体类构建的方式。即 Shape 为抽象类,Circle、Rectangle 及 Triangle 为实体类。
getArea()方法为抽象方法,功能为求得图形的面积;validate()方法也为抽象方法,对图形的属性进行合法性校验;toString()继承自 Object,功能为输出图形的面积信息。
父类定义子类构建、接口定义实现类构建和抽象类定义实体类构建,子类再重写父类中的validate()和getArea()方法。
主函数利用多态,例如:
ArrayList<Shape> w=new ArrayList<>();
w.add(new Rectangle(width, length));
【对三次题目集中用到的正则表达式技术的分析总结】
于我而言,正则表达式,是很陌生的话题,在接触Java之前也没有听说过。前两次大作业的正则表达式的使用只是简单的词的判断。
在计算Java保留字的题目中,关键词可以用不断循环和连续判断字符串是否相等来判断是否为关键字,所以也没有很好地训练自己使用正则表达式的能力。
在后续有连续三次的正则表达式的训练题,专门为了训练正则表达式的使用,因此我更加重视。这三道题目相对简单,大部分是字母与数字的混合形式并要求识别。
使用正则表达式,关键在Pattern的识别。
Pattern的书写,大部分情况下都是表示大多种情况,部分情况则需要具体情况具体分析。Matcher.matches()就是一个很好的例子。
匹配Pattern实例,只有完全匹配时才会返回true等,也可以是if的特别判例,具体情况具体分析。
7-4 统计Java程序中关键词的出现次数 (25 分)
编写程序统计一个输入的Java源码中关键字(区分大小写)出现的次数。说明如下:
Java中共有53个关键字
从键盘输入一段源码,统计这段源码中出现的关键字的数量
注释中出现的关键字不用统计
字符串中出现的关键字不用统计
统计出的关键字及数量按照关键字升序进行排序输出
未输入源码则认为输入非法
输入格式:
输入Java源码字符串,可以一行或多行,以exit行作为结束标志
输出格式:
当未输入源码时,程序输出Wrong Format
当没有统计数据时,输出为空
当有统计数据时,关键字按照升序排列,每行输出一个关键字及数量,格式为数量\t关键字
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
//Test public method
public HashMap(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
}
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
this.threshold = tableSizeFor(initialCapacity);
}
exit
结尾无空行
输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
1 float
3 if
2 int
2 new
2 public
3 this
2 throw
结尾无空行
【解题报告】
题目必须使用List、Set或Map中一种或多种,如完全未使用如上接口,不予评分
【源码】
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class Main6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner x = new Scanner(System.in);
StringBuilder a = new StringBuilder();
Map map=new TreeMap();
String[] blz = {"abstract", "assert", "boolean", "break", "byte", "case", "catch", "char", "class", "const", "continue", "default", "do", "double", "else", "enum", "extends", "false", "final", "finally", "float", "for", "goto", "if", "implements", "import", "instanceof", "int", "interface", "long", "native", "new", "null", "package", "private", "protected", "public", "return", "short", "static", "strictfp", "super", "switch", "synchronized", "this", "throw", "throws", "transient", "true", "try", "void", "volatile", "while"};
String kg,exit="exit";
int i,n,flag=0;
kg = x.nextLine();
while( !kg.equals(exit)) {
a.append(kg.replaceAll("//.*", " ").replaceAll("\".*\"", " "));//去掉"//"后和的内容以及双引号里的内容
kg = x.nextLine();
flag=1;
}
String b = a.toString().replaceAll("/\\*\\s*.*\\s*\\*/", " ");//去掉"/* */"里的内容,放入字符串b中
if(flag==0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
for(i=0;i< gjc.length;i++) {
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("\\b"+gjc[i]+"\\b");
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(b);
n=0;
while(matcher.find()) {
n++;
}
if(n!=0){
map.put(gjc[i], n);
}
}
String map1= String.valueOf(map);
String map2=map1.replace("{","").replace("}","");
String[] map3=map2.split(", ");
for (i=0;i< map3.length;i++){
String[] map4=map3[i].split("=");
System.out.println(map4[1]+"\t"+map4[0]);
}
}
}
【类图】
【SourceMonitor源码分析】
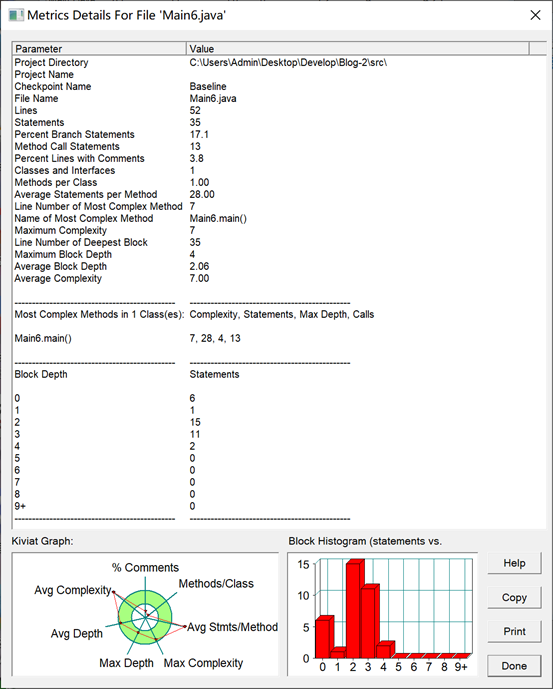
【Java集合框架应用的分析总结】
如果一个程序只包含固定数量的且其生命周期都是已知的对象,那么这是一个非常简单的程序。
通常,程序总是根据运行时才知道的某些条件去创建新对象。在此之前,不会知道你所需要对象的数量,甚至不知道确切的类型。为了解决这个普遍的编程问题,需要在任意时刻和任意位置创建任意数量的对象。所以,就不能依靠创建命名的引用来持有每一个对象,因为你不知道实际上会需要多少这样的引用。
List、Set和Map的区别:
前两者与Map的区别显而易见,前两者属于单个元素级别的存储,而Map是键值对的存储方式。
在无源码的情况下,可以先理解为List采用线性结构存储,元素可以为null。
ArrayList的定义:
1 public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E> 2 implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
Java集合类框架的基本接口:
首先集合类操作的对象,我们称为元素,而集合类接口的每一种具体的实现类都可以选择以它自己的方式对元素进行保存和排序。有的集合类允许重复的键,有的则不允许。
Java集合类里面最基本的接口有:
Collection:代表一组对象,每一个对象都是它的子元素。
List:有顺序的 collection,并且可以包含重复元素(顺序)。
Set:不保证有序,同时不包含重复元素的Collection(唯一)。
Map:可以把键(key) 映射到值(value) 的对象,键不能重复(键值对)。
Java 常见集合的数据结构以及其特点
List
ArrayList:Object 数组(查询快,增删慢,线程不安全,效率高)
Vector:Object数组(查询快,增删慢,线程安全,效率低)
LinkedList:双向链表,JDK1.6 之前是循环链表,JDK1.7 取消了循环(查询慢,增删快,线程不安全,效率高)
Map
HashMap:JDK1.8 之前 HashMap 由数组+链表组成的,数组是 HashMap 存储元素的主体,链表则是主要为了解决哈希冲突而存在的,即 “拉链法” 解决冲突。JDK1.8 以后在解决哈希冲突时有了较大的变化,当链表长度大于阈值(默认为8)时,将链表转化为红黑树,以减少搜索时间(哈希表对键进行散列,Map结构即映射表存放键值对)
LinkedHashMap:LinkedHashMap 继承自 HashMap,所以它的底层仍然是基于拉链式散列结构即由数组和链表或红黑树组成。另外,LinkedHashMap 在上面结构的基础上,增加了一条双向链表,使得键值对的插入顺序以及访问顺序等逻辑可以得以实现。
Hashtable:数组+链表组成的,数组是 HashMap 的主体,链表则是主要为了解决哈希冲突而存在的
TreeMap:红黑树(平衡二叉排序树)
Set
HashSet: 基于 HashMap 实现的,底层采用 HashMap 来保存元素(不保证有序,唯一)
LinkedHashSet:LinkedHashSet 继承与 HashSet,并且其内部是通过 LinkedHashMap 来实现的。有点类似于我们之前说的LinkedHashMap 其内部是基于 Hashmap 实现一样,不过还是有一点点区别的。
TreeSet:红黑树,自平衡的排序二叉树(可实现自然排序,例如 a-z)
三、踩坑心得
这三次的大作业,让我收获颇丰,但同时也让我踩坑不少。
难度主要集中在对类这一大模块的语法,类与类之间的关系的掌握,正则表达式的使用也是一块硬骨头。但这次大作业的正则表达式相对上次对正则表达式的使用难度明显提高,让我一开始有些无所适从。
这次的题目还涉及到对Map,List的使用,让我们初步了解了java中的链表、集合等数据结构。
本次Blog题量和涉及到的知识点相比起第一次Blog多了不少,通过自己实现类与类之间关系而得到一些经验。实现LIst,Map接口的使用的过程中遇到了很多的困难,在同学们的帮助下都一一得到了解决。新的知识点例如多态和接口还需要进一步地夯实基础,勤看课本。
四、改进建议
个人认为大作业的难度偏高,一星期的时间难以完全掌握,希望PTA大作业的难度能循序渐进。考虑到我这样的学困生能力欠缺,我希望老师们布置PTA大作业的时候可以分难度分等级要求同学们完成,学神们可以挑战难度巅峰的题目,学霸们也可以挑战高难度,也衷心希望老师能为我这样的学困生准备一些基础题目,可以让我的能力得到训练和锻炼,循序渐进,慢慢进步,不至于对太难的题目一下子失去所有的信心和热情。
五、总结
这三次大作业,对于我这样的学困生来说,题目大有挑战,能锻炼人的能力,但同时也很挫败我的自信心和学习的热情。题目集的难度很大,我可以由此发现自己还是有很多不足。
这三次大作业,我发现自己对正则表达式的运用还是不熟练,我应该要不断学习正则表达式,争取赶上大家的学习进度。
好不容易写完了这些题目,我总结了自己的阶段性学习情况。我掌握了正则表达式的各种表达方式以及正则表达式里的各种函数,了解了它们各自的作用,在java中用正则表达式实践了对字符串的操作。我认为正则表达式有着非常重要的作用,这对我今后的程序编写是有益处的。
我在今后的学习中要更加变得耐心,对于从未见过的知识要敢于接受,不能畏惧苦难。触类旁通,迎难而上,不能害怕接受新知识,在正则表达式方面还有许多未知的领域要勤加练习,还有很多函数需要去了解和训练。探索精神是必要的,探索精神就像我在书海上的灯塔,指引着我不断前进!


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号