线程
线程
正在执行的程序主体。
//一个单线程程序
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
for(int i = 0;i < 10000; i++){
System.out.print("Good");
}
}
}
多线程的情况
package com.thread.basic.print;
public class MyThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10000 ; i++) {
System.out.print("Hello ");
}
}
}
package com.thread.basic.print;
public class PrintThreadMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//多线程:主线程和MyThread
MyThread myThread = new MyThread();
myThread.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
System.out.print("Thread!");
}
}
}
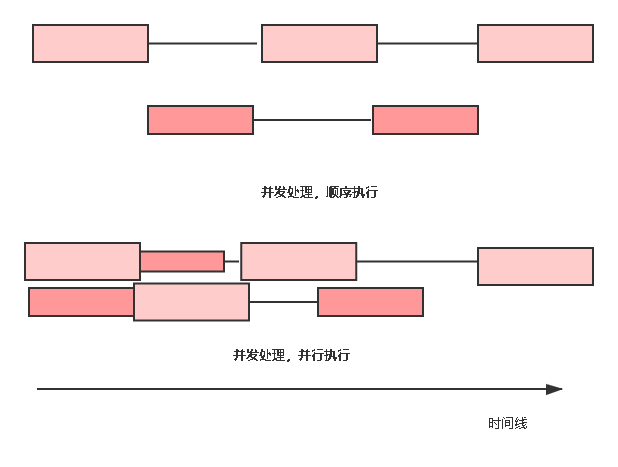
- 顺序:多个操作依次处理(两件事情,交个一个人做);
- 并行:多个操作同时处理(两件事情,交给两个人做);
- 并发:将一个操作分割成多个部分无序处理。
启动线程的几种方法
- Thread
- Runnable
- Callable(带结果返回)
- ThreadFactory
有些面试官喜欢为启动线程有哪几种方法?本质上只有一种,就是实现Runnable接口
package com.thread.basic.print;
public class MessageRunnable implements Runnable {
private String msg;
public MessageRunnable(String msg) {
this.msg = msg;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10000 ; i++) {
System.out.println(msg);
}
}
}
线程的互斥与协作
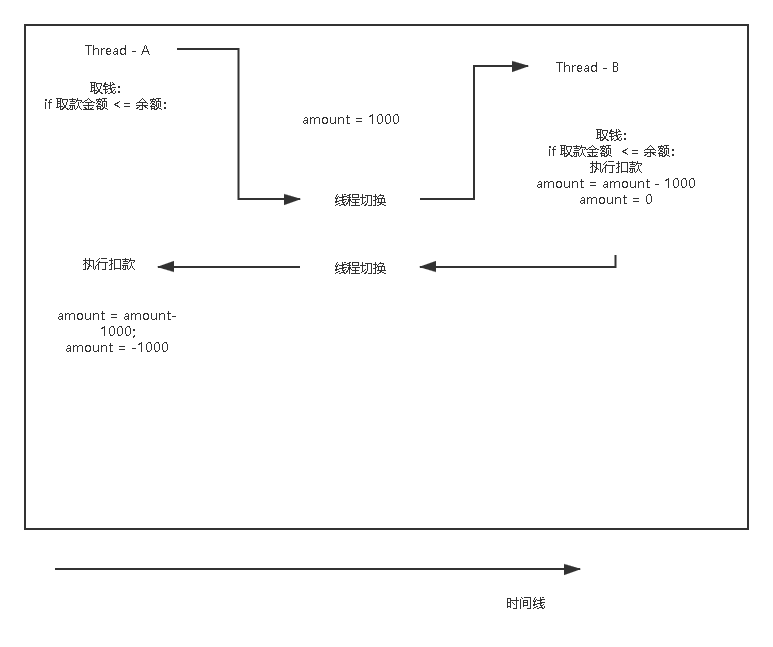
package com.thread.basic.sync;
public class Bank {
private int money;
private String name;
public Bank(int money, String name) {
this.money = money;
this.name = name;
}
//存款
public synchronized void deposit(int money){
this.money += money;
}
//取款
public synchronized boolean withdraw(int money){
if (this.money >= money){
this.money -= money;
return true;
}else {
return false;
}
}
public String getName(){
return this.name;
}
}
Synchronized
//代码块
synchronized(this/obj/xxx.Class){
}
//实例方法
synchronized void method(){
}
void method(){
synchronized(this){
}
}
//静态方法
static void method(){
synchronized(Something.class){
}
}
//当前线程是否持有锁
assert Thread.holdsLock(obj);
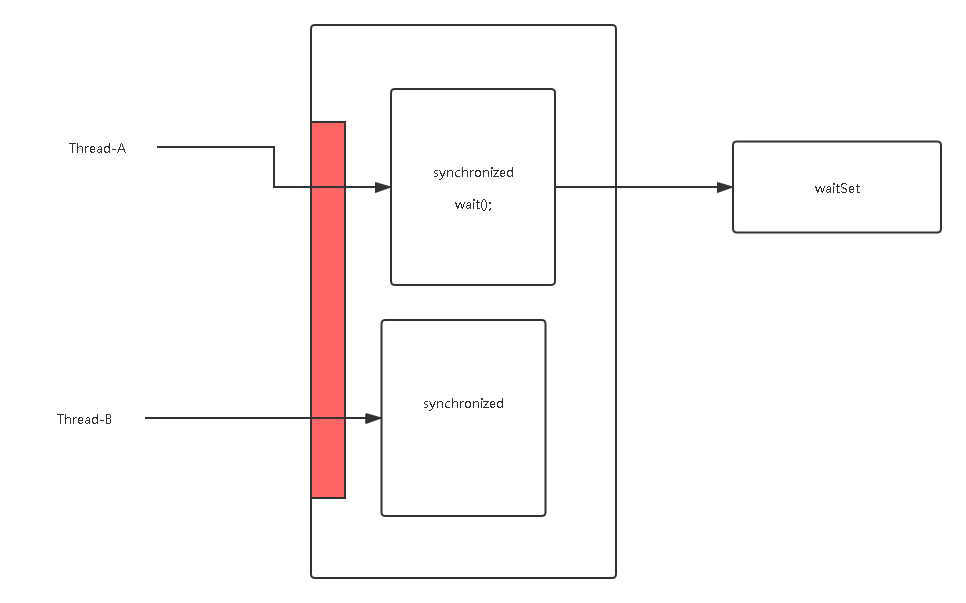
wait
将线程放入等待队列,释放锁
线程必须要持有锁
//执行前必须先持有锁
wait();
this.wait();
notify/notifyAll
唤醒线程抢锁,从等待队列去除一个/所有线程
线程必须要持有锁
notify();
notifyAll();
this.notifyAll();
obj.notifyAll();
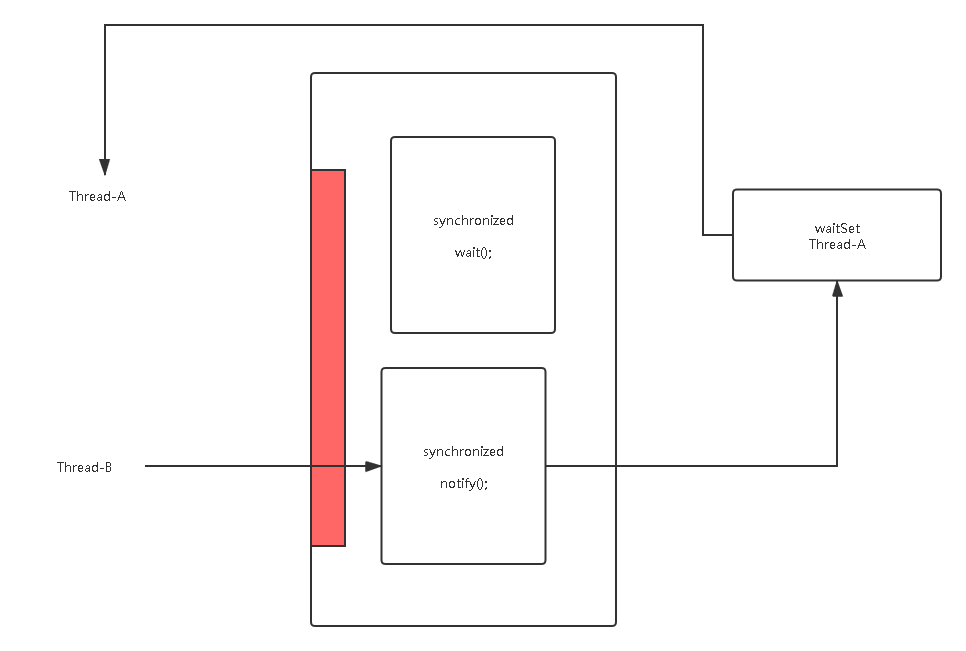
注:wait(),notify(),notifyAll()时Object类的方法,但是如果说是Thread类的方法也没有错,因为Object是所有类的父类
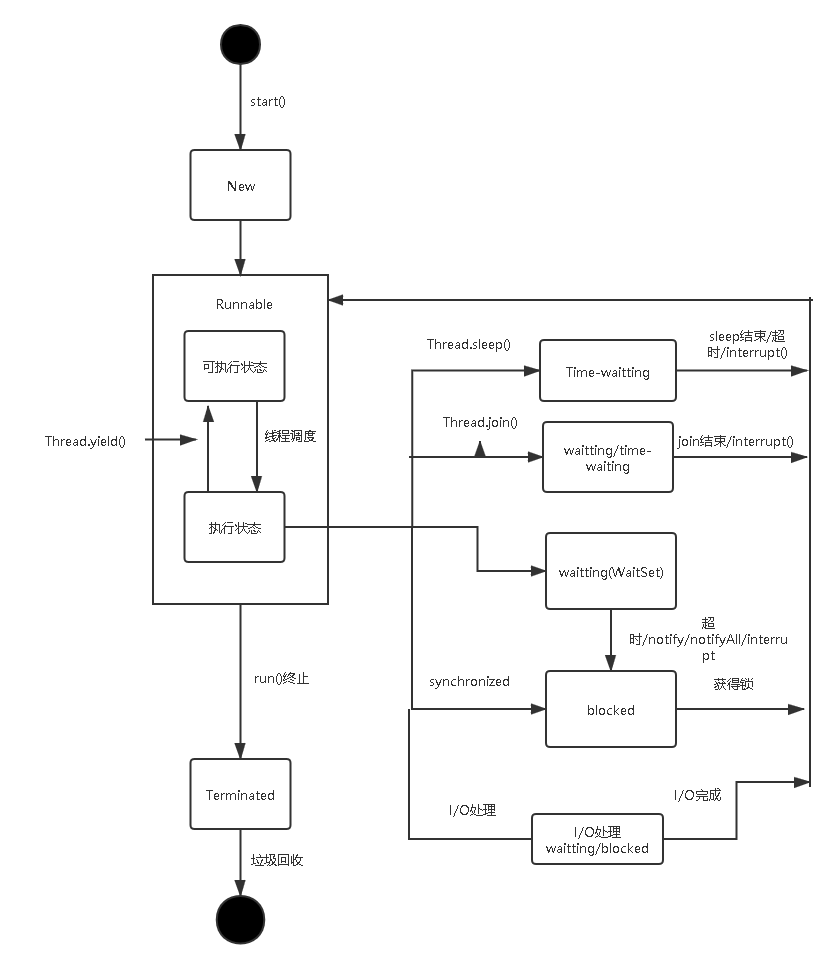
线程状态


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号