决策树分类器的构建及应用
决策树原理
决策树是属于机器学习监督学习分类算法中比较简单的一种,决策树是一个预测模型,代表对象属性与对象值之间的一种映射关系。树中每个节点表示某个对象,每个分叉路径代表某个可能的属性值,叶结点对应从根节点到该叶节点所经历的路径所表示的对象的值。决策树仅有单一输出,若欲有复数输出,可以建立独立的决策树以处理不同输出。
ID3算法
from math import log
from treeplotter import *
def get_cnt_dict(dataset, index=-1):
'''
当 index = -1 时(最后一列), 统计的是每个类别出现的次数
当 index = 其他值时, 统计的是某列特征的各个值出现的次数
'''
cnt_dict = {}
for record in dataset:
key = record[index]
if key not in cnt_dict:
cnt_dict[key] = 0
cnt_dict[key] += 1
# print(cnt_dict)
return cnt_dict
def get_cnt_dict_cont(dataset, index):
tmp_dataset = sorted(dataset, key=lambda record: record[index])
cnt_dict = {}
size = len(tmp_dataset)
if size < 1:
cnt_dict
for record in tmp_dataset:
key = record[index]
y = record[-1]
def get_max_y(y_list):
'''
采用 majority vote 的方法(进行多数投票)
'''
y_cnt_dict = {}
for key in y_list:
if key not in y_cnt_dict:
y_cnt_dict[key] = 0
y_cnt_dict[key] += 1
max_val = 0
max_key = 0
for key, val in y_cnt_dict.items():
if val > max_val:
max_val = val
max_key = key
max_y = max_key
return max_y
def get_new_dataset_cont(dataset, id_x, threshold):
new_dataset_less = []
new_dataset_greater = []
for record in dataset:
if record[id_x] <= threshold:
new_dataset_less.append(record[:id_x] + record[id_x + 1:])
else:
new_dataset_greater.append(record[:id_x] + record[id_x + 1:])
return new_dataset_less, new_dataset_greater
class Dataset(object):
def __init__(self, option):
if option == 'iris':
self.gen_iris_dataset()
def gen_MLA_dataset(self):
self.size = 5
self.dataset = [[1, 100, 1], [1, 100, 1], [1, 200, -1], [0, 100, -1], [0, 100, -1]]
# self.dataset = [[1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 1], [1, 0, -1], [0, 1, -1], [0, 1, -1]]
def gen_iris_dataset(self):
from sklearn import datasets
iris = datasets.load_iris()
self.x_name_list = iris.feature_names
self.y_name_list = iris.target_names
self.size = len(iris.data)
x_list = iris.data
y_list = iris.target
dataset = []
for i in range(self.size):
x = x_list[i].tolist()
record = [x for x in iris.data[i]]
y = int(y_list[i])
record.append(y)
dataset.append(record)
self.dataset = dataset
def get_index_list(self, shuffle=True, seed=None):
import numpy as np
index_list = np.arange(self.size)
if shuffle:
if seed:
np.random.seed(seed)
np.random.shuffle(index_list)
return index_list
def get_train_and_test_data(self, train_ratio=0.8, seed=0):
size = self.size
train_size = int(size * train_ratio)
test_size = size - train_size
index_list = self.get_index_list(seed=seed)
train_index = index_list[:train_size]
test_index = index_list[train_size:]
dataset = self.dataset
train_set = []
for i in train_index:
train_set.append(dataset[i])
test_set = []
for i in test_index:
test_set.append(dataset[i])
self.train_set = train_set
self.test_set = test_set
return train_set, test_set
class DecisionTree(object):
def __init__(self):
pass
def get_HD(self, dataset):
'''
计算经验熵, HD, empirical entrophy
H(D) = - Σ [ pi · lg(pi) ]
pi = Ci / D
'''
total_cnt = len(dataset)
y_cnt_dict = get_cnt_dict(dataset, -1)
HD = 0
for y, cnt in y_cnt_dict.items():
p = cnt / total_cnt
HD -= p * log(p, 2)
return HD
def get_HD_A_cont(self, id_x, dataset):
'''
计算连续属性的经验条件熵
'''
total_cnt = len(dataset)
dataset = sorted(dataset, key=lambda record: record[id_x])
# print(dataset)
min_HD_A_cont = 1e10
best_threshold = 0
y_list = [record[-1] for record in dataset]
# print(y_list)
for i in range(1, len(y_list)):
pre_x = dataset[i - 1][id_x]
now_x = dataset[i][id_x]
pre_y = dataset[i - 1][-1]
now_y = dataset[i][-1]
if pre_y != now_y:
new_dataset1 = dataset[:i]
HD1 = self.get_HD(new_dataset1)
p1 = i / total_cnt
new_dataset2 = dataset[i:]
HD2 = self.get_HD(new_dataset2)
p2 = 1 - p1
threshold = (pre_x + now_x) / 2
HD_A_cont = p1 * HD1 + p2 * HD2
if HD_A_cont < min_HD_A_cont:
min_HD_A_cont = HD_A_cont
best_threshold = threshold
return min_HD_A_cont, best_threshold
def get_best_feature_index_cont(self, dataset):
HD = self.get_HD(dataset)
feature_num = len(dataset[0]) - 1
max_info_gain = 0
best_feature_index = 0
best_threshold = 0
for feature_index in range(feature_num):
# find min_HD_A_cont
# so that info_gain_cont is max
HD_A_cont, threshold = self.get_HD_A_cont(feature_index, dataset)
info_gain = HD - HD_A_cont
# print(HD_A_cont, threshold, info_gain)
if info_gain > max_info_gain:
max_info_gain = info_gain
best_feature_index = feature_index
best_threshold = threshold
return best_feature_index, best_threshold
def create_tree_cont(self, dataset, x_name_list):
feature_name = [name for name in x_name_list]
y_list = [record[-1] for record in dataset]
if len(y_list) == 0:
return 0
y0 = y_list[0]
if y_list.count(y0) == len(y_list):
# 只剩一个类别
y = y0
return y
record0 = dataset[0]
if len(record0) == 1:
# 只剩 1 个属性, 无法继续划分, 投票决定叶子结点的类别
y = get_max_y(y_list)
return y
index, threshold = self.get_best_feature_index_cont(dataset)
name = feature_name[index] + '#' + str(threshold)
tree = {name: {}}
# feature_value1 = set([record[index] for record in dataset])
feature_value1 = '<= ' + str(threshold)
feature_value2 = '> ' + str(threshold)
del (feature_name[index])
sub_feature_name1 = [name for name in feature_name]
sub_feature_name2 = [name for name in feature_name]
new_dataset1, new_dataset2 = get_new_dataset_cont(dataset, index, threshold)
sub_tree1 = self.create_tree_cont(new_dataset1, sub_feature_name1)
tree[name][0] = sub_tree1
sub_tree2 = self.create_tree_cont(new_dataset2, sub_feature_name2)
tree[name][1] = sub_tree2
return tree
# 计算准确率
def get_accuracy(self, tree, test_set):
get_index = {'sepal length (cm)': 0, 'sepal width (cm)': 1, 'petal length (cm)': 2, 'petal width (cm)': 3}
cnt_all = len(test_set)
cnt_yes = 0
for ix in range(cnt_all):
sub_tree = tree
test_sample = test_set[ix]
# print(test_sample)
for i in range(10):
key = list(sub_tree.keys())[0]
# print(key)
pos = key.find('#')
name = key[:pos]
threshold = float(key[pos + 1:])
# print('name:', name)
# print('threshold:', threshold)
feature_index = get_index[name]
x = test_sample[feature_index]
# print('x:', x)
val_list = sub_tree[key]
if x <= threshold:
val = val_list[0]
else:
val = val_list[1]
if isinstance(val, int):
# print('test_y:', test_sample[-1])
# print('pred_y:', val)
if val == test_sample[-1]:
cnt_yes += 1
# print('index', i)
break
else:
sub_tree = val
print('准确率: %.2f%%' % (100 * cnt_yes / cnt_all))
if __name__ == '__main__':
ds = Dataset(option='iris')
train_set, test_set = ds.get_train_and_test_data(train_ratio=0.8, seed=2)
x_name_list = ds.x_name_list
dt = DecisionTree()
tree = dt.create_tree_cont(train_set, x_name_list)
print('id3 decision tree:\n', tree, '\n\n')
createPlot(tree)
dt.get_accuracy(tree, test_set)
C4.5 算法
C4.5 算法与ID3算法主要的区别是引入了新概念“信息增益率”, C4.5 是选择信息增益率最大的属性作为树节点。
def get_IV(self, dataset, index, threshold):
total_cnt = len(dataset)
x_cnt_dict = get_cnt_dict_cont(dataset, index, threshold)
IV = 0
for x, cnt in x_cnt_dict.items():
p = cnt / total_cnt
if p > 0:
IV -= p * log(p, 2)
return IV
分析
实验结果:
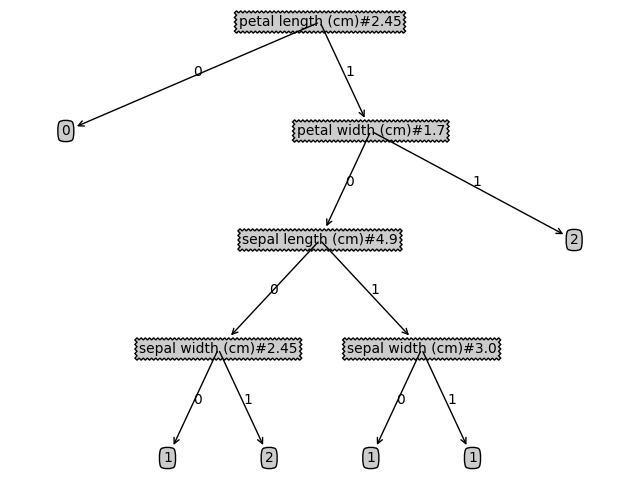
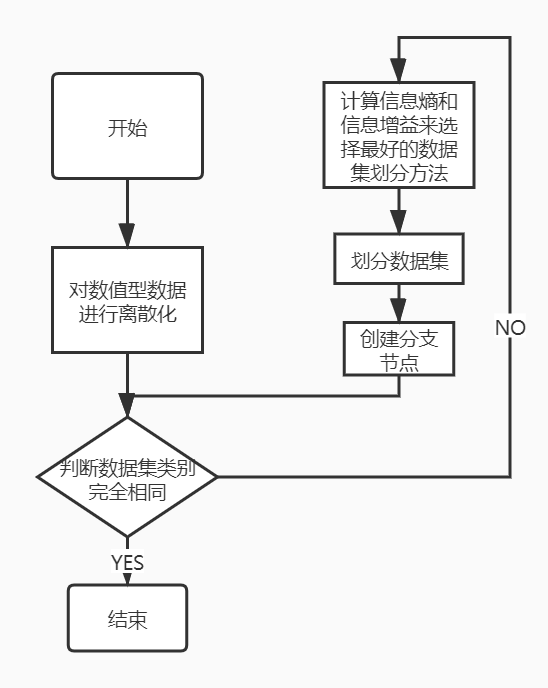
id3算法流程:
- 数据准备:需要对数值型数据进行离散化
- ID3算法构建决策树:
- 如果数据集类别完全相同,则停止划分
- 否则,继续划分决策树:
- 计算信息熵和信息增益来选择最好的数据集划分方法;
- 划分数据集
- 创建分支节点:
- 对每个分支进行判定是否类别相同,如果相同停止划分,不同按照上述方法进行划分。
C4.5算法仅仅是把信息增益转化成信息增益率,不再赘述。
ID3和C4.5主要区别
ID3算法通过计算每个属性的信息增益,认为信息增益高的是好属性,每次划分选取信息增益最高的属性为划分标准信息增益容易偏向取值较多的特征的问题
C4.5采用信息增益率的方法,它是信息增益和特征熵的比值,特征数越多的特征对应的特征熵越大,它作为分母,可以校正信息增益偏向取值较多的特征的问题
C4.5继承了ID3的有点,并在以下几个方面对ID3算法进行了改进:
- 用信息增益比来选择属性,克服了用信息增益选择属性是偏向选择去之多的属性的不足
- 在数的构造过程中进行剪枝
- 能够对连续的属性进行离散化处理
- 能够对不完整的数据进行处理


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号