字典树
字典树
在计算机科学中,trie,又称前缀树或字典树,是一种有序树,用于保存关联数组,其中的键通常是字符串。与二叉查找树不同,键不是直接保存在节点中,而是由节点在树中的位置决定。一个节点的所有子孙都有相同的前缀,也就是这个节点对应的字符串,而根节点对应空字符串。一般情况下,不是所有的节点都有对应的值,只有叶子节点和部分内部节点所对应的键才有相关的值。
字典树设计的核心思想是空间换时间,所以数据结构本身比较消耗空间。trie树常用于搜索提示。如当输入一个网址,可以自动搜索出可能的选择。当没有完全匹配的搜索结果,可以返回前缀最相似的可能。
如图,可以发现,这棵字典树用边来代表字母,而从根结点到树上某一结点的路径就代表了一个字符串。举个例子,1→4→8→12 表示的就是字符串 caa。
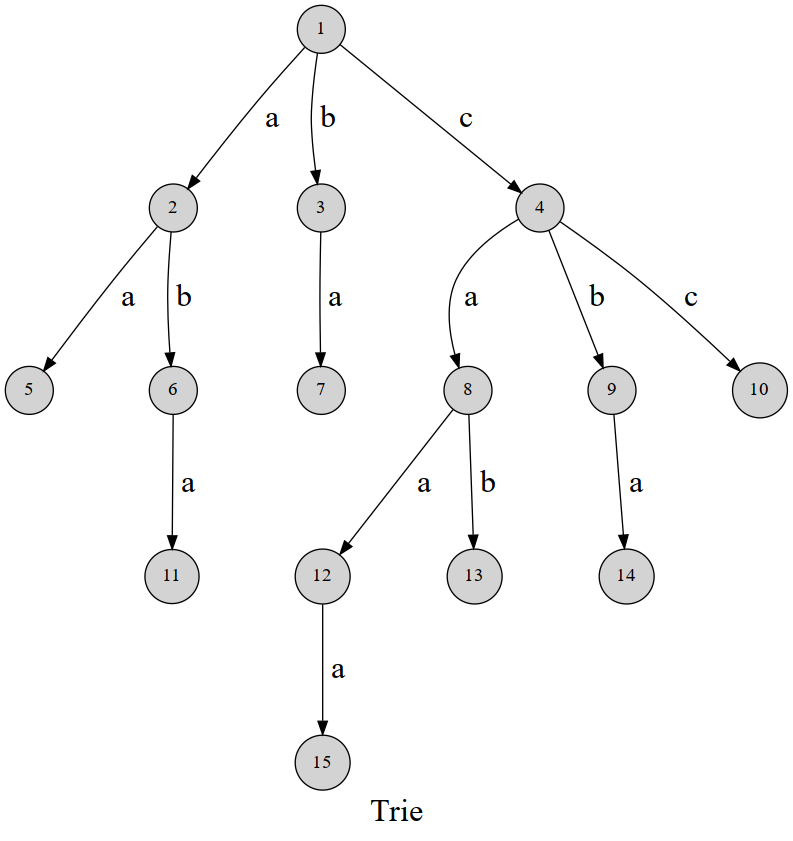
字典树的性质
- 根节点(Root)不包含字符,除根节点外的每一个节点都仅包含一个字符;
- 从根节点到某一节点路径上所经过的字符连接起来,即为该节点对应的字符串;
- 任意节点的所有子节点所包含的字符都不相同;
Trie 关键词查找过程
- 每次从根结点开始搜索;
- 获取关键词的第一个字符,根据该字符选择对应的子节点,转到该子节点继续检索;
- 在相应的子节点上,获取关键词的第二个字符,进一步选择对应的子节点进行检索;
- 以此类推,进行迭代过程;
- 在某个节点处,关键词的所有字母已被取出,则读取附在该节点上的信息,查找完成。
关键词的插入和查找过程的时间复杂度均为 O(key_length),空间复杂度 O(ALPHABET_SIZE * key_length * N) ,其中 N 是关键词的数量。
Trie 的应用
- 字符串检索:事先将已知的一些字符串(字典)的有关信息保存到 Trie 里,查找另外一些未知字符串是否出现过或者出现频率。
- 字符串最长公共前缀:Trie 利用多个字符串的公共前缀来节省存储空间,反之,当我们把大量字符串存储到一棵 Trie 上时,我们可以快速得到某些字符串的公共前缀。
- 排序:Trie 树是一棵多叉树,只要先序遍历整棵树,输出相应的字符串,便是按字典序排序的结果。
- 作为其他数据结构和算法的辅助结构:如后缀树,AC自动机等,AC自动机也可以理解为在tire树上进行kmp。
代码实现
tire模板
struct trie { int nex[100000][26], cnt; bool exist[100000]; // 该结点结尾的字符串是否存在 void insert(char *s, int l) { // 插入字符串 int p = 0; for (int i = 0; i < l; i++) { int c = s[i] - 'a'; if (!nex[p][c]) nex[p][c] = ++cnt; // 如果没有,就添加结点 p = nex[p][c]; } exist[p] = 1; } bool find(char *s, int l) { // 查找字符串 int p = 0; for (int i = 0; i < l; i++) { int c = s[i] - 'a'; if (!nex[p][c]) return 0; p = nex[p][c]; } return exist[p]; } };
检索字符串
对所有名字建 trie,再在 trie 中查询字符串是否存在、是否已经点过名,第一次点名时标记为点过名。
#include <cstdio> const int N = 500010; char s[60]; int n, m, ch[N][26], tag[N], tot = 1; int main() { scanf("%d", &n); for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) { scanf("%s", s + 1); int u = 1; for (int j = 1; s[j]; ++j) { int c = s[j] - 'a'; if (!ch[u][c]) ch[u][c] = ++tot; u = ch[u][c]; } tag[u] = 1; } scanf("%d", &m); while (m--) { scanf("%s", s + 1); int u = 1; for (int j = 1; s[j]; ++j) { int c = s[j] - 'a'; u = ch[u][c]; if (!u) break; // 不存在对应字符的出边说明名字不存在 } if (tag[u] == 1) { tag[u] = 2; puts("OK"); } else if (tag[u] == 2) puts("REPEAT"); else puts("WRONG"); } return 0; }

#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #define TREE_WIDTH 256 #define WORDLENMAX 128 struct trie_node_st { int count; int pass; //add a count for the part-include for example 'this is' then the 'is' is hited two times struct trie_node_st *next[TREE_WIDTH]; }; static struct trie_node_st root={0, 0, {NULL}}; static const char *spaces=" \t\n/.\"\'()"; void myfree(struct trie_node_st * rt) { for(int i=0; i<TREE_WIDTH; i++){ if(rt->next[i]!=NULL){ myfree(rt->next[i]); rt->next[i] = NULL; } } free(rt); return; } static int insert (const char *word) { int i; struct trie_node_st *curr, *newnode; if (word[0]=='\0'){ return 0; } curr = &root; for (i=0; ; ++i) { if (word[i] == '\0') { break; } curr->pass++;//count if (curr->next[ word[i] ] == NULL) { newnode = (struct trie_node_st*)malloc(sizeof(struct trie_node_st)); memset (newnode, 0, sizeof(struct trie_node_st)); curr->next[ word[i] ] = newnode; } curr = curr->next[ word[i] ]; } curr->count ++; return 0; } static void printword (const char *str, int n) { printf ("%s\t%d\n", str, n); } static int do_travel (struct trie_node_st *rootp) { static char worddump[WORDLENMAX+1]; static int pos=0; int i; if (rootp == NULL) { return 0; } if (rootp->count) { worddump[pos]='\0'; printword (worddump, rootp->count+rootp->pass); } for (i=0;i<TREE_WIDTH;++i) { worddump[pos++]=i; do_travel (rootp->next[i]); pos--; } return 0; } int main (void) { char *linebuf=NULL, *line, *word; size_t bufsize=0; int ret; while (1) { ret=getline (&linebuf, &bufsize, stdin); if (ret==-1) { break; } line=linebuf; while (1) { word = strsep (&line, spaces); if (word==NULL) { break; } if (word[0]=='\0') { continue; } insert (word); } } do_travel (&root); free (linebuf); for(int i=0; i<TREE_WIDTH; i++){ if(root.next[i]!=NULL){ myfree(root.next[i]); } } exit (0); }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号