线段树分治学习笔记
目录
- 线段树分治
- 代码实现
线段树分治
线段树分治是一种离线算法,它对时间轴构造了线段树,以处理时间段的处理
举个简单的例子,维护时间[1,4]:
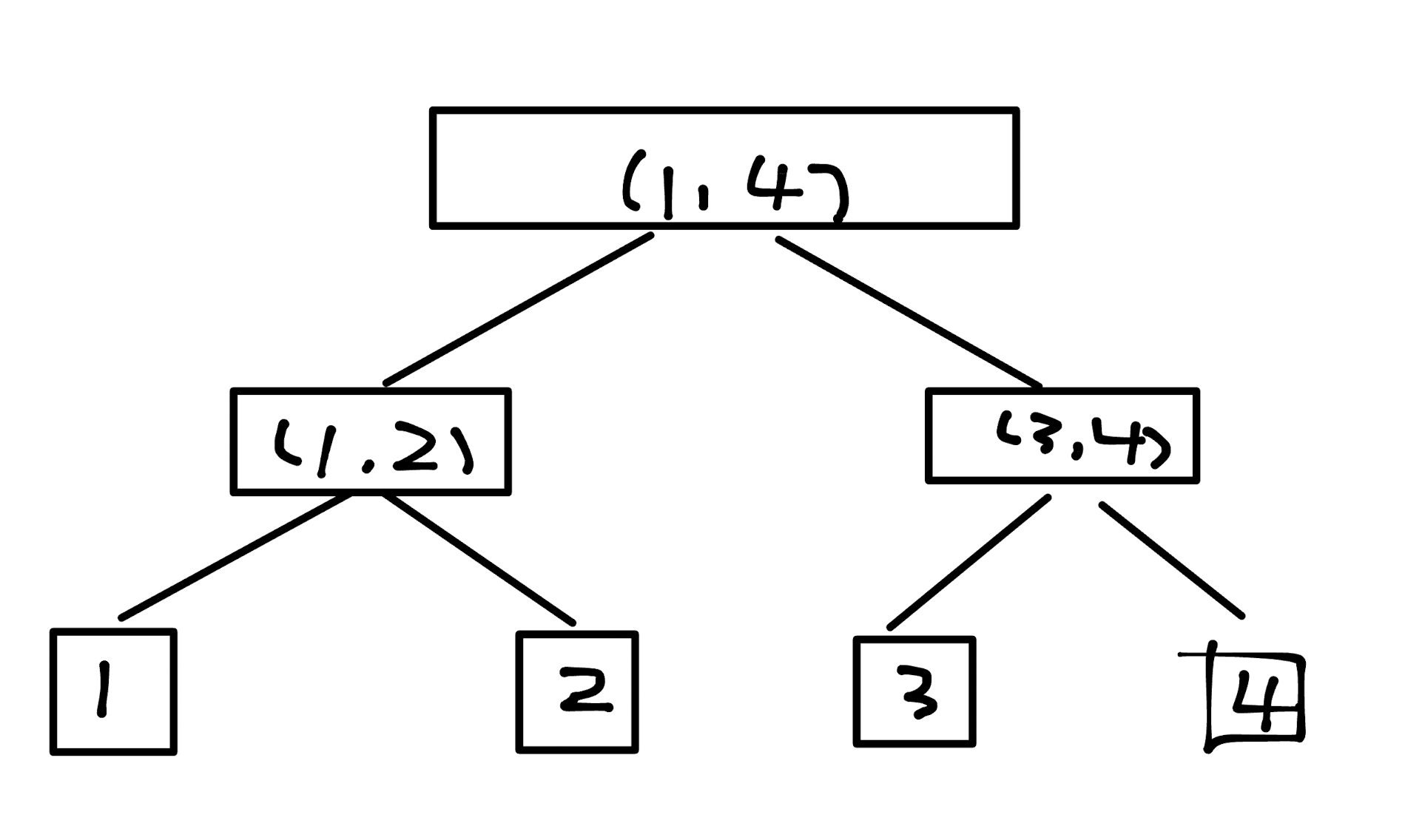
若某次修改从1延伸到3才结束,那么需要修改的便是[1,2]和[3,3]
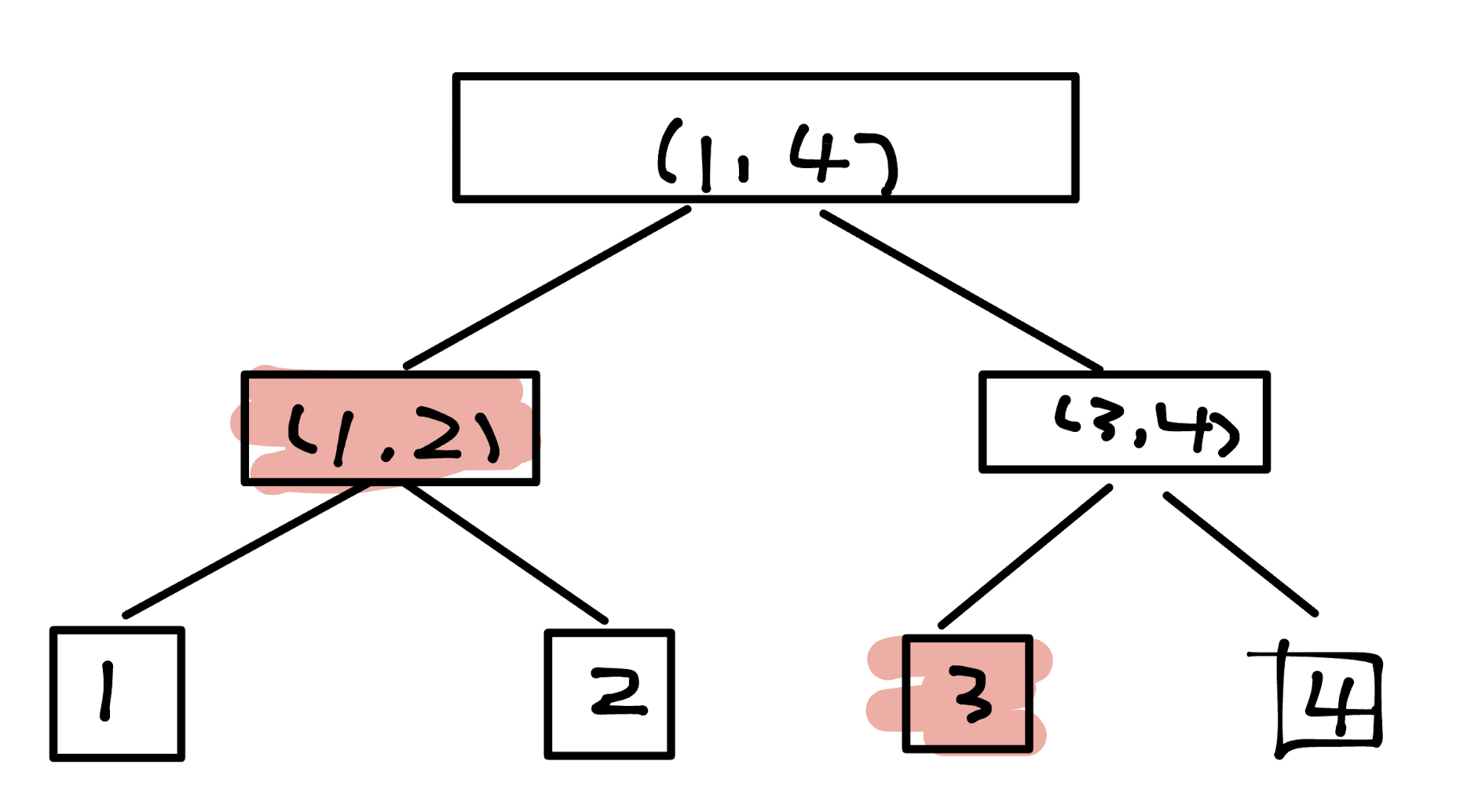
我们给每个节点分配一个vector来存储发生在这个时间段的所有操作。
最后对线段树做深度优先搜索,每次进入一个节点就完成这个节点上的操作,回到这个节点时又把这些操作撤销。
此处运用可撤销并查集维护连通性。
代码实现
//来自loj121 「离线可过」动态图连通性
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <stack>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 5e3+7;
const int M = 5e5+8;
#define PII pair<int, int>
typedef struct{ //操作
int x, y, opt;
}Opt;
Opt a[M];
class DSU{ //可撤销并查集
private:
int fa[N];
int dep[N];
stack<PII>sta;
public:
inline int size(){
return sta.size();
}
inline void init(int n){
while(!sta.empty())
sta.pop();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
fa[i] = i, dep[i] = 0;
}
inline int find(int x){
if(x == fa[x])
return x;
return find(fa[x]);
}
inline void join(int x, int y){ //秩合并
x = find(x);
y = find(y);
if(x == y)
return;
if(dep[x] > dep[y])
swap(x, y);
if(dep[x] == dep[y])
dep[y]++;
sta.push(make_pair(x, y));
fa[x] = y;
}
inline bool check(int x, int y){
return find(x) == find(y);
}
inline void undo(int now){ //撤销至第now次操作
while(sta.size() > now){
int x = sta.top().first;
int y = sta.top().second;
if(dep[y] == dep[x]+1)
dep[y]--;
sta.pop();
fa[x] = x;
}
return;
}
};
bool ans[M];
DSU UN;
vector<Opt>tree[M*5];
inline int lchild(int x){return x<<1;}
inline int rchild(int x){return x<<1|1;}
inline void modify(int p, int pl, int pr, int l, int r, int x){
if(l <= pl && r >= pr){
tree[p].push_back(a[x]);
return;
}
int mid = (pl+pr) >> 1;
if(mid >= l)
modify(lchild(p), pl, mid, l, r, x);
if(mid < r)
modify(rchild(p), mid+1, pr, l, r, x);
return;
}
inline void dfs(int p, int pl, int pr){
int tmp = UN.size();
for(auto i : tree[p])
UN.join(i.x, i.y);
if(pl == pr){
if(a[pl].opt == 2) //离线记录答案
ans[pl] = UN.check(a[pl].x, a[pr].y);
return;
}
int mid = (pl+pr) >> 1;
dfs(lchild(p), pl, mid);
dfs(rchild(p), mid+1, pr);
UN.undo(tmp);
}
int n, m;
int st[N][N];
int main(){
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
UN.init(n);
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
scanf("%d%d%d", &a[i].opt, &a[i].x, &a[i].y);
if(a[i].x > a[i].y)
swap(a[i].x, a[i].y);
if(!a[i].opt && !st[a[i].x][a[i].y])
st[a[i].x][a[i].y] = st[a[i].y][a[i].x] = i;
else if(a[i].opt == 1)
modify(1, 1, m, st[a[i].x][a[i].y], i-1, i), st[a[i].x][a[i].y] = st[a[i].y][a[i].x] = 0;
}
//没有终点的->在m结束
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for(int j = i+1; j <= n; j++)
if(st[i][j])
modify(1, 1, m, st[i][j], m, st[i][j]), st[i][j] = st[j][i] = 0;
dfs(1, 1, m);
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
if(a[i].opt == 2)
puts(ans[i] ? "Y" : "N");
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号