深入理解Spring容器初始化(二):BeanFactory的初始化
前言
我们知道,spring 的启动其实就是容器的启动,而一般情况下,容器指的其实就是上下文 ApplicationContext。
AbstractApplicationContext 作为整个 ApplicationContext 体系中最高级的抽象类,为除了 ComplexWebApplicationContext 和 SimpleWebApplicationContext 这两个容器外的全部容器,规定好了 refresh 的整体流程,所有的容器在完成一些自己的初始化配置后,都需要调用该 refresh 方法,依次完成指定内容的初始化。
也就是说,读懂了 AbstractApplicationContext.refresh() 方法,其实就读懂了容器的启动流程:
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// ================= 一、上下文的初始化 =================
// 准备上下文
prepareRefresh();
// 通知子类刷新内部工厂
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// 准备bean工厂以便在当前上下文中使用
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// ================= 二、BeanFactory的初始化 =================
// 对工厂进行默认后置处理
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// 使用后置处理器对工厂进行处理
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// 注册Bean后置处理器
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// ================= 三、事件,Bean及其他配置的初始化 =================
// 初始化此上下文的消息源
initMessageSource();
// 为此上下文初始化事件广播者
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// 初始化特定上下文子类中的其他特殊bean
onRefresh();
// 检查侦听器bean并注册
registerListeners();
// 实例化所有非懒加载的剩余单例
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// 完成刷新
finishRefresh();
}
// ================= 异常处理 =================
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// 销毁已创建的单例
destroyBeans();
// 重置上下文的激活状态
cancelRefresh(ex);
throw ex;
}
finally {
// 重置内部的一些元数据缓存
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
从总体来看,该方法描述的初始化过程大概分为三步:
笔者将基于 spring 源码 5.2.x 分支,分别通过五篇文章从源码分析 spring 容器的初始化过程。
本文是其中的第二篇文章,将介绍 BeanFactory 初始化。
相关文章:
-
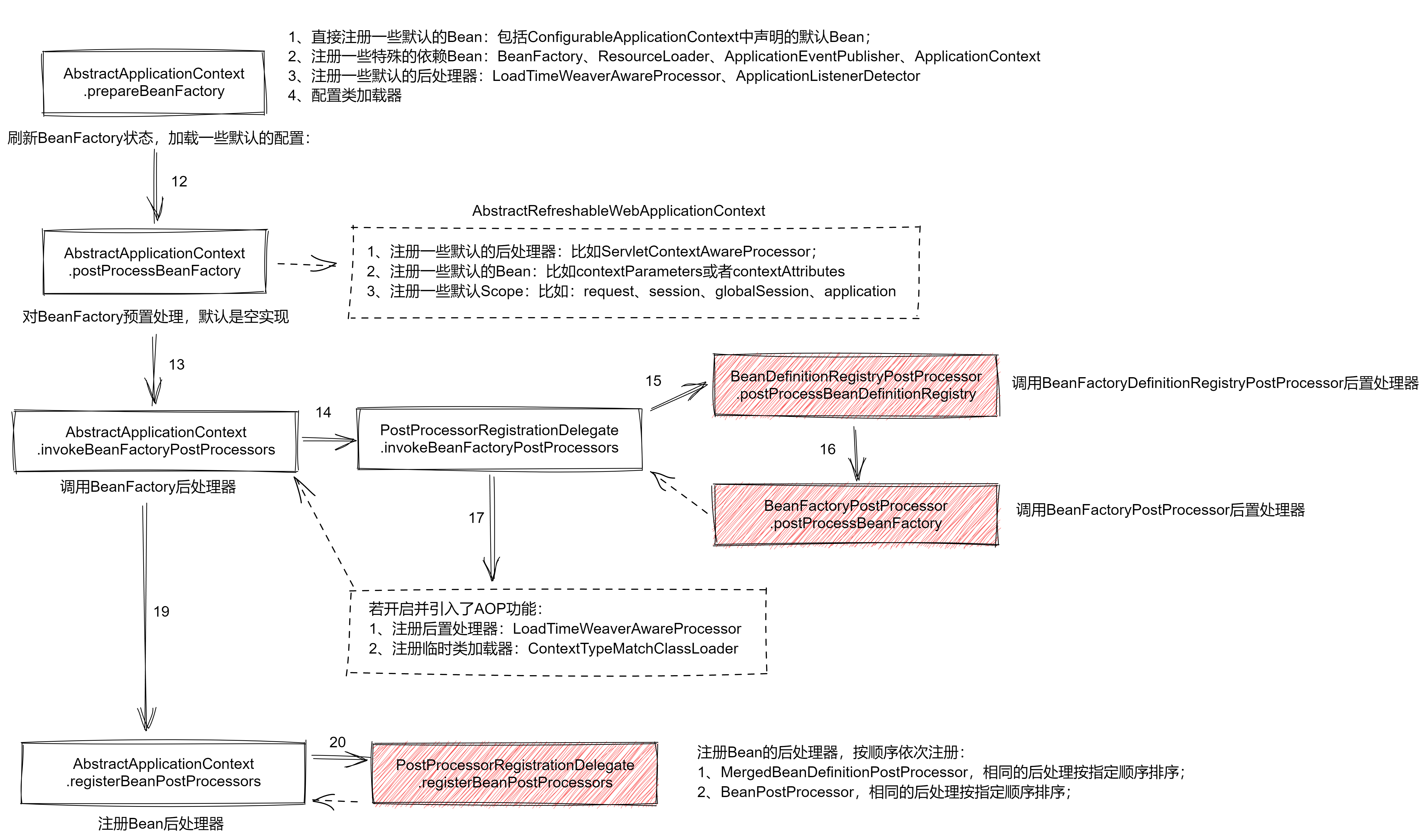
一、对工厂进行默认后置处理
AbstractApplicationContext.postProcessBeanFactory()是BeanFactory的第一步,该过程用于在用户自定义的BeanFactoryPostProcessor前,对BeanFactory进行一些默认的配置。在
AbstractApplicationContext中,这个方法是个空实现,需要子类实现它的具体逻辑,但是无外乎都是做以下三件事:- 向
BeanFactory注册默认的Bean后置处理器; - 向
BeanFactory注册默认的Bean作用域; - 向
BeanFactory注册一些默认的Bean;
我们以一个典型的实现类
AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext为例:protected void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { // 注册后置处理器ServletContextAwareProcessor beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ServletContextAwareProcessor(this.servletContext, this.servletConfig)); beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ServletContextAware.class); beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ServletConfigAware.class); // 注册web环境下一些必要组件 WebApplicationContextUtils.registerWebApplicationScopes(beanFactory, this.servletContext); WebApplicationContextUtils.registerEnvironmentBeans(beanFactory, this.servletContext, this.servletConfig); }1、注册默认Bean后置处理器
postProcessBeanFactory()最先调用了BeanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor()用于注册ServletContextAwareProcessor这个Bean后置处理器:// beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor @Override public void addBeanPostProcessor(BeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor) { Assert.notNull(beanPostProcessor, "BeanPostProcessor must not be null"); // Remove from old position, if any this.beanPostProcessors.remove(beanPostProcessor); // Track whether it is instantiation/destruction aware if (beanPostProcessor instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) { this.hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors = true; } if (beanPostProcessor instanceof DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor) { this.hasDestructionAwareBeanPostProcessors = true; } // Add to end of list this.beanPostProcessors.add(beanPostProcessor); }而对于
ServletContextAwareProcessor这个类,我们只需要关注它实现的postProcessBeforeInitialization接口:@Override public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { if (getServletContext() != null && bean instanceof ServletContextAware) { ((ServletContextAware) bean).setServletContext(getServletContext()); } if (getServletConfig() != null && bean instanceof ServletConfigAware) { ((ServletConfigAware) bean).setServletConfig(getServletConfig()); } return bean; }它将向所有实现了
ServletConfigAware的 bean 注册ServletContext和ServletConfig这两个 bean,这也是为什么要在postProcessBeanFactory中beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ServletContextAware.class); beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ServletConfigAware.class);忽略
ServletContextAware和ServletConfigAware的原因了,因此ServletContextAwareProcessor已经完成了这两者的功能。2、注册默认Bean作用域
registerWebApplicationScopes方法主要用于注册request,session,globalSession,application这四个作用域:public static void registerWebApplicationScopes(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, @Nullable ServletContext sc) { beanFactory.registerScope(WebApplicationContext.SCOPE_REQUEST, new RequestScope()); beanFactory.registerScope(WebApplicationContext.SCOPE_SESSION, new SessionScope()); if (sc != null) { ServletContextScope appScope = new ServletContextScope(sc); beanFactory.registerScope(WebApplicationContext.SCOPE_APPLICATION, appScope); // Register as ServletContext attribute, for ContextCleanupListener to detect it. sc.setAttribute(ServletContextScope.class.getName(), appScope); } beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ServletRequest.class, new RequestObjectFactory()); beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ServletResponse.class, new ResponseObjectFactory()); beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(HttpSession.class, new SessionObjectFactory()); beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(WebRequest.class, new WebRequestObjectFactory()); if (jsfPresent) { FacesDependencyRegistrar.registerFacesDependencies(beanFactory); } }3、注册默认Bean
registerEnvironmentBeans方法用于注册contextParameters和contextAttributes这两个环境 bean:public static void registerEnvironmentBeans(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory bf, @Nullable ServletContext servletContext, @Nullable ServletConfig servletConfig) { if (servletContext != null && !bf.containsBean(WebApplicationContext.SERVLET_CONTEXT_BEAN_NAME)) { bf.registerSingleton(WebApplicationContext.SERVLET_CONTEXT_BEAN_NAME, servletContext); } if (servletConfig != null && !bf.containsBean(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.SERVLET_CONFIG_BEAN_NAME)) { bf.registerSingleton(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.SERVLET_CONFIG_BEAN_NAME, servletConfig); } if (!bf.containsBean(WebApplicationContext.CONTEXT_PARAMETERS_BEAN_NAME)) { Map<String, String> parameterMap = new HashMap<>(); if (servletContext != null) { Enumeration<?> paramNameEnum = servletContext.getInitParameterNames(); while (paramNameEnum.hasMoreElements()) { String paramName = (String) paramNameEnum.nextElement(); parameterMap.put(paramName, servletContext.getInitParameter(paramName)); } } if (servletConfig != null) { Enumeration<?> paramNameEnum = servletConfig.getInitParameterNames(); while (paramNameEnum.hasMoreElements()) { String paramName = (String) paramNameEnum.nextElement(); parameterMap.put(paramName, servletConfig.getInitParameter(paramName)); } } bf.registerSingleton(WebApplicationContext.CONTEXT_PARAMETERS_BEAN_NAME, Collections.unmodifiableMap(parameterMap)); } if (!bf.containsBean(WebApplicationContext.CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTES_BEAN_NAME)) { Map<String, Object> attributeMap = new HashMap<>(); if (servletContext != null) { Enumeration<?> attrNameEnum = servletContext.getAttributeNames(); while (attrNameEnum.hasMoreElements()) { String attrName = (String) attrNameEnum.nextElement(); attributeMap.put(attrName, servletContext.getAttribute(attrName)); } } bf.registerSingleton(WebApplicationContext.CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTES_BEAN_NAME, Collections.unmodifiableMap(attributeMap)); } }二、使用后处理器对工厂进行处理
在调用完
AbstractApplicationContext.postProcessBeanFactory()后,BeanFactory中已经具备了一些 spring 默认的配置,此时再调用AbstractApplicationContext.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法,使用用户提供的工厂后置处理器BeanFactoryPostProcessor对BeanFactory进行后置处理。在
AbstractApplicationContext中,该方法实现如下:protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { // 借助后处理委托类调用全部的后置处理器 PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors()); // 如果存在loadTimeWeaver这个bean,则会配置上LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor这个后置处理器 // 然后设置临时的类加载器ContextTypeMatchClassLoader if (beanFactory.getTempClassLoader() == null && beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) { beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory)); beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader())); } } // AbstractApplicationContext public List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> getBeanFactoryPostProcessors() { return this.beanFactoryPostProcessors; // 这些是直接注册到上下文中的BeanFactoryPostProcessor }这里其实主要分为两部分逻辑:
- 借助后处理器委托类
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate完成对BeanFactory的后置处理; - 如果引入了
AOP,则需要为BeanFactory设置特殊的类加载器,从而允许生成Bean时织入切面逻辑;
第二部分很简洁,主要的逻辑都在第一部分。
1、后处理委托类
这里又出现了一个新类
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate,该类实际上是一个静态工具类,专门提供静态方法以用于处理上下文的后处理操作的,该类总共提供了两个方法:invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors():该方法用于对BeanFactory进行后置处理;registerBeanPostProcessors():该方法用于向上下文中注册Bean的后置处理器;
2、对BeanFactory进行后处理
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors()这个方法非常的长,不过逻辑还是很明确的:public static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors( ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> beanFactoryPostProcessors) { // Invoke BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors first, if any. Set<String> processedBeans = new HashSet<>(); // 如果BeanFactory实现了BeanDefinitionRegistry接口 if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) { // 将后置处理器分为两类: // 1.普通的BeanFactoryPostProcessor; // 2.BeanFactoryPostProcessor的子类BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor; BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = (BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory; List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> regularPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> registryProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessors) { if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) { BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryProcessor = (BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor; // 若是BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,则先调用该类的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法 registryProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry); registryProcessors.add(registryProcessor); } else { regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor); } } // Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans // uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them! // Separate between BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement // PriorityOrdered, Ordered, and the rest. List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> currentRegistryProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); // 先调用实现了PriorityOrdered接口的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false); for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) { currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class)); processedBeans.add(ppName); } } sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory); registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors); invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry); currentRegistryProcessors.clear(); // 再调用实现了Ordered接口的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false); for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) { currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class)); processedBeans.add(ppName); } } sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory); registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors); invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry); currentRegistryProcessors.clear(); // 最后调用没实现PriorityOrdered或者Ordered接口的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors boolean reiterate = true; while (reiterate) { reiterate = false; postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false); for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName)) { currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class)); processedBeans.add(ppName); reiterate = true; } } sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory); registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors); invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry); currentRegistryProcessors.clear(); } // Now, invoke the postProcessBeanFactory callback of all processors handled so far. invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryProcessors, beanFactory); invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory); } // 如果BeanFactory没有实现BeanDefinitionRegistry接口 else { // Invoke factory processors registered with the context instance. invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactoryPostProcessors, beanFactory); } // Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans // uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them! String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false); // 过滤掉已经调用过的处理器,然后把处理器分为三类: // 1.实现了PriorityOrdered接口的处理器; // 2.实现了Ordered接口的处理器; // 3.没有实现PriorityOrdered或Ordered接口的处理器; List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>(); List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>(); for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (processedBeans.contains(ppName)) { // skip - already processed in first phase above } else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) { priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class)); } else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) { orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName); } else { nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName); } } // 调用实现了PriorityOrdered接口的后置处理器 sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); // 调用实现了Ordered接口的后置处理器 List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(orderedPostProcessorNames.size()); for (String postProcessorName : orderedPostProcessorNames) { orderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class)); } sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); // 调用没有实现PriorityOrdered或Ordered接口的后置处理器 List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.size()); for (String postProcessorName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) { nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class)); } invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(nonOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); // 清除元数据 beanFactory.clearMetadataCache(); }由于
BeanFactoryPostProcessor存在一个子接口BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,它对应BeanFactory的一个子实现BeanDefinitionRegistry,通过BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor可以调整实现了BeanDefinitionRegistry的BeanFactory中对Bean定义的一些信息。由于
Bean的定义肯定要比Bean的创建更优先,因此需要先执行BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,然后再执行BeanFactoryPostProcessor。同时,又由于 spring 提供了一套排序机制,即处理时优先处理实现了
PriorityOrdered接口的处理器,再处理实现了Ordered接口的处理器,最后再处理两个接口都不实现的处理器,执行BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,与执行BeanFactoryPostProcessor时都还要根据排序区分执行顺序。因此,综合上文,这一步总体流程其实是这样的:
- 若
BeanFactory实现了BeanDefinitionRegistry接口,则优先完成此步骤:- 先调用实现了
PriorityOrdered接口的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor; - 再调用实现了
Ordered接口的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor; - 最后调用没有实现上述两接口的
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor;
- 先调用实现了
- 不管是否实现了
BeanDefinitionRegistry,都完成此步骤:- 先调用实现了
PriorityOrdered接口的BeanFactoryPostProcessor; - 再调用实现了
Ordered接口的BeanFactoryPostProcessor; - 最后调用没有实现上述两接口的
BeanFactoryPostProcessor;
- 先调用实现了
三、注册Bean后处理器
AbstractApplicationContext.registerBeanPostProcessors()是BeanFactory加载的第三步。这一步与调用BeanFactory一样,都通过后置处理委托类PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate进行:protected void registerBeanPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, this); }1、注册后处理器
registerBeanPostProcessors与 上文调用BeanFactory后置处理器逻辑基本一致:public static void registerBeanPostProcessors( ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, AbstractApplicationContext applicationContext) { String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanPostProcessor.class, true, false); // Register BeanPostProcessorChecker that logs an info message when // a bean is created during BeanPostProcessor instantiation, i.e. when // a bean is not eligible for getting processed by all BeanPostProcessors. int beanProcessorTargetCount = beanFactory.getBeanPostProcessorCount() + 1 + postProcessorNames.length; beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new BeanPostProcessorChecker(beanFactory, beanProcessorTargetCount)); // 依然将后置处理器分为三类: // 1.实现了PriorityOrdered接口的处理器; // 2.实现了Ordered接口的处理器; // 3.没有实现PriorityOrdered或Ordered接口的处理器; List<BeanPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); List<BeanPostProcessor> internalPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>(); List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>(); for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) { BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class); priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp); // 这里是用于框架内部使用的后置处理器 if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) { internalPostProcessors.add(pp); } } else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) { orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName); } else { nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName); } } // 注册实现了PriorityOrdered接口的后置处理器 sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors); // 注册实现了Ordered接口的后置处理器 List<BeanPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(orderedPostProcessorNames.size()); for (String ppName : orderedPostProcessorNames) { BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class); orderedPostProcessors.add(pp); if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) { internalPostProcessors.add(pp); } } sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors); // 注册没有实现PriorityOrdered或Ordered接口的后置处理器 List<BeanPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.size()); for (String ppName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) { BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class); nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp); if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) { internalPostProcessors.add(pp); } } registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, nonOrderedPostProcessors); // 注解框架内部使用的后置处理器 sortPostProcessors(internalPostProcessors, beanFactory); registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, internalPostProcessors); // 重新注册ApplicationListenerDetector,保证该处理器总是位于处理器链的最后一位,从而总是在最后被执行 // 该后置处理器用于支持spring的事件机制 beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(applicationContext)); }上述这些代码的逻辑也很明确:
- 先注册实现了
PriorityOrdered接口的BeanPostProcessor; - 再注册实现了
Ordered接口的BeanPostProcessor; - 接着注册没有实现上述两接口的
BeanPostProcessor; - 然后再注册框架内部使用的
BeanPostProcessor; - 最后注册
ApplicationListenerDetector,保证该后置处理器总是位于处理器链的末尾;
2、后处理器之间的优先级
在这一步,我们能看到,
BeanPostProcessor之间也会根据优先级区分创建 & 注册顺序,因此也就有了两个有意思的情况:- 后处理器本身也是一个
Bean,因此后处理创建时也会被后处理; - 后创建的后处理会被先创建的后处理器进行后处理;
基于上述两点,我们就可以理解,为什么有些
Aware本身就需要由后处理调用,但是仍然有别的后处理回去实现这些Aware接口,因为这些实现了接口的后处理本身也是一种Bean,也可以被先注册的后处理器进行处理。总结
当上下文刷新完毕,并且准备好了新的
BeanFactory后,需要对BeanFactory进行三步操作以完成BeanFactory本身的初始化:-
postProcessBeanFactory:对 bean 工厂进行预处理,包括注册一些默认的Bean后置处理器,设置默认的Bean作用域,以及注册默认Bean等; -
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors:使用注册到上下文中的BeanFactoryPostProcessor与BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor对BeanFactory进行后置处理; -
registerBeanPostProcessors:注册 bean 的后处理器,包括用户自定义的、spring 内部使用的,以及用于支持事件机制的ApplicationListenerDetector;
- 向


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号