实验3 C语言函数应用编程
一、实验目的
- 能正确使用c语法规则定义、声明、调用函数
- 能正确编写递归函数
- 针对具体问题场景,能合理抽象出独立的功能模块,正确定义函数并使用,使得代码更具可读性、 可维护性
- 针对具体问题场景,能正确、合理使用全局变量和局部static变量,解决实际问题
二、实验准备
- 函数定义、声明、调用的语法规则
- 什么是形参、什么是实参,以及,参数传递和返回过程
- 什么是递归函数,以及,递归函数的编写规范
- 全局变量、局部static变量的特性
三、实验内容
1. 实验任务1
在c开发环境下,输入如下程序。结合注释和运行结果,理解程序的功能,观察源代码中是如何使用函数 模块组织代码的。
task1.c
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <time.h> 4 #include <windows.h> 5 #define N 80 6 7 void print_text(int line, int col, char text[]); // 函数声明 8 void print_spaces(int n); // 函数声明 9 void print_blank_lines(int n); // 函数声明 10 11 int main() { 12 int line, col, i; 13 char text[N] = "hi, November~"; 14 15 srand(time(0)); // 以当前系统时间作为随机种子 16 17 for (i = 1; i <= 10; ++i) { 18 line = rand() % 25; 19 col = rand() % 80; 20 print_text(line, col, text); 21 Sleep(1000); // 暂停1000ms 22 } 23 return 0; 24 } 25 26 // 打印n个空格 27 void print_spaces(int n) { 28 int i; 29 30 for (i = 1; i <= n; ++i) 31 printf(" "); 32 } 33 34 // 打印n行空白行 35 void print_blank_lines(int n) { 36 int i; 37 38 for (i = 1; i <= n; ++i) 39 printf("\n"); 40 } 41 42 // 在第line行第col列打印一段文本 43 void print_text(int line, int col, char text[]) { 44 print_blank_lines(line - 1); // 打印(line-1)行空行 45 print_spaces(col - 1); // 打印(col-1)列空格 46 printf("%s", text); // 在第line行、col列输出text中字符串 47 }
2. 实验任务2
在c开发环境下,输入如下程序:
task2_1.c
1 // 利用局部static变量的特性,计算阶乘 2 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 3 #include <stdio.h> 4 5 long long fac(int n); // 函数声明 6 7 int main() { 8 int i, n; 9 10 printf("Enter n: "); 11 scanf("%d", &n); 12 for (i = 1; i <= n; ++i) 13 printf("%d! = %lld\n", i, fac(i)); 14 15 return 0; 16 } 17 18 // 函数定义 19 long long fac(int n) { 20 static long long p = 1; 21 22 p = p * n; 23 24 return p; 25 }
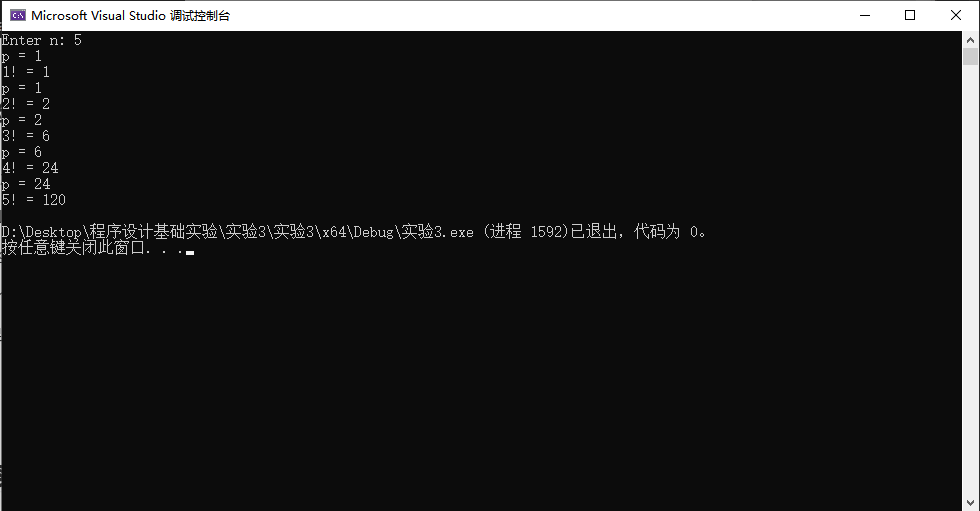
编译、运行程序,从键盘输入5,结合运行结果,理解函数模块fac()定义中,局部static变量p在这里起到的作用。
在代码line20和line22之间,增加一行代码,打印每次进入函数fac时局部变量p的值,结合实践结果,理解局部static变量的特性。
1 printf("p = %lld\n", p);
基于上述实践,先从理论上分析程序task2_2.c的结果是什么,然后,在软件中运行该程序,验证是否一致。
task2_2.c
1 // 练习:局部static变量特性 2 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 3 4 #include <stdio.h> 5 6 int func(int, int); // 函数声明 7 8 int main() { 9 int k = 4, m = 1, p1, p2; 10 11 p1 = func(k, m); // 函数调用 12 p2 = func(k, m); // 函数调用 13 printf("%d, %d\n", p1, p2); 14 15 return 0; 16 } 17 18 // 函数定义 19 int func(int a, int b) { 20 static int m = 0, i = 2; 21 22 i += m + 1; 23 m = i + a + b; 24 25 return m; 26 }
3. 实验任务3
已知数学函数式如下:(限定n取值范围为[0, 32])
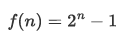
设计一个函数模块func(),用来实现:提供n的数值,返回该函数计算式的结果。
要求:
- 使用递归算法实现
- 不使用标准库函数pow()
补足代码task3.c中的函数模块定义部分,实现题目要求。
task3.c
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include <stdio.h> 3 4 long long func(int n); // 函数声明 5 6 int main() { 7 int n; 8 long long f; 9 10 while (scanf("%d", &n) != EOF) { 11 f = func(n); // 函数调用 12 printf("n = %d, f = %lld\n", n, f); 13 } 14 15 return 0; 16 }
4. 实验任务4
编写函数计算组合数,要求算法分别用迭代方式和递归方式实现。
设函数原型如下:int func(int n, int m);其功能是计算从n个不同元素中取出m个元素的组合数。
main函数代码已经在task4.c中给出,补足函数func()的定义,实现题目要求。
补足代码task4.c中函数模块定义部分,分别用两种方式实现函数:
- 实现方式1:迭代方式
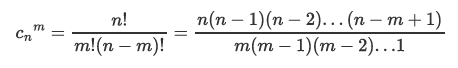
- 实现方式2:递归方式
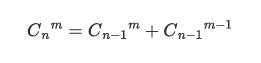
待补足的源码task4.c
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 int func(int n, int m); 3 int main() { 4 int n, m; 5 while(scanf("%d%d", &n, &m) != EOF) 6 printf("n = %d, m = %d, ans = %d\n", n, m, func(n, m)); 7 8 return 0; 9 } 10 // 函数定义 11 // 待补足。。。(分别用迭代思维和递归思维实现)
5. 实验任务5
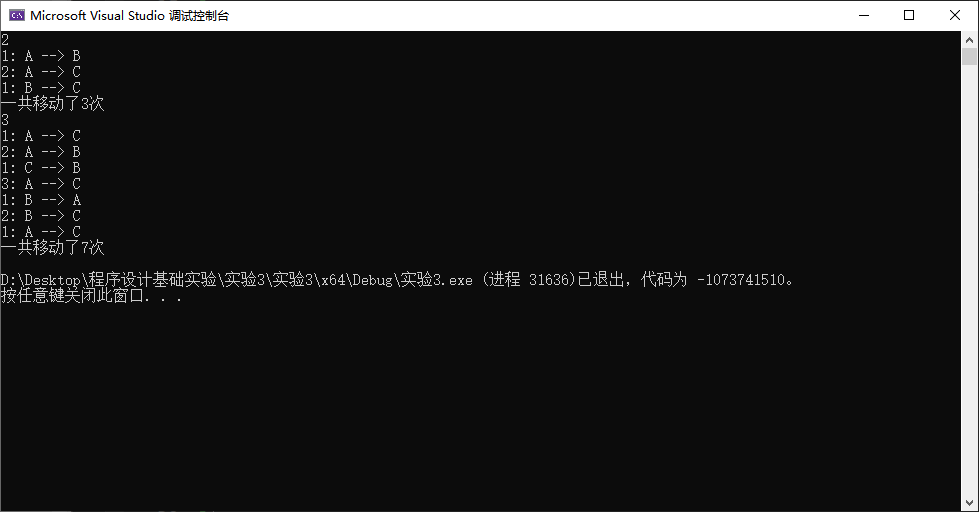
对教材「例4.9 Hanoi塔问题」稍做改写,使其满足以下要求:
- 支持多组输入:输入不同的n值,打印输出不同的移动盘子方案
- 对于每个n,除了打印盘子移动方案之外,还要打印输出移动盘子的总次数
6. 实验任务6
编写函数func,实现将一个长整型数s的每一数位上的奇数依次取出来,构成一个新的数,高位仍在高位,低位仍在低位,返回这个新数。例如,s=20231030时,调用函数fun后,返回313。
在主函数中,通过多组输入方式,多次调用fun(),实现对多组数据的测试。
7.实验任务7
编写程序,找出一个符合下列条件的数字:它的平方值与立方值一共使用了0到9十个数字,且一个数字只是用一次。
以17为例:
172 = 289
173 = 4913
17不满足条件,因为它的平方和立方只包含1,2,3,4,8,9这几个数字,没有包含0,5,6,7,而且,9重复了两次。
编写程序,找出符合条件的一个数字,只要找到一个就终止程序。打印出找到的数字。
四、实验结论
1. 实验任务1
task1.c:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <time.h> 4 #include <windows.h> 5 #define N 80 6 7 void print_text(int line, int col, char text[]); // 函数声明 8 void print_spaces(int n); // 函数声明 9 void print_blank_lines(int n); // 函数声明 10 11 int main() { 12 int line, col, i; 13 char text[N] = "hi, November~"; 14 15 srand(time(0)); // 以当前系统时间作为随机种子 16 17 for (i = 1; i <= 10; ++i) { 18 line = rand() % 25; 19 col = rand() % 80; 20 print_text(line, col, text); 21 Sleep(1000); // 暂停1000ms 22 } 23 return 0; 24 } 25 26 // 打印n个空格 27 void print_spaces(int n) { 28 int i; 29 30 for (i = 1; i <= n; ++i) 31 printf(" "); 32 } 33 34 // 打印n行空白行 35 void print_blank_lines(int n) { 36 int i; 37 38 for (i = 1; i <= n; ++i) 39 printf("\n"); 40 } 41 42 // 在第line行第col列打印一段文本 43 void print_text(int line, int col, char text[]) { 44 print_blank_lines(line - 1); // 打印(line-1)行空行 45 print_spaces(col - 1); // 打印(col-1)列空格 46 printf("%s", text); // 在第line行、col列输出text中字符串 47 }
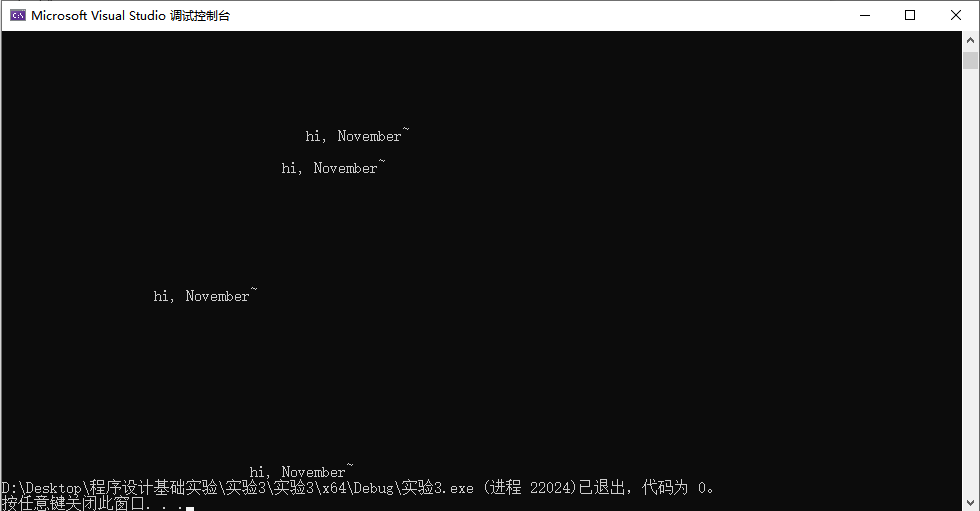
运行截图:
回答问题:
该程序的功能是在随机的位置(25行,80个空格内)生成打印文本“hi, November~”。
2. 实验任务2
task2_1.c
1 // 利用局部static变量的特性,计算阶乘 2 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 3 #include <stdio.h> 4 5 long long fac(int n); // 函数声明 6 7 int main() { 8 int i, n; 9 10 printf("Enter n: "); 11 scanf("%d", &n); 12 for (i = 1; i <= n; ++i) 13 printf("%d! = %lld\n", i, fac(i)); 14 15 return 0; 16 } 17 18 // 函数定义 19 long long fac(int n) { 20 static long long p = 1; 21 printf("p = %lld\n", p); 22 p = p * n; 23 24 return p; 25 }
运行截图:
task2_2.c
1 // 练习:局部static变量特性 2 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 3 4 #include <stdio.h> 5 6 int func(int, int); // 函数声明 7 8 int main() { 9 int k = 4, m = 1, p1, p2; 10 11 p1 = func(k, m); // 函数调用 12 p2 = func(k, m); // 函数调用 13 printf("%d, %d\n", p1, p2); 14 15 return 0; 16 } 17 18 // 函数定义 19 int func(int a, int b) { 20 static int m = 0, i = 2; 21 22 i += m + 1; 23 m = i + a + b; 24 25 return m; 26 }
运行截图:
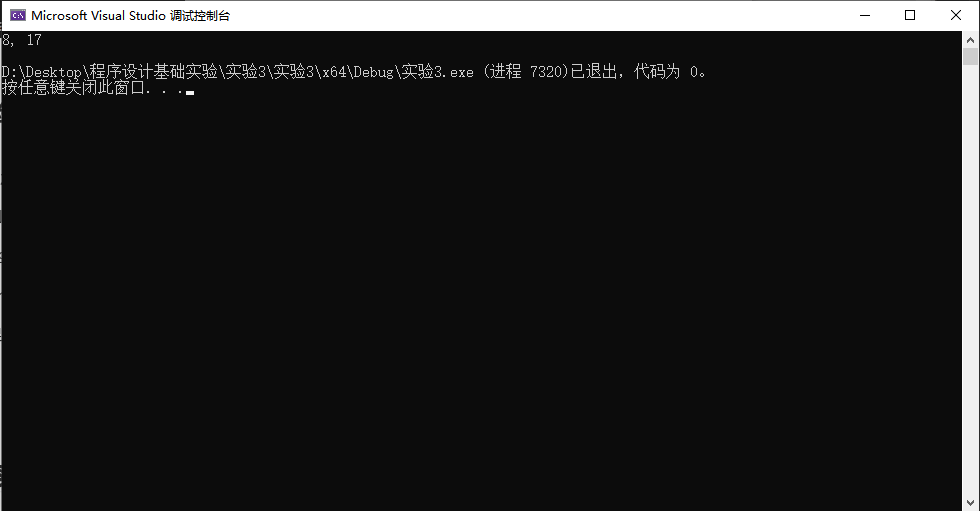
运行结果与我分析得到的结果一致。
回答问题:
- 局部static变量的生命周期与程序的执行周期相同,而不是随着函数的调用和返回而创建和销毁。它会在首次执行到定义它的代码行时初始化,并保持其值直到程序终止。
- 局部static变量仅在定义它的函数中可见,不能被其他函数访问。这使得它成为在函数内部共享信息的一种方式。
- 局部static变量被定义时,它会被自动初始化为默认值(例如数值类型为0,指针类型为NULL)。只有在第一次执行到定义它的代码行时才会发生初始化,之后每次函数调用都会保留上一次执行结束时的值。
- 局部static变量的内存空间在程序的整个生命周期中保持不变。它通常存储在静态数据区,而不是栈上,因此不会受到函数调用和返回的影响。
3. 实验任务3
task3.c
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include <stdio.h> 3 4 long long func(int n); // 函数声明 5 6 int main() { 7 int n; 8 long long f; 9 10 while (scanf("%d", &n) != EOF) { 11 f = func(n); // 函数调用 12 printf("n = %d, f = %lld\n", n, f); 13 } 14 15 return 0; 16 } 17 18 long long func(int n) { 19 if (n == 0) { 20 return 0; 21 } 22 else { 23 return 2 * func(n - 1) + 1; 24 } 25 }
运行截图:

4. 实验任务4
task4_1.c
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include <stdio.h> 3 4 int func(int n, int m); 5 6 int main() { 7 int n, m; 8 9 while (scanf("%d%d", &n, &m) != EOF) 10 printf("n = %d, m = %d, ans = %d\n", n, m, func(n, m)); 11 12 return 0; 13 } 14 // 函数定义 15 //迭代方法 16 int func(int n, int m) { 17 double ans = 1.0; 18 if (m > n) { 19 return 0; 20 } 21 22 for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) { 23 ans = ans * ((double)(n - i + 1) / (double)(i)); 24 } 25 26 return (int)ans; 27 }
运行截图:
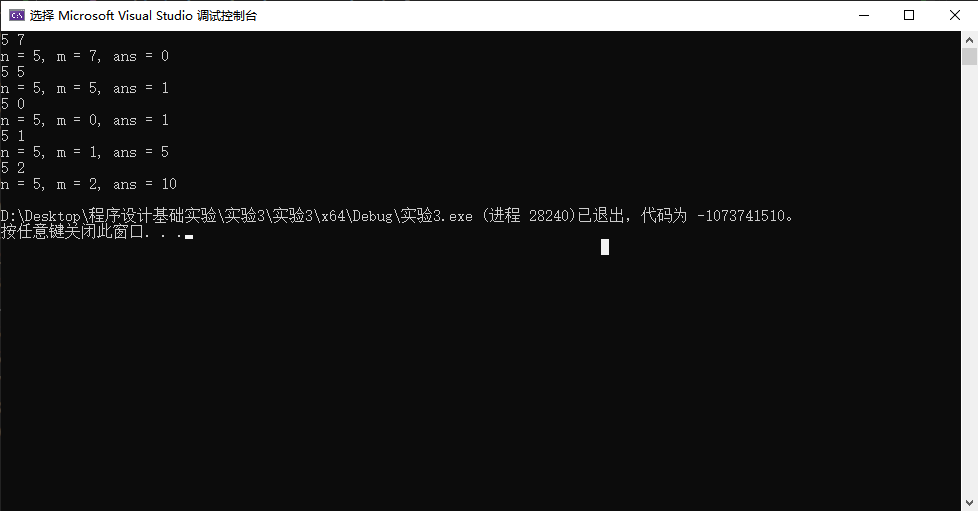
task4_2.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS #include <stdio.h> int func(int n, int m); int main() { int n, m; while (scanf("%d%d", &n, &m) != EOF) printf("n = %d, m = %d, ans = %d\n", n, m, func(n, m)); return 0; } // 函数定义 //递归方法 int func(int n, int m) { if (m > n) { return 0; } else if (m == n || m == 0) { return 1; } else { return func(n - 1, m) + func(n - 1, m - 1); } }
运行截图:

5. 实验任务5
task5.c
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include <stdio.h> 3 4 int a = 0; 5 6 void moveplate(unsigned nth, char from, char to) { 7 printf("%u: %c --> %c\n", nth, from, to); 8 ::a++; 9 } 10 11 void hanoi(unsigned n, char from, char temp, char to) { 12 if (n == 1) { 13 moveplate(n, from, to); 14 } 15 else { 16 hanoi(n - 1, from, to, temp); 17 moveplate(n, from, to); 18 hanoi(n - 1, temp, from, to); 19 } 20 } 21 22 int main() { 23 unsigned n; 24 25 while (scanf("%u", &n) != EOF) { 26 hanoi(n, 'A', 'B', 'C'); 27 printf("一共移动了%d次\n", ::a); 28 ::a = 0; 29 } 30 31 return 0; 32 }
运行截图:
6. 实验任务6
task6.c
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include <stdio.h> 3 #include <math.h> 4 5 long func(long s); // 函数声明 6 7 int main() { 8 long s, t; 9 10 printf("Enter a number: "); 11 while (scanf("%ld", &s) != EOF) { 12 t = func(s); // 函数调用 13 printf("new number is: %ld\n\n", t); 14 printf("Enter a number: "); 15 } 16 17 return 0; 18 } 19 // 函数定义 20 long func(long s) { 21 int num = 0; 22 int a; 23 int b = 1; 24 25 while (s != 0) { 26 a = s % 10; 27 if (a % 2 != 0) { 28 num = num + b * a; 29 b = b * 10; 30 } 31 s = s / 10; 32 } 33 34 return num; 35 }
运行截图:

7.实验任务
task7.c
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include <stdio.h> 3 #include <math.h> 4 5 int a[10]; 6 7 int if_OK() { 8 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { 9 if (a[i] != 1) { 10 return 0; 11 } 12 } 13 14 return 1; 15 } 16 17 int main() { 18 int n = 1; 19 int pingf; 20 int lif; 21 int yicif; 22 23 while (true) { 24 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { 25 a[i] = 0; 26 } 27 pingf = pow(n, 2); 28 lif = pow(n, 3); 29 30 int temp; 31 while (pingf != 0) { 32 temp = pingf % 10; 33 a[temp]++; 34 pingf = pingf / 10; 35 } 36 while (lif != 0) { 37 temp = lif % 10; 38 a[temp]++; 39 lif = lif / 10; 40 } 41 42 if (if_OK()) { 43 printf("%d\n", n); 44 break; 45 } 46 else { 47 n++; 48 } 49 } 50 }
运行截图:




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号