实验4 汇编应用编程和c语言程序反汇编分析
一、实验目的
二、实验结论
1. 实验任务1
编程:在屏幕中间分别显示绿色、绿底红色、白底蓝色的字符串'welcome to masm!'。
assume cs:code, ds:data, ss:stack data segment db 'welcome to masm!';输入信息存储 db 2h,24h,71h;颜色信息存储 data ends stack segment stack db 16 dup (0);栈空间存储环境变量 stack ends code segment start: mov ax,data mov ds,ax mov ax,stack mov ss,ax mov sp,16 ;完成对段地址赋值 mov ax,0B872h;开始输出位置 mov es,ax mov cx,3;循环次数 mov bx,16;在data中的偏移地址,用于设置颜色 s: push cx;外层循环的cx值保存栈中 mov cx,16;设置内层循环 mov si,0;显示区域中的偏移地址 mov di,0;数据段中的偏移地址,获取字母 s0: mov al,ds:[di] mov ah,ds:[bx] mov es:[si],ax add si,2;显示区域输入位置后移 inc di loop s0 pop cx;恢复外层循环的计数值cx mov ax,es add ax,00ah ;进行换行 mov es,ax inc bx;颜色值改变 loop s mov ax,4c00h int 21h code ends end start
汇编、链接、执行后实验结果:
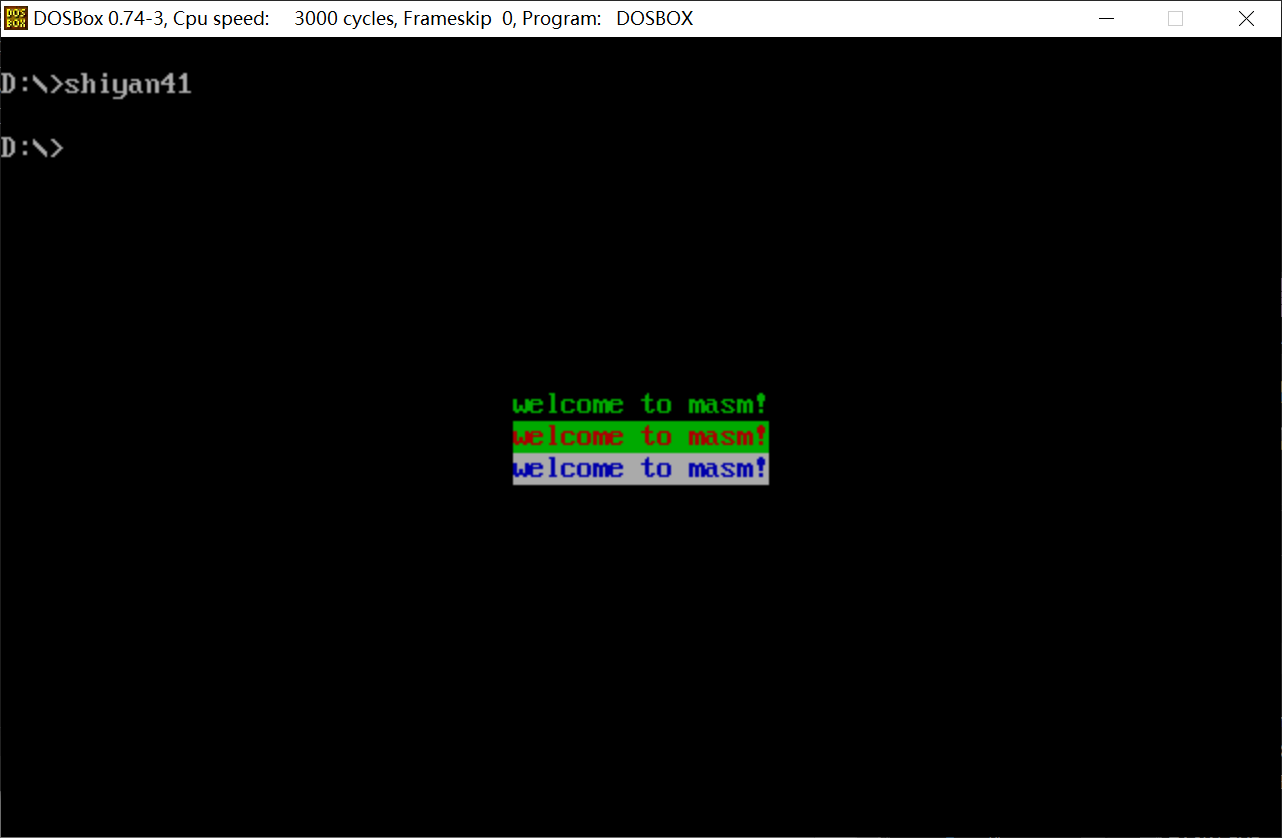
实现该实验操作重要的是对显存区域的了解,了解一行区域由180个字节组成,同时显存开始地址为B800H:0,通过一个页面由25行组成,通过简单的数学计算算出在中间区域进行显示的显存区域开始地址为B872H:0;
2.实验任务2
assume cs:code, ds:data data segment str db 'try', 0 data ends code segment start: mov ax, data mov ds, ax mov si, offset str mov al, 2 call printStr mov ah, 4ch int 21h printStr: push bx push cx push si push di mov bx, 0b800H mov es, bx mov di, 0 s: mov cl, [si] mov ch, 0 jcxz over mov ch, al mov es:[di], cx inc si add di, 2 jmp s over: pop di pop si pop cx pop bx ret code ends end start
运行结果:
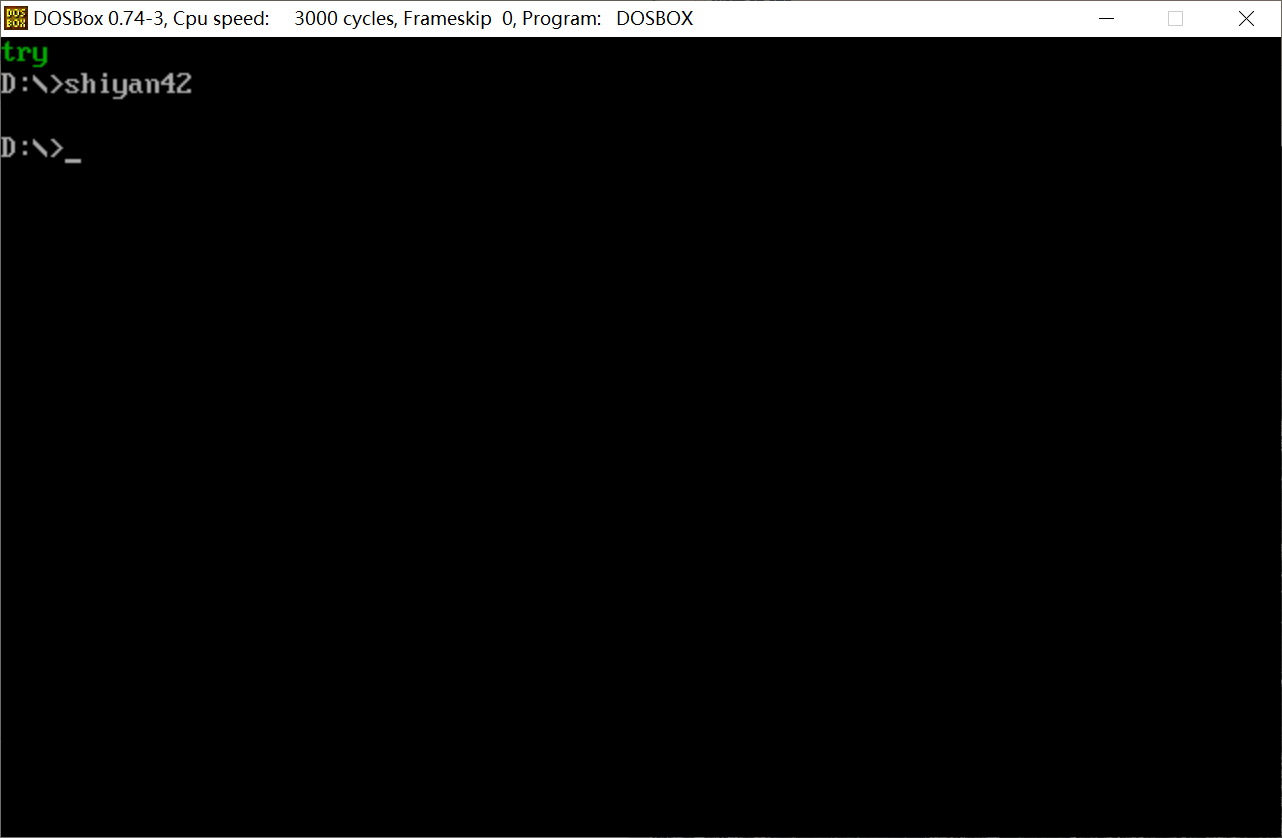
对源程序做如下修改:
把line3改为:
str db 'another try', 0
把line12改为:
mov al, 4
再次汇编、运行程序,观察运行结果。

基于运行结果,理解源代码,以及,组合使用转移指令call和ret实现子程序的原理与方法。具体地,在line18-40中:
1)line19-22, line36-39,这组对称使用的push、pop,这样用的目的是什么?
答:保护和恢复各寄存器的值,进行调用函数前的准备,以及函数调用后对寄存器值得还原。
2)line30的功能是什么?
答:line30行的代码内容为“mov es:[di], cx”。cx的低位存储字符的ASCII值,而高位存储字符颜色的属性值,所以line30的功能是将彩色字符写入地址为b800:d[i]的显存中。
3.实验任务3
- 子程序num2str:
- 功能:把0~2559之间的任意整数转换成数字字符串,例如,把1984转换成'1984'
- 入口参数
- 要转换的整数 —> ax
- 数字字符串的起始地址 —> ds:di (其中:数字字符串所在段的段地址—> ds,字符串
- 起始地址的偏移地址—>di)
- 出口参数:无
assume cs:code, ds:data data segment x dw 1984 str db 16 dup(0) data ends code segment start: mov ax, data mov ds, ax mov ax, x mov di, offset str call num2str mov ah, 4ch int 21h num2str: push ax push bx push cx push dx mov cx, 0 mov bl, 10 s1: div bl inc cx mov dl, ah push dx mov ah, 0 cmp al, 0 jne s1 s2: pop dx or dl, 30h mov [di], dl inc di loop s2 pop dx pop cx pop bx pop ax ret code ends end start
子任务1
反汇编:
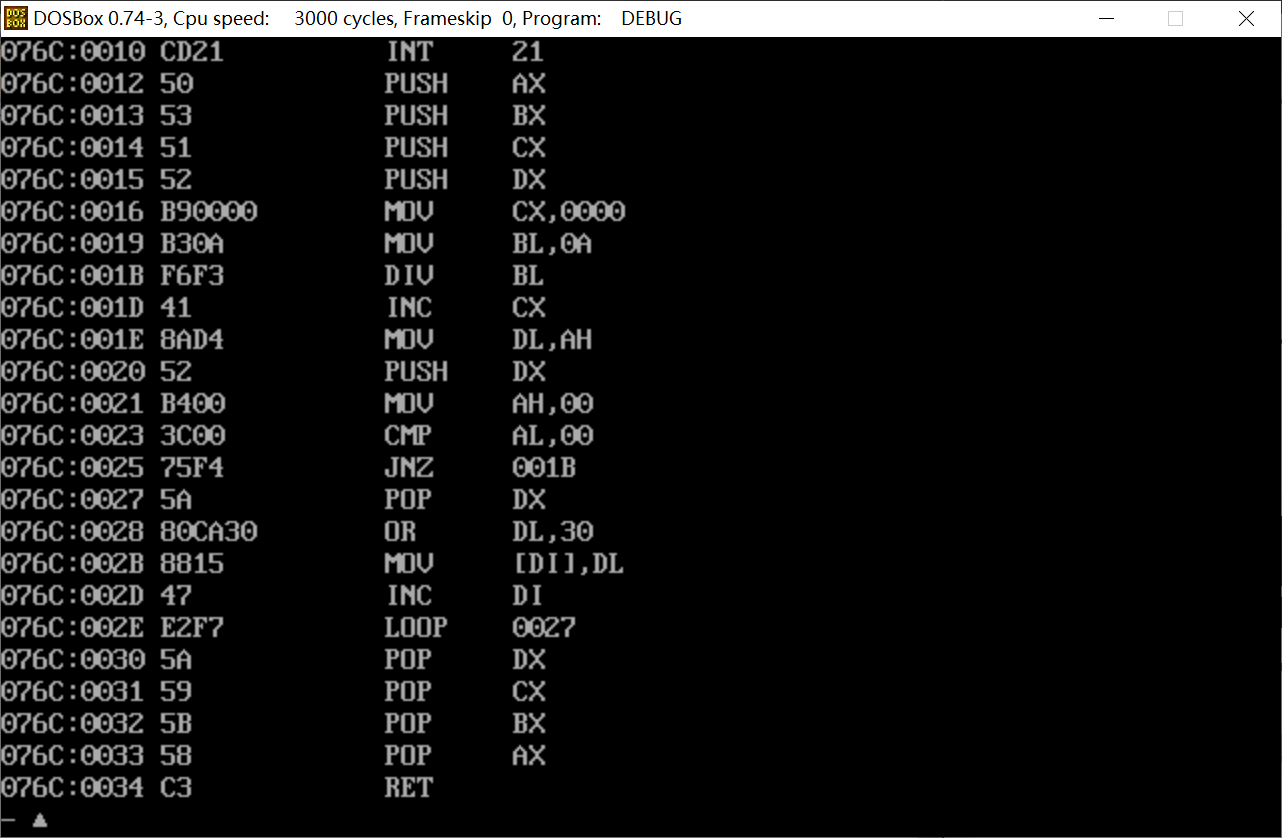
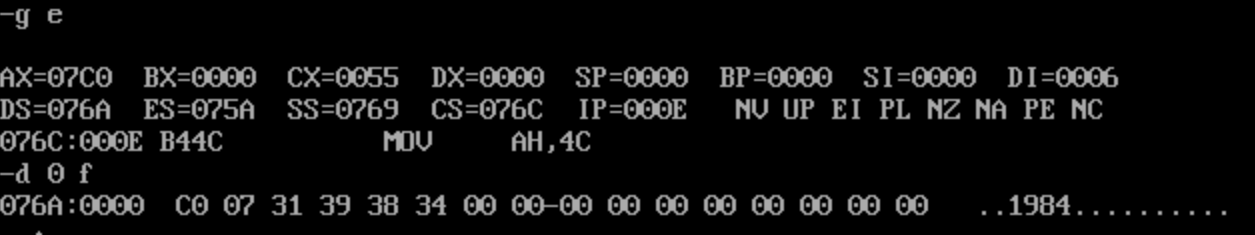
观察发现成功把转换后的数字字符串‘1984’存放在数据段中str标号后面的单元。
子任务2
assume cs:code, ds:data data segment x dw 1984 str db 16 dup(0) data ends code segment start: mov ax, data mov ds, ax mov ax, x mov di, offset str call num2str mov al, 2 call printStr mov ah, 4ch int 21h num2str: push ax push bx push cx push dx mov cx, 0 mov bl, 10 s1: div bl inc cx mov dl, ah push dx mov ah, 0 cmp al, 0 jne s1 s2: pop dx or dl, 30h mov [di], dl inc di loop s2 pop dx pop cx pop bx pop ax ret printStr: push bx push cx push si push di mov bx, 0b800H mov es, bx mov di, 0 mov si, offset str s: mov cl, [si] mov ch, 0 jcxz over mov ch, al mov es:[di], cx inc si add di, 2 jmp s over: pop di pop si pop cx pop bx ret code ends end start
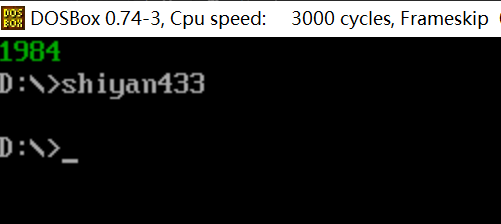
把task3.asm源代码中,line3中整数改成0~2559之间的任意数值,运行测试,观察结果。
将line3中整数改为2000
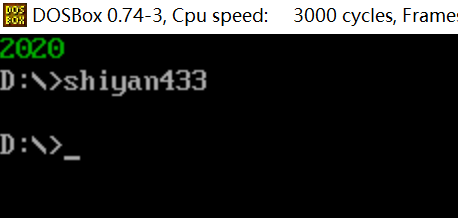
4.实验任务4
assume cs:code, ds:data data segment str db 80 dup(?) data ends code segment start: mov ax, data mov ds, ax mov si, 0 s1: mov ah, 1 int 21h mov [si], al cmp al, '#' je next inc si jmp s1 next: mov cx, si mov si, 0 s2: mov ah, 2 mov dl, [si] int 21h inc si loop s2 mov ah, 4ch int 21h code ends end start
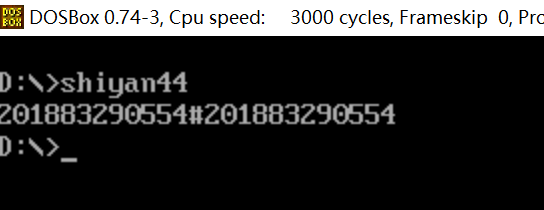
结合运行结果,理解程序功能,了解软中断指令。具体地:
5.实验任务5
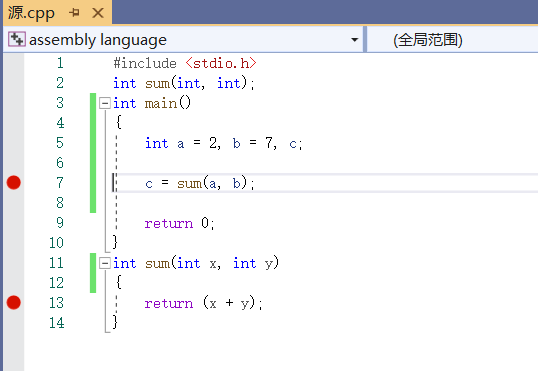
#include <stdio.h> int sum(int, int); int main() { int a = 2, b = 7, c; c = sum(a, b); return 0; } int sum(int x, int y) { return (x + y); }
在line7, line13分别设置断点,在调试模式下,查看反汇编代码。line6的反汇编代码如下图所示:
在调试模式下,查看反汇编代码:
line7的反汇编代码如下图所示:

line13的反汇编代码如下图所示:

分析反汇编代码,从汇编的角度,观察高级语言中参数传递和返回值是通过什么实现的,以及,参数入栈顺序,返回值的带回方式,等等。
1)从汇编的角度来看,高级语言中参数传递和返回值都是通过栈实现的,数据从ptr [b]、ptr [a]传入eax、ecx等寄存器。
2)调用函数时,形参参数入栈自右向左。先借助寄存器,将参数b 的地址压入堆栈寄存器eax,再将参数a 的值压入堆栈寄存器ecx。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号