实验4
实验任务1:
源代码GradeCalc.hpp
1 #pragma once 2 #include<vector> 3 #include<array> 4 #include<string> 5 6 class GradeCalc{ 7 public: 8 GradeCalc(const std::string &cname); 9 void input(int n); 10 void output() const; 11 void sort(bool ascending=false); 12 int min() const; 13 int max() const; 14 double average() const; 15 void info(); 16 private: 17 void compute(); 18 private: 19 std::string course_name; 20 std::vector<int> grades; 21 std::array<int,5> counts; 22 std::array<double,5> rates; 23 bool is_dirty; 24 };
源代码GradeCalc.cpp
1 #include<algorithm> 2 #include<array> 3 #include<cstdlib> 4 #include<iomanip> 5 #include<iostream> 6 #include<numeric> 7 #include<string> 8 #include<vector> 9 10 #include "GradeCalc.hpp" 11 12 GradeCalc::GradeCalc(const std::string &cname):course_name{cname},is_dirty{true}{ 13 counts.fill(0); 14 rates.fill(0); 15 } 16 17 void GradeCalc::input(int n){ 18 if(n<0){ 19 std::cerr << "无效输入!人数不能为负数\n"; 20 std::exit(1); 21 } 22 23 grades.reserve(n); 24 25 int grade; 26 27 for(int i=0;i<n;){ 28 std::cin>>grade; 29 30 if(grade<0||grade>100){ 31 std::cerr << "无效输入!分数须在[0,100]\n"; 32 continue; 33 } 34 35 grades.push_back(grade); 36 ++i; 37 } 38 is_dirty=true; 39 } 40 41 void GradeCalc::output() const{ 42 for(auto grade:grades) 43 std::cout << grade << ' '; 44 std::cout << std::endl; 45 } 46 47 void GradeCalc::sort(bool ascending){ 48 if(ascending) 49 std::sort(grades.begin(),grades.end()); 50 else 51 std::sort(grades.begin(),grades.end(),std::greater<int>()); 52 } 53 54 int GradeCalc::min() const{ 55 if(grades.empty()) 56 return -1; 57 58 auto it=std::min_element(grades.begin(),grades.end()); 59 return *it; 60 } 61 62 int GradeCalc::max() const{ 63 if(grades.empty()) 64 return -1; 65 66 auto it=std::max_element(grades.begin(),grades.end()); 67 return *it; 68 } 69 70 double GradeCalc::average() const { 71 if(grades.empty()) 72 return 0.0; 73 74 double avg=std::accumulate(grades.begin(),grades.end(),0.0)/grades.size(); 75 return avg; 76 } 77 78 void GradeCalc::info(){ 79 if(is_dirty) 80 compute(); 81 82 std::cout << "课程名称:\t" << course_name << std::endl; 83 std::cout << "平均分:\t" << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << average() << std::endl; 84 std::cout << "最高分:\t" << max() << std::endl; 85 std::cout << "最低分:\t" << min() << std::endl; 86 87 const std::array<std::string,5> grade_range{"[0,60)","[60,70)","[70,80)","[80,90)","[90,100]"}; 88 for(int i=grade_range.size()-1;i>=0;--i) 89 std::cout << grade_range[i] << "\t: " << counts[i] << "人\t" 90 << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << rates[i]*100 << "%\n"; 91 } 92 93 void GradeCalc::compute(){ 94 if(grades.empty()) 95 return; 96 counts.fill(0); 97 rates.fill(0.0); 98 for(auto grade:grades){ 99 if(grade<60) 100 ++counts[0]; 101 else if(grade<70) 102 ++counts[1]; 103 else if(grade<80) 104 ++counts[2]; 105 else if(grade<90) 106 ++counts[3]; 107 else 108 ++counts[4]; 109 } 110 for(int i=0;i<rates.size();++i) 111 rates[i]=counts[i]*1.0/grades.size(); 112 is_dirty=false; 113 }
源代码demo1.cpp
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<string> 3 #include "GradeCalc.hpp" 4 5 void test(){ 6 GradeCalc c1("OOP"); 7 8 std::cout << "录入成绩:\n"; 9 c1.input(5); 10 11 std::cout << "输出成绩:\n"; 12 c1.output(); 13 14 std::cout << "排序后成绩:\n"; 15 c1.sort();c1.output(); 16 17 std::cout << "**********成绩统计信息**********\n"; 18 c1.info(); 19 } 20 21 int main(){ 22 test(); 23 }
运行结果截图:
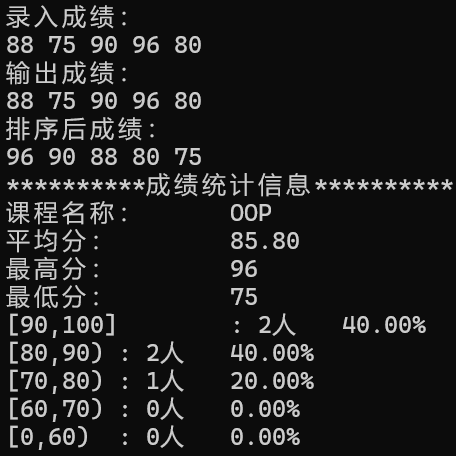
问题1:
std::string course_name;存储课程名称
std::vector<int> grades;存储所有学生的成绩
std::array<int,5> counts;统计每个分数段的人数
std::array<double,5> rates;存储每个分数段的百分比
问题2:
不合法,push_back是std::vector<int> grades的成员函数,grades是类的私有成员,只能在类的内部被其他成员函数调用,不能在外部测试模块中直接调用。
问题3:
(1)1次,is_dirty作用是当数据发生变化时标记为“脏数据”,确保只在需要时重新计算统计信息。
(2)不需要。只需要设置is_dirty=true,触发compute重新计算。
问题4:
在GradeCalc::info()中加。
1 if(!grades.empty()){ 2 std::vector<int> temp_grades=grades; 3 std::sort(temp_grades.begin(),temp_grades.end()); 4 double media=0.0; 5 size_t size=temp_grades.size(); 6 if(size%2==0){ 7 media=(temp_grades[size/2-1]+temp_grades[size/2])/2.0; 8 } 9 else{ 10 media=temp_grades[size/2]; 11 } 12 std::cout << "中位数:\t" << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << media << std::endl; 13 }
问题5:
不能去掉。若去掉,在多次调用compute()的情况下,会引发错误。
问题6:
(1)没有,程序仍然可以正常运行。
(2)有影响,当n较大时,去掉reserve(n)会导致vector多次触发扩容,增加内存分配开销。
实验任务2:
源代码GradeCalc.hpp
1 #pragma once 2 3 #include <array> 4 #include <string> 5 #include <vector> 6 7 class GradeCalc: private std::vector<int> { 8 public: 9 GradeCalc(const std::string &cname); 10 void input(int n); 11 void output() const; 12 void sort(bool ascending = false); 13 int min() const; 14 int max() const; 15 double average() const; 16 void info(); 17 18 private: 19 void compute(); 20 21 private: 22 std::string course_name; 23 std::array<int, 5> counts; 24 std::array<double, 5> rates; 25 bool is_dirty; 26 };
源代码GradeCalc.cpp
1 #include <algorithm> 2 #include <array> 3 #include <cstdlib> 4 #include <iomanip> 5 #include <iostream> 6 #include <numeric> 7 #include <string> 8 #include <vector> 9 #include "GradeCalc.hpp" 10 11 12 GradeCalc::GradeCalc(const std::string &cname): course_name{cname}, is_dirty{true}{ 13 counts.fill(0); 14 rates.fill(0); 15 } 16 17 void GradeCalc::input(int n) { 18 if(n < 0) { 19 std::cerr << "无效输入! 人数不能为负数\n"; 20 return; 21 } 22 23 this->reserve(n); 24 25 int grade; 26 27 for(int i = 0; i < n;) { 28 std::cin >> grade; 29 if(grade < 0 || grade > 100) { 30 std::cerr << "无效输入! 分数须在[0,100]\n"; 31 continue; 32 } 33 34 this->push_back(grade); 35 ++i; 36 } 37 38 is_dirty = true; 39 } 40 41 void GradeCalc::output() const { 42 for(auto grade: *this) 43 std::cout << grade << ' '; 44 std::cout << std::endl; 45 } 46 47 void GradeCalc::sort(bool ascending) { 48 if(ascending) 49 std::sort(this->begin(), this->end()); 50 else 51 std::sort(this->begin(), this->end(), std::greater<int>()); 52 } 53 54 int GradeCalc::min() const { 55 if(this->empty()) 56 return -1; 57 58 return *std::min_element(this->begin(), this->end()); 59 } 60 61 int GradeCalc::max() const { 62 if(this->empty()) 63 return -1; 64 65 return *std::max_element(this->begin(), this->end()); 66 } 67 68 double GradeCalc::average() const { 69 if(this->empty()) 70 return 0.0; 71 72 double avg = std::accumulate(this->begin(), this->end(), 0.0) / this->size(); 73 return avg; 74 } 75 76 void GradeCalc::info() { 77 if(is_dirty) 78 compute(); 79 80 std::cout << "课程名称:\t" << course_name << std::endl; 81 std::cout << "平均分:\t" << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << average() << std::endl; 82 std::cout << "最高分:\t" << max() << std::endl; 83 std::cout << "最低分:\t" << min() << std::endl; 84 85 const std::array<std::string, 5> grade_range{"[0, 60) ", 86 "[60, 70)", 87 "[70, 80)", 88 "[80, 90)", 89 "[90, 100]"}; 90 91 for(int i = static_cast<int>(grade_range.size())-1; i >= 0; --i) 92 std::cout << grade_range[i] << "\t: " << counts[i] << "人\t" 93 << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << rates[i]*100 << "%\n"; 94 } 95 96 void GradeCalc::compute() { 97 if(this->empty()) 98 return; 99 100 counts.fill(0); 101 rates.fill(0); 102 103 for(int grade: *this) { 104 if(grade < 60) 105 ++counts[0]; 106 else if (grade < 70) 107 ++counts[1]; 108 else if (grade < 80) 109 ++counts[2]; 110 else if (grade < 90) 111 ++counts[3]; 112 else 113 ++counts[4]; 114 } 115 116 for(size_t i = 0; i < rates.size(); ++i) 117 rates[i] = counts[i] * 1.0 / this->size(); 118 119 is_dirty = false; 120 }
源代码demo2.cpp
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 #include "GradeCalc.hpp" 4 5 void test() { 6 GradeCalc c1("OOP"); 7 8 std::cout << "录入成绩:\n"; 9 c1.input(5); 10 11 std::cout << "输出成绩:\n"; 12 c1.output(); 13 14 std::cout << "排序后成绩:\n"; 15 c1.sort(); c1.output(); 16 17 std::cout << "*************成绩统计信息*************\n"; 18 c1.info(); 19 20 } 21 22 int main() { 23 test(); 24 }
运行结果截图:
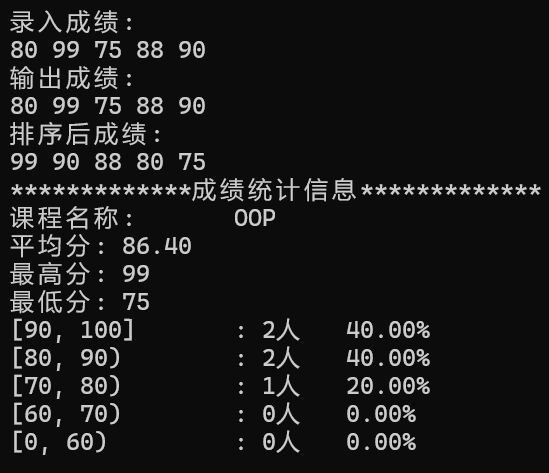
问题1:
class GradeCalc: private std::vector<int>
问题2:
不会。
不能,GradeCalc私有继承,基类std::vector<int>的所有公有接口会被隐藏,外部无法直接调用。
问题3:
组合中,grades是GradeCalc的私有成员变量,外部无法直接访问,必须通过成员变量grades的公有接口访问数据;继承中派生类内部可以使用基类接口,通过继承的基类接口访问数据。
问题4:
我认为组合方式更适合成绩计算这个问题场景。成绩计算类与成绩是has-a关系,组合更贴切;组合可以将成绩封装为私有成员,避免数据完整性被破坏。
实验任务3:
源代码Graph.hpp
1 #pragma once 2 3 #include<string> 4 #include<vector> 5 6 enum class GraphType{circle,triangle,rectangle}; 7 8 class Graph{ 9 public: 10 virtual void draw() {} 11 virtual ~Graph()=default; 12 }; 13 14 class Circle:public Graph{ 15 public: 16 void draw(); 17 }; 18 19 class Triangle:public Graph{ 20 public: 21 void draw(); 22 }; 23 24 class Rectangle:public Graph{ 25 public: 26 void draw(); 27 }; 28 29 class Canvas{ 30 public: 31 void add(const std::string& type); 32 void paint() const; 33 ~Canvas(); 34 35 private: 36 std::vector<Graph*> graphs; 37 }; 38 39 GraphType str_to_GraphType(const std::string& s); 40 Graph* make_graph(const std::string& type);
源代码Graph.cpp
1 #include<algorithm> 2 #include<cctype> 3 #include<iostream> 4 #include<string> 5 6 #include "Graph.hpp" 7 8 void Circle::draw(){ 9 std::cout << "draw a circle...\n"; 10 } 11 12 void Triangle::draw(){ 13 std::cout << "draw a triangle...\n"; 14 } 15 16 void Rectangle::draw(){ 17 std::cout << "draw a rectangle...\n"; 18 } 19 20 void Canvas::add(const std::string& type){ 21 Graph* g=make_graph(type); 22 if(g) 23 graphs.push_back(g); 24 } 25 26 void Canvas::paint() const{ 27 for(Graph* g:graphs) 28 g->draw(); 29 } 30 31 Canvas::~Canvas(){ 32 for(Graph* g:graphs) 33 delete g; 34 } 35 36 GraphType str_to_GraphType(const std::string& s){ 37 std::string t=s; 38 std::transform(s.begin(),s.end(),t.begin(), 39 [](unsigned char c){return std::tolower(c);}); 40 if(t=="circle") 41 return GraphType::circle; 42 if(t=="triangle") 43 return GraphType::triangle; 44 if(t=="rectangle") 45 return GraphType::rectangle; 46 return GraphType::circle; 47 } 48 49 Graph* make_graph(const std::string& type){ 50 switch (str_to_GraphType(type)){ 51 case GraphType::circle: return new Circle; 52 case GraphType::triangle: return new Triangle; 53 case GraphType::rectangle: return new Rectangle; 54 default: return nullptr; 55 } 56 }
源代码demo3.cpp
1 #include<string> 2 #include "Graph.hpp" 3 4 void test(){ 5 Canvas canvas; 6 7 canvas.add("circle"); 8 canvas.add("triangle"); 9 canvas.add("rectangle"); 10 canvas.paint(); 11 } 12 13 int main(){ 14 test(); 15 }
运行结果截图:
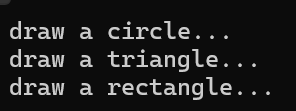
问题1:
(1)std::vector<Graph*> graphs;功能:存储和管理指向Graph派生类对象的指针,管理图形的生命周期。
(2)class Circle:public Graph
class Triangle:public Graph
class Rectangle:public Graph
问题2:
(1)会始终调用基类的draw(),输出为空。
(2)会出现对象切片问题,只保留基类部分,draw()调用将永远调用基类的空实现,无法正确管理动态创建的对象的内存。
(3)只调用基类的析构函数,派生类的析构函数不会被调用,会造成内存泄漏。
问题3:
Graph.hpp中,在enum class GraphType中添加star枚举值,添加Star类的声明class Star:public Graph{public:void draw();};。
Graph.cpp中,实现Star::draw(),修改str_to_GraphType函数,添加star的字符串映射,修改make_graph函数,添加Star的case。
demo3.cpp中,test()中添加Star的测试:canvas.add("star");。
问题4:
(1)在Canvas::~Canvas中被释放。
(2)利:直接控制对象生命周期。弊:容易导致内存泄漏,可能出现野指针,无法自动管理生命周期。
实验任务4:
问题描述:
支持多种具有不同特异功能的玩具(发声、发光等);
通过统一接口调用所有玩具的特异功能,体现多态性;
设计工厂类管理玩具集合,支持添加玩具、展示信息、批量测试功能;
运用组合复用附加功能(音乐、灯光),避免代码冗余。
对象关系:
继承关系:TalkingBear、GlowingRabbit、DancingPenguin均继承自抽象基类 Toy,重写纯虚函数实现个性化功能;
组合关系:具体玩具类通过包含soundPlayer或lightEffect对象,复用音乐播放和灯光效果功能;
源代码Toy.hpp
1 #pragma once 2 3 #include<string> 4 #include<vector> 5 #include<iostream> 6 #include<iomanip> 7 8 class Toy{ 9 public: 10 Toy(std::string name, std::string type, double price, std::string productionDate); 11 virtual ~Toy() = default; 12 13 void printBaseInfo() const{ 14 std::cout << "=========================================" << std::endl; 15 std::cout << "玩具名称:" << name << std::endl; 16 std::cout << "玩具类型:" << type << std::endl; 17 std::cout << "价格:" << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << price << " 元" << std::endl; 18 std::cout << "生产日期:" << productionDate << std::endl; 19 }; 20 virtual void showInfo() const = 0; 21 virtual void specialFunction() const = 0; 22 23 std::string getName() const { return name; } 24 std::string getType() const { return type; } 25 26 protected: 27 std::string name; 28 std::string type; 29 double price; 30 std::string productionDate; 31 }; 32 33 class SoundPlayer { 34 public: 35 void playMusic() const; 36 void playVoice(const std::string& line) const; 37 }; 38 39 class LightEffect { 40 public: 41 void flashLight(const std::string& color) const; 42 void steadyLight(const std::string& color) const; 43 }; 44 45 class TalkingBear:public Toy{ 46 public: 47 TalkingBear(std::string name, double price, std::string productionDate, std::string voiceLine); 48 void showInfo() const override; 49 void specialFunction() const override; 50 51 private: 52 SoundPlayer soundPlayer; 53 std::string voiceLine; 54 }; 55 56 class GlowingRabbit : public Toy { 57 public: 58 GlowingRabbit(std::string name, double price, std::string productionDate, std::string lightColor); 59 void showInfo() const override; 60 void specialFunction() const override; 61 62 private: 63 LightEffect lightEffect; 64 std::string lightColor; 65 }; 66 67 class ToyFactory { 68 public: 69 ~ToyFactory(); 70 void addToy(Toy* toy); 71 void showAllToys() const; 72 void testAllSpecialFunctions() const; 73 74 private: 75 std::vector<Toy*> toys; 76 };
源代码Toy.cpp
1 #include<algorithm> 2 #include<cctype> 3 #include<iostream> 4 #include<string> 5 #include<iomanip> 6 7 #include "Toy.hpp" 8 9 Toy::Toy(std::string name, std::string type, double price, std::string productionDate) 10 : name(name), type(type), price(price), productionDate(productionDate) {} 11 12 void SoundPlayer::playMusic() const { 13 std::cout << "[音乐播放] 播放欢快的儿童音乐~ " << std::endl; 14 } 15 16 void SoundPlayer::playVoice(const std::string& line) const { 17 std::cout << "[语音播放] " << line << std::endl; 18 } 19 20 void LightEffect::flashLight(const std::string& color) const { 21 std::cout << "[灯光效果] " << color << "色灯光闪烁中... " << std::endl; 22 } 23 24 void LightEffect::steadyLight(const std::string& color) const { 25 std::cout << "[灯光效果] " << color << "色灯光常亮" << std::endl; 26 } 27 28 TalkingBear::TalkingBear(std::string name, double price, std::string productionDate, std::string voiceLine) 29 : Toy(name, "毛绒发声玩具", price, productionDate), voiceLine(voiceLine) {} 30 31 void TalkingBear::showInfo() const { 32 printBaseInfo(); 33 std::cout << "特异功能:语音对话(专属台词:" << voiceLine << ")" << std::endl; 34 } 35 36 void TalkingBear::specialFunction() const { 37 std::cout << "\n【" << name << " 特异功能演示】" << std::endl; 38 soundPlayer.playMusic(); 39 soundPlayer.playVoice(voiceLine); 40 } 41 42 GlowingRabbit::GlowingRabbit(std::string name, double price, std::string productionDate, std::string lightColor) 43 : Toy(name, "毛绒发光玩具", price, productionDate), lightColor(lightColor) {} 44 45 void GlowingRabbit::showInfo() const { 46 printBaseInfo(); 47 std::cout << "特异功能:灯光效果(灯光颜色:" << lightColor << ")" << std::endl; 48 } 49 50 void GlowingRabbit::specialFunction() const { 51 std::cout << "\n【" << name << " 特异功能演示】" << std::endl; 52 lightEffect.flashLight(lightColor); 53 lightEffect.steadyLight(lightColor); 54 } 55 56 ToyFactory::~ToyFactory() { 57 for (Toy* toy : toys) { 58 delete toy; 59 } 60 toys.clear(); 61 } 62 63 void ToyFactory::addToy(Toy* toy) { 64 if (toy != nullptr) { 65 toys.push_back(toy); 66 } 67 } 68 69 void ToyFactory::showAllToys() const { 70 std::cout << "======= 玩具工厂 - 所有玩具信息 =======" << std::endl; 71 if (toys.empty()) { 72 std::cout << "工厂暂无玩具!" << std::endl; 73 return; 74 } 75 for (const Toy* toy : toys) { 76 toy->showInfo(); 77 } 78 std::cout << "=========================================" << std::endl; 79 } 80 81 void ToyFactory::testAllSpecialFunctions() const { 82 std::cout << "\n======= 玩具工厂 - 所有玩具特异功能测试 =======" << std::endl; 83 if (toys.empty()) { 84 std::cout << "工厂暂无玩具,无法测试特异功能!" << std::endl; 85 return; 86 } 87 for (const Toy* toy : toys) { 88 toy->specialFunction(); 89 std::cout << "-----------------------------------------" << std::endl; 90 } 91 }
源代码demo4.cpp
1 #include<string> 2 #include "Toy.hpp" 3 4 void test(){ 5 ToyFactory factory; 6 7 factory.addToy(new TalkingBear("憨憨熊", 99.99, "2025-01-15", "你好呀!我是憨憨熊,陪你一起玩~")); 8 factory.addToy(new GlowingRabbit("星光兔", 89.99, "2025-02-20", "粉紫")); 9 10 factory.showAllToys(); 11 factory.testAllSpecialFunctions(); 12 } 13 14 int main(){ 15 test(); 16 }
运行结果截图:
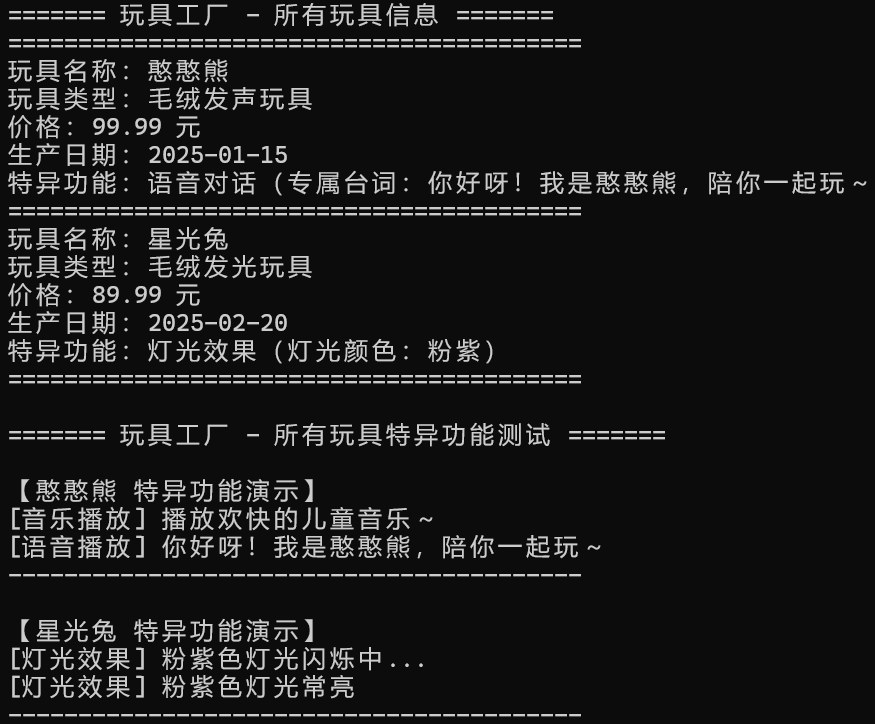
实验总结:
本次实验体会了组合和继承在相同问题场景以及不同问题场景下的使用,让我进一步理解如何使用组合和继承。在实验过程中,通过程序的报错,记住了纯虚函数未被派生类实现时无法实例化,若强制实例化并调用纯虚函数。会引发报错。当showInfo的前面几项输出一致时,可以在基类中定义一个非纯虚的辅助函数,统一实现“名称、类型、价格、生产日期”的输出。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号