常见字符串算法 II:自动机相关
Change Log
- 2025.8.7 新增 AC 自动机相关
- 2025.8.9 新增 回文自动机
1. AC 自动机
前置知识:KMP,Trie。
AC 自动机全称 Aho-Corasick Automaton 简称 ACAM。AC 自动机用途广泛,是重要字符串算法(\(8\) 级)。
1.1 算法描述与操作
KMP 算法是只能在一个文本串找一个模式串。AC 自动机可以在一个文本串找多个模式串。这是 KMP 和 AC 自动机的区别。当 KMP 处理多个模式串时,时间复杂度为 \(\mathcal{O}(\mid t\mid\times N+\sum{\mid s_i\mid})\),其中 \(N\) 是单次个数,当 \(N\) 过大时,无法接受。
和普通的 \(Trie\) 差不多,还是先建 \(Trie\),但是因为这个和 KMP 有着重要的关系,所以我们匹配的时候也会利用一个回退的指针,从而保证在 \(\mathcal{O}(N)\),对,和 \(next\) 的差不多。
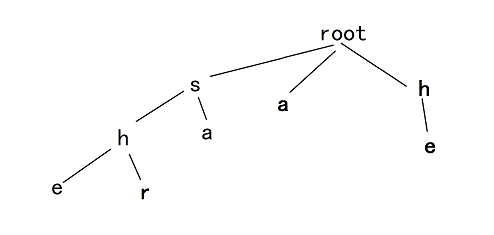
假设我们现在有这么一颗 \(Trie\)。
AC 自动机的精妙之处就是当匹配失败时,我们会有一个 fail 指针保证跳到的地方可以接着匹配。
而 fail 指针怎么确定呢?因为我们要保证可以接着匹配,所以我们要保证现在跳到的地方到根节点这一串是当前这一串的后缀,可能有点复杂。
我们先把 fail 指针画出来。
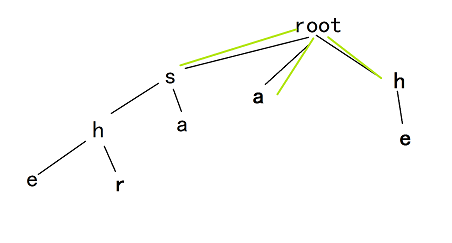
因为我们跳到的地方是当前已经匹配的后缀,所以需要运用到前面的已经确定的 fail 指针,所以第一层就是全部指向根节点。
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
int to = ch[0][i];
if(to) q.push(to);
}
然后就是愉快的 bfs。
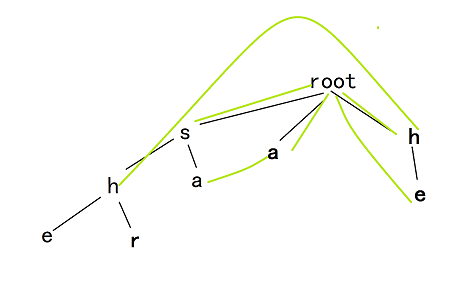
到了第二层,我们这个点就和他的父亲的 fail 指针的同样的儿子做比较,是不是很绕。
一直当前 \(root\to fail_u\) 是 \(root\to u\) 的最长后缀,我们要加进来,就看他们的下一位是不是相同,可以理解吧(其实就和 KMP 的操作一样)。
但是由于下一个节点不唯一,所以我们就找同位置的儿子,因为有的话就接上去了,然后更新。
但是万一没有下一个节点,由于我们想要一直搜索到底,所以我们就跳 fail 指针。
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
int to = ch[u][i];
if (to) {
fail[to] = ch[fail[u]][i];
q.push(to);
} else {
ch[u][i] = ch[fail[u]][i];
}
}
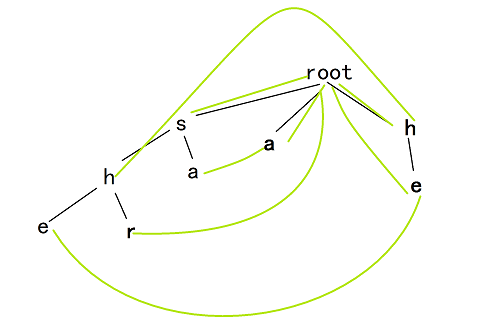
inline void get_fail() {
queue<int> q;
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
int to = ch[0][i];
if (to) q.push(to);
}
while (!q.empty()) {
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
int to = ch[u][i];
if (to)
fail[to] = ch[fail[u]][i], q.push(to);
else
ch[u][i] = ch[fail[u]][i];
}
}
return ;
}
接下来就是查找了,因为我们前面已经帮他跳 fail,所以一直搜索就完了。
但是因为搜索到这个点后,有多个 fail 指针可以回退,万一其中可能是某个串的结尾,所以我们需要循环。
inline int find(string s) {
int u = 0, ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) {
u = ch[u][get(s[i])];
for (int k = u; k && val[k] != -1; k = fail[k]) {
ans += val[k];
val[k] = -1;
}
}
return ans;
}
以上就是最基本的操作了,其实那些题的话,只需要改一些操作,例如辅助数组或者 \(val\),都是可以变通的,但是下面这个需要单独讲讲。
1.2 关于 fail 树
1.2.1 fail 树的应用
我们都知道,如果每次到一个点都要遍历 fail 点,会很耗费时间,因为搜索到一个点,顺着他 fail 指针的这条线上的都会遍历,所以我们每次都只需要将第一个点搜索过的次数加 \(1\),然后最后统一处理遍历就可以了。
但是这样又有一个问题,一个点可能有多个儿子,意思是他会继承多个儿子的 \(ans\) 值,而我们需要等到这个点继承完了所有的儿子点才能把他的给他的 fail 指针,熟不熟悉,就是拓扑排序,等到儿子继承完了再向上传递。
所以我们在建立 fail 指针的时候,入度数组要加 \(1\)。
int to = ch[u][i];
if (to) {
fail[to] = ch[fail[u]][i];
rd[ch[fail[u]][i]]++;
q.push(to);
}
找的时候我们找到第一个就行,消除遍历。
void find(char s[]) {
int u = 0;
for (int i = 0; s[i]; i++) {
u = ch[u][get(s[i])];
val[u]++;
}
topusort();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cout << val[a[i]] << endl;
return;
}
但是需要拓扑排序来向上传递。
void topusort() {
queue<int> q;
for (int i = 1; i < sz; i++)
if (rd[i] == 0) q.push(i);
while (!q.empty()) {
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
int v = fail[u];
rd[v]--;
val[v] += val[u];
if (rd[v] == 0) q.push(v);
}
return;
}
1.2.2 fail 树的性质
- 性质 \(0\):是一个有根树,支持时间戳拍平,可以支持数据结构,包括树剖、线段树。
- 性质 \(1\):对于节点 \(p\) 及其对应字符串 \(t_p\),对于其子树内部所有节点 \(q\in\operatorname{subtree}(p)\),都有 \(t_p\) 是 \(t_q\) 的后缀,且 \(t_p\) 是 \(t_q\) 的后缀 当且仅当 \(q\in\operatorname{subtree}(p)\)。
- 性质 \(2\):若 \(p\) 是终止节点,则 \(p\) 的子树全部都是终止节点。根据 fail 指针的定义,容易发现对于在 fail 树上具有祖先 - 后代关系的点对 \(p,q\),\(t_p\) 是 \(t_q\) 的 Border,这意味着 \(t_p\) 是 \(t_q\) 的后缀。因此,若 \(t_p\) 以某个单词结尾,则 \(t_q\) 也一定以该单词结尾,得证。
- 性质 \(3\):定义 \(ed_p\) 表示作为 \(t_p\) 后缀的单词数量。若单词互不相同,则 \(ed_p\) 等于 fail 树从 \(p\) 到根节点上单词节点的数量。若单词可以重复,则 \(t_p\) 等于这些单词节点所对应的单词的出现次数之和。
- 性质 4:把字符串 \(t\) 放在字典 \(s\) 的 AC 自动机上跑,得到的状态为 \(t\) 的最长后缀,满足它是 \(s\) 的前缀。
根据性质 \(3\),有这样一类问题:单词有带修权值,多次询问对于某个给定的字符串 \(S\),所有单词的权值乘以其在 \(S\) 中出现次数之和。根据常用结论,问题初步转化为 fail 树上带修点权,并对于 \(S\) 的每个前缀,查询该前缀所表示的状态到根的权值之和。
通常带修链求和要用到树剖,但查询具有特殊性质:一个端点是根。因此,与其单点修改链求和,不如 子树修改单点查询。实时维护每个节点的答案,这样修改一个点相当于更新子树,而查询时只需查单点。转化之前的问题需要树剖 + 数据结构 \(\log^2\) 维护,但转化后即可时间戳拍平 + 树状数组单 \(\log\) 小常数解决。
然后暂时不知道了。
1.3 例题
I. P3808 【模板】AC 自动机(简单版)
注意,相同编号的串出现多次仅算一次。
因此题目相当于求:文本串 \(t\) 在模式串 \(s_i\) 建出的 ACAM 上匹配时经过的所有节点到根的路径的并上单词节点的个数。
设当前状态为 \(p\),每次跳 \(p\) 的失配指针,加上经过节点表示的单词个数(单词可能相同)并标记,直到遇到标记节点 \(q\),说明 \(q\) 到根都已经被考虑到。注意上述过程并不改变 \(p\) 本身。时间复杂度线性。
// Problem: P3808 AC 自动机(简单版)
// Contest: Luogu
// URL: https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P3808
// Memory Limit: 512 MB
// Time Limit: 1000 ms
//
// Powered by CP Editor (https://cpeditor.org)
/*
author: Nimbunny
powered by c++14
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define pi pair<int, int>
// #define int long long
using namespace std;
const int INF = INT_MAX;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int N = 1e6 + 10, L = 26;
int n;
string s;
inline int read() {
int x;
cin >> x;
return x;
}
inline string read_s() {
string x;
cin >> x;
return x;
}
struct ACAM {
int idx, son[N][L], fa[N], ed[N];
inline void ins(string s) {
int p = 0;
for (auto x : s) {
int ch = x - 97;
if (!son[p][ch]) son[p][ch] = ++idx;
p = son[p][ch];
}
ed[p]++;
return ;
}
inline void build() {
queue<int> q;
for (int i = 0; i < L; i++)
if (son[0][i]) q.push(son[0][i]);
while (!q.empty()) {
int t = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < L; i++)
if (son[t][i]) {
fa[son[t][i]] = son[fa[t]][i];
q.push(son[t][i]);
} else
son[t][i] = son[fa[t]][i];
}
return ;
}
} acam;
signed main() {
cin.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false);
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) acam.ins(read_s());
int p = 0, ans = 0;
cin >> s;
acam.build();
for (auto x : s) {
int tmp = p = acam.son[p][x - 'a'];
while (acam.ed[tmp] != -1) {
ans += acam.ed[tmp];
acam.ed[tmp] = -1;
tmp = acam.fa[tmp];
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
II. P3121 [USACO15FEB] Censoring G
建出来 \(t\) 的 AC 自动机,并在 AC 自动机上标记结束节点(即某个 \(t_i\) 匹配到这个节点)。
之后逐位考虑 \(s\),在 AC 自动机上游走,每当遇到一个结束节点,我们就需要进行删除操作。
具体的,我们维护一个栈,删除时不断弹栈,直到弹出(被删除的串长)个元素后,我们就可以继续匹配了。
复杂度为 \(\mathcal{O}(\mid s\mid+ P\mid t_i\mid)\)。
P3121
// Problem: P3121 [USACO15FEB] Censoring G
// Contest: Luogu
// URL: https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P3121
// Memory Limit: 256 MB
// Time Limit: 1000 ms
//
// Powered by CP Editor (https://cpeditor.org)
/*
author: Nimbunny
powered by c++14
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define pi pair<int, int>
using namespace std;
const int INF = INT_MAX;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int n, idx, top;
int trie[N][26], fail[N], heap[N], sign[N];
int isend[N];
string s;
inline void insert(string s) {
int now = 0, len = s.size();
for (auto x : s) {
int ch = x - 'a';
if (!trie[now][ch]) trie[now][ch] = ++idx;
now = trie[now][ch];
}
isend[now] = len;
return;
}
inline void makefail() {
queue<int> q;
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++)
if (trie[0][i]) q.push(trie[0][i]);
while (!q.empty()) {
int now = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
if (!trie[now][i]) {
trie[now][i] = trie[fail[now]][i];
continue;
}
fail[trie[now][i]] = trie[fail[now]][i];
q.push(trie[now][i]);
}
}
return;
}
inline void solve(string s) {
int now = 0, len = s.size(), i = 0;
while (i < len) {
int x = s[i] - 97;
now = trie[now][x];
sign[++top] = now;
heap[top] = i;
if (isend[now]) {
top -= isend[now];
if (!top)
now = 0;
else
now = sign[top];
}
i++;
}
return;
}
inline string read_s() {
string x;
cin >> x;
return x;
}
signed main() {
cin.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false);
cin >> s >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) insert(read_s());
makefail();
solve(s);
for (int i = 1; i <= top; i++) cout << s[heap[i]];
return 0;
}
III. P5357 【模板】AC 自动机
建出模式串的 AC 自动机,之后把 S 放在自动机上跑,每扩展一位就把所在节点标记一次,表示当下前缀的某个后缀匹配到了这个节点。之后是统计答案,对于每个前缀的最长匹配后缀,其所有 border 也是被匹配的。
于是对于每个节点,其跳 fail 指针能到达的所有节点的标记需要累加上它的标记。
我们考虑 fail 指针形成的结构:每个节点指向一个深度比它浅的节,根节点指向自己。于是 fail 指针形成的结构是一棵树,在后文中我们称其为 fail 树。
一个节点的标记就是子树内标记和,利用 dfs 就可以统计答案了。
复杂度 \(\mathcal{O}(\mid S\mid+P\mid T_i\mid)\)。
P5357
// Problem: P5357 【模板】AC 自动机
// Contest: Luogu
// URL: https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P5357
// Memory Limit: 250 MB
// Time Limit: 1000 ms
//
// Powered by CP Editor (https://cpeditor.org)
/*
author: Nimbunny
powered by c++14
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define pi pair<int, int>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const int INF = INT_MAX;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
int n, tr[N][26], fail[N], idx;
int e[N], sum[N];
string s;
vector<int> G[N];
inline int insert(string s) {
int u = 0;
for (auto x : s) {
int ch = x - 97;
if (!tr[u][ch]) tr[u][ch] = ++idx;
u = tr[u][ch];
}
return u;
}
inline void bfs() {
queue<int> q;
for (int c = 0; c < 26; c++)
if (tr[0][c]) q.push(tr[0][c]);
while (!q.empty()) {
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int c = 0; c < 26; c++)
if (tr[u][c]) {
fail[tr[u][c]] = tr[fail[u]][c];
q.push(tr[u][c]);
} else
tr[u][c] = tr[fail[u]][c];
}
}
inline string read_s() {
string x;
cin >> x;
return x;
}
signed main() {
cin.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false);
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) e[i] = insert(read_s());
bfs();
for (int u = 1; u <= idx; u++) G[fail[u]].push_back(u);
cin >> s;
int u = 0;
for (auto x : s) {
int ch = x - 97;
u = tr[u][ch];
sum[u]++;
}
auto dfs = [&](int u, auto&& self) -> void {
for (auto v : G[u]) {
self(v, self);
sum[u] += sum[v];
}
};
dfs(0, dfs);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cout << sum[e[i]] << endl;
return 0;
}
IV. P5829 【模板】失配树
我们可以发现一个事实,一个字符串的 border 的 border 也是这个字符串的 border。
题目要求 \(s\) 长度为 \(p\) 的前缀 和长度为 \(q\) 前缀的最长公共 border 的长度,那么可知,如果两个前缀都有 border 那么可能包含着一个 border,是两个前缀的 border,也是他们 border 的 border,这不是找最近公共祖先吗。
那么是个人都知道了,我们先把这一个串找一遍 border,也就是跑 KMP 算法,这样就把任意前缀长度的 border 找出来,把其与其 border 建边,跑一遍最近公共祖先就好了。
P5829
// Problem: P5829 【模板】失配树
// Contest: Luogu
// URL: https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P5829
// Memory Limit: 512 MB
// Time Limit: 1000 ms
//
// Powered by CP Editor (https://cpeditor.org)
/*
author: Nimbunny
powered by c++14
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define pi pair<int, int>
using namespace std;
const int INF = INT_MAX;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int N = 1e6 + 10, L = 20;
int n;
string s;
inline int read() {
int x;
cin >> x;
return x;
}
struct fail_tree {
int fa[N][L], dep[N];
inline void init() {
for (int i = 1; i < L; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
fa[j][i] = fa[fa[j][i - 1]][i - 1];
return;
}
inline int lca(int u, int v) {
if (dep[u] < dep[v]) swap(u, v);
for (int i = L - 1; i >= 0; i--)
if (dep[fa[u][i]] >= dep[v]) u = fa[u][i];
for (int i = L - 1; i >= 0; i--)
if (fa[u][i] != fa[v][i]) u = fa[u][i], v = fa[v][i];
return fa[u][0];
}
} T;
struct KMP {
inline void kmp() {
for (int i = 2, j = 0; i <= n; i++) {
while (j != 0 && s[j + 1] != s[i]) j = T.fa[j][0];
if (s[j + 1] == s[i]) j++;
T.fa[i][0] = j;
T.dep[i] = T.dep[j] + 1;
}
return;
}
} S;
signed main() {
cin >> s;
n = s.size();
s = "#" + s;
T.dep[1] = 1;
S.kmp();
T.init();
int m = read();
while (m--) {
int x = read(), y = read();
cout << T.lca(x, y) << endl;
}
return 0;
}
V. P2444 [POI 2000] 病毒
建出 AC 自动机,考虑长度无限的字符串的等价定义。
实际上,我们只需要在 AC 自动机(这里指 Trie 图)上找到一个环,使得这个环不经过任何结束节点。
于是按照之前的方法把结束节点预处理出来,在剩下的图上找个环即可。
复杂度为 \(\mathcal{O}(\sum{\mid s_i\mid})\)。
P2444
// Problem: P2444 [POI 2000] 病毒
// Contest: Luogu
// URL: https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P2444
// Memory Limit: 500 MB
// Time Limit: 1000 ms
//
// Powered by CP Editor (https://cpeditor.org)
/*
author: aimbunny
powered by c++14
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define pi pair<int, int>
using namespace std;
const int INF = INT_MAX;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int N = 3e4 + 10;
int n;
bool v[N], f[N];
queue<int> q;
struct node {
int t[2], f;
bool c;
};
struct AcAutomaton {
node a[N];
int idx = 0;
inline void insert(string c) {
int u = 0;
for (auto x : c)
if (!a[u].t[x - 48]) {
a[u].t[x - 48] = ++idx;
u = idx;
} else
u = a[u].t[x - 48];
a[u].c = true;
return;
}
inline void PutFail() {
if (a[0].t[0] > 0) q.push(a[0].t[0]);
if (a[0].t[1] > 0) q.push(a[0].t[1]);
while (q.size()) {
int h = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i <= 1; i++)
if (a[h].t[i] > 0) {
q.push(a[h].t[i]);
int td = a[h].f;
while (td > 0 && a[td].t[i] <= 0) td = a[td].f;
if (a[td].t[i] <= 0)
a[a[h].t[i]].f = 0;
else {
a[a[h].t[i]].f = a[td].t[i];
if (a[a[td].t[i]].c) a[a[h].t[i]].c = true;
}
} else
a[h].t[i] = a[a[h].f].t[i];
}
return;
}
} S;
void dfs(int d) {
v[d] = true;
for (int i = 0; i <= 1; i++)
if (v[S.a[d].t[i]]) {
cout << "TAK" << endl;
exit(0);
} else if (!S.a[S.a[d].t[i]].c && !f[S.a[d].t[i]]) {
f[S.a[d].t[i]] = true;
dfs(S.a[d].t[i]);
}
v[d] = false;
return;
}
inline string read_s() {
string x;
cin >> x;
return x;
}
signed main() {
cin.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false);
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) S.insert(read_s());
S.PutFail();
dfs(0);
cout << "NIE" << endl;
return 0;
}
*VI. P5319 [BJOI2019] 奥术神杖
观察到这个式子很恶心,没法统计(你甚至没法计算),所以要做点变化,取个对数即得:
所以我们现在的目标就从最大化原来那个恶心的根式,变成最大化后面那个和式。注意到这是类似 01 分数规划的形式,考虑二分一个答案 \(x\),则原式子会变为:
所以现在我们的目标就是,对于 \(x\),最大化左边那个式子,然后比较它和 \(0\) 的关系,从而找到二分应该如何调整左右边界。
而我们想求出这个值,只需要给 AC 自动机上每个状态的权值设置为它在 fail 树上到根结点的权值和即可,状态初始权值仅有结束状态有,为 \(\ln{vi}\)。并记录每个状态到根结点的状态数 \(cnt\),每次给每个结点减去 \(xcnt\) 即可。
考虑 dp,设 \(f_{i,j}\) 表示前 \(i\) 个字符,匹配到第 \(j\) 个状态,能得到的最大权值,转移的时候直接按照刚刚求好的权值加一加即可。
注意,这里要按照拓扑序来转移,而由于 AC 自动机构建的特殊性,加入结点的顺序就是拓扑序,直接做就好了。记得再维护一下路径以便输出答案。时间复杂度 \(\mathcal{O}(n \sum{\mid s_i\mid \log\log v_i})\)。
P5319
// Problem: P5319 [BJOI2019] 奥术神杖
// Contest: Luogu
// URL: https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P5319
// Memory Limit: 125 MB
// Time Limit: 1000 ms
//
// Powered by CP Editor (https://cpeditor.org)
/*
author: Nimbunny
powered by c++14
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define pi pair<int, int>
using namespace std;
const int INF = INT_MAX;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int N = 2e3 + 10;
const double eps = 1e-6, inf = 1e10;
int n, ans[N];
string t, s;
double f[N][N];
pair<int, int> path[N][N];
struct ACAM {
struct node {
int t[10], f, cnt;
double val;
} a[N];
int idx = 1;
inline void insert(string s, int n, double v) {
int p = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int c = s[i] - 48;
if (!a[p].t[c]) a[p].t[c] = ++idx;
p = a[p].t[c];
}
a[p].val = v;
a[p].cnt = 1;
return;
}
inline void build() {
queue<int> q;
for (int c = 0; c < 10; c++)
if (a[1].t[c]) {
a[a[1].t[c]].f = 1;
q.push(a[1].t[c]);
} else
a[1].t[c] = 1;
while (!q.empty()) {
int p = q.front();
q.pop();
a[p].cnt += a[a[p].f].cnt;
a[p].val += a[a[p].f].val;
for (int c = 0; c < 10; c++)
if (a[p].t[c])
a[a[p].t[c]].f = a[a[p].f].t[c],
q.push(a[p].t[c]);
else
a[p].t[c] = a[a[p].f].t[c];
}
return;
}
} acam;
inline void getans(int x, int p) {
if (!x) return;
getans(x - 1, path[x][p].first);
ans[x] = path[x][p].second;
return;
}
inline bool dp(double mid) {
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= acam.idx; j++) f[i][j] = -inf;
f[0][1] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= acam.idx; i++)
acam.a[i].val -= acam.a[i].cnt * mid;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= acam.idx; j++) {
if (f[i - 1][j] == -inf) continue;
if (t[i] == '.')
for (int c = 0, p; c < 10; c++) {
p = acam.a[j].t[c];
if (f[i - 1][j] + acam.a[p].val > f[i][p]) {
f[i][p] = f[i - 1][j] + acam.a[p].val;
path[i][p] = make_pair(j, c);
}
}
else {
int p = acam.a[j].t[t[i] - 48];
if (f[i - 1][j] + acam.a[p].val > f[i][p]) {
f[i][p] = f[i - 1][j] + acam.a[p].val;
path[i][p] = make_pair(j, t[i] - 48);
}
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= acam.idx; i++)
acam.a[i].val += acam.a[i].cnt * mid;
int pos = -1;
double mx = -inf;
for (int i = 1; i <= acam.idx; i++)
if (f[n][i] > mx) {
mx = f[n][i];
pos = i;
}
if (mx > eps) return getans(n, pos), true;
return false;
}
inline int read() {
int x;
cin >> x;
return x;
}
inline string read_s() {
string x;
cin >> x;
return x;
}
signed main() {
cin.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false);
int m;
cin >> n >> m >> t;
t = "#" + t;
for (int i = 1, v; i <= m; i++) {
string s = "#" + read_s();
acam.insert(s, s.size() - 1, log(read()));
}
acam.build();
double l = 0, r = 21, mid, ret = -1;
while ((r - l) > eps) {
mid = (l + r) / 2;
if (dp(mid))
l = mid, ret = mid;
else
r = mid;
}
dp(ret);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cout << ans[i];
return 0;
}
VII. P5231 [JSOI2012] 玄武密码
建出 AC 自动机,将 \(s\) 放在 AC 自动机上匹配,标记匹配节点。
之后根据 fail 树的性质,将被标记节点的 fail 树祖先标记。
之后只需要查询每个串的代表节点 Trie 树上最深的被标记祖先节点即可。
复杂度 \(\mathcal{O}(s+\sum{\mid t\mid})\)。
P5231
// Problem: P5231 [JSOI2012] 玄武密码
// Contest: Luogu
// URL: https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P5231
// Memory Limit: 512 MB
// Time Limit: 2000 ms
//
// Powered by CP Editor (https://cpeditor.org)
/*
author: Nimbunny
powered by c++14
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define pi pair<int, int>
// #define int long long
// #pragma GCC optimize(2)
using namespace std;
const int INF = INT_MAX;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int N = 1e7 + 10, M = 1e5 + 10;
int n, lent;
int vis[N];
string tmp[M], t;
queue<int> q;
struct ACAM {
int trie[N][26], tot, fail[N], cnt[N];
inline void ins(string str) {
int u = 0;
for (auto x : str) {
int ch = x - 'A';
if (!trie[u][ch]) trie[u][ch] = ++tot;
u = trie[u][ch];
}
cnt[u]++;
return;
}
inline void build() {
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++)
if (trie[0][i]) {
q.push(trie[0][i]);
fail[trie[0][i]] = 0;
}
while (!q.empty()) {
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
if (trie[u][i])
fail[trie[u][i]] = trie[fail[u]][i],
q.push(trie[u][i]);
else
trie[u][i] = trie[fail[u]][i];
}
}
int p = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < lent; i++) {
p = trie[p][t[i] - 'A'];
for (int k = p; k && !vis[k]; k = fail[k]) vis[k] = 1;
}
return;
}
} acam;
inline int Query(string str) {
int len = str.size(), p = 0, res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
p = acam.trie[p][str[i] - 'A'];
if (vis[p]) res = i + 1;
}
return res;
}
inline int read() {
int x;
cin >> x;
return x;
}
inline string read_s() {
string x;
cin >> x;
return x;
}
signed main() {
cin.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false);
lent = read(), n = read();
t = read_s();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) acam.ins(tmp[i] = read_s());
acam.build();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cout << Query(tmp[i]) << endl;
return 0;
}
VIII. P3041 [USACO12JAN] Video Game G
建出 AC 自动机后,我们利用 fail 树的性质,预处理匹配到每个节点能产生多少次匹配。
之后进行最优化即可。
本题数据范围较小,直接设状态为 \(f_{i,p}\) 表示考虑前 \(i\) 个字符匹配到节点 \(p\) 的最大值即可。
复杂度为 \(\mathcal{O}(m\sum{\mid s_i\mid})\)。
P3041
// Problem: P3041 [USACO12JAN] Video Game G
// Contest: Luogu
// URL: https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P3041
// Memory Limit: 125 MB
// Time Limit: 1000 ms
//
// Powered by CP Editor (https://cpeditor.org)
/*
author: Nimbunny
powered by c++14
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define pi pair<int, int>
// #define int long long
// #pragma GCC optimize(2)
using namespace std;
const int INF = INT_MAX;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int N = 1e3 + 10;
int n, k, fail[N * N], f[N][N], idx;
struct TRIE {
int son[4], val;
} trie[N];
inline int read() {
int x;
cin >> x;
return x;
}
inline string read_s() {
string x;
cin >> x;
return x;
}
inline void insert(string st) {
int u = 0;
for (auto x : st) {
int v = x - 'A';
if (!trie[u].son[v]) trie[u].son[v] = ++idx;
u = trie[u].son[v];
}
trie[u].val++;
return;
}
inline void build() {
queue<int> q;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
if (trie[0].son[i]) {
q.push(trie[0].son[i]);
fail[trie[0].son[i]] = 0;
}
while (!q.empty()) {
int now = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
if (trie[now].son[i]) {
fail[trie[now].son[i]] = trie[fail[now]].son[i];
q.push(trie[now].son[i]);
} else
trie[now].son[i] = trie[fail[now]].son[i];
}
trie[now].val += trie[fail[now]].val;
}
return;
}
signed main() {
cin.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false);
n = read(), k = read();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) insert(read_s());
build();
memset(f, -127, sizeof f);
f[0][0] = 0;
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++)
for (int j = 0; j <= idx; j++)
for (int s = 0; s < 3; s++)
f[i][trie[j].son[s]] =
max(f[i][trie[j].son[s]],
f[i - 1][j] + trie[trie[j].son[s]].val);
for (int i = 0; i <= idx; i++) ans = max(ans, f[k][i]);
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
IX. P2414 [NOI2011] 阿狸的打字机
可以利用类似可持久化的思想建出来 Trie,具体的,遇到删除操作时将当前节点跳到父亲。之后再建 AC 自动机。
如果暴力求答案,考虑把第 \(y\) 个字符串涉及到的节点打上标记,之后查询第 \(x\) 个字符串的终止节点 fail 子树内有多少个标记点即可。
于是可以离线询问,扩展字符则给对应节点加标记,删除则删除当前标记并回退,查询时用一个树状数组统计子树答案即可。
复杂度为 \(\mathcal{O}((n+m)\log{n})\)。
P2414
// Problem: P2414 [NOI2011] 阿狸的打字机
// Contest: Luogu
// URL: https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P2414
// Memory Limit: 125 MB
// Time Limit: 1000 ms
//
// Powered by CP Editor (https://cpeditor.org)
/*
author: Nimbunny
powered by c++14
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define pi pair<int, int>
#define lowbit(x) (x & (-x))
using namespace std;
const int INF = INT_MAX;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
inline int read() {
int x;
cin >> x;
return x;
}
string ss;
int nd[N], n, tot;
int ans[N];
int c[N];
int dfn[N], low[N], tim;
int ql[N], qr[N];
void Modify(int x, int w) {
while (x <= tim) c[x] += w, x += lowbit(x);
}
int getsum(int x) {
int ret = 0;
while (x) ret += c[x], x -= lowbit(x);
return ret;
}
struct Node {
int vis[26], Vis[26], fail, fa, lt;
} t[N];
struct Question {
int x, y, id, ans;
bool operator<(const Question &other) const {
return y < other.y;
}
} q[N];
void GetFail() {
queue<int> Q;
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++)
if (t[0].vis[i]) Q.push(t[0].vis[i]);
while (!Q.empty()) {
int u = Q.front();
Q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++)
if (t[u].vis[i]) {
t[t[u].vis[i]].fail = t[t[u].fail].vis[i];
Q.push(t[u].vis[i]);
} else
t[u].vis[i] = t[t[u].fail].vis[i];
}
}
struct Line {
int v, next;
} e[N << 1];
int h[N], cnt = 1;
inline void Add(int u, int v) {
e[cnt] = (Line){v, h[u]};
h[u] = cnt++;
}
void dfs(int u) {
dfn[u] = ++tim;
for (int i = h[u]; i; i = e[i].next) dfs(e[i].v);
low[u] = tim;
return;
}
void DFS(int u) {
Modify(dfn[u], 1);
if (t[u].lt)
for (int i = ql[t[u].lt]; i <= qr[t[u].lt]; ++i)
q[i].ans =
getsum(low[nd[q[i].x]]) - getsum(dfn[nd[q[i].x]] - 1);
for (int i = 0; i < 26; ++i)
if (t[u].Vis[i]) DFS(t[u].Vis[i]);
Modify(dfn[u], -1);
return;
}
signed main() {
cin.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false);
cin >> ss;
ss = "#" + ss;
int now = 0;
for (int i = 1, l = ss.size() - 1; i <= l; i++) {
// if (ss[i] >= 'a' && ss[i] <= 'z')
if (islower(ss[i])) {
if (!t[now].vis[ss[i] - 'a']) {
t[now].vis[ss[i] - 'a'] = ++tot;
t[tot].fa = now;
}
now = t[now].vis[ss[i] - 'a'];
}
if (ss[i] == 'B') now = t[now].fa;
if (ss[i] == 'P') {
nd[++n] = now;
t[now].lt = n;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i <= tot; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < 26; j++) t[i].Vis[j] = t[i].vis[j];
int Q = read();
GetFail();
for (int i = 1; i <= tot; i++) Add(t[i].fail, i);
dfs(0);
for (int i = 1; i <= Q; i++) {
q[i].x = read(), q[i].y = read();
q[i].id = i;
}
sort(q + 1, q + Q + 1);
for (int i = 1, pos = 1; i <= Q; i = pos) {
ql[q[i].y] = i;
while (q[pos].y == q[i].y) pos++;
qr[q[i].y] = pos - 1;
}
DFS(0);
for (int i = 1; i <= Q; ++i) ans[q[i].id] = q[i].ans;
for (int i = 1; i <= Q; ++i) cout << ans[i] << endl;
return 0;
}
X. CF1038F Wrap Around
考虑极限,假设 \(T^{\infty}\) 匹配到了 \(s\) 的某个位置 \(p\),那么在后面再匹配一个 \(T\),必须还匹配在位置 \(p\)。
并且,如果 \(T^{\infty}\) 没有完整匹配过 \(s\),那么在后面再匹配一个 \(T\),仍然不会完整匹配过 \(s\)。
于是可以枚举 \(p\) 做 DP,求出所有不含 \(s\) 作为子串的 \(T\),再求补集即可。
复杂度为 \(\mathcal{O}(n\mid s\mid^2)\)。
CF1038F
// Problem: CF1038F Wrap Around
// Contest: Luogu
// URL: https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/CF1038F
// Memory Limit: 250 MB
// Time Limit: 2000 ms
//
// Powered by CP Editor (https://cpeditor.org)
/*
author: Nimbunny
powered by c++14
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define pi pair<int, int>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int INF = INT_MAX;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int N = 50;
int n, m, dp[N][N][2], ans;
bool g[N];
string st;
signed main() {
cin.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false);
cin >> n >> st;
m = st.size();
st = "#" + st;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
bool flag = true;
int x = 1, y = i;
while (y <= m) {
if (st[x] != st[y]) flag = false;
x++, y++;
}
g[i - 1] = flag;
}
dp[1][1][1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
for (int x = 1; x < i; x++)
for (int o = 0; o <= 1; o++) {
if ((i - x >= m || g[i - x]) &&
(n + 1 - i >= m || g[n + 1 - i]))
dp[i][i][o ^ 1] += dp[i - 1][x][o];
dp[i][x][o] += (1 + (x + m <= i)) * dp[i - 1][x][o];
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
ans += (dp[n][i][1] - dp[n][i][0]) * (n + 1 - i);
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
XI. CF547E Mike and Friends
之前我们每次询问都是 \(s_{1\dots n}\),可以先建出来 AC 自动机再依次处理。
现在加上了区间限制,考虑差分成 \(s_{1\dots l−1}\) 和 \(s_{1\dots r}\) 两个前缀问题。
一种思路是询问离线,建出完整的 AC 自动机后,我们从第一个串开始,每次给涉及到的点打标记,查询时做子树查询。
复杂度为 \(\mathcal{O}((\sum{\mid s_i\mid+m})\log(\sum{\mid s_i\mid}))\)。
还有一种思路是在线构造 AC 自动机,这做法的优势在于如果每次询问 \(k\le r\) 可以做到完全在线。
在线构造 AC 自动机过程比较复杂,需要用到二进制分组的思想,这里不详细展开,留给感兴趣的同学探索。
只论在线构造 AC 自动机,复杂度为 \(\mathcal{O}(n\log{n})\),\(n\) 为字符串长度和。
CF547E
// Problem: CF547E Mike and Friends
// Contest: Luogu
// URL: https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/CF547E
// Memory Limit: 250 MB
// Time Limit: 3000 ms
//
// Powered by CP Editor (https://cpeditor.org)
/*
author: Nimbunny
powered by c++14
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ffe(it, v) \
for (__typeof(v.begin()) it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
#define endl '\n'
#define pi pair<int, int>
#define ll long long
#define lowbit(x) (x & (-x))
using namespace std;
const int INF = INT_MAX;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int N = 2e5, Q = 5e5;
const int ALPHA = 26;
int n, qu;
string s[N + 10];
int ch[N + 10][ALPHA + 10], fail[N + 10], ncnt, ed[N + 10],
ans[Q + 10];
inline void insert(string s, int id) {
int cur = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) {
if (!ch[cur][s[i] - 'a']) ch[cur][s[i] - 'a'] = ++ncnt;
cur = ch[cur][s[i] - 'a'];
}
ed[id] = cur;
return;
}
inline void getfail() {
queue<int> q;
for (int i = 0; i < ALPHA; i++)
if (ch[0][i]) q.push(ch[0][i]);
while (!q.empty()) {
int x = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < ALPHA; i++) {
if (ch[x][i]) {
fail[ch[x][i]] = ch[fail[x]][i];
q.push(ch[x][i]);
} else
ch[x][i] = ch[fail[x]][i];
}
}
return;
}
int hd[N + 10], to[N + 10], nxt[N + 10], ec;
inline void adde(int u, int v) {
to[++ec] = v;
nxt[ec] = hd[u];
hd[u] = ec;
return;
}
int tim, bgt[N], edt[N];
inline void dfs(int x) {
bgt[x] = ++tim;
for (int e = hd[x]; e; e = nxt[e]) dfs(to[e]);
edt[x] = tim;
return;
}
int t[N];
inline void add(int x, int v) {
for (int i = x; i <= (ncnt + 1); i += lowbit(i)) t[i] += v;
return;
}
inline int query(int x) {
int ret = 0;
for (int i = x; i; i &= (i - 1)) ret += t[i];
return ret;
}
vector<pair<pi, int> > qv[N + 10];
inline int read() {
int x;
cin >> x;
return x;
}
inline string read_s() {
string x;
cin >> x;
return x;
}
signed main() {
cin.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false);
cin >> n >> qu;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) insert(s[i] = read_s(), i);
getfail();
for (int i = 1; i <= ncnt; i++) adde(fail[i], i);
dfs(0);
for (int i = 1; i <= qu; i++) {
int l = read(), r = read(), k = read();
qv[r].push_back({{i, 1}, k});
qv[l - 1].push_back({{i, -1}, k});
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int cur = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < s[i].size(); j++) {
cur = ch[cur][s[i][j] - 'a'];
add(bgt[cur], 1);
}
ffe(it, qv[i]) {
int x = it->second, id = it->first.first,
mul = it->first.second;
ans[id] +=
mul * (query(edt[ed[x]]) - query(bgt[ed[x]] - 1));
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= qu; i++) cout << ans[i] << endl;
return 0;
}
*XII. P3735 [HAOI2017] 字符串
字符串相等的条件等价于 \(\mid a\mid=\mid b\mid\) 且 \(\operatorname{lcp}(a, b)+\operatorname{lcs}(a, b)+k\ge\mid a\mid\)。
多串匹配考虑 ACAM,建出正串和反串的 ACAM,注意是同一个 ACAM。
对于一个 \(s\) 的子串 \(s[x,x+\mid p_i\mid−1]\),和 \(p_i\) 匹配的条件为 \(s\) 存在长度不超过 \(k\) 的子串 \(s[l,r]\) 使得在正串 ACAM 能匹配到 \(p_i[1,l−x]\),反串 ACAM 能匹配到 \(p^{′}_i[1,r−x]\)。
考虑强制让中间间隔为 \(k\),这样可能会造成计数重复,不过之后减去 \(k′=k−1\) 的答案可以差分出真正的答案。
根据 fail 树的性质,每个子树内的节点的代表串的 border 之一是子树根的代表串。
设 \(p_i[1,j]\) 正串在 ACAM 上的节点为 \(u\),后缀 \(p^{′}_i[1,\mid p_i\mid−j−k]\) 反串在 ACAM 上的节点为 \(v\)。
设 \(s\) 中以 \(pos\) 结尾的前缀,在 ACAM 上的节点是 \(x\),以 \(pos+k+1\) 开始的后缀节点为 \(y\)。
则 \((x,y)\) 对 \((u,v)\) 有贡献当且仅当 \(x\) 在 \(u\) 子树内且 \(y\) 在 \(v\) 子树内。
这是一个二维数点问题,时间复杂度为 \(\mathcal{O}(n\log{n})\)。
P3735
// Problem: P3735 [HAOI2017] 字符串
// Contest: Luogu
// URL: https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P3735
// Memory Limit: 250 MB
// Time Limit: 1000 ms
//
// Powered by CP Editor (https://cpeditor.org)
/*
author: Nimbunny
powered by c++14
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define pi pair<int, int>
#define lowbit(x) (x & (-x))
using namespace std;
const int INF = INT_MAX;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int N = 4e5 + 10;
inline int read() {
int x;
cin >> x;
return x;
}
int k, n, m, root, tot, cnt;
int trie[N][94], fail[N], ans[N], bel[N], in[N], out[N];
char str[N], s[N];
struct node {
int id, p1, p2, v1, v2;
};
vector<node> v[N];
vector<pi> ve[N];
struct edge {
int to, nxt;
} e[N];
int head[N], edge_cnt;
void add(int from, int to) {
e[++edge_cnt] = {to, head[from]};
head[from] = edge_cnt;
return;
}
struct BIT {
int t[N];
inline void update(int x) {
while (x <= cnt) t[x]++, x += lowbit(x);
return;
}
inline int query(int x) {
int sum = 0;
while (x) sum += t[x], x -= lowbit(x);
return sum;
}
inline int ask(int l, int r) {
return query(r) - query(l - 1);
}
} T1, T2;
void insert(int id) {
int len = strlen(s + 1), p = root;
for (int i = 1; i <= len; i++) {
int ch = s[i] - 33;
if (!trie[p][ch]) trie[p][ch] = ++tot;
p = trie[p][ch];
}
p = root;
bel[len + 1] = 0;
for (int i = len; i; i--) {
int ch = s[i] - 33;
if (!trie[p][ch]) trie[p][ch] = ++tot;
p = trie[p][ch];
bel[i] = p;
}
p = root;
for (int i = 0; i <= len - k; i++) {
node t = {id, bel[i + k + 1], bel[i + k], 0, 0};
if (!i) t.p2 = -1;
v[p].push_back(t);
p = trie[p][s[i + 1] - 33];
}
return;
}
void build() {
queue<int> q;
for (int i = 0; i < 94; i++)
if (trie[root][i]) q.push(trie[root][i]);
while (!q.empty()) {
int x = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 94; i++) {
int y = trie[x][i];
if (y)
fail[y] = trie[fail[x]][i], q.push(y);
else
trie[x][i] = trie[fail[x]][i];
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= tot; i++) add(fail[i], i);
int p = root;
for (int i = n; i; i--) bel[i] = p = trie[p][str[i] - 33];
p = root;
for (int i = 0; i <= n - k; i++) {
ve[p].push_back({bel[i + k + 1], bel[i + k]});
p = trie[p][str[i + 1] - 33];
}
return;
}
void dfs_dfn(int x) {
in[x] = ++cnt;
for (int i = head[x]; i; i = e[i].nxt) dfs_dfn(e[i].to);
out[x] = cnt;
return;
}
void dfs_ans(int x) {
for (int i = 0; i < v[x].size(); i++) {
node t = v[x][i];
v[x][i].v1 = T1.ask(in[t.p1], out[t.p1]);
if (t.p2 != -1) v[x][i].v2 = T2.ask(in[t.p2], out[t.p2]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < ve[x].size(); i++) {
T1.update(in[ve[x][i].first]);
T2.update(in[ve[x][i].second]);
}
for (int i = head[x]; i; i = e[i].nxt) dfs_ans(e[i].to);
for (int i = 0; i < v[x].size(); i++) {
node t = v[x][i];
ans[t.id] += T1.ask(in[t.p1], out[t.p1]) - t.v1;
if (t.p2 != -1)
ans[t.id] -= T2.ask(in[t.p2], out[t.p2]) - t.v2;
}
return;
}
signed main() {
cin.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false);
k = read();
cin >> str + 1;
m = read();
n = strlen(str + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
cin >> s + 1;
int l = strlen(s + 1);
if (l > k)
insert(i);
else
ans[i] = n - l + 1;
}
build();
dfs_dfn(root);
dfs_ans(root);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) cout << ans[i] << endl;
return 0;
}
1.4 小结
为了解决多串模式匹配问题,我们将 KMP 的思想扩展到 Trie 树上,AC 自动机因此诞生。
比起 AC 自动机,fail 树的树形结构更为重要,通常复杂的字符串问题都需要放在 fail 树思考,搭配各种树上数据结构解决。
做好字符串问题离不开对于自动机结构本质的理解,所以这节课的内容一定要完全弄懂,之后进行更深层的字符串问题学习才不会吃力。
2. 回文自动机(PAM)
Manacher 算法可以求出来每个位置的最大回文半径,但我们还想获得更多的信息。
回顾 ACAM,我们可以判断某个字符串在文本串中是否出现过。
那我们是否能搭建一个类似的结构,判断某个回文字符串是否出现过呢?我们也尝试搭建一个自动机,叫做回文自动机。
注意,实际上回文自动机的结构和后缀自动机 (SAM) 更为接近。
2.1 算法流程
PAM 有两个初始状态,分别代表长度为 \(−1,0\) 的回文串。我们可以称它们为奇根,偶根。它们不表示任何实际的字符串,仅作为初始状态存在,这与其他自动机的根节点是异曲同工的。
其余每个节点表示原串的一个回文子串,一条转移边表示在当前串两边各添加一个字符。对每个节点我们定义 fail 指针,指向状态内最长回文后缀偶根的 fail 指针指向奇根,而我们并不关心奇根的 fail 指针,因为奇根不可能失配(奇根转移出的下一个状态长度为 \(1\),即单个字符。一定是回文子串)。
类似几乎所有的自动机,我们增量构造回文自动机。考虑构造完前 \(p−1\) 个字符的回文自动机后,向自动机中添加在原串里位置为 \(p\) 的字符。
我们从以上一个字符结尾的最长回文子串对应的节点开始,不断沿着 fail 指针走,直到找到一个节点满足 \(s_p=s_{p−len−1}\),即满足此节点所对应回文子串的上一个字符与待添加字符相同。
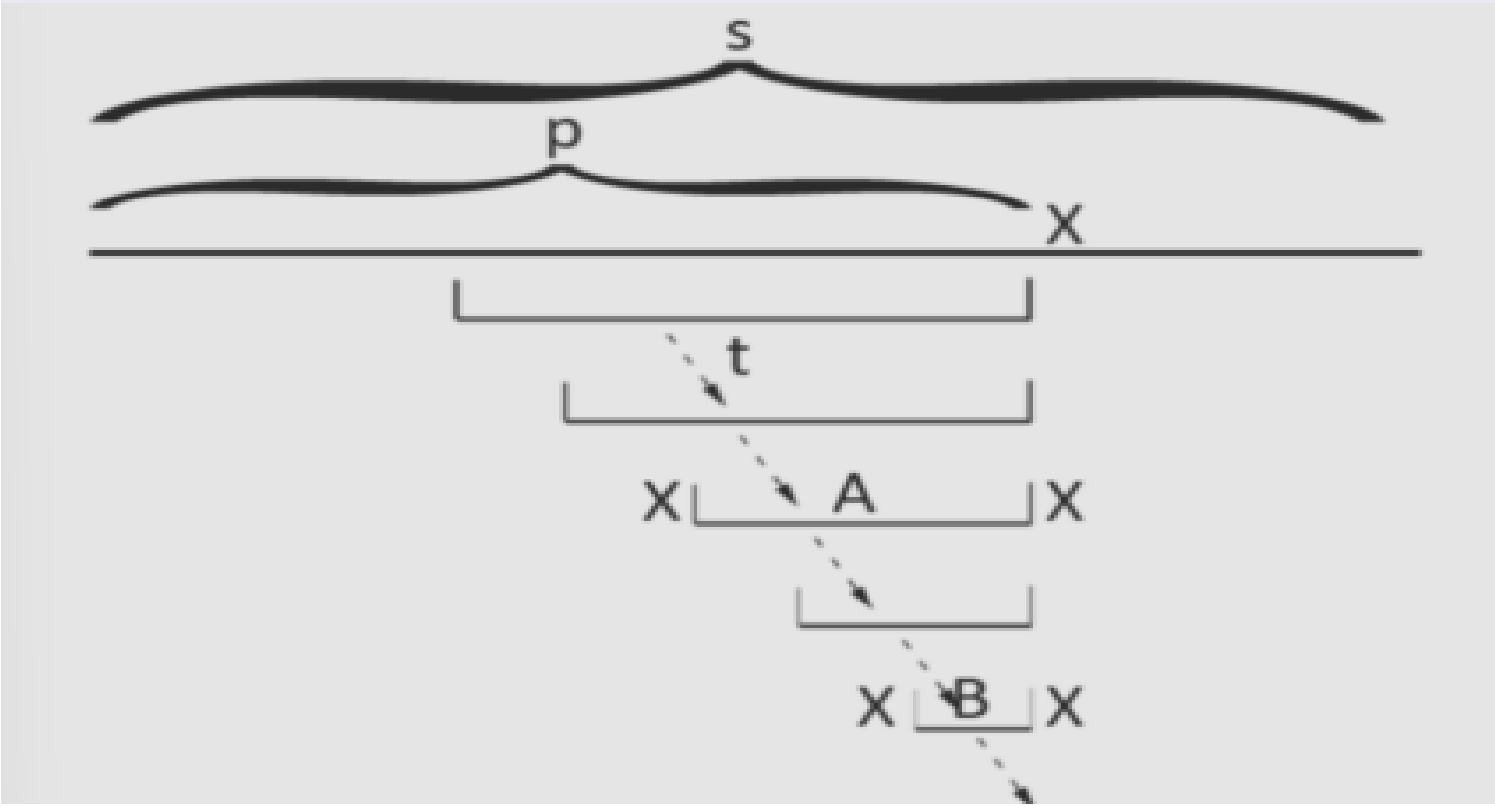
通过跳 fail 指针找到 A 所对应的节点,然后两边添加 X 就到了现在的回文串了 (即 XAX),很显然,这个节点就是以 \(p\) 结尾的最长回文子串对应的树上节点。此时要判断一下:没有这个节点,就需要新建。
然后我们还需要求出新建的节点的 fail 指针。具体方法与上面的过程类似,不断跳转 fail 指针,从 A 出发,即可找到 XAX 的最长回文后缀 XBX,将对应节点设为 fail 指针所指的对象即可。
node a[N];
int lst, cnt;
PAM() {
a[0].len = 0;
a[0].fail = 1;
a[1].len = -1;
a[1].fail = 0;
lst = 0;
cnt = 1;
}
int get_fail(int x, int lim) {
while (s[lim - a[x].len - 1] != s[lim]) x = a[x].fail;
return x;
}
void insert(int c, int lim) {
int p = get_fail(lst, lim);
if (!a[p].ch[c]) {
a[++cnt].len = a[p].len + 2;
int q = get_fail(a[p].fail, lim);
a[cnt].fail = a[q].ch[c];
a[cnt].num = a[a[cnt].fail].num + 1;
a[p].ch[c] = cnt;
}
lst = a[p].ch[c];
return;
}
2.2 线性状态数证明
2.2.1 定理
对于一个字符串 \(s\),它的本质不同回文子串个数最多只有 \(\mid s\mid\) 个。
2.2.2 证明
考虑使用数学归纳法。
- 当 \(\mid s\mid=1\) 时,结论显然成立。
- 当 \(\mid s\mid>1\) 时,设 \(t=s+c\)。假设结论对 \(s\) 串成立。考虑以最后一个字符 \(c\) 结尾的回文子串,假设它们的左端点由小到大排序为 \(l_1,l_2,\dots,l_k\)。由于 \(t_{l_1..\mid t\mid}\) 是回文串,因此对于所有位置 \(l_1\le p\le\mid t\mid\),有 \(t_{p..\mid t\mid}=t_{l_1..l_1+\mid t\mid−p}\)。所以,对于 \(1<i\le k\),\(t_{l_i..\mid t\mid}\) 已经在 \([1\dots\mid t\mid−1]\) 中出现过。因此,每次增加一个字符,本质不同的回文子串个数最多增加 \(1\) 个。
2.2.3 复杂度分析
空间复杂度显然是 \(\mathcal{O}(n)\)。
新建字符的跳 fail 操作可以类比 KMP:找最长的回文后缀。每次往回跳都会让当前状态指向的字符串长度减少,而每次新增字符最多让当前状态指向的字符串长度 \(+2\),跳 fail 操作的时间复杂度是 \(\mathcal{O}(n)\) 的。
同时也可以证明,求 fail 的操作也是 \(\mathcal{O}(n)\) 的。
所以总时间复杂度是 \(\mathcal{O}(n)\)。
2.3 例题
I. CodeChef Palindromeness
题意
给出一个字符串 \(s\)。求其所有非空子串的回文程度之和。
定义一个字符串 \(s\) 的回文程度为:
- 如果 \(s\) 不是回文串,回文程度为 \(0\);
- 如果 \(s\) 只有一个字符,回文程度为 \(1\);
- 对于其他情况,其回文程度为 \(1+s[1,\lfloor\frac{\mid s\mid}2\rfloor]\) 的回文程度。
\(\mid s\mid\le10^5\)。
构建回文树,现在的问题就是要求出当前回文串节点的长度的一半的那个回文串所代表的节点。
定义 tran 指针指向长度最长并且长度小于等于当前节点长度一半的回文串所代表的节点,也就是不超过一半的最长回文后缀。
如果当前点的长度为 \(1\),tran 指针不存在。
否则,从构建回文树时的父亲节点 (注意不是 fail 指针) 的 tran 指针开始暴力跳 fail,直到找到满足要求的点,就找到了当前节点的 tran 指针。
之后只需要在回文树上 dp 即可。
CC PALPROB
// Problem: Palindromeness
// Contest: CodeChef - LTIME23
// URL: https://www.codechef.com/problems/PALPROB
// Memory Limit: 256 MB
// Time Limit: 3000 ms
//
// Powered by CP Editor (https://cpeditor.org)
/*
author: Nimbunny
powered by c++14
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define pi pair<int, int>
#define int long long
// #pragma GCC optimize(2)
using namespace std;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
string ch;
inline int read() {
int x;
cin >> x;
return x;
}
struct node {
int len, ff, son[26];
} t[N];
struct Parlindromic_Automaton {
int last, tot, cnt[N], val[N], half[N];
inline void init() {
memset(t, 0, sizeof t);
memset(cnt, 0, sizeof cnt);
t[tot = 1].len = -1;
t[0].ff = t[1].ff = 1;
return;
}
inline void extend(int c, int n, string s) {
int p = last;
while (s[n - t[p].len - 1] != s[n]) p = t[p].ff;
if (!t[p].son[c]) {
int v = ++tot, k = t[p].ff;
t[v].len = t[p].len + 2;
while (s[n - t[k].len - 1] != s[n]) k = t[k].ff;
t[v].ff = t[k].son[c];
t[p].son[c] = v;
if (t[v].len == 1)
half[v] = 0;
else {
int pos = half[p];
while (s[n - t[pos].len - 1] != s[n] ||
(2 + t[pos].len) * 2 > t[v].len)
pos = t[pos].ff;
half[v] = t[pos].son[c];
}
val[v] =
1 +
(t[v].len / 2 == t[half[v]].len ? val[half[v]] : 0);
}
last = t[p].son[c];
cnt[last]++;
}
inline int calc() {
int ret = 0;
for (int i = tot; i; i--) cnt[t[i].ff] += cnt[i];
for (int i = tot; i; i--) ret += cnt[i] * val[i];
return ret;
}
} pam;
inline void solve() {
cin >> ch;
ch = "#" + ch;
pam.init();
for (int i = 1, l = ch.size(); i < l; i++)
pam.extend(ch[i] - 'a', i, ch);
cout << pam.calc() << endl;
return;
}
signed main() {
cin.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false);
int _ = read();
while (_--) solve();
return 0;
}
II. P4762 [CERC2014] Virus synthesis
题意
给出一个字符串 \(s\),你需要从一个空串开始构造出 \(s\),可以进行以下操作:
- 在开头或末尾添一个字符。
- 把当前字符串全部翻转后拼接在原串的开头或结尾。
最小化操作次数。
\(\mid s\mid\le10^5\)。
建出回文自动机。记 \(f_i\) 表示从空串得到 \(i\) 节点的代表串需要的最小代价,答案就是 \(\min(f_i+n−len_i)\)。
转移边对应转移方程:\(f_i\gets f_j+1\)。
tran 指针对应转移方程:\(f_i\gets f_j+\frac{len_i}2−len_j\)。
于是用上一题的方法求出 tran 指针后在回文自动机上 dp 即可。
时间复杂度 \(\mathcal{O}(n)\)。
P4762
// Problem: P4762 [CERC2014] Virus synthesis
// Contest: Luogu
// URL: https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P4762
// Memory Limit: 125 MB
// Time Limit: 1000 ms
//
// Powered by CP Editor (https://cpeditor.org)
/*
author: Nimbunny
powered by c++14
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define pi pair<int, int>
// #define int long long
// #pragma GCC optimize(2)
using namespace std;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int n, tot, last, ans;
int fail[N], len[N], trans[N], f[N];
int ch[N][5];
string s;
inline int read() {
int x;
cin >> x;
return x;
}
inline int change(char c) {
if (c == 'A') return 1;
if (c == 'G') return 2;
if (c == 'C') return 3;
return 4;
}
inline void init() {
for (int i = 0; i <= tot; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= 4; j++) ch[i][j] = 0;
fail[0] = tot = 1;
len[1] = -1;
last = 0;
return;
}
inline int getfail(int x, int pos) {
while (s[pos - len[x] - 1] != s[pos]) x = fail[x];
return x;
}
inline void add(int c, int pos) {
int p = getfail(last, pos);
if (!ch[p][c]) {
int q = ++tot, tmp;
len[q] = len[p] + 2;
tmp = getfail(fail[p], pos);
fail[q] = ch[tmp][c];
ch[p][c] = q;
if (len[q] <= 2)
trans[q] = fail[q];
else {
tmp = trans[p];
while (s[pos - len[tmp] - 1] != s[pos] ||
((len[tmp] + 2) << 1) > len[q])
tmp = fail[tmp];
trans[q] = ch[tmp][c];
}
}
last = ch[p][c];
return;
}
inline void solve() {
cin >> s;
n = s.size();
s = '#' + s;
init();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) add(change(s[i]), i);
ans = n;
queue<int> q;
for (int i = 2; i <= tot; i++) f[i] = len[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= 4; i++)
if (ch[0][i]) q.push(ch[0][i]);
while (!q.empty()) {
int x = q.front();
q.pop();
f[x] =
min(f[x], f[trans[x]] + 1 + len[x] / 2 - len[trans[x]]);
ans = min(ans, n - len[x] + f[x]);
for (int i = 1; i <= 4; i++) {
if (!ch[x][i]) continue;
int to = ch[x][i];
f[to] = min(f[to], f[x] + 1);
q.push(to);
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
return;
}
signed main() {
cin.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false);
int _ = read();
while (_--) solve();
return 0;
}
III. P4287 [SHOI2011] 双倍回文
建出回文自动机,可以得到这个串的 \(\mathcal{O}(\mid S\mid)\) 个本质不同的回文子串。
接下来只需要对每个回文串判断是否长度为偶数且前一半也是回文串,利用 tran 指针即可。
时间复杂度为 \(\mathcal{O}(\mid S\mid)\)。
P4287
// Problem: P4287 [sHOI2011] 双倍回文
// Contest: Luogu
// URL: https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P4287
// Memory Limit: 500 MB
// Time Limit: 1000 ms
//
// Powered by CP Editor (https://cpeditor.org)
/*
author: Nimbunny
powered by c++14
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define pi pair<int, int>
// #define int long long
// #pragma GCC optimize(2)
using namespace std;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int N = 5e5 + 10;
int n;
string s;
struct Parlindromic_Automaton {
int cnt, last, half[N];
struct node {
int L, fath, tr[26];
node() {}
node(int l, int father) {
L = l, fath = father;
for (int i = 0; i ^ 26; i++) tr[i] = 0;
}
} nd[N];
inline int newnode() {
nd[++cnt] = {0, 0};
return cnt;
}
inline void init() {
for (int i = 0; i <= cnt; i++) nd[i] = node(0, 0);
cnt = last = 1;
nd[0] = node(0, 1), nd[1] = node(-1, 0);
return;
}
inline void extend(string s) {
int l = s.size();
for (int i = 0; i ^ l; i++) {
int c = s[i] - 'a', p = last;
while (s[i] ^ s[i - nd[p].L - 1]) p = nd[p].fath;
if (!nd[p].tr[c]) {
int cur = newnode(), q = nd[p].fath, r = half[p];
nd[cur].L = nd[p].L + 2;
while (s[i] ^ s[i - nd[q].L - 1]) q = nd[q].fath;
nd[cur].fath = nd[q].tr[c];
nd[p].tr[c] = cur;
if (nd[cur].L <= 2)
half[cur] = nd[cur].fath;
else {
while (s[i] ^ s[i - nd[r].L - 1] ||
(nd[r].L + 2 << 1) > nd[cur].L)
r = nd[r].fath;
half[cur] = nd[r].tr[c];
}
}
last = nd[p].tr[c];
}
return;
}
inline int solve() {
int t = 0;
for (int i = 2; i <= cnt; i++)
if (t < nd[i].L && nd[half[i]].L << 1 == nd[i].L &&
!(nd[half[i]].L & 1))
t = nd[i].L;
return t;
}
} pam;
signed main() {
cin.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false);
cin >> n >> s;
pam.init(), pam.extend(s);
cout << pam.solve() << endl;
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号