NIO(二):Channel通道
一.Channel概述
channel(通道):进行IO的连接通道,为NIO的几个核心(Buffer,selector,channel)之一,相比于IO的stream具有较高的性能。
IO |
单向传输 |
NIO |
异步双向传输 |
使用时需要和buffer(缓冲区一切使用),将数据暂存入Buffer中,通过channel通道连接传输buffer以此传输数据。

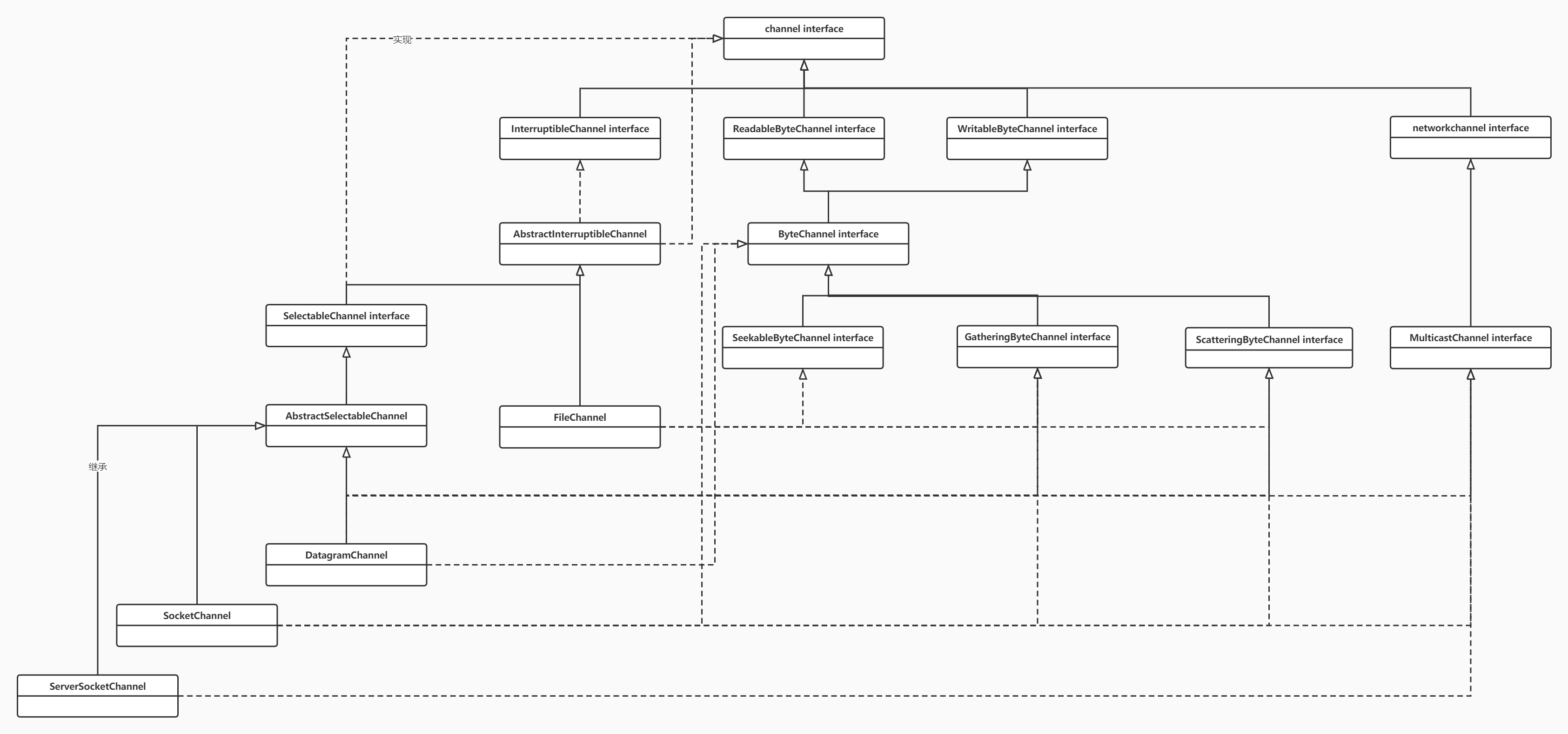
二.channel继承结构
其中主要的几个实现类如下:
-
FileChannel: 本地文件传输通道
-
SocketChannel: 通过TCP传输通道
-
ServerSocketChannel: 监听新的TCP连接,并创建一个新的SocketChannel,通过.open()方法进行创建。
-
DatagramChannel: 发送和接收UDP数据包的channel
通过Buffer的两种传输数据方式:
-
非直接缓冲区传输数据 - - > ByteBuffer.allocate()方法;
-
直接缓冲区传输数据 - - > ByteBuffer.allocateDriect()方法;
几种获取channel的方式:
-
本地通过FileInPutStream/FileOutPutStream 使用getChannel()方法获取;
-
本地FileChannel 的open()方法获取;
-
本地RandomAccessFile的getChannel()方法获取;
-
网络socket、ServerSocket、DatagramSocket
三.FileInputStream获取通道方式
非直接缓冲区方式,再程序与本地磁盘中,并不是直接进行数据的交流。而是在用户和内核之间通过复制的形式。每次read 和write 都在中间进行复制。程序可以控制数据。
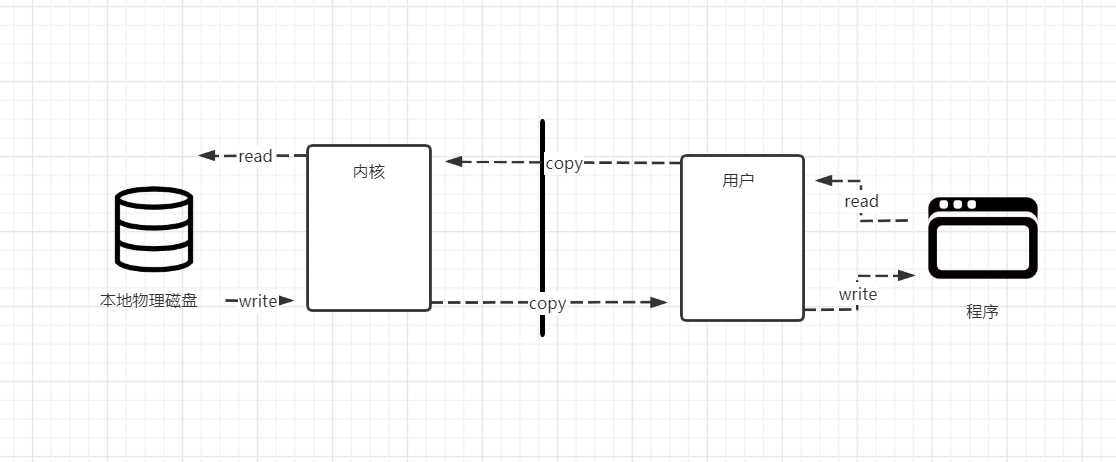
流程:FileInputStream写入文件 --> FileOutputStream的getChannel()获取通道 --> 开辟一个具有一定容量的buffer缓冲区 --> 将缓冲区的内容通过channel传输 --> 关闭流
1 //使用非直接缓冲区 传输数据 2 //通过流的方式 3 @Test 4 public void NoDirect(){ 5 6 FileInputStream fileInputStream = null; 7 FileOutputStream fileOutputStream =null; 8 FileChannel fileInputStreamChannel = null; 9 FileChannel fileOutputStreamChannel = null; 10 long start = 0; 11 12 try { 13 //查看耗时 14 start = System.currentTimeMillis(); 15 16 //写入 17 fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("D:/DataTestFile/1.zip"); 18 //读取到 19 fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("D:/DataTestFile/2.zip"); 20 21 //使用通道进行文件传输 22 //在传输前先获取传输通道channel 23 fileInputStreamChannel = fileInputStream.getChannel(); 24 fileOutputStreamChannel = fileOutputStream.getChannel(); 25 26 //将数据写入缓冲区 --> 开辟缓冲区容量 --> 后使用通道传输 27 ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); 28 29 //将通道中的数据送入缓冲区 数据为空时跳出循环 30 while(fileInputStreamChannel.read(buf) != -1){ 31 //切换读写模式 32 buf.flip(); 33 //读出缓冲区的数据写入通道中 34 fileOutputStreamChannel.write(buf); 35 //清空缓冲区 36 buf.clear(); 37 } 38 39 40 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 41 e.printStackTrace(); 42 } catch (IOException e) { 43 e.printStackTrace(); 44 } 45 //最终需要执行的步骤 需要关闭流 和通道 46 finally { 47 //写入流关闭 48 if (fileInputStream != null){ 49 try { 50 fileInputStream.close(); 51 } catch (IOException e) { 52 e.printStackTrace(); 53 } 54 } 55 //读出流关闭 56 if (fileOutputStream != null){ 57 try { 58 fileOutputStream.close(); 59 } catch (IOException e) { 60 e.printStackTrace(); 61 } 62 } 63 if (fileInputStreamChannel != null){ 64 try { 65 fileInputStreamChannel.close(); 66 } catch (IOException e) { 67 e.printStackTrace(); 68 } 69 } 70 //读出通道关闭 71 if (fileOutputStreamChannel != null){ 72 try { 73 fileOutputStreamChannel.close(); 74 } catch (IOException e) { 75 e.printStackTrace(); 76 } 77 } 78 //查看耗时 79 long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); 80 System.out.println("总共耗时:"+(end-start)); 81 } 82 83 84 }
测试数据大小
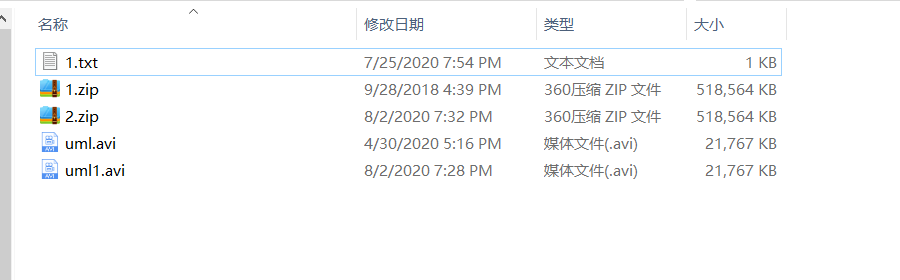
使用IO流的方式(FileInPutStream/FileOutPutStream)写入文件或者读取文件,FileInPutStream实现方式:(FileOutPutStream 与之类似)
1 public FileInputStream(String name) throws FileNotFoundException { 2 this(name != null ? new File(name) : null); 3 } 4 5 6 7 8
//获取本地文件 9 public File(String pathname) { 10 if (pathname == null) { 11 throw new NullPointerException(); 12 } 13 this.path = fs.normalize(pathname); 14 this.prefixLength = fs.prefixLength(this.path); 15 }
三.FileChannel方式+mapped*ByteBuffer(内存映射文件)传输数据
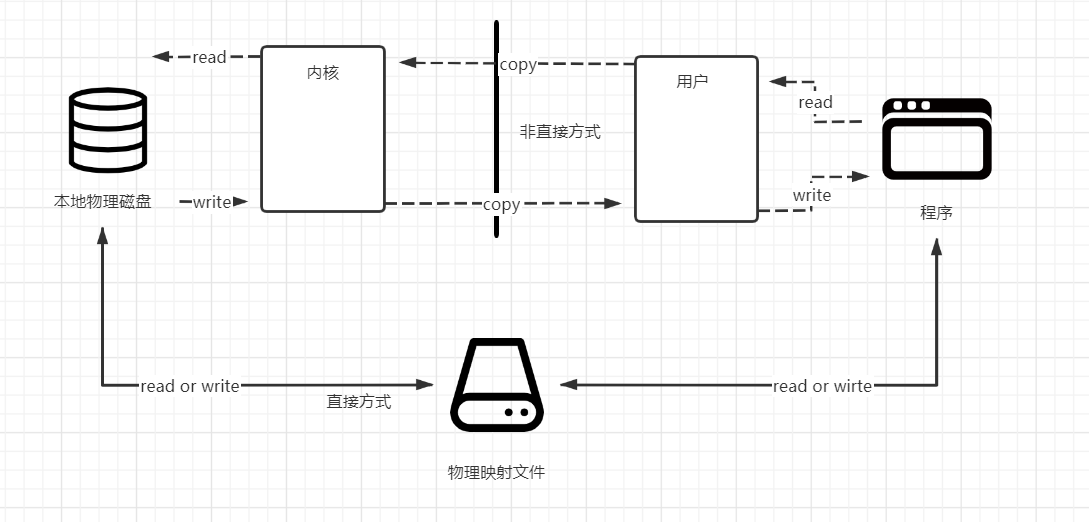
直接传输方式,在本地形成一个本地映射文件,程序通过本地映射直接传输给物理磁盘,没有复制的操作。在传输速度上优于非直接的传输
但是程序的数据一旦交给映射文件,程序将无法控制数据。
流程: FileChannel.open 获取通道 (写入和读取文件,并规定Read Or Write ,create等方式) - - > .map(将通道的一个区域映射到内存中) - - > 将映射文件中的数据存入数组,写入或读出到MappedByteBuffer
1 /* 2 * 通过直接缓冲区的方式进行传输数据 3 * 通过使用映射文件的方式MappedByteBuffer传输 4 * */ 5 @Test 6 public void Driect(){ 7 8 FileChannel fileInChannel = null; 9 FileChannel fileOutChannel = null; 10 MappedByteBuffer mappedInByteBuffer = null; 11 MappedByteBuffer mappedOutByteBuffer = null; 12 long start = 0; 13 14 try { 15 //耗时查询 16 start = System.currentTimeMillis(); 17 18 fileInChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("D:/DataTestFile/1.zip"), StandardOpenOption.READ,StandardOpenOption.WRITE); 19 fileOutChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("D:/DataTestFile/2.zip"), StandardOpenOption.READ, StandardOpenOption.WRITE,StandardOpenOption.CREATE); 20 21 //使用内存映射文件 ,杜绝非直接缓存区中的通过用户态 和核心态的相互复制影响性能的问题 22 //直接通过本地映射文件。但是一旦传输后,不归程序所管理 23 mappedInByteBuffer = fileInChannel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_ONLY, 0, fileInChannel.size()); 24 mappedOutByteBuffer = fileOutChannel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, fileInChannel.size()); 25 26 //直接对缓冲区进行读写操作 27 //定义一个数组,将映射文件的数据存入其中 28 byte[] bt = new byte[mappedInByteBuffer.limit()]; 29 //先从本地映射文件中读取 后写入传输 30 mappedInByteBuffer.get(bt); 31 mappedOutByteBuffer.put(bt); 32 33 34 } catch (IOException e) { 35 e.printStackTrace(); 36 } 37 finally { 38 if (fileInChannel != null){ 39 try { 40 fileInChannel.close(); 41 } catch (IOException e) { 42 e.printStackTrace(); 43 } 44 } 45 if (fileOutChannel != null){ 46 try { 47 fileOutChannel.close(); 48 } catch (IOException e) { 49 e.printStackTrace(); 50 } 51 } 52 53 //耗时结束查询 54 long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); 55 System.out.println("总共耗时:"+(end-start)); 56 57 }

相比较于非直接的方式,在相同资源下的第一次传输,性能更高。传输速度更快。
五.分散传输
将一个整体文件,分散成多个部分,使用多缓冲区分别进行分散。
流程:使用RandomAccessFile读取写入文件 - - > 通过RandomAccessFile.getChannel 获取通道 - - > 将两个开辟的缓冲区,存入数组中,并循环读入通道 - - > 转换成可以直观查看的String类型
1 package com.cllover.nio; 2 3 import org.junit.Test; 4 5 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 6 import java.io.IOException; 7 import java.io.RandomAccessFile; 8 import java.nio.ByteBuffer; 9 import java.nio.channels.FileChannel; 10 11 /* 12 * @Author chengpunan 13 * @Description //TODO 18609 14 * @Date 7:29 PM 7/25/2020 15 * @Param 16 * @return 17 * 18 * 分散读写和聚集读写测试类 19 * Disperse:分散读写 20 * gather: 聚集读写 21 **/ 22 public class DisperseAndGather { 23 24 // 分散读写 将通道中的数据分散到缓冲区中, 25 @Test 26 public void Disperse(){ 27 RandomAccessFile randomAccessFile = null; 28 FileChannel randomAccessFileChannel = null; 29 30 try { 31 //随机访问文件流以RW形式访问某文件 32 randomAccessFile = new RandomAccessFile("D:/DataTestFile/1.txt","rw"); 33 34 //获取通道 35 randomAccessFileChannel = randomAccessFile.getChannel(); 36 37 //开辟两个缓冲区 38 ByteBuffer byteBuffer100 = ByteBuffer.allocate(100); 39 ByteBuffer byteBuffer200 = ByteBuffer.allocate(200); 40
//数值初始化:存入两个缓冲区的数据
41 //分散读取 42 ByteBuffer[] byteBuffer = {byteBuffer100,byteBuffer200}; 43 44 //存入读取通道 45 randomAccessFileChannel.read(byteBuffer); 46 47 for (ByteBuffer bf: byteBuffer) { 48 bf.flip(); //切换读写方式 49 } 50 //转换成字符串 51 //public String(byte bytes[], int offset, int length) 52 System.out.println(new String(byteBuffer[0].array(),0,byteBuffer[0].limit())); 53 System.out.println("----------------------------------"); 54 System.out.println(new String(byteBuffer[1].array(),0,byteBuffer[1].limit())); 55 56 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 57 e.printStackTrace(); 58 } catch (IOException e) { 59 e.printStackTrace(); 60 } 61 finally { 62 if (randomAccessFile != null){ 63 try { 64 randomAccessFile.close(); 65 } catch (IOException e) { 66 e.printStackTrace(); 67 } 68 } 69 if (randomAccessFileChannel != null){ 70 try { 71 randomAccessFileChannel.close(); 72 } catch (IOException e) { 73 e.printStackTrace(); 74 } 75 } 76 if (randomAccessFile != null){ 77 try { 78 randomAccessFile.close(); 79 } catch (IOException e) { 80 e.printStackTrace(); 81 } 82 } 83 } 84 85 } 86 87 }
将单独两个开辟的缓冲区,存入数组之中。存入通道后,用foreach循环遍历index[0]和index[1]缓冲区上的内容,并进行写入。
1 //分散读取:数组初始化 2 ByteBuffer[] byteBuffer = {byteBuffer100,byteBuffer200}; 3 4 //存入读取通道 5 randomAccessFileChannel.read(byteBuffer); 6 7 for (ByteBuffer bf: byteBuffer) { 8 bf.flip(); //切换读写方式 9 }
资源内容:

运行结果:
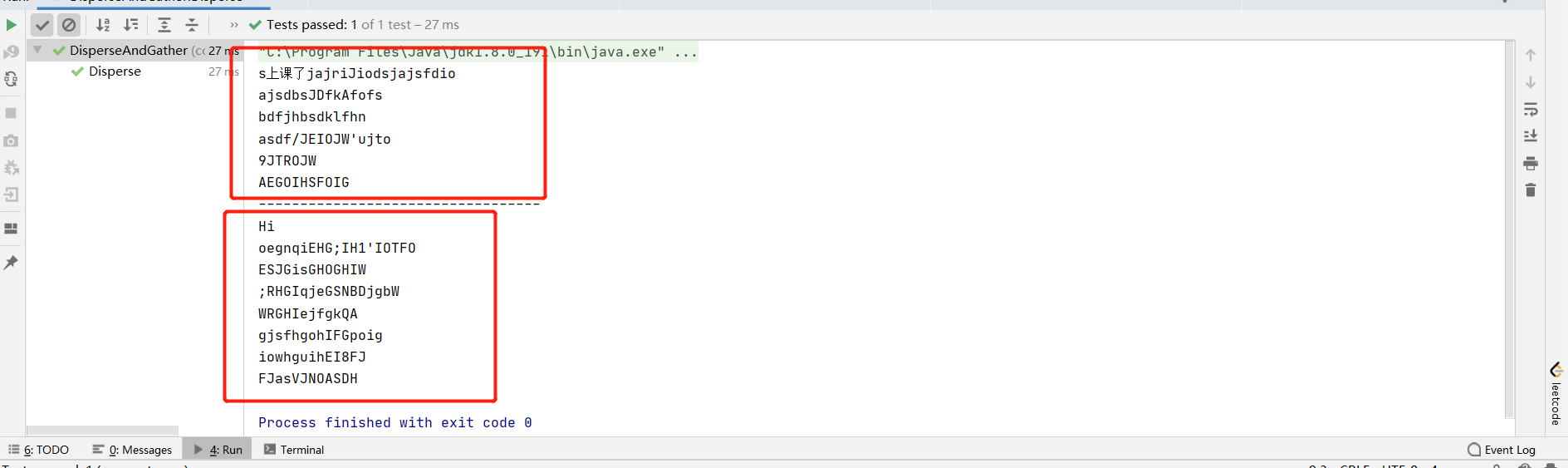
聚集写入:
1 //聚集写入 2 RandomAccessFile randomAccessFile1 = new RandomAccessFile("D:/DataTestFile/2.txt", "rw"); 3 FileChannel channel = randomAccessFile1.getChannel(); 4 //将全部内容。将上段代码红色部分,存入数组中的数据直接通过通道写入另一个文件中 5 channel.write(byteBuffer);
写入文件后,原本文件中的内容会被覆盖或者丢失。
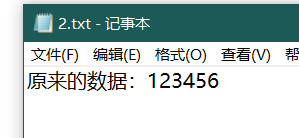
写入后:

六.总结
channel作为一个连接通道,支持异步传输。
总是基于Buffer缓冲区配合使用。
在传输时,需要在buffer中暂存入数据后开启channel通道,进行读写操作。
下一篇将会写关于网络传输 和 selector的用法。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号