BigInteger
平时在存储整数的时候, Java 中默认是 int 类型, int 类型有取值范围: -2147483648 ~ 2147483647. 如果数字过大, 我们可以使用 long 类型, 但是如果 long 类型也表示不下怎么办呢?
long 类型最大可以存储的数字 (二进制形式):
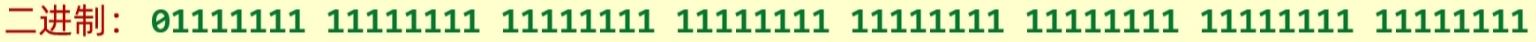
转为十进制形式为:

就需要用到 BigInteger, 可以理解为非常非常大的整数.
有多大呢? 理论上最大到 42 亿的 21 亿次方, 基本上在内存撑爆之前, 都无法达到这个上限.
BigInteger 能表示的范围很大, 从很小的数字如 1, 2, -1, -2, 到很大很大的数字, 只要是整数, 都可以表示.
BigInteger 类的常用的成员方法:

获取 BigInteger 的对象有四种方法, 其中前三种为构造方法:

public BigInteger(int num, Random rnd) // 获取随机大整数, 范围: [0 ~ 2 的 num 次方 -1]
public BigInteger(String val) // 获取指定的大整数, 字符串里面必须是整数, 不能是小数或者 a b 等字母
public BigInteger(String val, int radix) // 获取指定进制的大整数
public static BigInteger valueOf(long val) // 静态方法获取 BigInteger 的对象, 内部有优化
BigInteger 对象一旦创建, 内部记录的值是不能发生改变的.
程序示例:
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. 获取一个随机的大整数
Random r = new Random();
BigInteger bd1 = new BigInteger(4, r);
System.out.println(bd1); // [0 ~ 15]
}
}
程序示例:
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 2. 获取一个指定的大整数, 可以超出 long 的取值范围
// 细节: 字符串中必须是整数, 否则会报错
// BigInteger bd2 = new BigInteger("1.1"); // NumberFormatException: For input string: "1.1"
// System.out.println(bd2);
// BigInteger bd3 = new BigInteger("abc"); // NumberFormatException: For input string: "abc"
// System.out.println(bd3);
}
}
程序示例:
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 3. 获取指定进制的大整数
// 细节:
// 1. 字符串中的数字必须是整数
// 2. 字符串中的数字必须要跟进制吻合.
// 比如二进制中, 那么只能写 0 和 1, 写其他的就报错.
BigInteger bd1 = new BigInteger("100", 10);
System.out.println(bd1); // 100
BigInteger bd2 = new BigInteger("100", 2);
System.out.println(bd2); // 4
// BigInteger bd4 = new BigInteger("123", 2); // NumberFormatException: For input string: "123" under radix 2
// System.out.println(bd4);
}
}
valueOf() 方法只能接受 long 类型的参数, 参数范围超过了 long 的话, 方法无法接受, 就报错了.
程序示例:
import java.math.BigInteger;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 4. 静态方法获取 BigInteger 的对象, 内部有优化
// 细节:
// 1. 能表示范围比较小, 只能在 long 的取值范围之内, 如果超出 long 的范围就不行了.
BigInteger bd1 = BigInteger.valueOf(100);
System.out.println(bd1); // 100
// BigInteger bd2 = BigInteger.valueOf(10000000000000000000000000L); // Long number too large, java: 整数太大
// System.out.println(bd2);
}
}
程序示例:
import java.math.BigInteger;
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 4. 静态方法获取 BigInteger 的对象, 内部有优化.
// 细节:
// 2. 在内部对常用的数字: -16 ~ 16 进行了优化.
// 提前把 -16 ~ 16 先创建好 BigInteger 的对象, 如果多次获取不会重新创建新的.
BigInteger bd5 = BigInteger.valueOf(16);
BigInteger bd6 = BigInteger.valueOf(16);
System.out.println(bd5 == bd6); // true
BigInteger bd7 = BigInteger.valueOf(17);
BigInteger bd8 = BigInteger.valueOf(17);
System.out.println(bd7 == bd8); // false
}
}
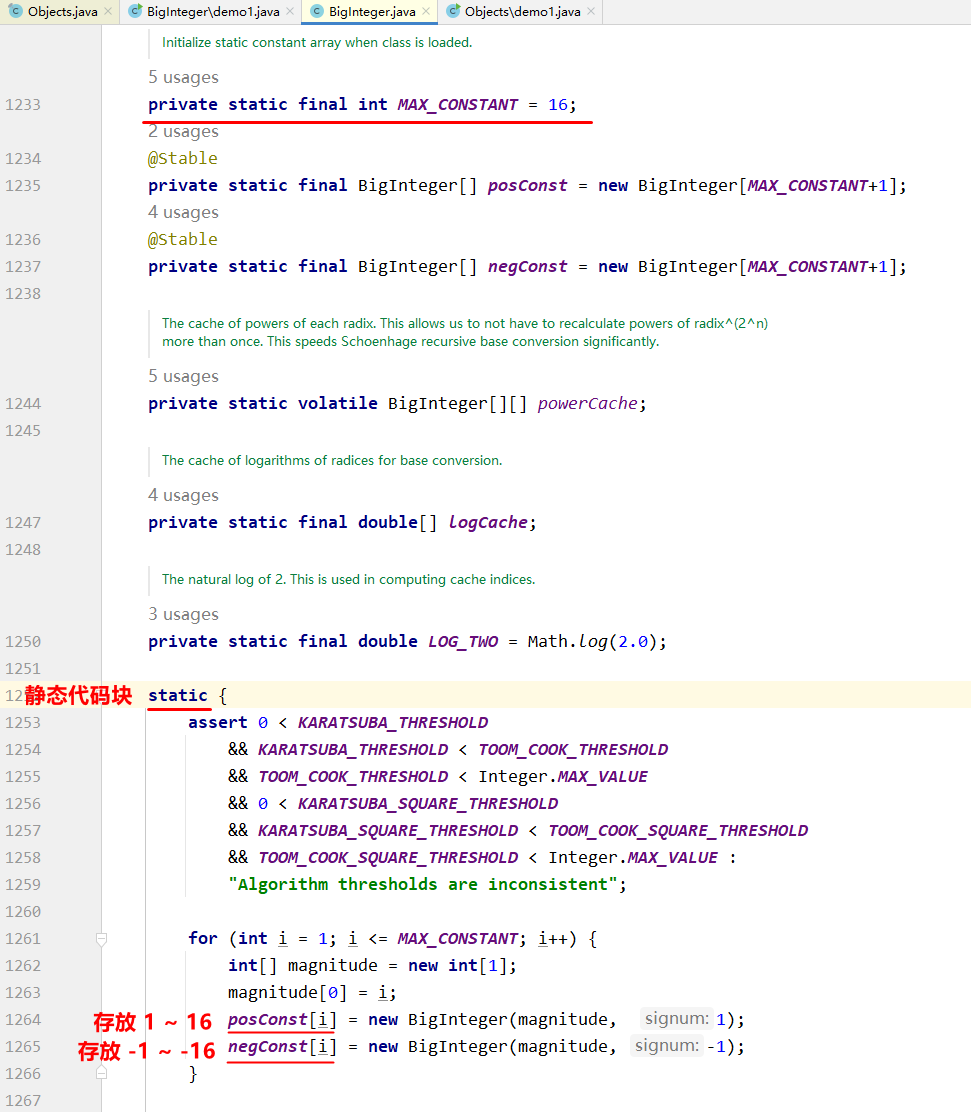
查看 BigInteger 的源码:
存储 -16 ~ 16 这些 BigInteger 对象的方式:
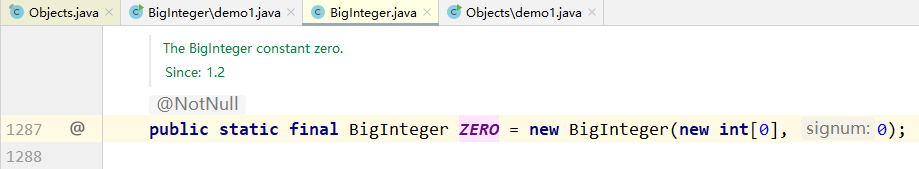
0 这个 BigInteger 对象:
valueOf() 方法:

程序示例:
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 5. 对象一旦创建内部的数据不能发生改变
BigInteger bd9 = BigInteger.valueOf(1);
BigInteger bd10 = BigInteger.valueOf(2);
// 此时, 不会修改参与计算的 BigInteger 对象中的值, 而是产生了一个新的 BigInteger 对象记录结果 3
BigInteger result = bd9.add(bd10);
System.out.println(result); // 3
System.out.println(bd9 == result); // false
System.out.println(bd10 == result); // false
}
}
BigInteger 类的常见的成员方法:

程序示例:
import java.math.BigInteger;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
public BigInteger add(BigInteger val) 加法
public BigInteger subtract(BigInteger val) 减法
public BigInteger multiply(BigInteger val) 乘法
public BigInteger divide(BigInteger val) 除法, 获取商
public BigInteger[] divideAndRemainder(BigInteger val) 除法, 获取商和余数
public boolean equals(Object x) 比较是否相同
public BigInteger pow(int exponent) 次幂
public BigInteger max/min(BigInteger val) 返回较大值/较小值
public int intValue(BigInteger val) 转为int类型整数, 超出范围数据有误
*/
// 1. 创建两个 BigInteger 对象
BigInteger bd1 = BigInteger.valueOf(10);
BigInteger bd2 = BigInteger.valueOf(3);
System.out.println("---------------------------------");
// 2. 加法
BigInteger bd3 = bd1.add(bd2);
System.out.println(bd3); // 13
System.out.println("---------------------------------");
// 3. 除法, 获取商和余数
BigInteger[] arr = bd1.divideAndRemainder(bd2);
System.out.println(arr.length); // 2
System.out.println(arr[0]); // 3
System.out.println(arr[1]); // 1
System.out.println("---------------------------------");
// 4. 比较是否相同
BigInteger bd4 = BigInteger.valueOf(10);
BigInteger bd5 = BigInteger.valueOf(10);
boolean equal1 = bd4.equals(bd5);
System.out.println(equal1); // true
BigInteger bd6 = BigInteger.valueOf(10);
BigInteger bd7 = BigInteger.valueOf(1);
boolean equal2 = bd6.equals(bd7);
System.out.println(equal2); // false
System.out.println("---------------------------------");
// 5. 次幂
BigInteger bd8 = bd1.pow(2);
System.out.println(bd8); // 100
System.out.println("---------------------------------");
// 6. max
BigInteger bd9 = bd1.max(bd2);
System.out.println(bd9); // 10
System.out.println(bd9 == bd1); // true
System.out.println(bd9 == bd2); // false
// 说明没有创建新的 BigInteger 对象, 而是返回了比较大的那个值
System.out.println("---------------------------------");
// 7. 转为 int 类型整数, 超出范围数据有误
BigInteger bd10 = BigInteger.valueOf(2147483647L);
int i1 = bd10.intValue();
System.out.println(i1); // 2147483647
BigInteger bd11 = BigInteger.valueOf(2147483648L);
int i2 = bd11.intValue();
System.out.println(i2); // -2147483648, 出错了
BigInteger bd12 = BigInteger.valueOf(200);
double v = bd12.doubleValue();
System.out.println(v); // 200.0
// 还有 longValue(), floatValue() 等方法
}
}
BigInteger 底层存储方式:
对于计算机而言, 其实是没有数据类型的概念的, 都是 0101010101.
数据类型是编程语言自己规定的.
这是一个超过 long 类型的数字以及它的二进制补码:

进入 BigInteger 的源码:
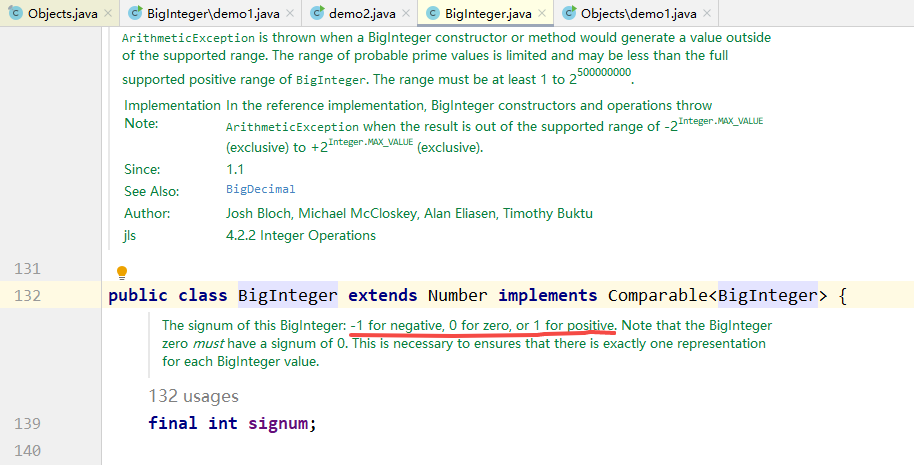
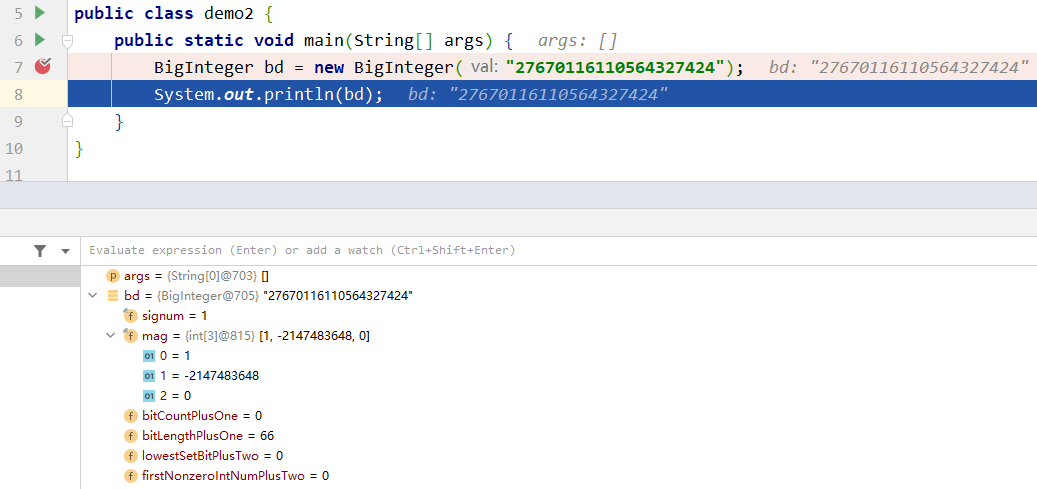
signum 成员变量表示 BigInteger 表示的数字的符号, 若 signum 是 -1, 则表示数字为负数, 若 signum 是 0, 则表示这个数字是 0, 若 sugnum 是 1, 则表示这个数字是正数.
mag 这个数组存储的就是数据, 由于数据很大, 所以将其拆分, 将一个很大的数拆成很多个小段, 每一个小段都会放到一个数组当中.
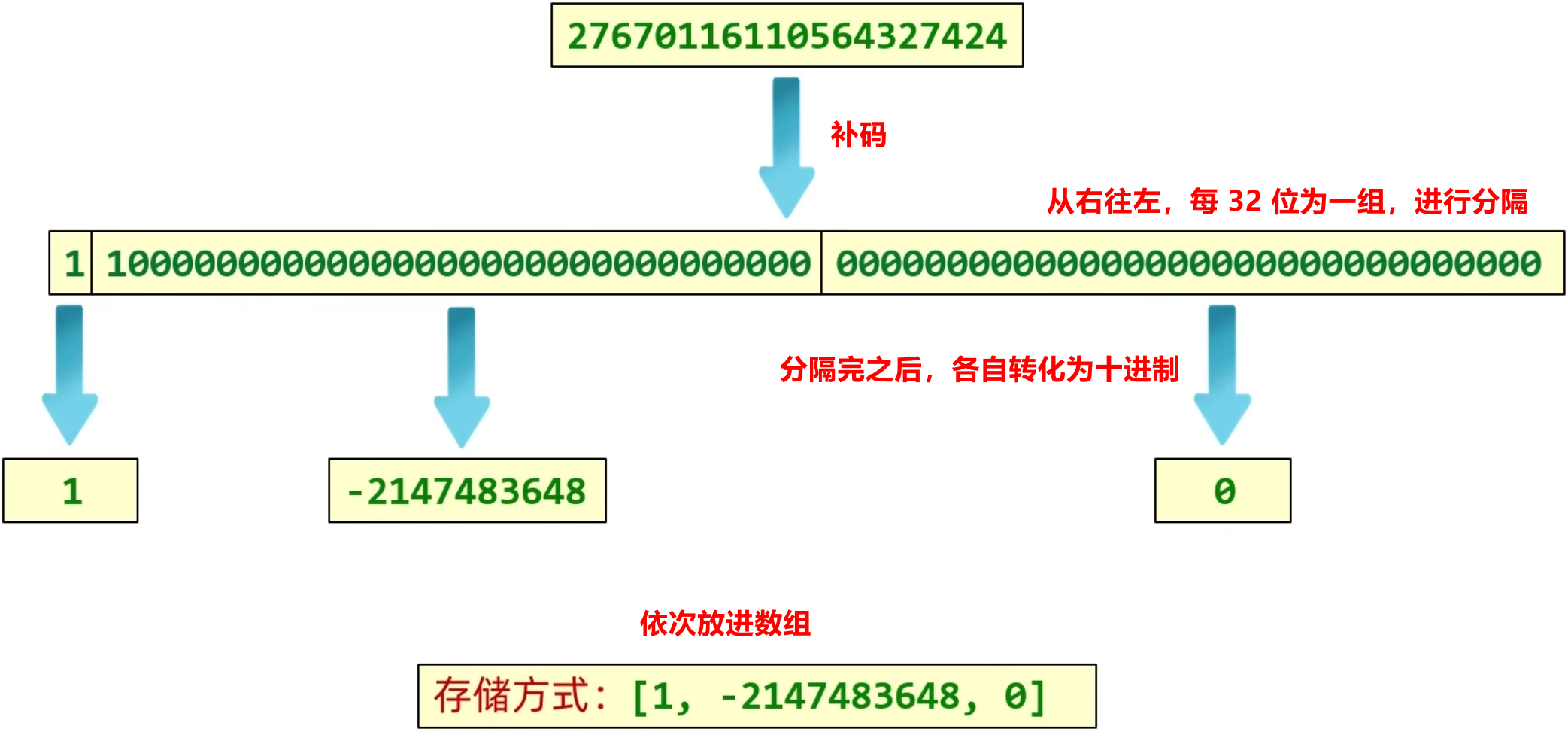
signum 和 mag 两种方式相结合, 就能表示大数字.
通过打断点的方式查看 BigInteger 对象:
Java 中, 数组是有最大长度的, 数组的最大长度是 int 的最大值: 2147483647.
在真实情况下, 电脑的内存一般是扛不住这么大的数组的, 即电脑的内存无法创建这么大的数组.
在此处, mag 数组是 int 类型的. 因此, 数组中每一位能表示的数字: -2147483648 ~ 2147483647
于是可以说,
数组中最多能存储元素个数: 21 亿多
数组中每一位能表示的数字个数: 42 亿多
因此, BigInteger 能表示的最大数字为: 42 亿的 21 亿次方
实际中绝大部分电脑都没有这么大的内存, 因此可以认为 BigInteger 类型的数字是无穷大的.


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号