异常
异常就是程序出现的问题.
Java 中有很多异常, 这些异常组成了 Java 的异常体系.
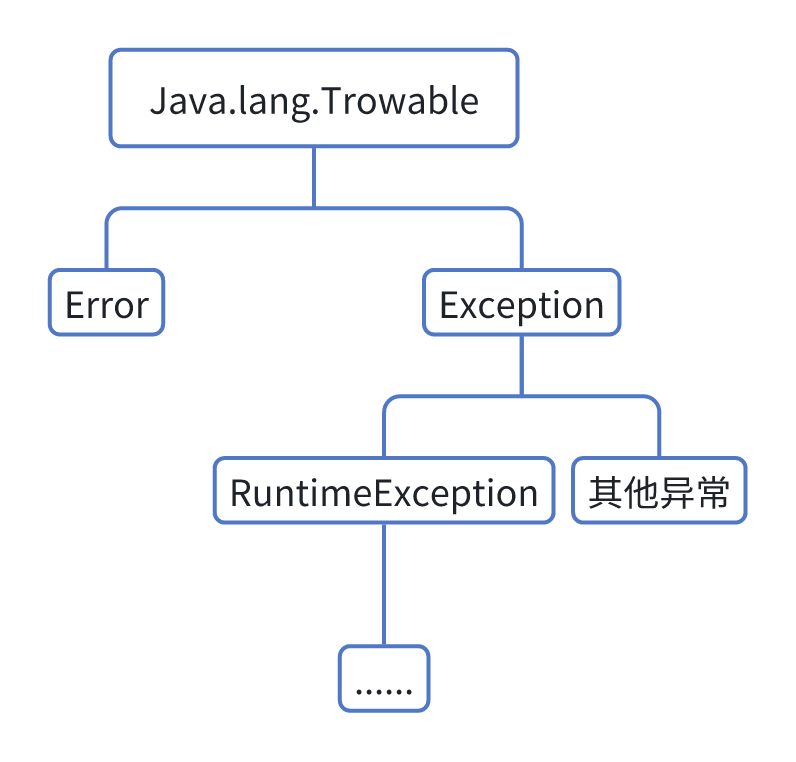
Error: 代表的系统级别错误 (属于严重问题), 系统一旦出现问题, Sun 公司会把这些错误封装成 Error 对象. Error 是给 Sun 公司自己用的, 不是给我们程序员用的, 因此我们开发人员不用管它.
Exception: 叫做异常, 代表程序可能出现的问题. 我们通常会用 Exception 以及他的子类来封装程序出现的问题.
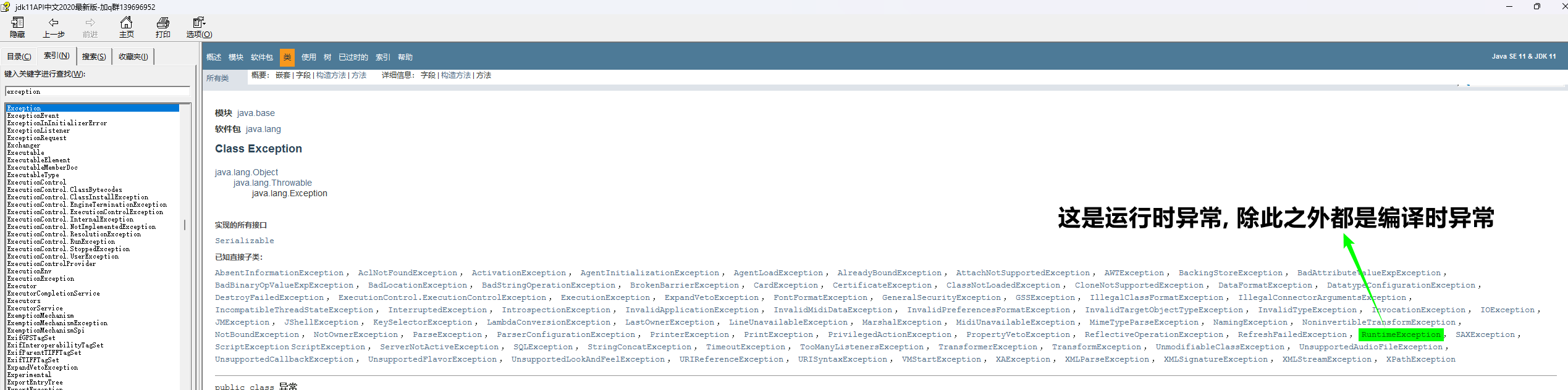
运行时异常: RuntimeException 及其子类, 编译阶段不会出现异常提醒. 是运行时出现的异常 (如: 数组索引越界异常).
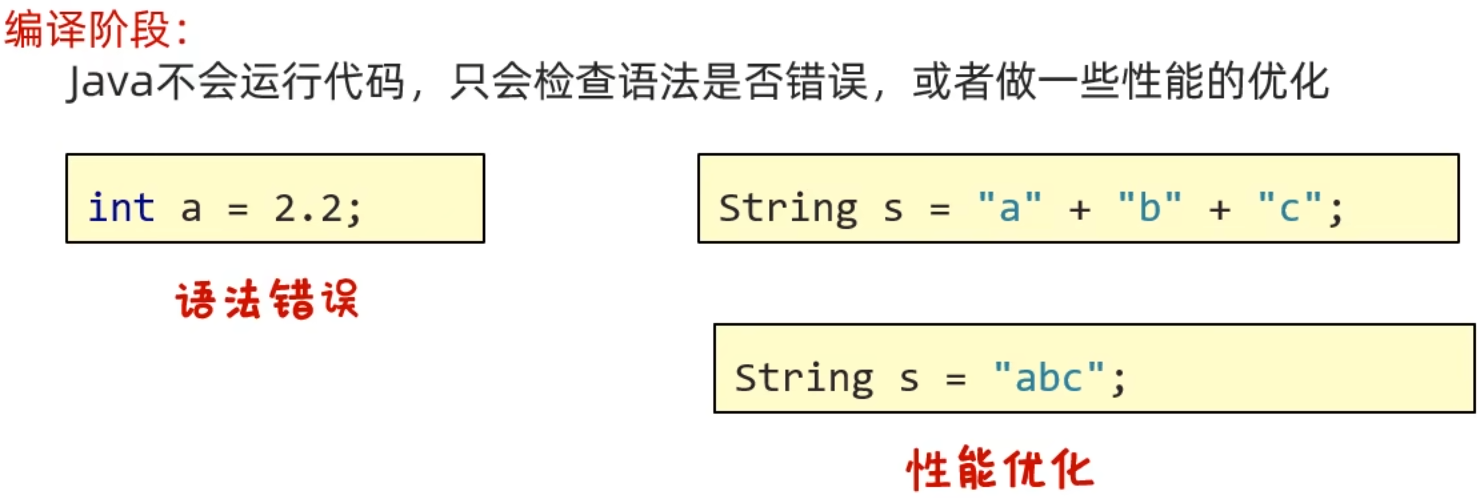
编译时异常: 编译阶段就会出现异常提醒的 (如: 日期解析异常)

编译时异常的目的是提醒程序员检查本地信息.
程序示例:
import java.text.ParseException;
public class ExceptionDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
// 编译时异常(在编译阶段,必须要手动处理,否则代码报错)
/*String time = "2030年1月1日";
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日");
Date date = sdf.parse(time);
System.out.println(date);*/
// 运行时异常(在编译阶段是不需要处理的,是代码运行时出现的异常)
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
System.out.println(arr[10]);// ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
}
}
运行时异常就是代码出错而导致的问题.
异常的作用
作用一: 异常是用来查询 bug 的关键参考信息
作用二: 异常可以作为方法内部的一种特殊返回值, 以便通知调用者底层的执行情况
程序示例:
public class ExceptionDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
异常作用一:异常是用来查询bug的关键参考信息
异常作用二:异常可以作为方法内部的一种特殊返回值,以便通知调用者底层的执行情况
*/
Student[] arr = new Student[3];// null null null
String name = arr[0].getName();
System.out.println(name);
}
}
程序示例:
public class ExceptionDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
异常作用一:异常是用来查询bug的关键参考信息
异常作用二:异常可以作为方法内部的一种特殊返回值,以便通知调用者底层的执行情况
*/
Student2 stu = new Student2("张三,23");
System.out.println(stu);
}
}
public class Student2 {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student2() {
}
public Student2(String str) {//"张三,23"
String[] arr = str.split("-");
//arr 0: 张三,23
this.name = arr[0];
this.age = Integer.parseInt(arr[1]);
}
public Student2(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
/**
* 获取
* @return name
*/
public String getName() {
return name;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param name
*/
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
/**
* 获取
* @return age
*/
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param age
*/
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String toString() {
return "Student2{name = " + name + ", age = " + age + "}";
}
}
程序示例:
public class ExceptionDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
异常作用一:异常是用来查询bug的关键参考信息
异常作用二:异常可以作为方法内部的一种特殊返回值,以便通知调用者底层的执行情况
*/
// 1.创建学生对象
Student s1 = new Student();
// 年龄:(同学) 18~40岁
s1.setAge(50);// 就知道了50赋值失败
// 选择1:自己悄悄处理
// 选择2:打印在控制台上
}
}
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
/**
* 获取
* @return name
*/
public String getName() {
return name;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param name
*/
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
/**
* 获取
* @return age
*/
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param age
*/
public void setAge(int age) {
if(age < 18 || age > 40){
//System.out.println("年龄超出范围");
throw new RuntimeException();
}else{
this.age = age;
}
}
public String toString() {
return "Student{name = " + name + ", age = " + age + "}";
}
}
异常的处理方式:
程序示例:
public class ExceptionDemo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
JVM默认处理异常的方式:
1. 把异常的名称,异常原因及异常出现的位置等信息输出在了控制台
2. 程序停止执行,异常下面的代码不会再执行了
*/
System.out.println("狂踹瘸子那条好腿");
System.out.println(2 / 0);// 算术异常 ArithmeticException
System.out.println("是秃子终会发光");
System.out.println("火鸡味锅巴");
}
}

目的: 当代码出现异常时, 可以让程序继续往下执行.
程序示例:
public class ExceptionDemo6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
自己处理(捕获异常)
格式:
try {
可能出现异常的代码;
} catch(异常类名 变量名) {
异常的处理代码;
}
好处:可以让程序继续往下执行,不会停止
*/
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};
try {
// 可能出现异常的代码;
System.out.println(arr[10]);// 此处出现了异常,程序就会在这里创建一个ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException对象
// new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
// 拿着这个对象到catch的小括号中对比,看括号中的变量是否可以接收这个对象
// 如果能被接收,就表示该异常就被捕获(抓住),执行catch里面对应的代码
// 当catch里面所有的代码执行完毕,继续执行try...catch体系下面的其他代码
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
// 如果出现了ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException异常,我该如何处理
System.out.println("索引越界了");
}
System.out.println("看看我执行了吗?");
}
}
程序示例:
public class ExceptionDemo7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
自己处理(捕获异常)灵魂四问:
灵魂一问:如果try中没有遇到问题,怎么执行?
会把try里面所有的代码全部执行完毕,不会执行catch里面的代码
注意:
只有当出现了异常才会执行catch里面的代码
*/
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};
try {
System.out.println(arr[0]);// 1
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("索引越界了");
}
System.out.println("看看我执行了吗?");// 看看我执行了吗?
}
}
程序示例:
public class ExceptionDemo8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
自己处理(捕获异常)灵魂四问:
灵魂二问:如果try中可能会遇到多个问题,怎么执行?
会写多个catch与之对应
细节:
如果我们要捕获多个异常,这些异常中如果存在父子关系的话,那么父类一定要写在下面
了解性:
在JDK7之后,我们可以在catch中同时捕获多个异常,中间用|进行隔开
表示如果出现了A异常或者B异常的话,采取同一种处理方案
*/
// JDK7
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};
try {
System.out.println(arr[10]);// ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
System.out.println(2 / 0);// ArithmeticException
String s = null;
System.out.println(s.equals("abc"));
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException | ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("索引越界了");
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
System.out.println("空指针异常");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Exception");
}
System.out.println("看看我执行了吗?");
}
}
程序示例:
public class ExceptionDemo9 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
自己处理(捕获异常)灵魂三问:
如果try中遇到的问题没有被捕获,怎么执行?
相当于try...catch的代码白写了,最终还是会交给虚拟机进行处理。
*/
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};
try {
System.out.println(arr[10]);// new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
System.out.println("空指针异常");
}
System.out.println("看看我执行了吗?");
}
}
程序示例:
public class ExceptionDemo10 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
自己处理(捕获异常)灵魂四问:
如果try中遇到了问题,那么try下面的其他代码还会执行吗?
下面的代码就不会执行了,直接跳转到对应的catch当中,执行catch里面的语句体
但是如果没有对应catch与之匹配,那么还是会交给虚拟机进行处理
*/
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};
try {
System.out.println(arr[10]);
System.out.println("看看我执行了吗?... try");
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("索引越界了");
}
System.out.println("看看我执行了吗?... 其他代码");
}
}
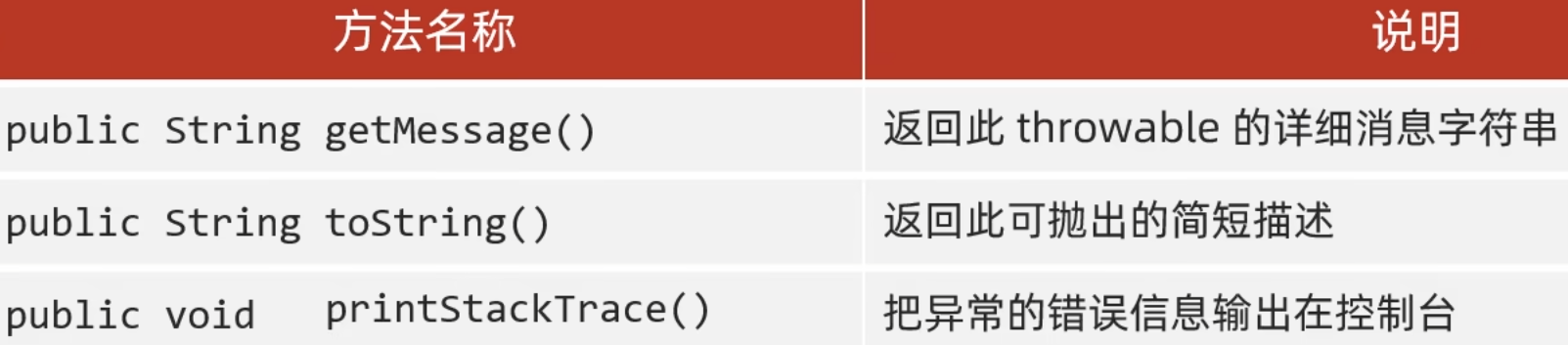
Throwable 的成员方法
程序示例:
public class ExceptionDemo11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
public String getMessage() 返回此 throwable 的详细消息字符串
public String toString() 返回此可抛出的简短描述
public void printStackTrace() 在底层是利用System.err.println进行输出
把异常的错误信息以红色字体输出在控制台
细节:仅仅是打印信息,不会停止程序运行
*/
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};
/*
try {
System.out.println(arr[10]);
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
*//* String message = e.getMessage();
System.out.println(message);//Index 10 out of bounds for length 6*//*
*//* String str = e.toString();
System.out.println(str);//java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: Index 10 out of bounds for length 6*//*
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("看看我执行了吗?");*/
// 正常的输出语句
// System.out.println(123);
// 错误的输出语句(而是用来打印错误信息)
// System.err.println(123);
}
}
抛出异常

程序示例:
public class ExceptionDemo12 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
throws:写在方法定义处,表示声明一个异常。告诉调用者,使用本方法可能会有哪些异常。
throw :写在方法内,结束方法。手动抛出异常对象,交给调用者。方法中下面的代码不再执行了。
需求:
定义一个方法求数组的最大值
*/
int[] arr = null;
int max = 0;
try {
max = getMax(arr);
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
System.out.println("空指针异常");
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("索引越界异常");
}
System.out.println(max);
}
public static int getMax(int[] arr)/* throws NullPointerException,ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException*/ {
if (arr == null) {
// 手动创建一个异常对象,并把这个异常交给方法的调用者处理
// 此时方法就会结束,下面的代码不会再执行了
throw new NullPointerException();
}
if (arr.length == 0) {
// 手动创建一个异常对象,并把这个异常交给方法的调用者处理
// 此时方法就会结束,下面的代码不会再执行了
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
System.out.println("看看我执行了吗?");
int max = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] > max) {
max = arr[i];
}
}
return max;
}
}
自定义异常

程序示例:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
需求:
键盘录入自己心仪的女朋友姓名和年龄。
姓名的长度在 3 - 10之间,
年龄的范围为 18 - 40岁,
超出这个范围是异常数据不能赋值,需要重新录入,一直录到正确为止。
提示:
需要考虑用户在键盘录入时的所有情况。
比如:录入年龄时超出范围,录入年龄时录入了abc等情况
*/
// 1.创建键盘录入的对象
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
// 2.创建女朋友的对象
GirlFriend gf = new GirlFriend();
while (true) {
// 3.接收女朋友的姓名
try {
System.out.println("请输入你心仪的女朋友的名字");
String name = sc.nextLine();
gf.setName(name);
// 4.接收女朋友的年龄
System.out.println("请输入你心仪的女朋友的年龄");
String ageStr = sc.nextLine();
int age = Integer.parseInt(ageStr);
gf.setAge(age);
// 如果所有的数据都是正确的,那么跳出循环
break;
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NameFormatException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (AgeOutOfBoundsException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 5.打印
System.out.println(gf);
}
}
public class GirlFriend {
private String name;
private int age;
public GirlFriend() {
}
public GirlFriend(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
/**
* 获取
* @return name
*/
public String getName() {
return name;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param name
*/
public void setName(String name) {
int len = name.length();
if (len < 3 || len > 10) {
throw new NameFormatException(name + "格式有误,长度应该为:3~10");
}
this.name = name;
}
/**
* 获取
* @return age
*/
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param age
*/
public void setAge(int age) {
if (age < 18 || age > 40) {
throw new AgeOutOfBoundsException(age + "超出了范围");
}
this.age = age;
}
public String toString() {
return "GirlFriend{name = " + name + ", age = " + age + "}";
}
}
public class NameFormatException extends RuntimeException {
// 技巧:
// NameFormat:当前异常的名字,表示姓名格式化问题
// Exception:表示当前类是一个异常类
// 运行时:RuntimeException 核心 就表示由于参数错误而导致的问题
// 编译时:Exception 核心 提醒程序员检查本地信息
public NameFormatException() {
}
public NameFormatException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
public class AgeOutOfBoundsException extends RuntimeException {
public AgeOutOfBoundsException() {
}
public AgeOutOfBoundsException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号