使用PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager优化HTTP连接管理的技巧,HttpClient 5迁移
使用PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager优化HTTP连接管理的技巧
一、PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager简介
Apache HttpClient是Java开发者使用最广泛的HTTP客户端库之一。它提供各种功能,包括多线程比较容易的应用、请求连接自动管理、SSL安全连接、HTTP状态不正常解决、Cookies管理等。PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager是Apache HttpClient中的一个连接管理器,它提供了一个基于连接池技术的HTTP连接管理器。使用连接池技术是为了避免为每个请求都创建和销毁一个连接的开销,而是通过连接池维护一个可重复使用的连接池,大大提高了性能。
二、创建HttpClient对象
在使用PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager优化HTTP连接管理之前,我们需要先创建一个HttpClient对象。在创建HttpClient对象时,我们需要使用PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager作为HttpClient对象的连接管理器参数。
CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClients.custom()
.setConnectionManager(new PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager())
.build();上面的代码创建了一个基于连接池技术的连接管理器,然后通过setConnectionManager方法将其设置为HttpClient对象的连接管理器,并且通过build方法创建了一个CloseableHttpClient对象。
三、连接池管理参数的配置
与其它连接池一样,PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager也提供了一些参数,可以调整池实现的外观和行为,这些参数可以通过调用某些方法来设置。下面是几个常用的池参数的设置方法:
1.设置每个路由的最大连接数
每个路由的最大连接可以被设成一个单独的值,这种情况下,最大连接数量不会超过这个值,也不会超过PoolConcurrencyPolicy所设定的上限。可以通过setDefaultMaxPerRoute方法来设置:
PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager cm = new PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager();
// Increase max total connection to 200
cm.setMaxTotal(200);
// Increase default max connection per route to 20
cm.setDefaultMaxPerRoute(20);2.设置最大连接数
通过setMaxTotal方法来设置池的最大连接数量:
PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager cm = new PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager();
// Increase max total connection to 200
cm.setMaxTotal(200);3.设置请求超时时间
可以通过setConnectionRequestTimeout方法来设置请求连接超时时间:
PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager cm = new PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager();
// Increase max total connection to 200
cm.setMaxTotal(200);
// Set connection request timeout
cm.setConnectionRequestTimeout(5000);4.设置连接超时时间和读取超时时间
可以通过setConnectTimeout和setSocketTimeout方法设置连接超时时间和读取超时时间:
PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager cm = new PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager();
// Increase max total connection to 200
cm.setMaxTotal(200);
// Set connection timeout and socket timeout
cm.setConnectTimeout(5000);
cm.setSocketTimeout(10000);四、使用连接池
完成以上设置后,我们就可以利用PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager的连接池技术,来优化HTTP连接管理。下面是使用连接池的代码:
// Create a new HTTP GET request
HttpGet httpGet = new HttpGet("http://www.example.com");
// Create HttpClient with a connection pool manager
PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager cm = new PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager();
// Set the maximum number of total connections
cm.setMaxTotal(100);
// Create an HttpClient object
CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClients.custom()
.setConnectionManager(cm)
.build();
// Execute the request
CloseableHttpResponse response = httpClient.execute(httpGet);
// Do something with response
// Release the connection
response.close();五、结论
通过使用PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager优化HTTP连接管理,可以大大提高应用程序的性能。它采用连接池技术来维护一个可重复使用的连接池,避免为每个请求都创建和销毁一个连接的开销。在创建HttpClient对象时,需要使用PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager作为连接管理器参数。同时,也可以通过一些参数的设置,来调整连接池的行为。
Apache HttpClient5 RestTemplate 连接池_mob64ca140f67e3的技术博客_51CTO博客
一、背景
HTTP协议是无状态的协议,即每一次请求都是互相独立的。因此它的最初实现是,每一个http请求都会打开一个tcp socket连接,当交互完毕后会关闭这个连接。
HTTP协议是全双工的协议,所以建立连接与断开连接是要经过三次握手与四次挥手的。显然在这种设计中,每次发送Http请求都会消耗很多的额外资源,即连接的建立与销毁。
于是,HTTP协议的也进行了发展,通过持久连接的方法来进行socket连接复用。
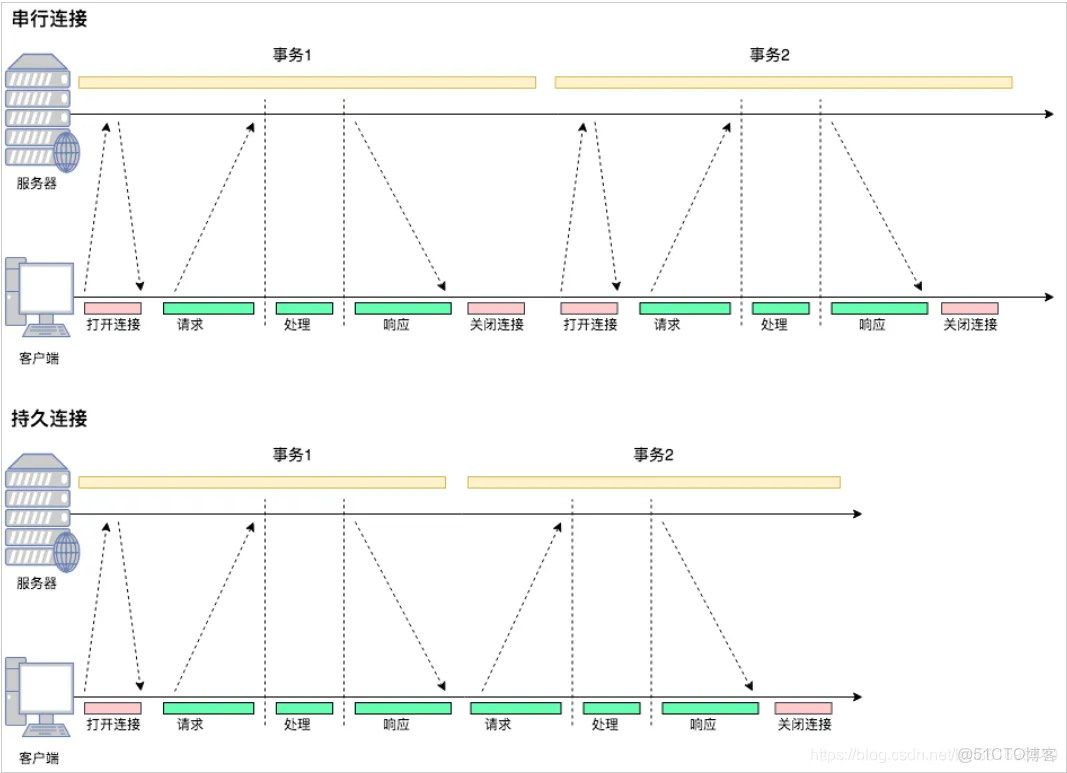
从图中可以看到:
- 在串行连接中,每次交互都要打开关闭连接
- 在持久连接中,第一次交互会打开连接,交互结束后连接并不关闭,下次交互就省去了建立连接的过程。
持久连接的实现有两种:HTTP/1.0+的keep-alive与HTTP/1.1的持久连接。
二、HTTP/1.0+的Keep-Alive
从1996年开始,很多HTTP/1.0浏览器与服务器都对协议进行了扩展,那就是“keep-alive”扩展协议。
注意,这个扩展协议是作为1.0的补充的“实验型持久连接”出现的。keep-alive已经不再使用了,最新的HTTP/1.1规范中也没有对它进行说明,只是很多应用延续了下来。
使用HTTP/1.0的客户端在首部中加上"Connection:Keep-Alive",请求服务端将一条连接保持在打开状态。服务端如果愿意将这条连接保持在打开状态,就会在响应中包含同样的首部。如果响应中没有包含"Connection:Keep-Alive"首部,则客户端会认为服务端不支持keep-alive,会在发送完响应报文之后关闭掉当前连接。
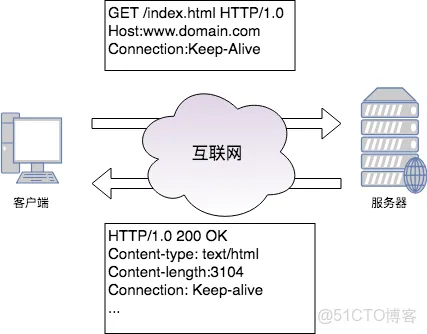
通过keep-alive补充协议,客户端与服务器之间完成了持久连接,然而仍然存在着一些问题:
- 在HTTP/1.0中keep-alive不是标准协议,客户端必须发送Connection:Keep-Alive来激活keep-alive连接。
- 代理服务器可能无法支持keep-alive,因为一些代理是"盲中继",无法理解首部的含义,只是将首部逐跳转发。所以可能造成客户端与服务端都保持了连接,但是代理不接受该连接上的数据。
三、HTTP/1.1的持久连接
HTTP/1.1采取持久连接的方式替代了Keep-Alive。
HTTP/1.1的连接默认情况下都是持久连接。如果要显式关闭,需要在报文中加上Connection:Close首部。即在HTTP/1.1中,所有的连接都进行了复用。
然而如同Keep-Alive一样,空闲的持久连接也可以随时被客户端与服务端关闭。不发送Connection:Close不意味着服务器承诺连接永远保持打开。
四、HttpClient如何生成持久连接
HttpClien中使用了连接池来管理持有连接,同一条TCP链路上,连接是可以复用的。HttpClient通过连接池的方式进行连接持久化。
其实“池”技术是一种通用的设计,其设计思想并不复杂:
- 当有连接第一次使用的时候建立连接
- 结束时对应连接不关闭,归还到池中
- 下次同个目的的连接可从池中获取一个可用连接
- 定期清理过期连接
所有的连接池都是这个思路,不过我们看HttpClient源码主要关注两点:
- 连接池的具体设计方案,以供以后自定义连接池参考
- 如何与HTTP协议对应上,即理论抽象转为代码的实现
4.1 HttpClient连接池的实现
HttpClient关于持久连接的处理在下面的代码中可以集中体现,下面从MainClientExec摘取了和连接池相关的部分,去掉了其他部分:
这里看到了在Http请求过程中对连接的处理是和协议规范是一致的,这里要展开讲一下具体实现。
PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager是HttpClient默认的连接管理器,首先通过requestConnection()获得一个连接的请求,注意这里不是连接。
可以看到返回的ConnectionRequest对象实际上是一个持有了Future<CPoolEntry>,CPoolEntry是被连接池管理的真正连接实例。
从上面的代码我们应该关注的是:
Future<CPoolEntry> future = this.pool.lease(route, state, null)
如何从连接池CPool中获得一个异步的连接,Future<CPoolEntry>
HttpClientConnection conn = leaseConnection(future, timeout, tunit)
如何通过异步连接Future<CPoolEntry>获得一个真正的连接HttpClientConnection
4.2 Future<CPoolEntry>
看一下CPool是如何释放一个Future<CPoolEntry>的,AbstractConnPool核心代码如下:
上面的代码逻辑有几个重要点:
- 连接池有个最大连接数,每个route对应一个小连接池,也有个最大连接数
- 不论是大连接池还是小连接池,当超过数量的时候,都要通过LRU释放一些连接
- 如果拿到了可用连接,则返回给上层使用
- 如果没有拿到可用连接,HttpClient会判断当前route连接池是否已经超过了最大数量,没有到上限就会新建一个连接,并放入池中
- 如果到达了上限,就排队等待,等到了信号量,就重新获得一次,等待不到就抛超时异常
- 通过线程池获取连接要通过ReetrantLock加锁,保证线程安全
到这里为止,程序已经拿到了一个可用的CPoolEntry实例,或者抛异常终止了程序。
4.3 HttpClientConnection
五、HttpClient如何复用持久连接?
在上一章中,我们看到了HttpClient通过连接池来获得连接,当需要使用连接的时候从池中获得。
对应着第三章的问题:
- 当有连接第一次使用的时候建立连接
- 结束时对应连接不关闭,归还到池中
- 下次同个目的的连接可从池中获取一个可用连接
- 定期清理过期连接
我们在第四章中看到了HttpClient是如何处理1、3的问题的,那么第2个问题是怎么处理的呢?
即HttpClient如何判断一个连接在使用完毕后是要关闭,还是要放入池中供他人复用?再看一下MainClientExec的代码
可以看到,当使用连接发生过请求之后,有连接重试策略来决定该连接是否要重用,如果要重用就会在结束后交给HttpClientConnectionManager放入池中。
那么连接复用策略的逻辑是怎么样的呢?
看一下父类的复用策略
总结一下:
- 如果request首部中包含Connection:Close,不复用
- 如果response中Content-Length长度设置不正确,不复用
- 如果response首部包含Connection:Close,不复用
- 如果reponse首部包含Connection:Keep-Alive,复用
- 都没命中的情况下,如果HTTP版本高于1.0则复用
从代码中可以看到,其实现策略与我们第二、三章协议层的约束是一致的。
六、HttpClient如何清理过期连接
在HttpClient4.4版本之前,在从连接池中获取重用连接的时候会检查下是否过期,过期则清理。
之后的版本则不同,会有一个单独的线程来扫描连接池中的连接,发现有离最近一次使用超过设置的时间后,就会清理。默认的超时时间是2秒钟。
可以看到在HttpClientBuilder进行build的时候,如果指定了开启清理功能,会创建一个连接池清理线程并运行它。
总结一下:
- 只有在HttpClientBuilder手动设置后,才会开启清理过期与空闲连接
- 手动设置后,会启动一个线程死循环执行,每次执行sleep一定时间,调用HttpClientConnectionManager的清理方法清理过期与空闲连接。
七、本文总结
- HTTP协议通过持久连接的方式,减轻了早期设计中的过多连接问题
- 持久连接有两种方式:HTTP/1.0+的Keep-Avlive与HTTP/1.1的默认持久连接
- HttpClient通过连接池来管理持久连接,连接池分为两个,一个是总连接池,一个是每个route对应的连接池
- HttpClient通过异步的Future<CPoolEntry>来获取一个池化的连接
- 默认连接重用策略与HTTP协议约束一致,根据response先判断Connection:Close则关闭,在判断Connection:Keep-Alive则开启,最后版本大于1.0则开启
- 只有在HttpClientBuilder中手动开启了清理过期与空闲连接的开关后,才会清理连接池中的连接
- HttpClient4.4之后的版本通过一个死循环线程清理过期与空闲连接,该线程每次执行都sleep一会,以达到定期执行的效果
八、httpcleint线程池重要设置
setMaxTotal 和 setDefaultMaxPerRoute
HttpUtils工具类(一)常见的HttpUtils工具类及如何自定义java的http连接池-CSDN博客
HttpUtils工具类(二)Apache HttpClient 5 使用详细教程_apache client5-CSDN博客
HttpUtils工具类(三)OKHttpClient使用详细教程-CSDN博客
一、几种常见的Http调用方式
- Apache HttpClient
- OKhttpClient
- Hutool封装的HttpUtils
- Spring RestTemplate
- Java 原生的HttpURLConnection
1. 使用 Apache HttpClient
Apache HttpClient 是一个功能强大的 HTTP 客户端库,支持同步和异步请求。它适用于处理更加复杂的场景,如认证、连接池、多线程、上传文件等。
特点:
- 功能强大:Apache HttpClient 是一个久经考验的库,支持多种复杂的场景,包括连接池、代理、认证、重定向、Cookie 管理等。
- 扩展性好:可以通过丰富的 API 进行灵活配置,满足复杂的企业级应用需求。
- 同步阻塞:Apache HttpClient 默认是同步阻塞模式,适用于同步请求。
优点:
- 成熟稳定,经过长时间的验证,企业级项目中广泛使用。
- 适合需要复杂 HTTP 操作的场景,如带有重试、认证和状态维护的请求。
缺点:
- 比较重量级,学习曲线稍陡峭。
一、Apache HttpClient 5介绍
Apache HttpClient 5 是一个功能齐全且高度可定制的 HTTP 客户端库, 其专门用于发送 HTTP 请求、处理 HTTP 响应并支持各种 HTTP 协议特性。特别适合处理复杂的 HTTP 请求需求,如多协议支持、认证、连接池、代理等。它适合中大型项目或需要高级 HTTP 特性的应用开发。
(1)核心特性
-
功能强大:
- 同步与异步支持:支持同步和异步的 HTTP 请求处理,异步请求在处理大量并发请求时能够显著提高效率。
- 连接池管理:内置的连接池机制能提高并发处理性能,减少资源消耗。
- 多种认证机制:支持多种认证方式,包括 Basic、Digest、NTLM、Kerberos 等,能够处理多种安全场景。
- 支持Cookie管理:内置 Cookie 管理功能,能够自动处理服务端返回的 Cookie 并在后续请求中使用,模拟浏览器行为。
-
协议支持广泛:
- HTTP/1.1 和 HTTP/2 支持:支持现代 HTTP 协议,包括 HTTP/2 的多路复用和流优先级等特性,提升了网络请求效率;特别是 HTTP/2 多路复用的优势。
- SSL/TLS 支持:支持 HTTPS,提供自定义 SSL/TLS 配置,确保通信的安全性。HttpClient 5 可以方便地处理 HTTPS 请求,支持定制化的 SSL/TLS 配置。
-
灵活性和可扩展性:
- 易于扩展和定制:允许开发者根据需要进行灵活的定制,HttpClient 5 的设计高度模块化,用户可以根据需要对连接管理、重定向策略、请求重试策略、代理设置等进行灵活定制。
- 代理支持:可以轻松配置 HTTP 或 SOCKS 代理,用于跨网络访问和隐私保护。
-
健壮的错误处理机制:
- 自动重试和重定向处理:内置的重试机制和自动重定向处理,可以减少由于网络问题导致的失败请求。开发者可以定制是否启用自动重定向。
(2)Apache HttpClient 5 的新特性
与之前的 4.x 版本相比,HttpClient 5 进行了大量的改进和优化,特别是在性能和安全性方面:
- HTTP/2 支持:提供了完整的 HTTP/2 支持,包括多路复用、流优先级等特性。
- 更好的异步支持:在处理并发请求时,通过异步模型极大提升了响应速度和吞吐量。
- 灵活的响应处理:通过改进的响应处理 API,可以更方便地处理大型响应体,避免内存溢出问题。
(3)在 Java 项目的主要使用场景及缺点
使用场景:
- RESTful API 客户端:与第三方 API 交互,发送各种 HTTP 请求。
- Web 爬虫:抓取网页内容,处理重定向、Cookie 等。
- 分布式系统通信:用于微服务间的 HTTP 通信。
- 测试与自动化:模拟 HTTP 请求,进行集成和自动化测试。
- 代理与网关:处理请求代理和认证机制。
- 文件上传下载:实现大文件的传输。
- 认证交互:处理 OAuth2、JWT 等认证协议。
- 安全通信:处理 HTTPS 请求,确保数据安全。
缺点:
- 学习曲线陡峭:高级特性(如自定义连接池、SSL 配置、异步请求等)较为复杂,新手需要时间学习和掌握。
- 体积较大:相比轻量级客户端,如 OkHttp,HttpClient 依赖库较多,可能不适合小型项目。
- 性能消耗高:默认配置下的内存和 CPU 占用较高,需调整才能达到最佳性能。
- 配置繁琐:高级定制(如连接管理、认证、代理)需要较多配置,增加开发复杂度。
- 异步编程复杂:异步请求的回调、错误处理等逻辑复杂,增加代码难度。
二、在实际项目中的应用
(1)引入maven配置
首先,你需要将 HttpClient 5 的依赖加入到项目中。pom.xml 文件如下:
-
<dependency>
-
<groupId>org.apache.httpcomponents.client5</groupId>
-
<artifactId>httpclient5</artifactId>
-
<version>5.1</version>
-
</dependency>
(2)自定义HttpUtils工具类---实现连接管理、重试策略等
-
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
-
import org.apache.hc.client5.http.DnsResolver;
-
import org.apache.hc.client5.http.classic.methods.HttpPost;
-
import org.apache.hc.client5.http.classic.methods.HttpUriRequestBase;
-
import org.apache.hc.client5.http.config.RequestConfig;
-
import org.apache.hc.client5.http.impl.classic.CloseableHttpClient;
-
import org.apache.hc.client5.http.impl.classic.CloseableHttpResponse;
-
import org.apache.hc.client5.http.impl.classic.HttpClients;
-
import org.apache.hc.client5.http.impl.io.PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager;
-
import org.apache.hc.client5.http.impl.io.PoolingHttpClientConnectionManagerBuilder;
-
import org.apache.hc.core5.http.HttpEntity;
-
import org.apache.hc.core5.http.io.SocketConfig;
-
import org.apache.hc.core5.http.message.BasicHeader;
-
import org.apache.hc.core5.util.Timeout;
-
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
-
-
import java.io.Closeable;
-
import java.io.IOException;
-
import java.net.InetAddress;
-
import java.net.URI;
-
import java.net.UnknownHostException;
-
import java.util.Map;
-
-
-
/**
-
* @author 响叮当
-
* @since 2024/8/15 14:10
-
**/
-
-
-
public class ApacheHttpClientUtil {
-
-
private CloseableHttpClient httpClient;
-
-
-
public void init() {
-
SocketConfig socketConfig = SocketConfig.custom()
-
.setSoTimeout(Timeout.ofMilliseconds(1000))
-
.build();
-
-
PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager connectionManager = PoolingHttpClientConnectionManagerBuilder
-
.create()
-
.setDefaultSocketConfig(socketConfig)
-
.setMaxConnTotal(1000)
-
.setMaxConnPerRoute(50)
-
.build();
-
-
RequestConfig requestConfig = RequestConfig.custom()
-
.setConnectionRequestTimeout(Timeout.ofMilliseconds(8000))
-
.setResponseTimeout(Timeout.ofMilliseconds(8000))
-
.setConnectTimeout(Timeout.ofMilliseconds(8000))
-
.build();
-
-
httpClient = HttpClients
-
.custom()
-
.disableContentCompression()
-
.setConnectionManager(connectionManager)
-
.setDefaultRequestConfig(requestConfig)
-
.build();
-
}
-
-
-
public CloseableHttpResponse getOrHead(String url, String method, Map<String, String> headers) throws IOException {
-
HttpUriRequestBase request = new HttpUriRequestBase(method, URI.create(url));
-
BasicHeader[] head = mapToHeaders(headers);
-
request.setHeaders(head);
-
return httpClient.execute(request);
-
}
-
-
-
public CloseableHttpResponse post(String url, Map<String, String> headers, HttpEntity httpEntity) throws IOException {
-
HttpPost request = new HttpPost(url);
-
BasicHeader[] head = mapToHeaders(headers);
-
request.setHeaders(head);
-
request.setEntity(httpEntity);
-
return httpClient.execute(request);
-
}
-
-
public static BasicHeader[] mapToHeaders(Map<String, String> map) {
-
BasicHeader[] headers = new BasicHeader[map.size()];
-
int i = 0;
-
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : map.entrySet()) {
-
headers[i++] = new BasicHeader(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
-
}
-
return headers;
-
}
-
-
public static void closeQuietly(Closeable is) {
-
if (is != null) {
-
try {
-
is.close();
-
} catch (Exception ex) {
-
log.error("Resources encounter an exception when closing,ex:{}", ex.getMessage());
-
}
-
}
-
}
-
-
}
功能概述
- 初始化 HTTP 客户端:
init()方法初始化CloseableHttpClient,配置连接池、请求超时和套接字超时。- 连接池配置:通过
PoolingHttpClientConnectionManagerBuilder设置最大连接数(1000)和每路由的最大连接数(50),用于高并发场景。 - 请求配置:包括连接超时、请求超时和响应超时,确保在合理的时间内处理请求。
- 连接池配置:通过
- HTTP 请求处理:
- GET/HEAD 请求:
getOrHead()方法可发送 GET 或 HEAD 请求,并接受自定义请求头。 - POST 请求:
post()方法可发送 POST 请求,支持自定义请求头和实体。
- GET/HEAD 请求:
- 资源管理:
closeQuietly()方法用于关闭资源,避免抛出异常。
(3)代码中的具体实现
1、Get请求
-
-
public void testGet() {
-
String url = "http://xxx.com.cn";
-
try {
-
// 1、构建入参、添加 headers
-
Map<String, String> headers = new HashMap<>();
-
-
// 2、发起http请求
-
CloseableHttpResponse httpResponse = apacheHttpClientUtil.getOrHead(url, "GET", headers);
-
-
// 3、返回结果,异常处理
-
if (httpResponse.getCode() == 200) {
-
String resStr = EntityUtils.toString(httpResponse.getEntity());
-
log.info("request_success, response:{}, httpResponse_Code:{}, reasonPhrase:{}", resStr, httpResponse.getCode(), httpResponse.getReasonPhrase());
-
} else {
-
log.error("request_fail, httpResponse_Code:{}, reasonPhrase:{}", httpResponse.getCode(), httpResponse.getReasonPhrase());
-
}
-
} catch (Exception e) {
-
log.error("request_udmp_fail, ex:{}", e);
-
}
-
}
2、POST请求-常规
-
-
public void testPost( PostReq req) {
-
String url = "http://xxx.com.cn";
-
try {
-
// 1、构建入参、添加 headers
-
StringEntity stringEntity = new StringEntity(JSONUtil.toJsonStr(req), ContentType.APPLICATION_JSON);
-
Map<String, String> headers = new HashMap<>();
-
-
// 2、发起http请求
-
CloseableHttpResponse httpResponse = apacheHttpClientUtil.post(url, headers, stringEntity);
-
-
// 3、返回结果,异常处理
-
if (httpResponse.getCode() == 200) {
-
String resStr = EntityUtils.toString(httpResponse.getEntity());
-
log.info("request_success, response:{}, httpResponse_Code:{}, reasonPhrase:{}", resStr, httpResponse.getCode(), httpResponse.getReasonPhrase());
-
} else {
-
log.error("request_fail, httpResponse_Code:{}, reasonPhrase:{}", httpResponse.getCode(), httpResponse.getReasonPhrase());
-
}
-
} catch (Exception e) {
-
log.error("request_udmp_fail, ex:{}", e);
-
}
-
}
3、POST请求-上传文件
-
/**
-
* 上传文件
-
* @param multipartFile
-
* @param token
-
* @param key
-
* @return
-
*/
-
-
public UploadRes testPostFile(
-
MultipartFile multipartFile,
-
String token,
-
String key
-
) {
-
UploadRes res = null;
-
String url = "http://xxx.com.cn";
-
try {
-
// 1、构建File参数
-
File file = new File(multipartFile.getOriginalFilename());
-
try (FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file)) {
-
fos.write(multipartFile.getBytes());
-
}
-
MultipartEntityBuilder builder = MultipartEntityBuilder.create();
-
builder.addBinaryBody("file", file, ContentType.MULTIPART_FORM_DATA, "ex.xlsx");
-
-
// 2、构建其他参数
-
builder.addTextBody("token", token, ContentType.TEXT_PLAIN);
-
builder.addTextBody("key", key, ContentType.TEXT_PLAIN);
-
HttpEntity multipartEntity = builder.build();
-
-
// 3、需要加 header,在这里加
-
Map<String, String> headers = new HashMap<>();
-
-
// 4、发起http请求
-
CloseableHttpResponse httpResponse = apacheHttpClientUtil.post(url, headers, multipartEntity);
-
-
// 5、返回结果,异常处理
-
if (httpResponse.getCode() == 200) {
-
String resStr = EntityUtils.toString(httpResponse.getEntity());
-
res = JSONUtil.toBean(resStr, UploadRes.class);
-
log.info("request_success, response:{}, httpResponse_Code:{}, reasonPhrase:{}", resStr, httpResponse.getCode(), httpResponse.getReasonPhrase());
-
} else {
-
log.error("request_fail, httpResponse_Code:{}, reasonPhrase:{}", httpResponse.getCode(), httpResponse.getReasonPhrase());
-
}
-
} catch (Exception e) {
-
log.error("request_udmp_fail, ex:{}", e);
-
}
-
return res;
-
}
(4)高级用法
1、处理重定向
HttpClient 5 默认会处理 3XX 重定向,但你也可以自定义行为。
-
CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClients.custom()
-
.disableRedirectHandling() // 禁用自动重定向
-
.build();
2、SSL/TLS 支持
使用 HttpClient 5 可以轻松处理 HTTPS 请求,下面展示如何自定义 SSL 配置。
-
import org.apache.hc.core5.ssl.SSLContextBuilder;
-
import org.apache.hc.client5.http.impl.classic.HttpClients;
-
import javax.net.ssl.SSLContext;
-
-
SSLContext sslContext = SSLContextBuilder.create()
-
.loadTrustMaterial((chain, authType) -> true) // 信任所有证书
-
.build();
-
-
CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClients.custom()
-
.setSSLContext(sslContext)
-
.build();
3、处理异步请求
如果你需要发送异步 HTTP 请求,可以使用 HttpAsyncClient。
-
import org.apache.hc.client5.http.impl.async.CloseableHttpAsyncClient;
-
import org.apache.hc.client5.http.impl.async.HttpAsyncClients;
-
import org.apache.hc.core5.concurrent.FutureCallback;
-
import org.apache.hc.client5.http.classic.methods.HttpGet;
-
-
CloseableHttpAsyncClient asyncClient = HttpAsyncClients.createDefault();
-
-
asyncClient.start();
-
-
HttpGet request = new HttpGet("https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/1");
-
-
asyncClient.execute(request, new FutureCallback<>() {
-
-
public void completed(CloseableHttpResponse response) {
-
System.out.println("Response received: " + response.getCode());
-
}
-
-
-
public void failed(Exception ex) {
-
System.out.println("Request failed: " + ex.getMessage());
-
}
-
-
-
public void cancelled() {
-
System.out.println("Request cancelled");
-
}
-
});
4、处理 Cookie
-
import org.apache.hc.client5.http.cookie.BasicCookieStore;
-
import org.apache.hc.client5.http.impl.classic.HttpClients;
-
import org.apache.hc.client5.http.cookie.CookieStore;
-
-
CookieStore cookieStore = new BasicCookieStore();
-
CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClients.custom()
-
.setDefaultCookieStore(cookieStore)
-
.build();
5、HTTPDNS支持
-
// 当域名为www.baidu.com结尾时候,转到local的机器上
-
String Target_IP= "127.0.0.1";
-
String[] domains = new String[]{"www.baidu.com"};
-
-
DnsResolver dnsResolver = new DnsResolver() {
-
-
public InetAddress[] resolve(String host) throws UnknownHostException {
-
if (host.endsWith(domains[0]))) {
-
return new InetAddress[]{InetAddress.getByName(Target_IP)};
-
}
-
return new InetAddress[0];
-
}
-
-
-
public String resolveCanonicalHostname(String s) {
-
return null;
-
}
-
};
-
-
-
// @PostConstruct
-
public void init() {
-
SocketConfig socketConfig = SocketConfig.custom()
-
.setSoTimeout(Timeout.ofMilliseconds(1000))
-
.build();
-
-
PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager connectionManager = PoolingHttpClientConnectionManagerBuilder
-
.create()
-
.setDnsResolver(dnsResolver) // 这里是HttpDns配置
-
.setDefaultSocketConfig(socketConfig)
-
.setMaxConnTotal(1000)
-
.setMaxConnPerRoute(50)
-
.build();
OkHttpClient是一个由 Square 公司开发的 HTTP 客户端库,用于在 Android 和 Java 应用中进行网络请求。它支持同步和异步请求、连接池、超时设置、拦截器等功能,适合用于高性能网络请求,特别是在需要处理复杂的网络操作时。一、OKHttpClient介绍
主要特点
-
同步和异步请求:
-
同步请求会在当前线程等待响应,适合不需要并发的简单请求。
-
异步请求会将网络操作交由后台线程处理,不会阻塞主线程,适合需要并发处理或在 Android 等环境中使用。
-
-
连接池: OkHttp 默认会使用连接池来复用 HTTP 连接,从而提高性能,减少连接的建立和关闭的开销。
-
拦截器 (Interceptor): 拦截器允许在请求和响应时进行操作,例如可以在请求发送前添加认证信息,或在响应到达后进行日志记录。
-
自动处理 HTTP/2 和 SPDY: OkHttp 默认支持 HTTP/2 协议,可以提升多路复用性能,使多个请求共享一个 TCP 连接。
-
缓存机制: OkHttp 提供了默认的缓存机制,可以根据 HTTP 响应头自动缓存请求结果,减少重复网络请求。
-
超时控制: 可以对连接、读取和写入操作分别设置超时,避免长时间无响应的请求卡住应用。
二、在实际项目中的应用
(1)引入maven配置
-
<!-- ok的Http连接池 -->
-
<dependency>
-
<groupId>com.squareup.okhttp3</groupId>
-
<artifactId>okhttp</artifactId>
-
<version>4.9.3</version>
-
</dependency>
(2)自定义HttpUtils工具类
-
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
-
import com.yan.project.httpUtils.okHttp2.HttpRequestBody;
-
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
-
import okhttp3.*;
-
-
import java.io.Closeable;
-
import java.io.File;
-
import java.io.IOException;
-
import java.io.InputStream;
-
import java.util.Map;
-
import java.util.Objects;
-
import java.util.Set;
-
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
-
-
@Slf4j
-
public class OkHttpUtils {
-
private OkHttpUtils() {
-
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Utility class");
-
}
-
-
private static final String MIME_JSON = "application/json
在《扫清盲点,如何正确的从HttpClient 3.x系统升级到HttpClient 4.x》一文中已经详细的指明 HttpClient 3.x 迁移到 HttpClient 4.x 相关的变更点以及升级替换策略。本文针对HttpClient 4.5.x 之后 被 @Deprecated 注解后的废弃 / 过期 API(SSL证书验证相关),如何进行替换进行相关总结。
1. 针对 SSLContext 和 SSLContextBuilder 过期的替换
如果是在 HttpClient 4.5.x 之前,访问https的时候使用SSLContextBuilder来建立对象,那么在代码中会看到过期的语法提示,
在IDEA中使用 Alt + Enter 会出现提示在4.5.x的SSLContextBuilder已经过期,替换策略为:删除原来的import,重新导入 httpcore jar中的SSLContextBuilder进行替换。经调查发现:SSLContext 和 SSLContextBuilder 的API从原来的 org.apache.http.conn.ssl 包挪到了 org.apache.http.ssl 包,基本的用法什么的都没有变化。

替换代码如下,删除掉旧的import,导入新的 org.apache.http.ssl 下的引用
-
// Fixing deprecated code to use current HttpClient implementations Sekito.Lv 01/30/2019 11:29 Start
-
import org.apache.http.ssl.SSLContexts;
-
import org.apache.http.ssl.SSLContextBuilder;
-
-
//import org.apache.http.conn.ssl.SSLContexts;
-
//import org.apache.http.conn.ssl.SSLContextBuilder;
-
// Fixing deprecated code to use current HttpClient implementations Sekito.Lv 01/30/2019 11:29 End
2. 针对 4.4.x 之后版本 SSLConnectionSocketFactory 中静态变量过期的替换
在 SSLConnectionSocketFactory 中静态变量有如下3个
- STRICT_HOSTNAME_VERIFIER
- BROWSER_COMPATIBLE_HOSTNAME_VERIFIER
- ALLOW_ALL__HOSTNAME_VERIFIER
在代码源码中可以看到该三个静态变量都已经被 @Deprecated 注解了,在方法中使用会出现过期提示。

替换策略如下:
在《扫清盲点,如何正确的从HttpClient 3.x系统升级到HttpClient 4.x》一文中HttpClient 3.x 和 4.x 废弃API一览里已经给出过期API的官方链接,在这里面可以查到新的替换API
ALLOW_ALL_HOSTNAME_VERIFIER → NoopHostnameVerifier
BROWSER_COMPATIBLE_HOSTNAME_VERIFIER → DefaultHostnameVerifier
STRICT_HOSTNAME_VERIFIER → DefaultHostnameVerifier示例代码:
-
// Fixing deprecated code to use current HttpClient implementations Sekito.Lv 01/30/2019 11:29 Start
-
-
// 4.4 之前用法,已经过期的API
-
// SSLConnectionSocketFactory factory = new SSLConnectionSocketFactory(
-
// sslContext, new String[] { "TLSv1" }, null,
-
// SSLConnectionSocketFactory.BROWSER_COMPATIBLE_HOSTNAME_VERIFIER);
-
-
SSLConnectionSocketFactory factory = new SSLConnectionSocketFactory(
-
sslContext, new String[] { "TLSv1" }, null,
-
new DefaultHostnameVerifier());
-
// Fixing deprecated code to use current HttpClient implementations Sekito.Lv 01/30/2019 11:29 End
注:本文原创由`bluetata`发布于blog.csdn.net、转载请务必注明出处。
// 不重试 new DefaultHttpRequestRetryStrategy(0,TimeValue.ZERO_MILLISECONDS) //默认重试的 异常 和 返回code: Arrays.asList( InterruptedIOException.class, UnknownHostException.class, ConnectException.class, ConnectionClosedException.class, NoRouteToHostException.class, SSLException.class), Arrays.asList( HttpStatus.SC_TOO_MANY_REQUESTS, HttpStatus.SC_SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE)package org.apache.hc.client5.http; import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.hc.client5.http.impl.DefaultHttpRequestRetryStrategy; import org.apache.hc.client5.http.impl.classic.CloseableHttpClient; import org.apache.hc.client5.http.impl.classic.HttpClientBuilder; import org.apache.hc.core5.http.ClassicHttpRequest; import org.apache.hc.core5.http.HttpRequest; import org.apache.hc.core5.http.HttpResponse; import org.apache.hc.core5.http.io.support.ClassicRequestBuilder; import org.apache.hc.core5.http.protocol.HttpContext; import org.apache.hc.core5.util.Args; import org.apache.hc.core5.util.TimeValue; /** * @Description: RetryTest * @Author: gaoyb * @Version: 2025/4/30 15:50 */ public class RetryTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { final ClassicHttpRequest httpGet = ClassicRequestBuilder.get("https://httpbin.org/status/503") .build(); CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClientBuilder .create() // .setRetryStrategy(new CustomRetryStrategy(3, TimeValue.ofSeconds(3))) .setRetryStrategy( // new DefaultHttpRequestRetryStrategy( // 0, // TimeValue.ZERO_MILLISECONDS // ) new DefaultHttpRequestRetryStrategy() ) .build(); httpClient.execute(httpGet, response -> { System.out.println(response.getCode() + " " + response.getReasonPhrase()); return null; }); } static class CustomRetryStrategy implements HttpRequestRetryStrategy { private final int maxRetries; private final TimeValue retryInterval; public CustomRetryStrategy(final int maxRetries, final TimeValue retryInterval) { this.maxRetries = maxRetries; this.retryInterval = retryInterval; } @Override public boolean retryRequest( final HttpRequest request, final IOException exception, final int execCount, final HttpContext context) { Args.notNull(request, "request"); Args.notNull(exception, "exception"); if (execCount > this.maxRetries) { // Do not retry if over max retries return false; } return true; } @Override public boolean retryRequest( final HttpResponse response, final int execCount, final HttpContext context) { Args.notNull(response, "response"); return execCount <= this.maxRetries; } @Override public TimeValue getRetryInterval(HttpResponse response, int execCount, HttpContext context) { System.out.println("Retrying HTTP request after " + retryInterval.toString()); return retryInterval; } } }package org.apache.hc.client5.http; import javax.net.ssl.SSLSession; import org.apache.hc.client5.http.classic.methods.HttpGet; import org.apache.hc.client5.http.config.ConnectionConfig; import org.apache.hc.client5.http.config.RequestConfig; import org.apache.hc.client5.http.config.TlsConfig; import org.apache.hc.client5.http.impl.DefaultHttpRequestRetryStrategy; import org.apache.hc.client5.http.impl.classic.CloseableHttpClient; import org.apache.hc.client5.http.impl.classic.HttpClients; import org.apache.hc.client5.http.impl.io.PoolingHttpClientConnectionManagerBuilder; import org.apache.hc.client5.http.protocol.HttpClientContext; import org.apache.hc.client5.http.ssl.DefaultClientTlsStrategy; import org.apache.hc.client5.http.ssl.HostnameVerificationPolicy; import org.apache.hc.client5.http.ssl.NoopHostnameVerifier; import org.apache.hc.client5.http.ssl.TrustAllStrategy; import org.apache.hc.core5.http.io.entity.EntityUtils; import org.apache.hc.core5.http.message.StatusLine; import org.apache.hc.core5.http.ssl.TLS; import org.apache.hc.core5.ssl.SSLContexts; import org.apache.hc.core5.util.TimeValue; import org.apache.hc.core5.util.Timeout; /** * @Description: RetryTest * @Author: gaoyb * @Version: 2025/4/30 15:50 */ public class SSLTest { public static void main(final String[] args) throws Exception { try (final CloseableHttpClient httpclient = HttpClients.custom() .setConnectionManager( /* HttpClientConnectionManager */ PoolingHttpClientConnectionManagerBuilder.create() .setDefaultConnectionConfig( ConnectionConfig.custom() .setConnectTimeout(Timeout.ofSeconds(3)) .build() ) .setTlsSocketStrategy( // setTlsSocketStrategy(TlsSocketStrategy) 替代 setSSLSocketFactory /* TlsSocketStrategy */ new DefaultClientTlsStrategy( SSLContexts.custom() // 替代 SSLContextBuilder.create() .loadTrustMaterial(TrustAllStrategy.INSTANCE) .build(), HostnameVerificationPolicy.CLIENT, NoopHostnameVerifier.INSTANCE ) // org.apache.hc.client5.http.impl.io.PoolingHttpClientConnectionManagerBuilder.createConnectionOperator // 替代 RegistryBuilder.<ConnectionSocketFactory>create() // .register("http", PlainConnectionSocketFactory.INSTANCE) // .register("https", new SSLConnectionSocketFactory(sslContext, NoopHostnameVerifier.INSTANCE)) ) .setMaxConnTotal(200)// maxTotal > 0 ? maxTotal : defaultMaxTotal=setMaxTotal .setMaxConnPerRoute(25)// maxPerRoute > 0 ? maxPerRoute : defaultMaxPerRoute=setDefaultMaxPerRoute .setDefaultTlsConfig( /* TlsConfig */ TlsConfig.custom() .setHandshakeTimeout(Timeout.ofSeconds(3)) .setSupportedProtocols(TLS.V_1_0, TLS.V_1_1, TLS.V_1_2, TLS.V_1_3) .build() ) .build()) .setDefaultRequestConfig( RequestConfig.custom() .setConnectionRequestTimeout(Timeout.ofMinutes(3)) .setResponseTimeout(Timeout.ZERO_MILLISECONDS)// 超时值为零将解释为无限超时。 .build() ) .setConnectionManagerShared(true) .setRoutePlanner(/* DefaultProxyRoutePlanner */ null) .setRetryStrategy(new DefaultHttpRequestRetryStrategy(0, TimeValue.ZERO_MILLISECONDS))//不重试 .build(); // HttpComponentsClientHttpRequestFactory requestFactory =//org.springframework.http.client.HttpComponentsClientHttpRequestFactory; // new HttpComponentsClientHttpRequestFactory(); // requestFactory.setHttpClient(httpClient);// this method is not accepting the CloseableHttpClient object // requestFactory.setConnectTimeout(30000); // requestFactory.setReadTimeout(30000); //This method is deprecated in spring boot 3.0 // requestFactory.setConnectionRequestTimeout(30000); // return new RestTemplate(requestFactory); ) { final HttpGet httpget = new HttpGet("https://httpbin.org/"); System.out.println("Executing request " + httpget.getMethod() + " " + httpget.getUri()); // 执行请求 [请求方法] [请求URI] final HttpClientContext clientContext = HttpClientContext.create(); httpclient.execute(httpget, clientContext, response -> { System.out.println("----------------------------------------"); System.out.println(httpget + "->" + new StatusLine(response)); EntityUtils.consume(response.getEntity()); final SSLSession sslSession = clientContext.getSSLSession(); if (sslSession != null) { System.out.println("SSL protocol " + sslSession.getProtocol()); // SSL 协议 [协议版本] System.out.println("SSL cipher suite " + sslSession.getCipherSuite()); // SSL 加密套件 [加密套件名称] } return null; }); } } } -




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号