阿里开源规则引擎QLExpress-入门实战
1.背景
最近研究低代码实现后端业务逻辑相关功能,使用LiteFlow作为流程编排后端service服务, 但是LiteFlow官方未提供图形界面编排流程。且LiteFlow语法对于,通过使用json来定义流程的可视化也不够友好(二开麻烦)。因此尝试使用LiteFlow底层使用的是QLExpress,来实现可视化逻辑编排。本文记录研究过程及其一些功能总结。
2.简介
什么是QLExpress脚本引擎?
QLExpress(Quick Language Express)是阿里巴巴开源的一门动态脚本引擎解析工具,起源于阿里巴巴的电商业务,旨在解决业务规则、表达式、数学计算等动态脚本的解析问题。
3.QLExpress实战
maven依赖配置
<!--规则引擎-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>QLExpress</artifactId>
<version>3.2.0</version>
</dependency>3.1 基础例子
ExpressRunner runner = new ExpressRunner();
DefaultContext<String, Object> context = new DefaultContext<String, Object>();
context.put("a", 1);
context.put("b", 2);
context.put("c", 3);
String express = "a + b * c";
Object r = runner.execute(express, context, null, true, false);
System.out.println(r);3.2 低代码实战
模拟低代码中动态if功能
3.2.1 需求描述
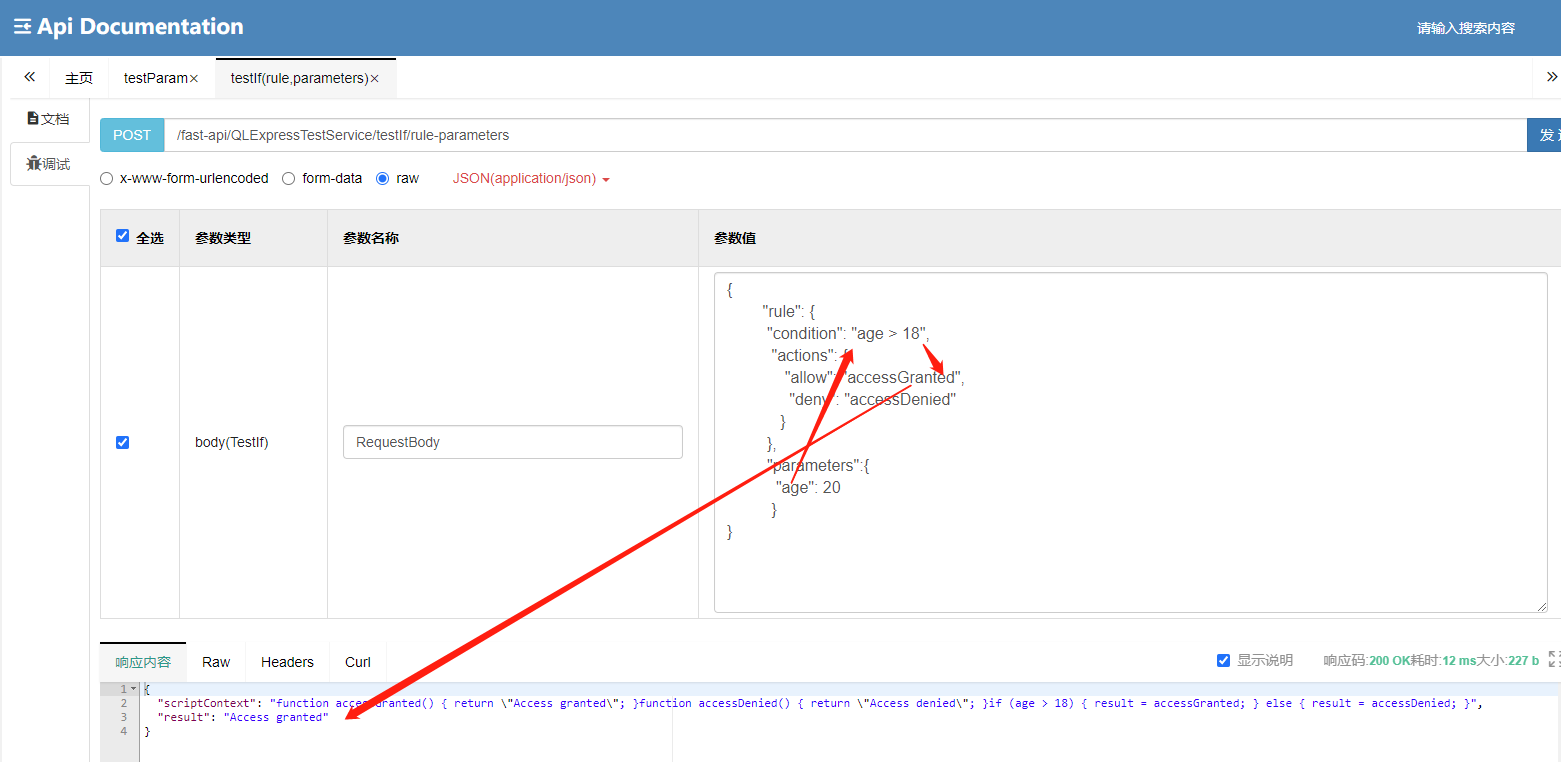
要实现不硬编码,动态执行包含if的程序逻辑。必须使用声明式可复用数据结构,如下json定义
{
"rule": {
"condition": "age > 18",
"actions": {
"allow": "accessGranted",
"deny": "accessDenied"
}
},
"parameters": {
"age": 20
}
}- rule: 规则定义部分, 包含条件节点和执行节点
- parameters: 定义参数部分,定义参数名称及默认值
执行过程:
- 低代码引擎解析规则部分,转化未低成脚本语言
- 读取从入参中读取流程变量配置,设置上下文
- 执行运算并获取结果
下面使用springboot项目具体实现
3.2.1 使用规则引擎
@Service
public class QLExpressTestService {
public Map<String, Object> testIf(Map<String, Object > rule, Map<String, Object > parameters) throws Exception {
// 根据 Map 对象动态生成 QLExpress 表达式
String condition = (String) rule.get("condition");
Map<String, String> actionsMap = (Map<String, String>) rule.get("actions");
String allowAction = actionsMap.get("allow");
String denyAction = actionsMap.get("deny");
// 定义 allowAccess 和 denyAccess 方法
String qlExpress = "function accessGranted() { return \"Access granted\"; }" +
"function accessDenied() { return \"Access denied\"; }" +
"if (" + condition + ") { result = " + allowAction + "; } else { result = " + denyAction + "; }";
// 执行 QLExpress 表达式
ExpressRunner runner = new ExpressRunner();
DefaultContext<String, Object> context = new DefaultContext<>();
context.put("age", parameters.getOrDefault("age", 20)); // 设置年龄为20岁
Object result = runner.execute(qlExpress, context, null, true, false);
System.out.println("Result: " + result);
return Map.of("scriptContext", qlExpress, "result", result);
}
}3.3.2 运行结果
参考文档
阿里开源规则引擎QLExpress-入门实战
规则引擎简介
规则引擎由推理引擎发展而来,是一种嵌入在应用程序中的组件,实现了将业务决策从应用程序代码中分离出来,并使用预定义的语义模块编写业务决策。接受数据输入,解释业务规则,并根据业务规则做出业务决策。
规则引擎
常用的规则引擎目前主要有Drools、Aviator、Easyrule、QLExpress,如下表格是对这些规则引擎的分析对比:
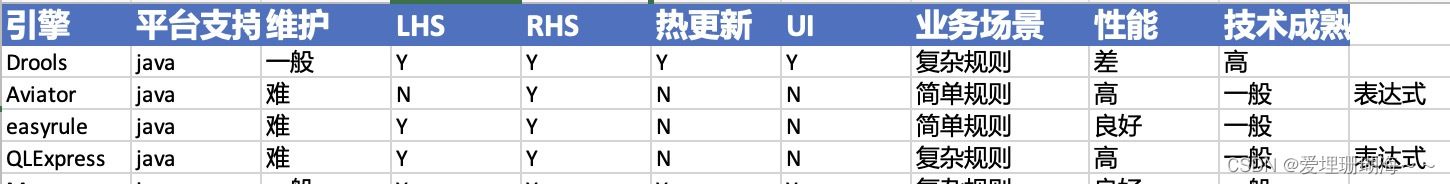
结合本人实际项目,我们的项目业务属性是电商,对性能要求比较高,因此发现阿里开源的QLExpress更适合现实的诉求,下面的章节将以电商促销活动的例子介绍QLExpress如何落地实操到业务代码中的
电商促销活动示例
比如我们的购物车现在有两个商品,对应的商品SKU分别为11120781和11120782,商品11120781参与的单品促销优惠活动,11120782参与的是单品促销打折活动,假设这两个商品来自同一个店家,店家给的运费优惠是满100减50关于两个活动规则的介绍如下:
单品促销优惠
该活动是在商品价格基础上优惠xxx元,比如商品原价为150,促销优惠50元,则优惠后的金额为150-50=100
单品促销打折
该活动是在商品价格基础上进行折扣,比如商品原价为150,促销打折5折,则优惠后的金额为150*0.5=75
第一步 引入依赖包
如下图所示,引入QLExpress的包
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>QLExpress</artifactId>
<version>3.2.0</version>
</dependency>编写针对某一类活动规则的业务接口
此接口主要处理同一类型规则的逻辑,以上述的单品促销为例,代码示例如下:
/**
* 查询商品促销活动匹配单品促销规则计算后的优惠金额
*
* @param promotionList 参与的促销活动
* @param productPrice 商品价格
* @return
*/
private List<Double> querySinglePromotionPrice(List<Promotion> promotionList, double productPrice) {
List<Double> nicePrices = Lists.newArrayList();
DefaultContext<String, Object> context = new DefaultContext<>();
ExpressRunner expressRunner = new ExpressRunner();
promotionList = promotionList.stream().filter(r -> "singlePromotion".equals(r.getPromotionType())).collect(Collectors.toList());
for (Promotion promotion : promotionList) {
//查询促销活动对应的规则模版配置信息
RuleTemplate template = queryRuleTemplate(promotion.getPromotionType());
String express = template.getExpress();
context.put("price", productPrice);
context.put("promotionType", promotion.getPromotionWay());
context.put("promotionValue", Double.parseDouble(promotion.getPromotionValue()));
System.out.println("参与促销活动【" + promotion.getPromotionName() + "】优惠前的商品金额:" + productPrice);
Object execute = null;
try {
execute = expressRunner.execute(express, context, null, true, true);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("计算规则[" + template.getTemplateName() + "]时发生异常,原因:" + e.getMessage());
}
System.out.println("优惠后的金额:" + execute);
nicePrices.add((Double) execute);
}
return nicePrices;
}涉及到的运费计算,代码示例如下:
private double queryMinShippingFree(List<Promotion> promotionList,double productPrice,double freeShipping ){
DefaultContext<String, Object> context = new DefaultContext<>();
double minShipping = 0.0;
List<Double> niceShipping = Lists.newArrayList();
ExpressRunner expressRunner = new ExpressRunner();
promotionList = promotionList.stream().filter(r -> "freeShipping".equals(r.getPromotionType())).collect(Collectors.toList());
for (Promotion promotion : promotionList) {
RuleTemplate template = queryRuleTemplate(promotion.getPromotionType());
String express = template.getExpress();
String condition = promotion.getConditionConfig();
context.put("price", productPrice);
context.put("amount", Double.parseDouble(JSONObject.parseObject(condition).getString("amountCondition")));
context.put("shippingPrice",freeShipping);
context.put("promotionValue", Double.parseDouble(JSONObject.parseObject(condition).getString("promotionAmount")));
System.out.println("参与促销活动【" + promotion.getPromotionName() + "】优惠前的运费:" + freeShipping);
Object execute = null;
try {
execute = expressRunner.execute(express, context, null, true, true);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("计算规则[" + template.getTemplateName() + "]时发生异常,原因:" + e.getMessage());
}
niceShipping.add((Double) execute);
}
if(niceShipping.isEmpty()){
return minShipping;
}
minShipping = Collections.min(niceShipping);
System.out.println("优惠后的运费:" + minShipping);
return minShipping;
}封装以上两个方法,输出购物车中的最终优惠金额,代码示例如下:
/**
* 计算最优促销活动价格
*
* @param cart 购物车信息
* @param shippingFee 运费
* @return 计算出最优价格
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public double queryMinPromotionPrice(String cart,double shippingFee) {
JSONArray cartArray = JSONObject.parseArray(cart);
double sum = 0.0,sumNicePrice = 0.0,sumNiceShipping = 0.0;
for(int i=0;i<cartArray.size();i++){
double minNicePrice = 0.0d;
String productCode = cartArray.getJSONObject(i).getString("productCode");
double productPrice = cartArray.getJSONObject(i).getDoubleValue("price");
//查询商品参与的促销活动
List<Promotion> promotionList = queryPromotion(productCode);
sum += productPrice;
//根据促销活动匹配的规则计算出优惠价格
List<Double> nicePrices = querySinglePromotionPrice(promotionList, productPrice);
//计算出最便宜的优惠价格
minNicePrice = Collections.min(nicePrices);
sumNicePrice +=minNicePrice;
//运费
double niceShipping = queryMinShippingFree(promotionList,productPrice,shippingFee);
sumNiceShipping+=niceShipping;
}
sum = sum+shippingFee;
System.out.println("参与促销之前购物车结算价格为:"+sum);
sumNicePrice = sumNicePrice+sumNiceShipping;
System.out.println("参与促销之后购物车结算价格金额:" + sumNicePrice);
return sumNicePrice;
}暴露给外部的http接口,代码示例如下:
@PostMapping("/queryMinPromotionPrice")
public double queryMinPromotionPrice(String cart,double shippingFee) {
System.out.println("开始获取商品优惠金额");
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
double minPrice = expressService.queryMinPromotionPrice(cart,shippingFee);
System.out.println("获取商品优惠金额结束,耗时:"+(System.currentTimeMillis()-startTime)+"毫秒");
return minPrice;
}以上的这行代码 RuleTemplate template = queryRuleTemplate(promotion.getPromotionType());是代表规则表达式的模版,可以配置在数据看中,如下图所示:
以上代码,通过postman或者insomnia工具,执行结果如下图所示: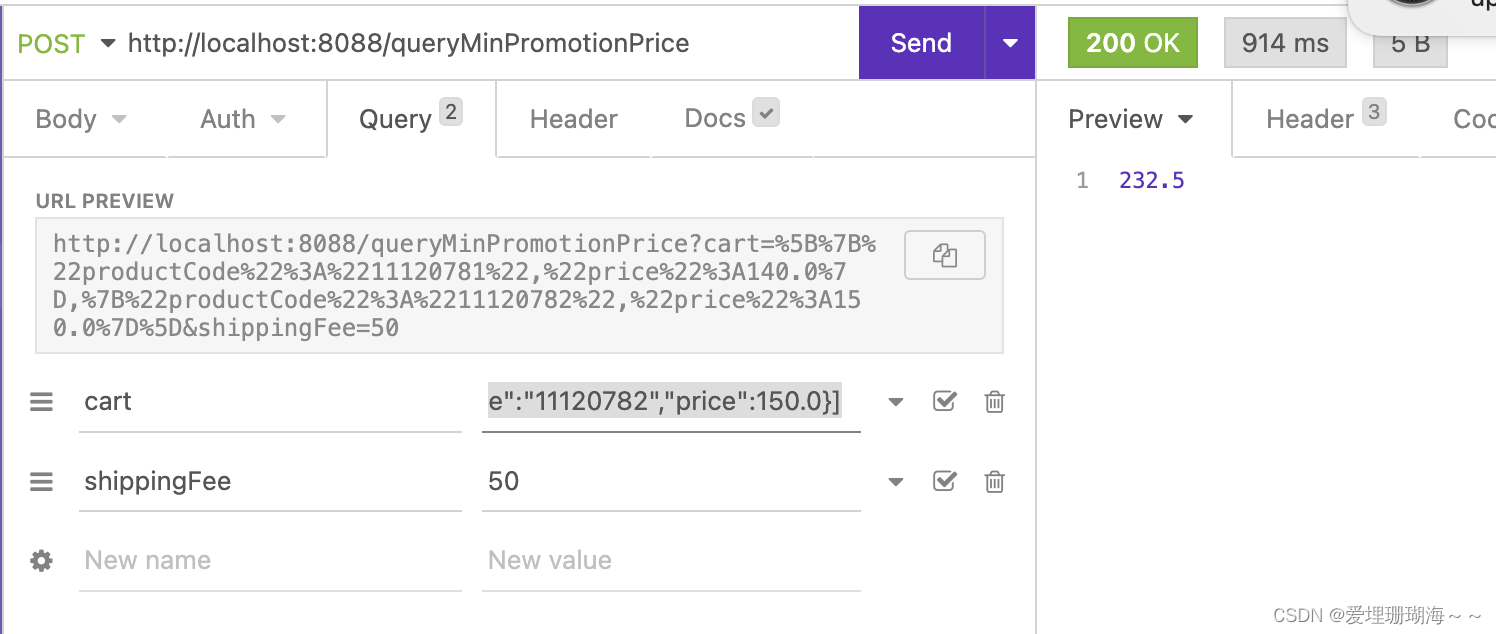
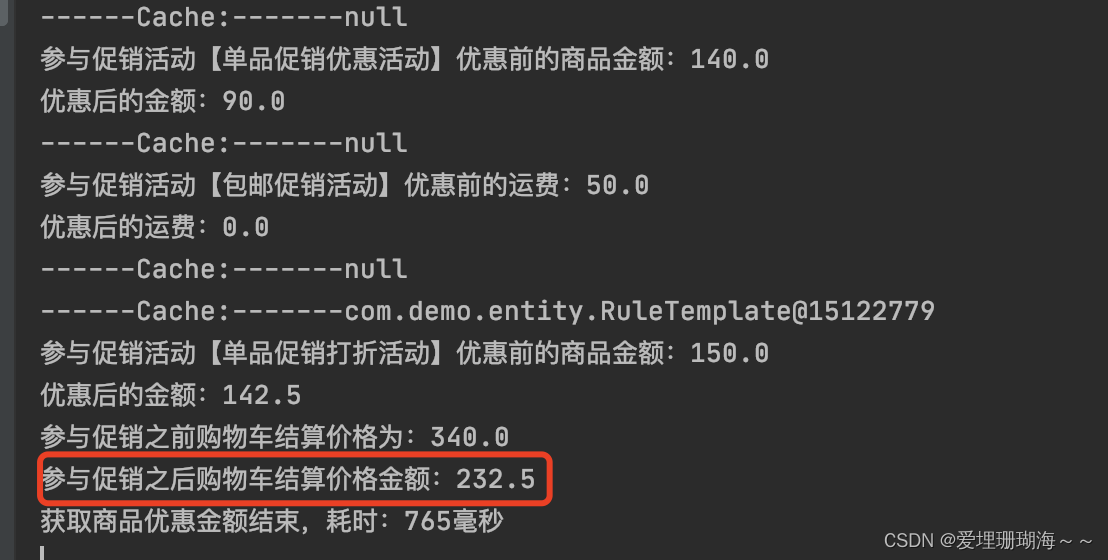
执行过程打印log信息如下图所示:



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号