Spring源码解析4——自定义标签的解析
1、解析函数入口
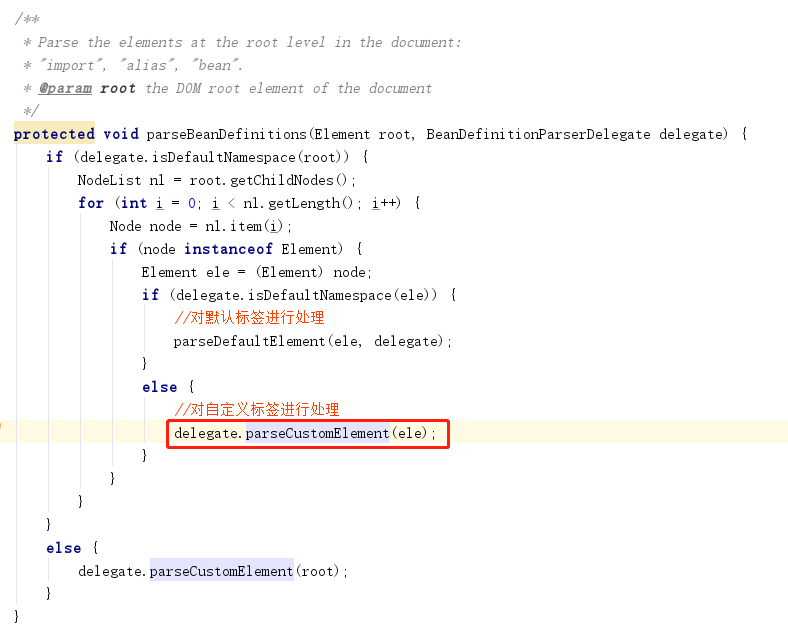
2、自定义标签的使用
Spring可以为系统提供可配置化支持,简单做法就是直接基于Spring的标准bean来配置,但是spring的标准bean在配置较为复杂或是需要更多丰富控制的时候,会显得非常笨拙。一般做法会用原生态的方式解析定义好的XML文件,然后转化为配置对象。
Spring提供了一种更简单的配置方式,可扩展的Schema的支持,这是一个简化复杂配置的方案,可扩展的Spring配置需要Spring-Core包的支持。
- 定义一个普通的POJO,只是用来接收配置文件
package xxx.xxx;
/**
* Created by chelong on 2020/9/19
*/
public class Product {
String productName;
String productPrice;
//省略getter和setter
}
- 定义一个XSD文件描述组件内容
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<schema xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
targetNamespace="http://www.lexueba.com/schema/product"
xmlns:tns="http://www.lexueba.com/schema/product"
elementFormDefault="qualified">
<element name="product">
<complexType>
<attribute name="id" type="string"/>
<attribute name="productName" type="string"/>
<attribute name="productPrice" type="string"/>
</complexType>
</element>
</schema>
①、xsd文件描述了一个新的targetNamespace;
②、并在这个空间中定义了一个name为product的element,product的3个属性id、productName和productPrice,其中这个三个属性的类型为string。这三个属性主要用于验证配置文件中自定义格式;
③、XSD文件是XML DTD的替代者,使用XSD Schema语言编写。
- 创建一个class,实现BeanDefinitionParser接口,解析xsd文件中的定义和组件定义
package xxx.xxx.customtag;
import xxx.xxx.Product;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionBuilder;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.AbstractSingleBeanDefinitionParser;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import org.w3c.dom.Element;
public class ProductBeanDefinitionParser extends AbstractSingleBeanDefinitionParser {
//获取Element对应的类
protected Class getBeanClass(Element element) {
return Product.class;
}
//从element中解析并提取对应的元素
protected void doParse(Element element, BeanDefinitionBuilder bean) {
String productName = element.getAttribute("productName");
String productPrice = element.getAttribute("productPrice");
//将提取的数据放入到BeanDefinitionBuilder.java类型的实例中,待到完成所有bean的解析后统一注册到beanFactory中。
if (StringUtils.hasText(productName)) {
bean.addPropertyValue("productName", productName);
}
if (StringUtils.hasText(productPrice)) {
bean.addPropertyValue("productPrice", productPrice);
}
}
}
- 创建一个Handler文件,扩展自NamespaceHandlerSupport,目的是将组件注册到Spring容器
package xxx.xxx.customtag;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.NamespaceHandlerSupport;
public class MyProductNamespaceHandler extends NamespaceHandlerSupport {
@Override
public void init() {
registerBeanDefinitionParser("product", new ProductBeanDefinitionParser());
}
}
- 1、编写spring.handlers和spring.schemas文件,默认位置是在工程的/META-INF/文件夹 下。2、也可以通过Spring的扩展或者修改源码的方式改变路径,不做方法2的介绍。
Spring.handlers
http\://wwww.lexueba.com/schema/product=xxx.xxx.customtag.MyProductNamespaceHandler
Spring.shemas
http\://www.lexueba.com/schema/product.xsd=product.xsd
- 编写spring的配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:mytag="http://www.lexueba.com/schema/product"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd
http://www.lexueba.com/schema/product http://www.lexueba.com/schema/product.xsd
">
<mytag:product id="productBean" productName="hugo" productPrice="18" />
</beans>
- main函数测试
package xxx.xxx.customtag;
import xxx.xxx.Product;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class testMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// org.springframework.beans.factory.parsing.BeanDefinitionParsingException: Configuration problem: Unable to locate Spring NamespaceHandler for XML schema namespace [http://www.lexueba.com/schema/product]
//Offending resource: class path resource [spring-product.xml]
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-product.xml");
Product product =(Product) context.getBean("productBean");
System.out.println(product.toString());
}
}
报错如下:

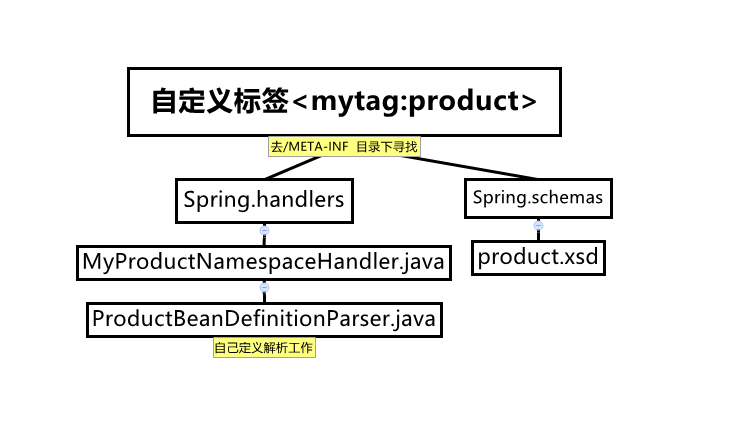
自定义解析流程:



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号