Spring源码解析2——默认标签的解析(一)
1、bean标签的解析及注册
1.1、bean标签解析前准备
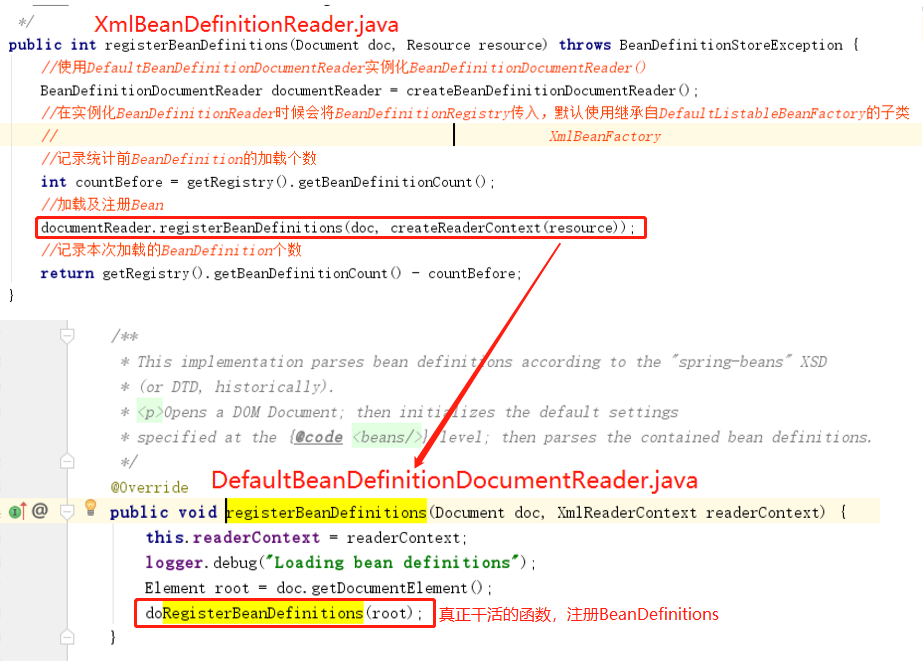
通过org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.BeanDefinitionParserDelegate类型的delegate对象和org.w3c.dom.Element类型的root对象,解析xml文件中的默认标签。

1.2、默认bean标签的解析
通过解析得到BeanDefinitionHolder类型的实例,经过这个方法后,BeanDefinitionHolder已经包含了我们配置文件的各种属性了,例如:class、name、id、alias之类。
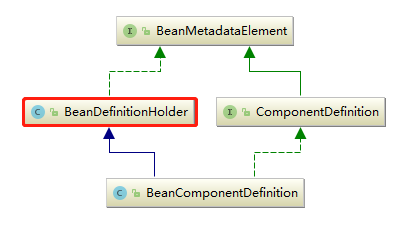
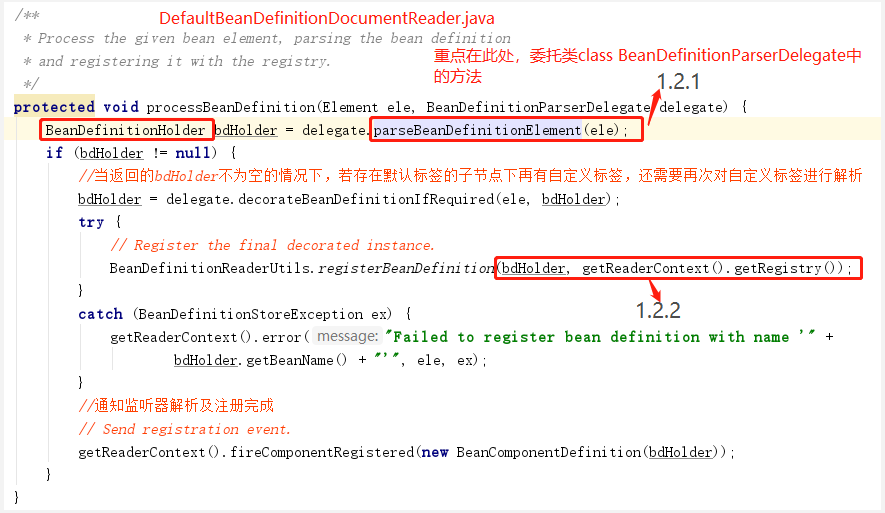
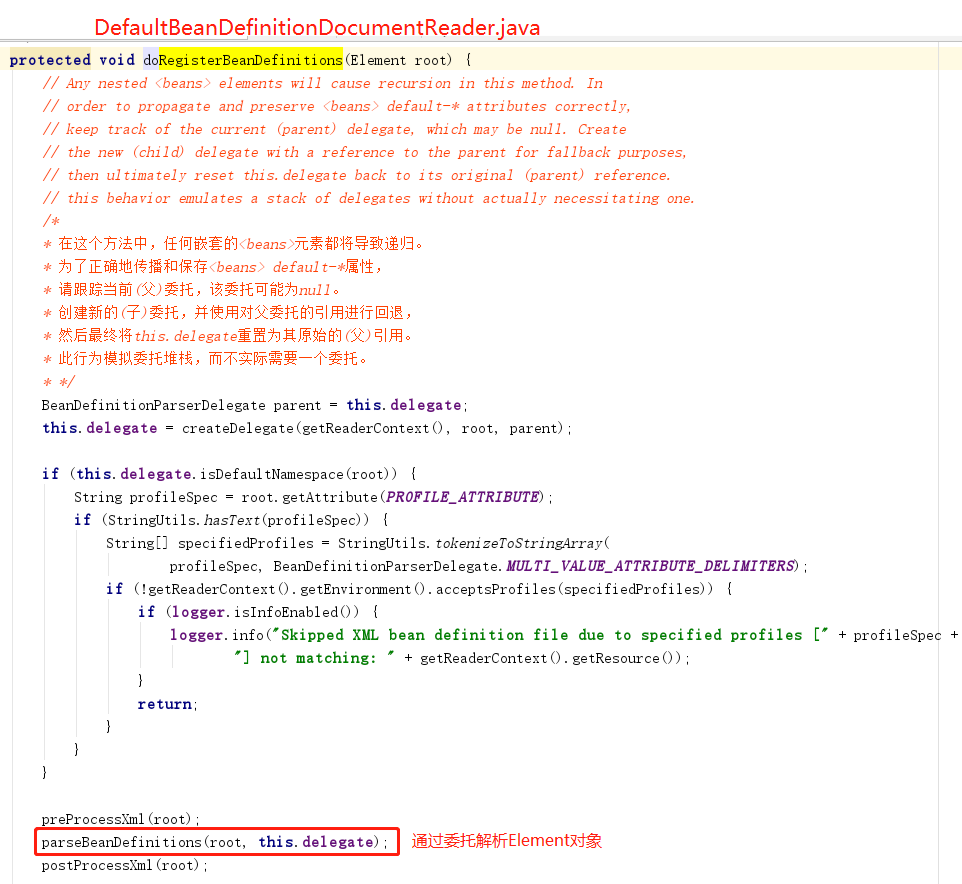
①、首先委托BeanDefinitionDelegate 类的parseBeanDefinitionElement() 方法进行元素析,返回BeanDefinitionHolder 类型的实例bdHolder , 经过这个方法后,bdHolder 实例已经包含我们配置文件中配置的各种属性了,例如class 、name、id 、alias 之类的属性。
②、当返回的bdHolder 不为空的情况下若存在默认标签的子节点下再有自定义属性, 还需要再次对自定义标签进行解析。
③、解析完成后, 需要对解析后的bdHolder 进行注册,同样, 注册操作委托给了BeanDefinitionReaderUtils 的registerBeanDefinition() 方法。
④、最后发出响应事件,通知相关的监昕器,这个bean 已经加载完成了。
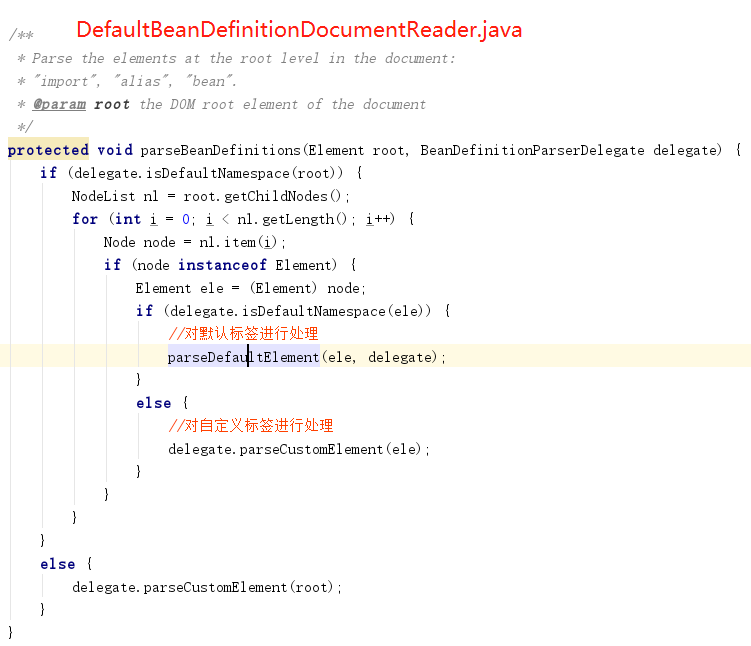
1.2.1、通过下面解析得到BeanDefinitionHolder类型的实例
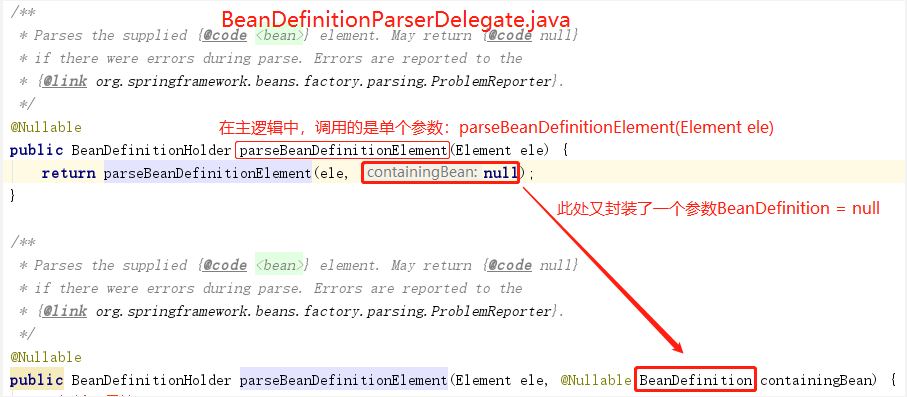
解析Element类型的实例ele,得到<bean
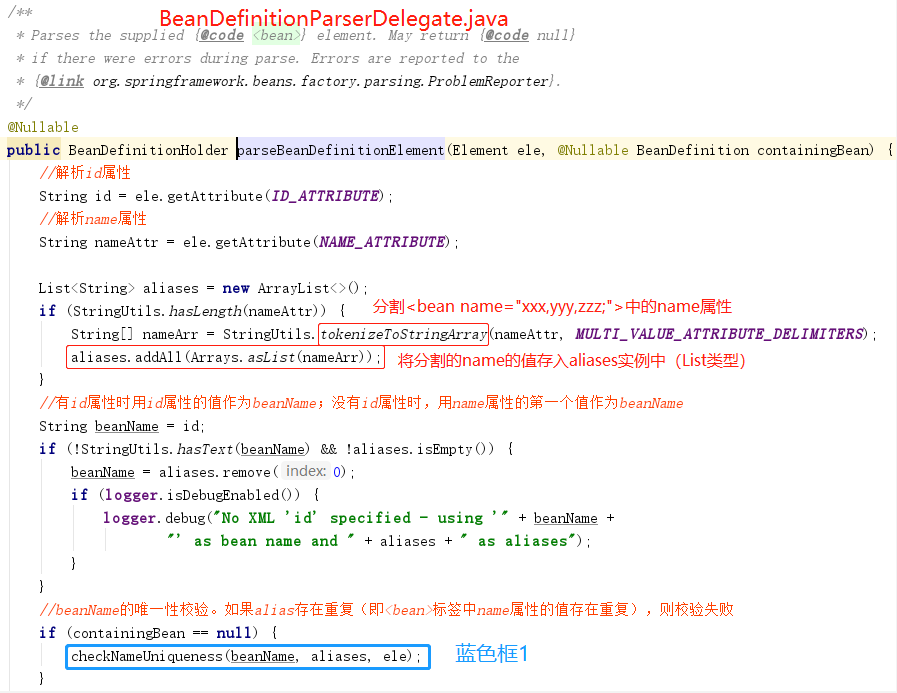

①、提取元素中的id 以及name 属性。
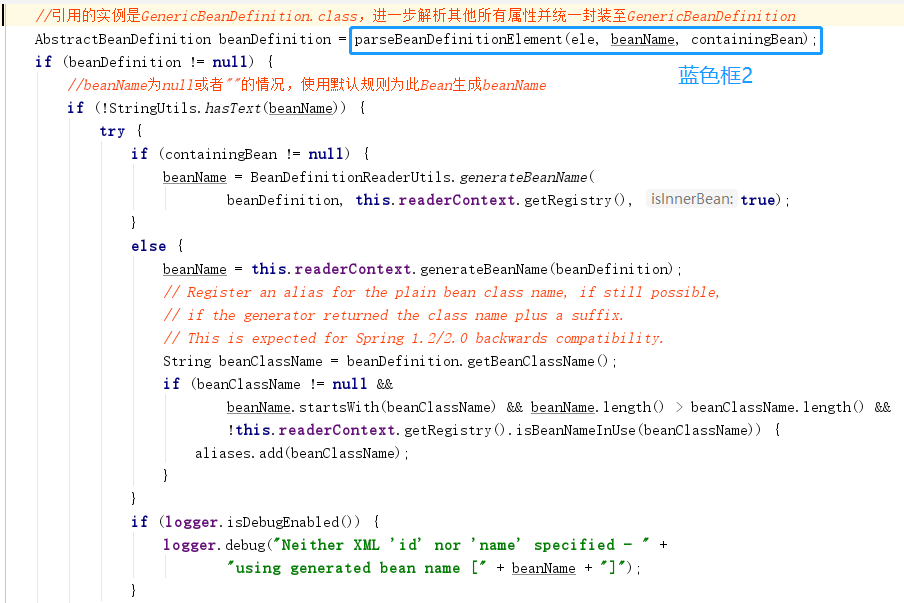
②、进一步解析其他所有属性并统一封装至GenericBeanDefinition 类型的实例中。
③、如果检测到bean 没有指定beanName ,那么使用默认规则为此Bean 生成beanName 。
④、将获取到的信息封装到BeanDefinitionHolder 的实例中。
上面图中的解析过程,蓝色框中的方法比较重要,对蓝色框的逻辑分析:
-
蓝色框1:
![clipboard]()
-
蓝色框1-findFirshMatch()
![clipboard]()
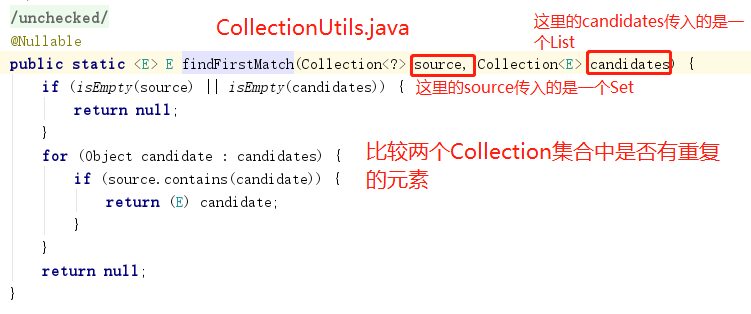
此处为Spring框架定义的集合操作工具类(CollectionUtils.java),findFirstMatch(Collection<?> source,Collection<E
- 蓝色框2:
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.java
@Nullable
public AbstractBeanDefinition parseBeanDefinitionElement(
Element ele, String beanName, @Nullable BeanDefinition containingBean) {
//用来记录正在加载的beanName
this.parseState.push(new BeanEntry(beanName));
//解析class属性
String className = null;
if (ele.hasAttribute(CLASS_ATTRIBUTE)) {
className = ele.getAttribute(CLASS_ATTRIBUTE).trim();
}
//解析parent属性
String parent = null;
if (ele.hasAttribute(PARENT_ATTRIBUTE)) {
parent = ele.getAttribute(PARENT_ATTRIBUTE);
}
try {
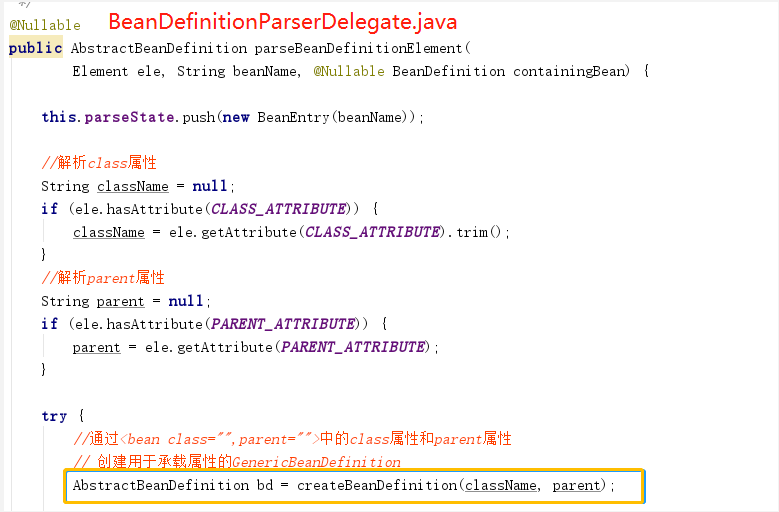
//通过<bean class="",parent="">中的class属性和parent属性
// 创建用于承载属性的GenericBeanDefinition
AbstractBeanDefinition bd = createBeanDefinition(className, parent);
//硬编码解析默认bean的各种属性
parseBeanDefinitionAttributes(ele, beanName, containingBean, bd);
//提取description
bd.setDescription(DomUtils.getChildElementValueByTagName(ele, DESCRIPTION_ELEMENT));
//解析元数据
parseMetaElements(ele, bd);
//解析lookup-method属性,动态替换抽象方法的返回值
parseLookupOverrideSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides());
//解析replaced-method属性,动态替换原有方法
parseReplacedMethodSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides());
//解析构造函数
parseConstructorArgElements(ele, bd);
//解析property子元素
parsePropertyElements(ele, bd);
//解析qualifier子元素
parseQualifierElements(ele, bd);
bd.setResource(this.readerContext.getResource());
bd.setSource(extractSource(ele));
return bd;
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
error("Bean class [" + className + "] not found", ele, ex);
}
catch (NoClassDefFoundError err) {
error("Class that bean class [" + className + "] depends on not found", ele, err);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
error("Unexpected failure during bean definition parsing", ele, ex);
}
finally {
this.parseState.pop();
}
return null;
}
- 蓝色框2-ParseState.java:
![clipboard]()
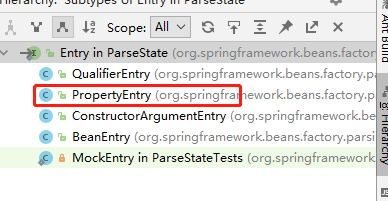
final class ParseState 和 interface Entry 的关系类图:
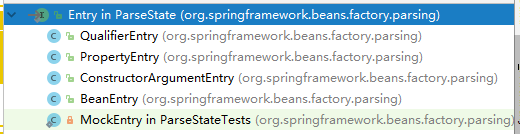
Spring中的ParseState.java是对JDK中的LinkedList<E
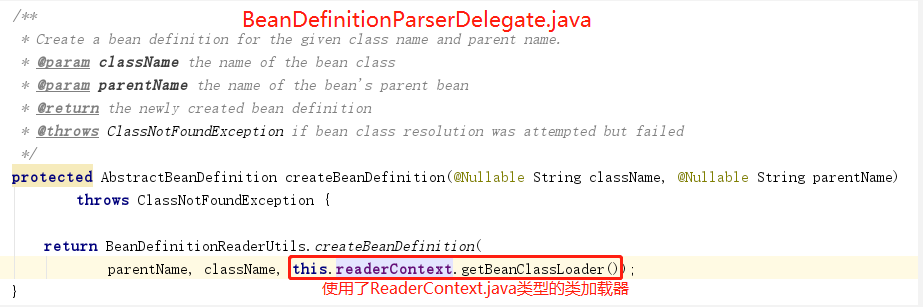
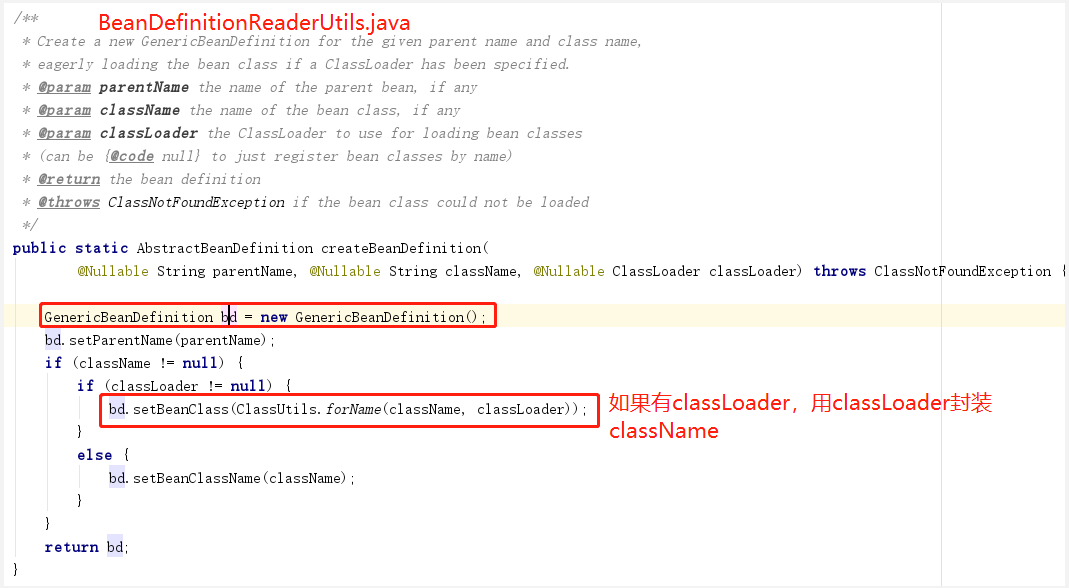
- 蓝色框2-createBeanDefinition():
![clipboard]()
![clipboard]()
![clipboard]()
GenericBeanDefinition.java的UML图:
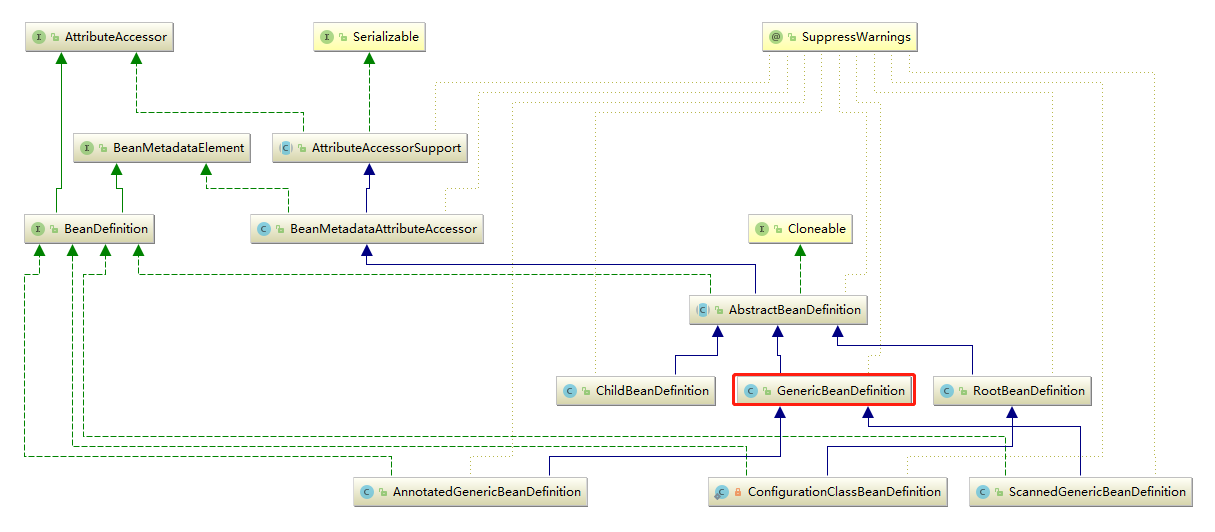
BeanDefinition是一个接口,在Spring中存在三种实现:RootBeanDefinition.java、ChildBeanDefinition.java、GenericBeanDefinition.java。三种实现均继承了AbstractBeanDefinition.abstract。BeanDefinition.interface是<bean
<
Spring3.0以后,用的官方建议用GenericBeanDefinition.java替代RootBeanDefinition.java、ChildBeanDefinition.java。
- 蓝色框2-parseBeanDefinitionAttributes():
硬编码解析:scope、singleton、abstract、lazy-init、dependency-on属性,存入GenericBeanDefinition.java中
/**
* Apply the attributes of the given bean element to the given bean * definition.
* @param ele bean declaration element
* @param beanName bean name
* @param containingBean containing bean definition
* @return a bean definition initialized according to the bean element attributes
*/
public AbstractBeanDefinition parseBeanDefinitionAttributes(Element ele, String beanName,
@Nullable BeanDefinition containingBean, AbstractBeanDefinition bd) {
//解析scope属性或者singleton属性,scope和singleton只能指定其中指定其中一个,否则会报错
if (ele.hasAttribute(SINGLETON_ATTRIBUTE)) {
error("Old 1.x 'singleton' attribute in use - upgrade to 'scope' declaration", ele);
}
else if (ele.hasAttribute(SCOPE_ATTRIBUTE)) {
bd.setScope(ele.getAttribute(SCOPE_ATTRIBUTE));
}
else if (containingBean != null) {
// Take default from containing bean in case of an inner bean definition.
//在嵌入beanDefinition情况下,且没有单独指定scope属性则使用父类默认的属性。
bd.setScope(containingBean.getScope());
}
//解析abstract属性
if (ele.hasAttribute(ABSTRACT_ATTRIBUTE)) {
bd.setAbstract(TRUE_VALUE.equals(ele.getAttribute(ABSTRACT_ATTRIBUTE)));
}
//解析lazy-init属性
String lazyInit = ele.getAttribute(LAZY_INIT_ATTRIBUTE);
if (isDefaultValue(lazyInit)) {
lazyInit = this.defaults.getLazyInit();
}
//如果没有设置或设置成其他字符,都会被设置为false
bd.setLazyInit(TRUE_VALUE.equals(lazyInit));
//解析autowire属性
String autowire = ele.getAttribute(AUTOWIRE_ATTRIBUTE);
bd.setAutowireMode(getAutowireMode(autowire));
//解析dependency-on属性
if (ele.hasAttribute(DEPENDS_ON_ATTRIBUTE)) {
String dependsOn = ele.getAttribute(DEPENDS_ON_ATTRIBUTE);
bd.setDependsOn(StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(dependsOn, MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS));
}
//解析autowire-candidate属性
String autowireCandidate = ele.getAttribute(AUTOWIRE_CANDIDATE_ATTRIBUTE);
if (isDefaultValue(autowireCandidate)) {
String candidatePattern = this.defaults.getAutowireCandidates();
if (candidatePattern != null) {
String[] patterns = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(candidatePattern);
bd.setAutowireCandidate(PatternMatchUtils.simpleMatch(patterns, beanName));
}
}
else {
bd.setAutowireCandidate(TRUE_VALUE.equals(autowireCandidate));
}
//解析primary属性
if (ele.hasAttribute(PRIMARY_ATTRIBUTE)) {
bd.setPrimary(TRUE_VALUE.equals(ele.getAttribute(PRIMARY_ATTRIBUTE)));
}
//解析init-method属性
if (ele.hasAttribute(INIT_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE)) {
String initMethodName = ele.getAttribute(INIT_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE);
bd.setInitMethodName(initMethodName);
}
else if (this.defaults.getInitMethod() != null) {
bd.setInitMethodName(this.defaults.getInitMethod());
bd.setEnforceInitMethod(false);
}
//解析destroy-method属性
if (ele.hasAttribute(DESTROY_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE)) {
String destroyMethodName = ele.getAttribute(DESTROY_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE);
bd.setDestroyMethodName(destroyMethodName);
}
else if (this.defaults.getDestroyMethod() != null) {
bd.setDestroyMethodName(this.defaults.getDestroyMethod());
bd.setEnforceDestroyMethod(false);
}
//解析factory-method属性
if (ele.hasAttribute(FACTORY_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE)) {
bd.setFactoryMethodName(ele.getAttribute(FACTORY_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE));
}
//解析factory-bean属性
if (ele.hasAttribute(FACTORY_BEAN_ATTRIBUTE)) {
bd.setFactoryBeanName(ele.getAttribute(FACTORY_BEAN_ATTRIBUTE));
}
return bd;
}
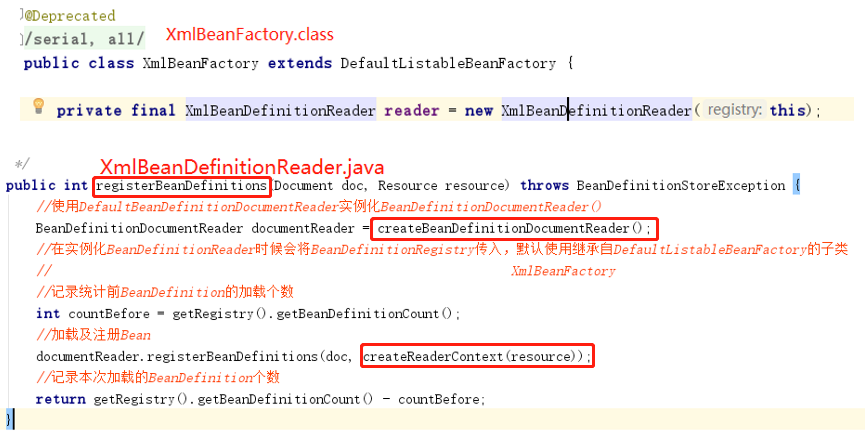
1.2.2、将得到的BeanDefinitionHolder.java类型的实例,里面存储着<bean>的配置信息,注册到BeanDefinitionRegistry.interface类型的实例XmlBeanFactory.java中。Spring容器的BeanDefinitionRegistry.interface就像是Spring配置信息的数据库,主要是以map形式保存,后续直接从BeanDefinitionRegistry.interface(implement XmlBeanFactory.java)中拿数据。

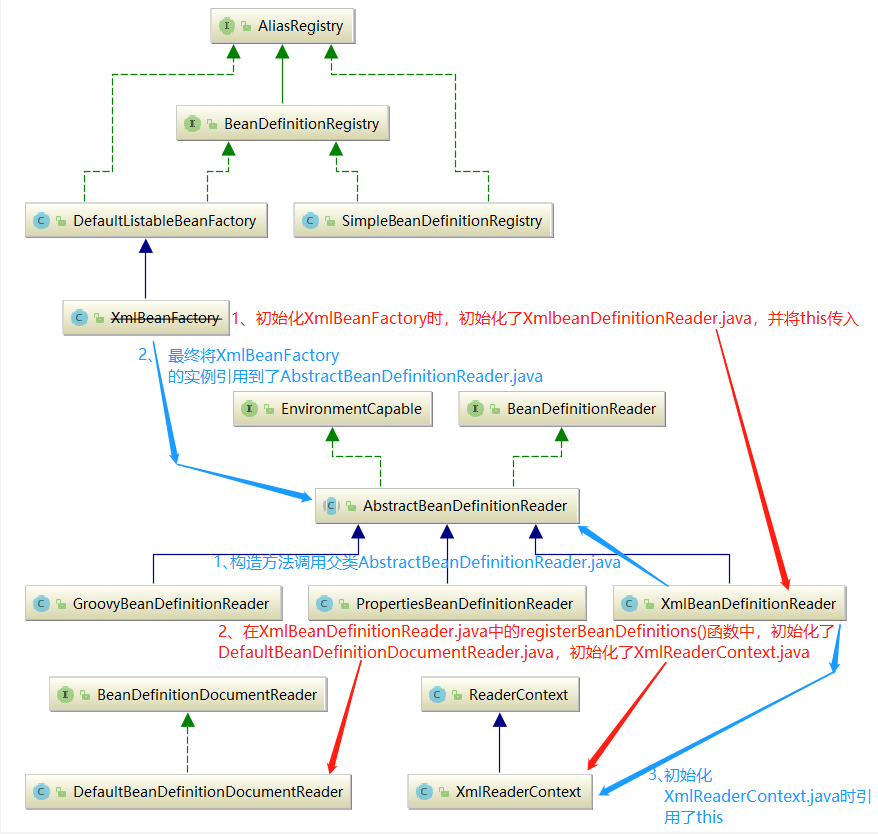
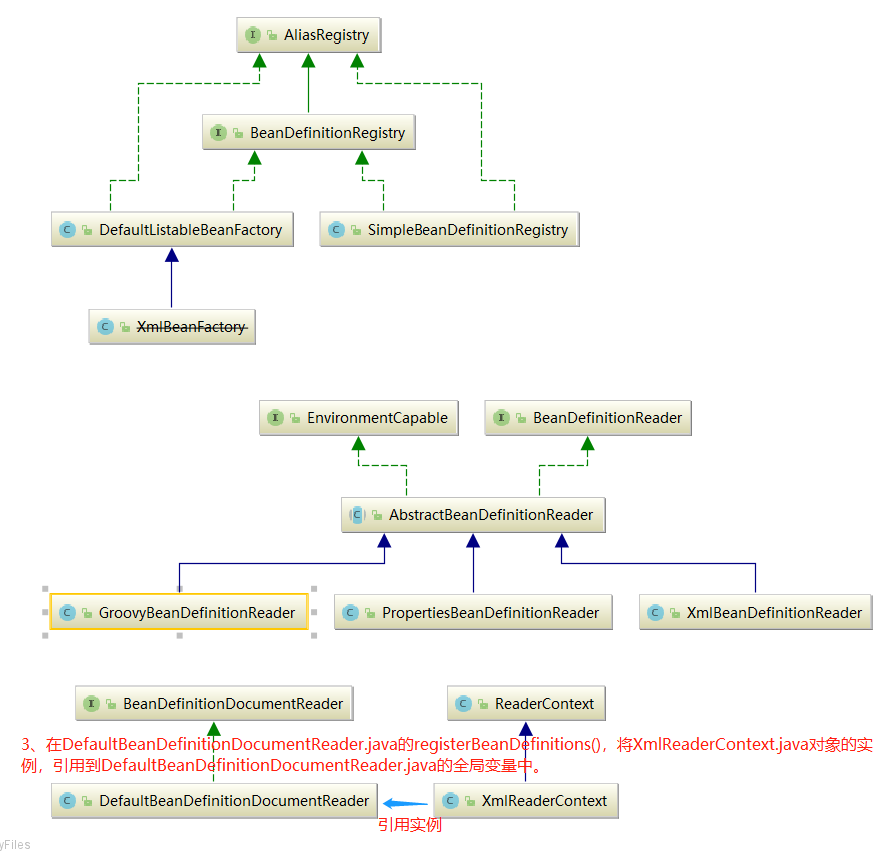
蓝色线条调用顺序:1->2、3

在Spring中有很多class通过在其他class的构造函数传入this来达到将该实例本身传递到下一个class实例中,以达到单例效果。
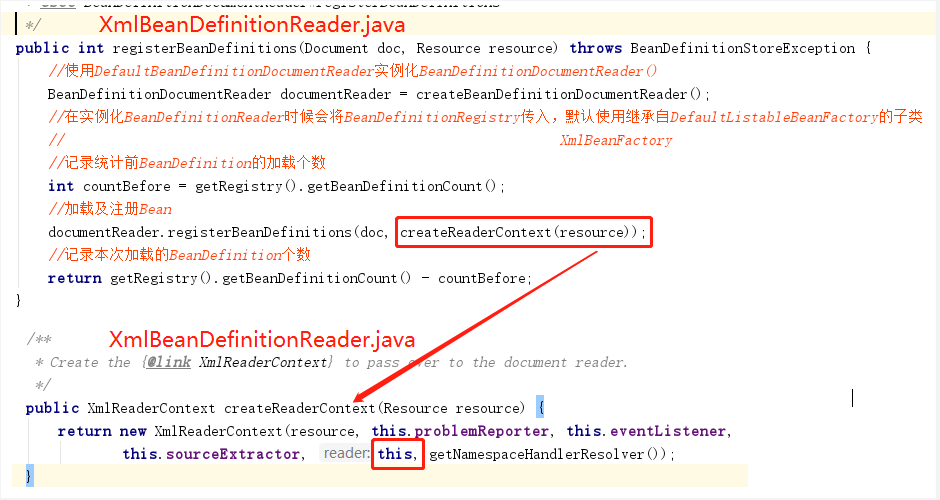
红色线条调用顺序:1->2
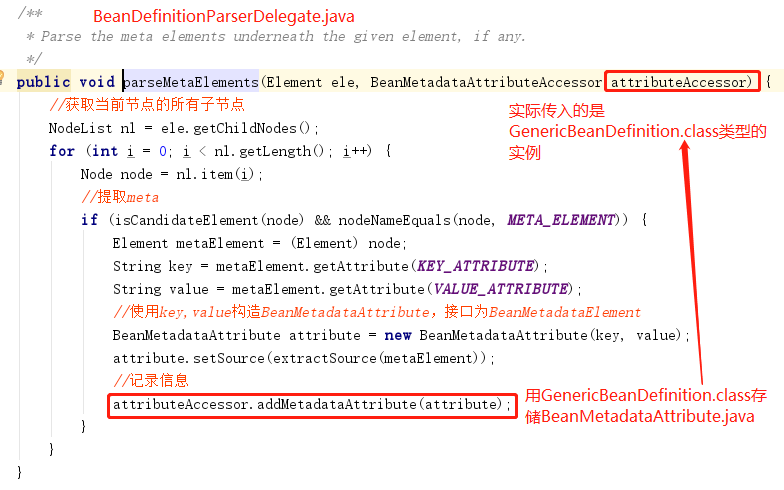
1.2.3、解析子元素<meta>
- meta元素的使用
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="testBean" name="testBean2,testBean3;" class="xxx.xxx.TestBean">
<meta key="testStr" value="meta"></meta>
</bean>
</beans>
package xxx.xxx;
public class TestBean {
}
package xxx.xxx;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;
public class AppTest {
@Test
public void testBean() {
BeanFactory beanFactory = new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource("spring-bean.xml"));
System.out.println(((XmlBeanFactory) beanFactory).getBeanDefinition("testBean").getAttribute("testStr"));
}
}
这段代码并不会体现在TestBean.java 的属性当中,而是一个额外的声明,当需要使用里面的信息的时候可以通过BeanDefinition 的getAttribute(key)方法进行获取。
BeanMeatadataAttribute.java implement BeanMetadataElement.interface
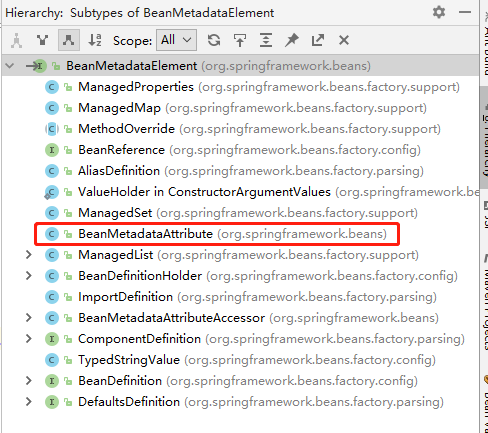
1.2.4、解析子元素<lookup-method>
子元素<lookup-method
它是把一个方法声明为返回某种类型的bean ,但实际要返回的bean 是在配置文件里面配置的,此方法可用在设计有些可插拔的功能上,解除程序依赖。
- 首先我们创建一个父类。
package xxx.xxx.lookupmethod;
public class Animal {
public void showMe(){
System.out.println("Animal...");
}
}
- 创建其子类并覆盖showMe 方法。
package xxx.xxx.lookupmethod;
public class Dog extends Animal {
public void showMe(){
System.out.println("Dog");
}
}
- 创建调用方法。
package xxx.xxx.lookupmethod;
public abstract class GetAnimalBean {
public void showMe(){
this.getBean().showMe();
}
public abstract Animal getBean();
}
- 配置文件spring-lookUpMethod.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="dog" class="xxx.xxx.lookupmethod.Dog" scope="prototype"/>
<bean id="getAnimalBean" class="xxx.xxx.lookupmethod.GetAnimalBean">
<lookup-method name="getBean" bean="dog"/>
</bean>
</beans>
- 创建测试方法。
package xxx.xxx.lookupmethod;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class testMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Caused by: org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCreationException: Error creating bean with name 'getAnimalBean' defined in class path resource [spring-lookUpMethod.xml]: Instantiation of bean failed; nested exception is java.lang.ExceptionInInitializerError
// at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.instantiateBean(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:1258)
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-lookUpMethod.xml");
GetAnimalBean bean = (GetAnimalBean) context.getBean("getAnimalBean");
bean.showMe();
}
}
报错如下

按照上面的配置和编写实体类,我们的java代码通过ApplicationContext在获取GetAnimalBean类型的实例中报错了,目前还没有找到问题的原因。
下面是Spring解析<lookup-mehtod


上面的代码逻辑与parseMetaElements()(1.2.3、解析子元素<meta>)大同小异,最大的区别就是在if 判断中的节点名称在这里被修改为LOOKUP_METHOD_ELEMENT。还有,在数据存储上面通过使用LookupOverride 类型的实体类来进行数据承载并记录在AbstractBeanDefinition.java(GenericBeanDefinition.java extends AbstractBeanDefinition.java)中的methodOverrides 属性中。methodOverrides的实例中封装了一个Set<MethodOverride
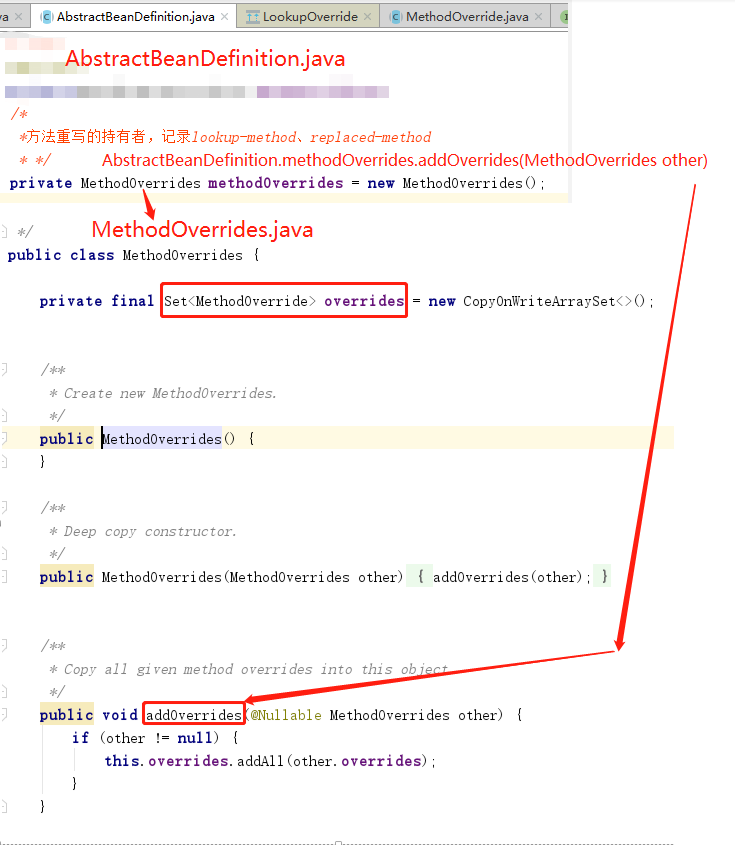
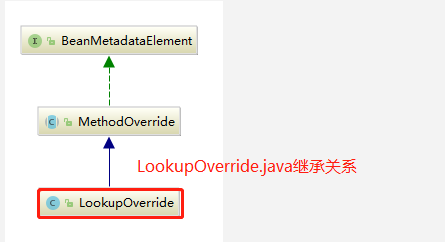
1.2.5、解析子元素
- 被替代的方法
package xxx.xxx.replacedmethod;
public class ChangeMethod {
public void originalFun(){
System.out.println("changeMe...");
}
}
- 替代的方法(替代者)
package xxx.xxx.replacedmethod;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.MethodReplacer;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class ReplacerMethod implements MethodReplacer {
@Override
public Object reimplement(Object obj, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("我替换了原有方法...");
return null;
}
}
- 配置替代者生效spring-replacedMethod.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="replacer" class="xxx.xxx.replacedmethod.ReplacerMethod"/>
<bean id="changeMethod" class="xxx.xxx.replacedmethod.ChangeMethod">
<replaced-method name="originalFun" replacer="replacer"/>
</bean>
</beans>
- main方法测试
package xxx.xxx.replacedmethod;
import xxx.xxx.lookupmethod.GetAnimalBean;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class testMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-replacedMethod.xml");
ChangeMethod bean = (ChangeMethod) context.getBean("changeMethod");
bean.originalFun();
}
}
报错如下(和1.2.4<lookup-method
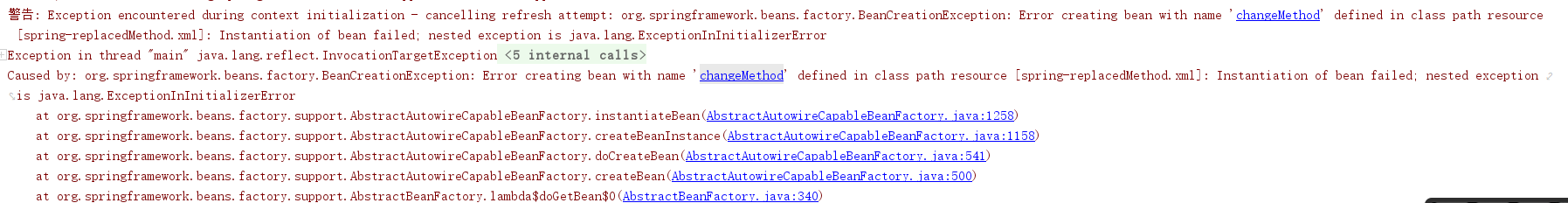
下面是Spring解析<replaced-method

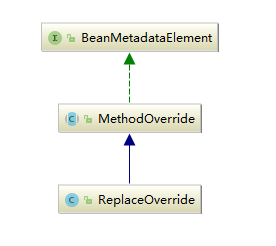
我们可以看到无论是<look-up
1.2.6、解析子元素<constructor-arg>
- 首先创建一个java的Bean
package xxx.xxx.constructorArg;
public class ConstructorBean {
private String username;
private String password;
public ConstructorBean(String username, String password) {
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "ConstructorBean{" +
"username='" + username + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
- 用xml文件对构造函数进行配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="constructorBean" class="xxx.xxx.constructorArg.ConstructorBean">
<constructor-arg index="0">
<value>chenglong</value>
</constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg index="1">
<value>******</value>
</constructor-arg>
</bean>
</beans>
- 用ClassPathXmlApplicaitonContext实例函数加载
package xxx.xxx.constructorArg;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class testMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-constructorBean.xml");
ConstructorBean bean = (ConstructorBean) context.getBean("constructorBean");
System.out.println(bean);
}
}
下面是Spring解析<constructor-arg

/**
* Parse a constructor-arg element.
*/
public void parseConstructorArgElement(Element ele, BeanDefinition bd) {
//提取index属性
String indexAttr = ele.getAttribute(INDEX_ATTRIBUTE);
//提取type属性
String typeAttr = ele.getAttribute(TYPE_ATTRIBUTE);
//提取name属性
String nameAttr = ele.getAttribute(NAME_ATTRIBUTE);
if (StringUtils.hasLength(indexAttr)) {
try {
int index = Integer.parseInt(indexAttr);
if (index < 0) {
error("'index' cannot be lower than 0", ele);
}
else {
try {
this.parseState.push(new ConstructorArgumentEntry(index));
//解析<constructor-arg>标签下对应的子标签
Object value = parsePropertyValue(ele, bd, null);
ConstructorArgumentValues.ValueHolder valueHolder = new ConstructorArgumentValues.ValueHolder(value);
if (StringUtils.hasLength(typeAttr)) {
valueHolder.setType(typeAttr);
}
if (StringUtils.hasLength(nameAttr)) {
valueHolder.setName(nameAttr);
}
valueHolder.setSource(extractSource(ele));
//不允许重复指定相同的参数
if (bd.getConstructorArgumentValues().hasIndexedArgumentValue(index)) {
error("Ambiguous constructor-arg entries for index " + index, ele);
}
else {
bd.getConstructorArgumentValues().addIndexedArgumentValue(index, valueHolder);
}
}
finally {
this.parseState.pop();
}
}
}
catch (NumberFormatException ex) {
error("Attribute 'index' of tag 'constructor-arg' must be an integer", ele);
}
}
else {
try {
//没有index属性则忽略此属性,自动寻找构造函数中对应的参数
this.parseState.push(new ConstructorArgumentEntry());
Object value = parsePropertyValue(ele, bd, null);
ConstructorArgumentValues.ValueHolder valueHolder = new ConstructorArgumentValues.ValueHolder(value);
if (StringUtils.hasLength(typeAttr)) {
valueHolder.setType(typeAttr);
}
if (StringUtils.hasLength(nameAttr)) {
valueHolder.setName(nameAttr);
}
valueHolder.setSource(extractSource(ele));
bd.getConstructorArgumentValues().addGenericArgumentValue(valueHolder);
}
finally {
this.parseState.pop();
}
}
}
逻辑梳理:配置中指定了index属性:
①、解析Constructor-arg 的子元素。
②、使用ConstructorArgumentValues. ValueHolder 类型来封装解析出来的元素。
③、将type 、name 和index 属性一并封装在ConstructorArgumentValues. ValueHolder 类型中并添加至当前BeanDefinition 的constructorArgumentValues 的indexedArgumentValues 属性中。
配置中没有指定index属性:
①、解析constructor-arg 的子元素。
②、使用ConstructorArgumentValues. ValueHolder 类型来封装解析出来的元素。
③、将type 、name 和index 属性一并封装在ConstructorArgumentValues.ValueHolder 类型中并添加至当前BeanDefinition 的constructorArgumentValues 的genericArgumentValues 属性中。
解析<constructor-arg
/**
* Get the value of a property element. May be a list etc.
* Also used for constructor arguments, "propertyName" being null in this case.
*/
@Nullable
public Object parsePropertyValue(Element ele, BeanDefinition bd, @Nullable String propertyName) {
String elementName = (propertyName != null ?
"<property> element for property '" + propertyName + "'" :
"<constructor-arg> element");
//一个<constructor-arg>标签下只能包含一种子元素:<ref>,<value>,<list>等
// Should only have one child element: ref, value, list, etc.
NodeList nl = ele.getChildNodes();
Element subElement = null;
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
//对应的description或者meta不处理
if (node instanceof Element && !nodeNameEquals(node, DESCRIPTION_ELEMENT) &&
!nodeNameEquals(node, META_ELEMENT)) {
// Child element is what we're looking for.
if (subElement != null) {
error(elementName + " must not contain more than one sub-element", ele);
}
else {
subElement = (Element) node;
}
}
}
//解析constructor-arg上的ref属性
boolean hasRefAttribute = ele.hasAttribute(REF_ATTRIBUTE);
//解析constructor-arg上的value属性
boolean hasValueAttribute = ele.hasAttribute(VALUE_ATTRIBUTE);
if ((hasRefAttribute && hasValueAttribute) ||
((hasRefAttribute || hasValueAttribute) && subElement != null)) {
/*在constructor-arg上不存在:
* 1、同时既有ref属性,又有value属性
* 2、存在ref属性或者value属性且又有子元素
* */
error(elementName +
" is only allowed to contain either 'ref' attribute OR 'value' attribute OR sub-element", ele);
}
if (hasRefAttribute) {
//ref属性的处理,使用RuntimeBeanReference封装对应的ref名称
String refName = ele.getAttribute(REF_ATTRIBUTE);
if (!StringUtils.hasText(refName)) {
error(elementName + " contains empty 'ref' attribute", ele);
}
RuntimeBeanReference ref = new RuntimeBeanReference(refName);
ref.setSource(extractSource(ele));
return ref;
}
else if (hasValueAttribute) {
//value属性的处理,使用TypedStringValue封装
TypedStringValue valueHolder = new TypedStringValue(ele.getAttribute(VALUE_ATTRIBUTE));
valueHolder.setSource(extractSource(ele));
return valueHolder;
}
else if (subElement != null) {
//解析子元素
return parsePropertySubElement(subElement, bd);
}
else {
//既没有ref也没有value也没有子元素,Spring就会报错
// Neither child element nor "ref" or "value" attribute found.
error(elementName + " must specify a ref or value", ele);
return null;
}
}
从代码上来看,对构造函数中属性元素的解析,经历了以下几个过程:
1、 略过description 或者meta 。
2、 提取constructor-arg 上的ref 和 value 属性,以便于根据规则验证正确性,其规则为在constructor-arg 上不存在以下情况:
①、同时既有ref 属性又有value 属性。
②、存在ref 属性或者value 属性且又有子元素。
3、ref 属性的处理。使用RuntimeBeanReference 封装对应的ref 名称,如:<constructor-arg ref="a"
4、value属性的处理。使用TypedStringValue 封装,如:<constructor-arg value=” a ” <constructor-arg value=” a ” >>
5. 子元素的处理,如下代码:
<constructor-arg>
<map>
<entry key=” key ” value=” value” />
</map>
</constructor- arg>
而对于子元素的处理, 例如这里提到的在构造函数中又嵌入了子元素<value
/**
* Parse a value, ref or collection sub-element of a property or
* constructor-arg element.
* @param ele subelement of property element; we don't know which yet
* @param bd the current bean definition (if any)
*/
@Nullable
public Object parsePropertySubElement(Element ele, @Nullable BeanDefinition bd) {
return parsePropertySubElement(ele, bd, null);
}
/**
* Parse a value, ref or collection sub-element of a property or
* constructor-arg element.
* @param ele subelement of property element; we don't know which yet
* @param bd the current bean definition (if any)
* @param defaultValueType the default type (class name) for any
* {@code <value>} tag that might be created
*/
@Nullable
public Object parsePropertySubElement(Element ele, @Nullable BeanDefinition bd, @Nullable String defaultValueType) {
if (!isDefaultNamespace(ele)) {
return parseNestedCustomElement(ele, bd);
}
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, BEAN_ELEMENT)) {
BeanDefinitionHolder nestedBd = parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele, bd);
if (nestedBd != null) {
nestedBd = decorateBeanDefinitionIfRequired(ele, nestedBd, bd);
}
return nestedBd;
}
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, REF_ELEMENT)) {
// A generic reference to any name of any bean.
String refName = ele.getAttribute(BEAN_REF_ATTRIBUTE);
boolean toParent = false;
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(refName)) {
// A reference to the id of another bean in a parent context.
//解析parent
refName = ele.getAttribute(PARENT_REF_ATTRIBUTE);
toParent = true;
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(refName)) {
error("'bean' or 'parent' is required for <ref> element", ele);
return null;
}
}
if (!StringUtils.hasText(refName)) {
error("<ref> element contains empty target attribute", ele);
return null;
}
RuntimeBeanReference ref = new RuntimeBeanReference(refName, toParent);
ref.setSource(extractSource(ele));
return ref;
}
//对idref元素的解析
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, IDREF_ELEMENT)) {
return parseIdRefElement(ele);
}
//对value子元素的解析
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, VALUE_ELEMENT)) {
return parseValueElement(ele, defaultValueType);
}
//对null子元素的解析
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, NULL_ELEMENT)) {
// It's a distinguished null value. Let's wrap it in a TypedStringValue
// object in order to preserve the source location.
TypedStringValue nullHolder = new TypedStringValue(null);
nullHolder.setSource(extractSource(ele));
return nullHolder;
}
//解析array子元素
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, ARRAY_ELEMENT)) {
return parseArrayElement(ele, bd);
}
//解析list子元素
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, LIST_ELEMENT)) {
return parseListElement(ele, bd);
}
//解析set子元素
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, SET_ELEMENT)) {
return parseSetElement(ele, bd);
}
//解析map子元素
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, MAP_ELEMENT)) {
return parseMapElement(ele, bd);
}
//解析props子元素
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, PROPS_ELEMENT)) {
return parsePropsElement(ele);
}
else {
error("Unknown property sub-element: [" + ele.getNodeName() + "]", ele);
return null;
}
}
1.2.7、解析子元素<property>
/**
* Parse property sub-elements of the given bean element.
*/
public void parsePropertyElements(Element beanEle, BeanDefinition bd) {
NodeList nl = beanEle.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
if (isCandidateElement(node) && nodeNameEquals(node, PROPERTY_ELEMENT)) {
parsePropertyElement((Element) node, bd);
}
}
}

解析<property
/**
* Get the value of a property element. May be a list etc.
* Also used for constructor arguments, "propertyName" being null in this case.
*/
//通过是否传入String propertyName区别要解析的Element。
//1、propertyName=null,要解析的Element为<constructor-arg>;2、propertyName="xxx",要解析的Element为<property name="xxx">
@Nullable
public Object parsePropertyValue(Element ele, BeanDefinition bd, @Nullable String propertyName) {
String elementName = (propertyName != null ?
"<property> element for property '" + propertyName + "'" :
"<constructor-arg> element");
//一个<constructor-arg>标签下只能包含一种子元素:<ref>,<value>,<list>等
// Should only have one child element: ref, value, list, etc.
NodeList nl = ele.getChildNodes();
Element subElement = null;
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
//对应的description或者meta不处理
if (node instanceof Element && !nodeNameEquals(node, DESCRIPTION_ELEMENT) &&
!nodeNameEquals(node, META_ELEMENT)) {
// Child element is what we're looking for.
if (subElement != null) {
error(elementName + " must not contain more than one sub-element", ele);
}
else {
subElement = (Element) node;
}
}
}
//解析constructor-arg上的ref属性
boolean hasRefAttribute = ele.hasAttribute(REF_ATTRIBUTE);
//解析constructor-arg上的value属性
boolean hasValueAttribute = ele.hasAttribute(VALUE_ATTRIBUTE);
if ((hasRefAttribute && hasValueAttribute) ||
((hasRefAttribute || hasValueAttribute) && subElement != null)) {
/*在constructor-arg上不存在:
* 1、同时既有ref属性,又有value属性
* 2、存在ref属性或者value属性且又有子元素
* */
error(elementName +
" is only allowed to contain either 'ref' attribute OR 'value' attribute OR sub-element", ele);
}
if (hasRefAttribute) {
//ref属性的处理,使用RuntimeBeanReference封装对应的ref名称
String refName = ele.getAttribute(REF_ATTRIBUTE);
if (!StringUtils.hasText(refName)) {
error(elementName + " contains empty 'ref' attribute", ele);
}
RuntimeBeanReference ref = new RuntimeBeanReference(refName);
ref.setSource(extractSource(ele));
return ref;
}
else if (hasValueAttribute) {
//value属性的处理,使用TypedStringValue封装
TypedStringValue valueHolder = new TypedStringValue(ele.getAttribute(VALUE_ATTRIBUTE));
valueHolder.setSource(extractSource(ele));
return valueHolder;
}
else if (subElement != null) {
//解析子元素
return parsePropertySubElement(subElement, bd);
}
else {
//既没有ref也没有value也没有子元素,Spring就会报错
// Neither child element nor "ref" or "value" attribute found.
error(elementName + " must specify a ref or value", ele);
return null;
}
}
可以看到上面函数与构造函数注入方式不同的是将返回值使用PropertyValue.java 进行封装,并记录在了BeanDefinition.java 中的propertyValues 属性中。





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号