2025杭电多校第五场 四角洲行动、“合理”避税、随机反馈、k-MEX 个人题解
k-MEX
组合数 #数学
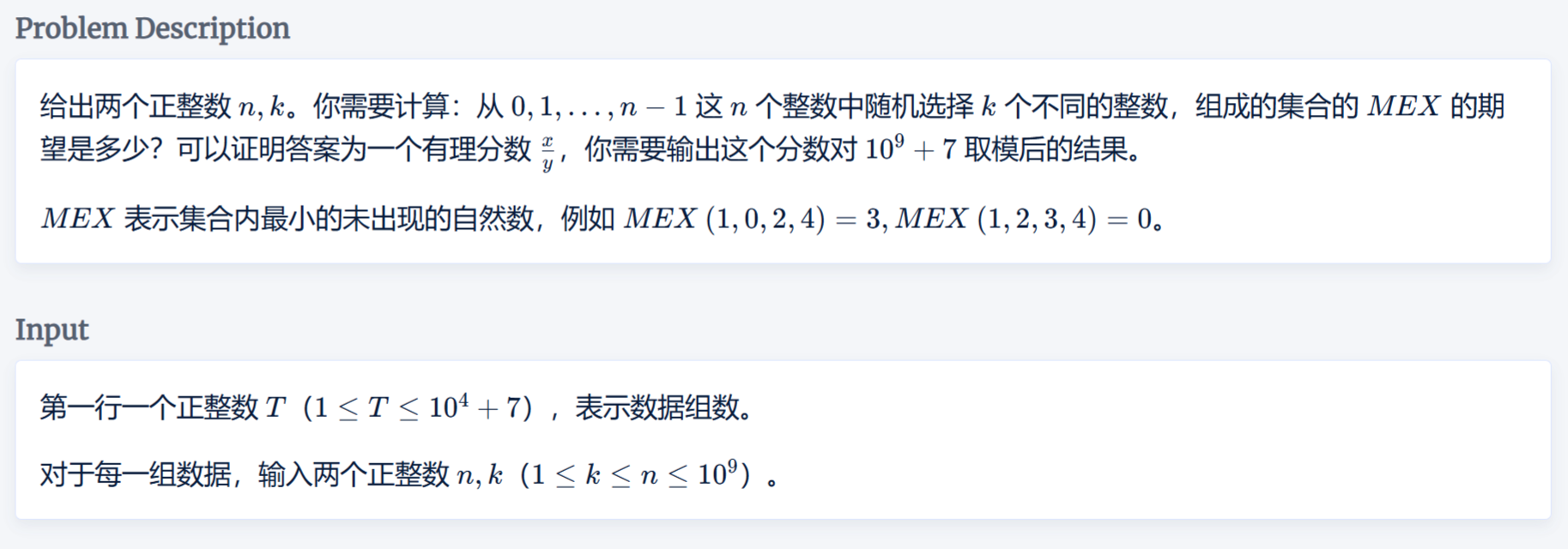
题目
思路
用费马小定理求逆元即可
代码实现
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<cmath>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
#define rep(i, a, b) for(ll i = (a); i <= (b); i ++)
#define per(i, a, b) for(ll i = (a); i >= (b); i --)
#define see(stl) for(auto&ele:stl)cout<<ele<<" "; cout<<'\n';
const int N=1e9;
const ll mod=1e9+7;
ll qpow(ll a,ll b){
a%=mod;ll res=1;
while(b){
if(b%2){res*=a;res%=mod;}
a*=a;a%=mod;b>>=1;
}
return res;
}
void eachT(){
int n,k;cin>>n>>k;
cout<<((k)*qpow(n+1-k,mod-2)%mod)%mod<<'\n';
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
// inv0(1e9);
int t=1;
cin>>t;
while(t--)eachT();
}
随机反馈
dp #概率dp
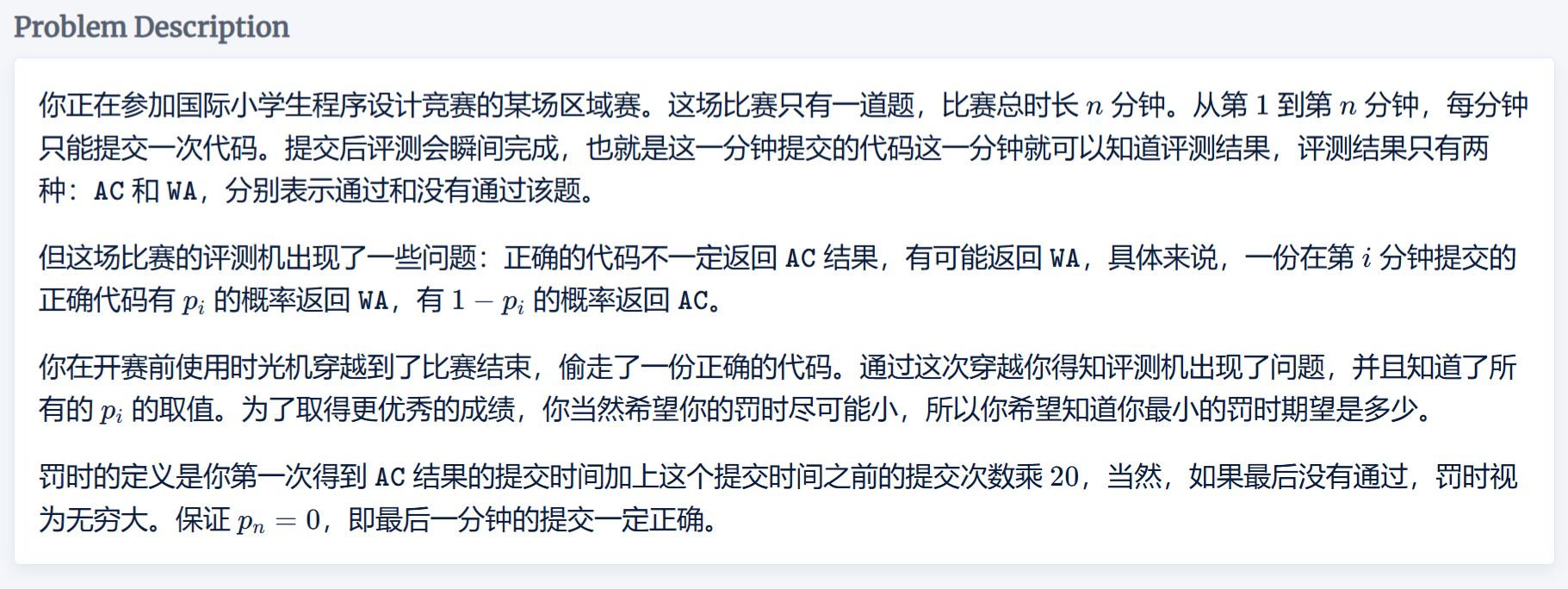
题目
思路
状态定义:
\(dp[i]\)代表从第\(n\)分钟到第\(i\)分钟倒序遍历,决策完第\(i\)分钟是否交题后,最终的罚时期望是多少
转移方程:
初始值:
\(dp[n]=n\)代表第\(n\)分钟罚时只能是\(n\)
对于第\(i\)分钟,如果不交题,那么状态与\(i+1\)分钟完全一致;
如果交题,那么有\(1-p_{i}\)的概率变为\(i\)(第\(i\)分钟前不交题,第\(i\)分钟交题然后过了),有\(p_{i}\)的概率变为\(dp[i+1]+20\)(在原有的基础上罚时20分钟)
特别需要注意,本题不可以将\(printf与cin\ cout\)混用,否则会\(T\)
代码实现
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<cmath>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<map>
#include<iomanip>
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
#define rep(i, a, b) for(ll i = (a); i <= (b); i ++)
#define per(i, a, b) for(ll i = (a); i >= (b); i --)
#define see(stl) for(auto&ele:stl)cout<<ele<<" "; cout<<'\n';
const int N=1e5+5;
const double inf=1e9;
int x[N];
double p[N],dp[N];
void eachT(){
int n;cin>>n;
rep(i,1,n){
cin>>x[i];p[i]=1.0*x[i]/1000;
}
dp[n]=n;
per(i,n-1,1){
dp[i]=min(dp[i+1],(1-p[i])*i+p[i]*(dp[i+1]+20));
}
cout<<fixed<<setprecision(10)<<dp[1]<<'\n';
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
int t=1;
cin>>t;
while(t--)eachT();
}
"合理"避税
二分 #贪心
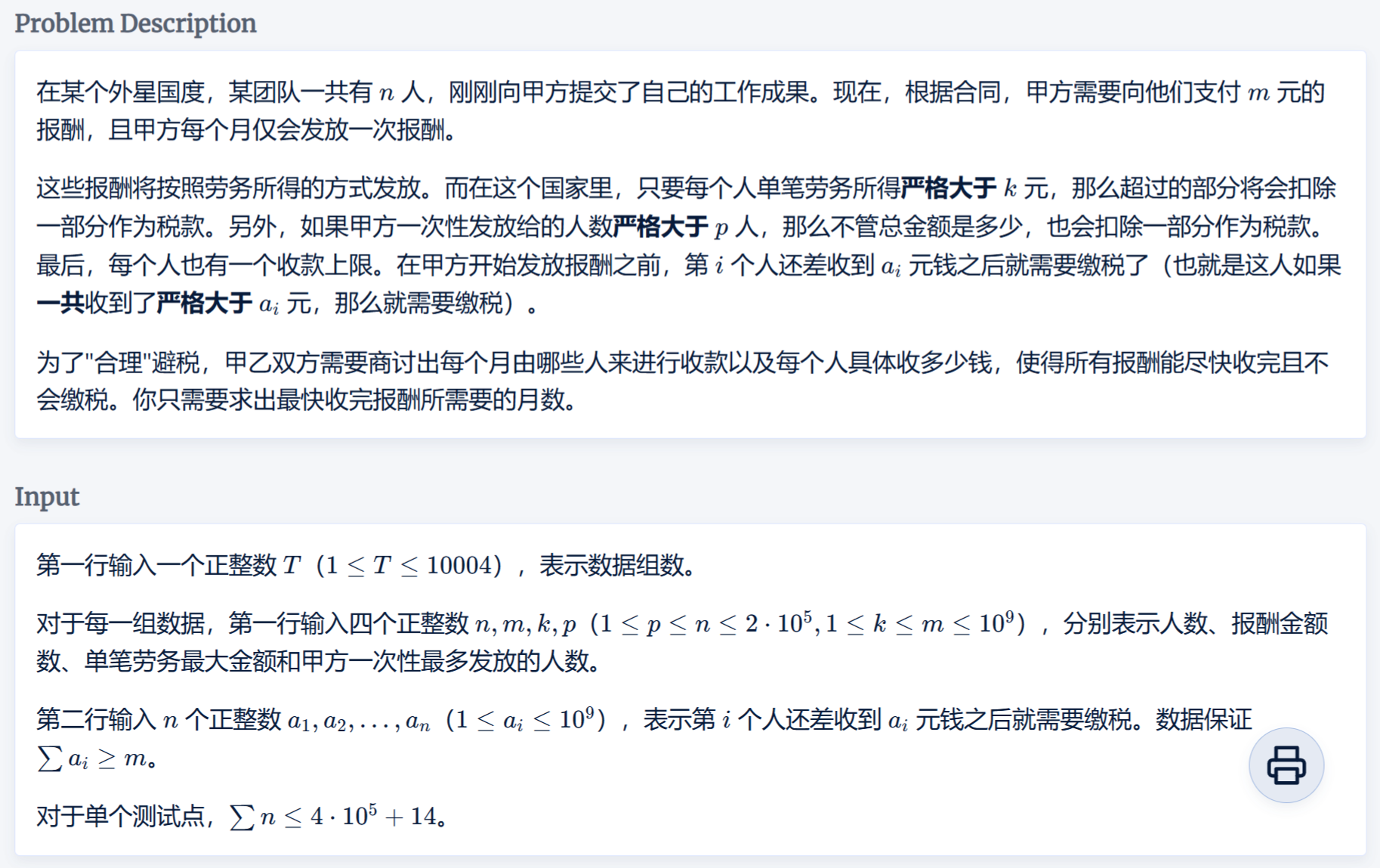
题目
思路
由于要求最少次数(月份),所以尝试二分答案来判断合法性。
设当前二分的次数为\(t\),则需要保证每个人每次所得小于等于\(k\),每次最多给\(p\)人,\(t\)次后第\(i\)人的总共所得不能超过\(a_{i}\)
-
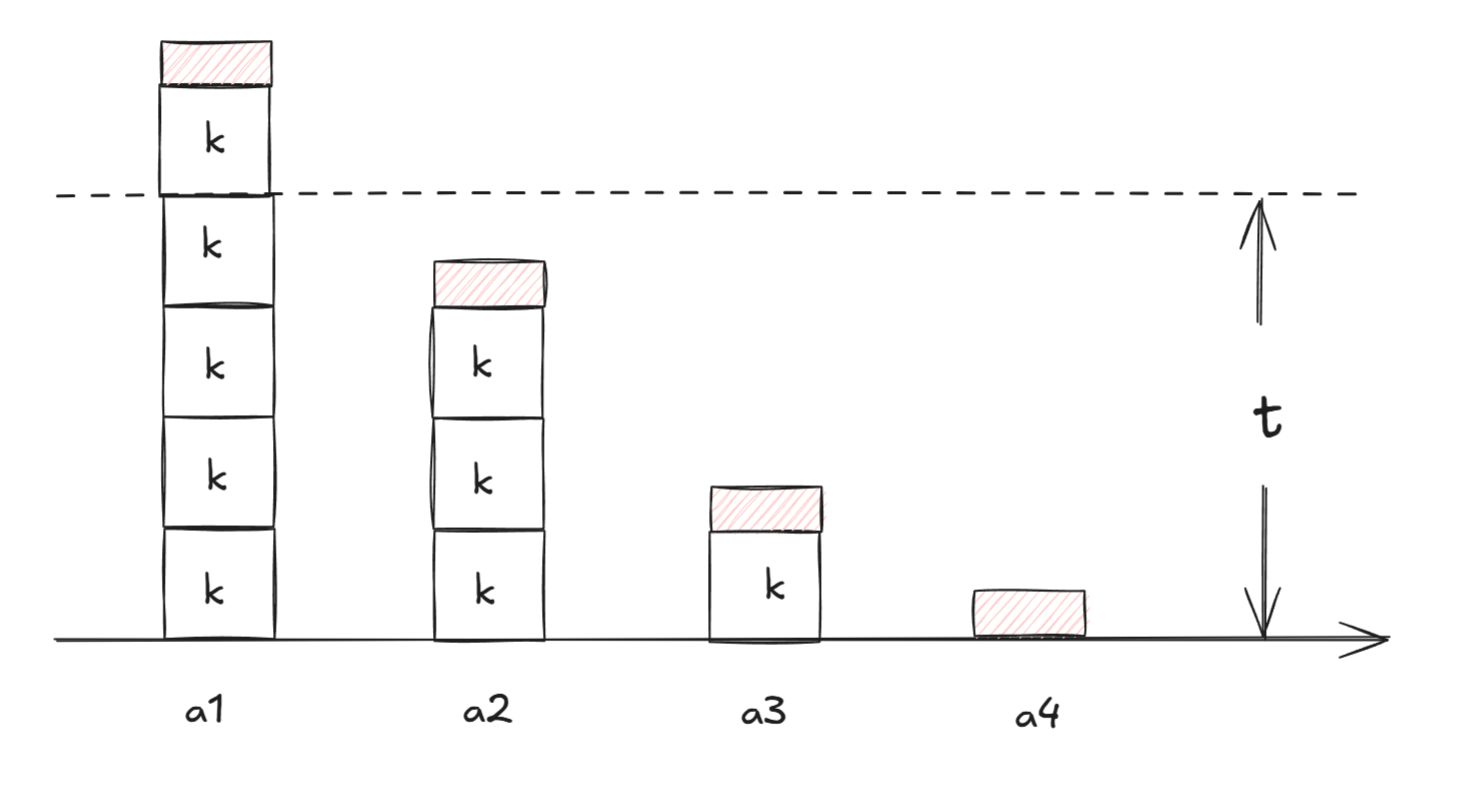
如下图所示,为了尽可能地少用次数,每个人每次能给\(k\)元就给\(k\)元
-
如果\(a_{i}>k\times t\),那么就是第一列的情况,这\(t\)次中全都选\(k\)
-
红色部分为\(a_{i}\%k\),在取完所有能取的\(k\)后,自然要按照这些余数从小到大取
-
创建变量\(num\)用于记录这\(t\)次选取中选了多少个\(k\),\(rest=t\times p-num\)用于记录还剩多少次选取机会
-
在选完\(num\)个\(k\)后,再从大到小选取\(rest\)个\(a_{i}\%k\)即为当前\(t\)下的最优选法
-
判断全部选完后的总钱数与\(m\)的关系即可二分
代码实现
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<cmath>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
#define rep(i, a, b) for(ll i = (a); i <= (b); i ++)
#define per(i, a, b) for(ll i = (a); i >= (b); i --)
//#define see(stl) for(auto&ele:stl)cout<<ele<<" "; cout<<'\n';
const ll inf = 1e7 + 5;
const int N = 4e5 + 20;
ll a[N], k, p, n, m;
bool check(ll t) {
if (t * p * k < m)return 0;
ll num = 0;
priority_queue<int>q;
rep(i, 0, n - 1) {
if(a[i]/k<t){
num+=a[i]/k;
q.push(a[i]%k);
}else{
num+=t;
}
}
ll cmp, rest = t * p - num;
rest = min(rest, n);
if (rest <= 0)cmp = t * p * k;
else {
cmp=num*k;
while(rest&&!q.empty()){
cmp+=q.top();
q.pop();
rest--;
}
}
if (cmp < m)return 0;
return 1;
}
void eachT() {
cin >> n >> m >> k >> p;
vector<int>mo(n);
rep(i, 1, n)cin >> a[i - 1];
ll l = floor(1.0 * m / (p * k))-1, r = 1e9 + 1;
while (l + 1 < r) {
ll mid = l + r >> 1;
if (check(mid))r = mid;
else l = mid;
}
cout << r << '\n';
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
ll t = 1;
cin >> t;
while (t--) { eachT(); }
}
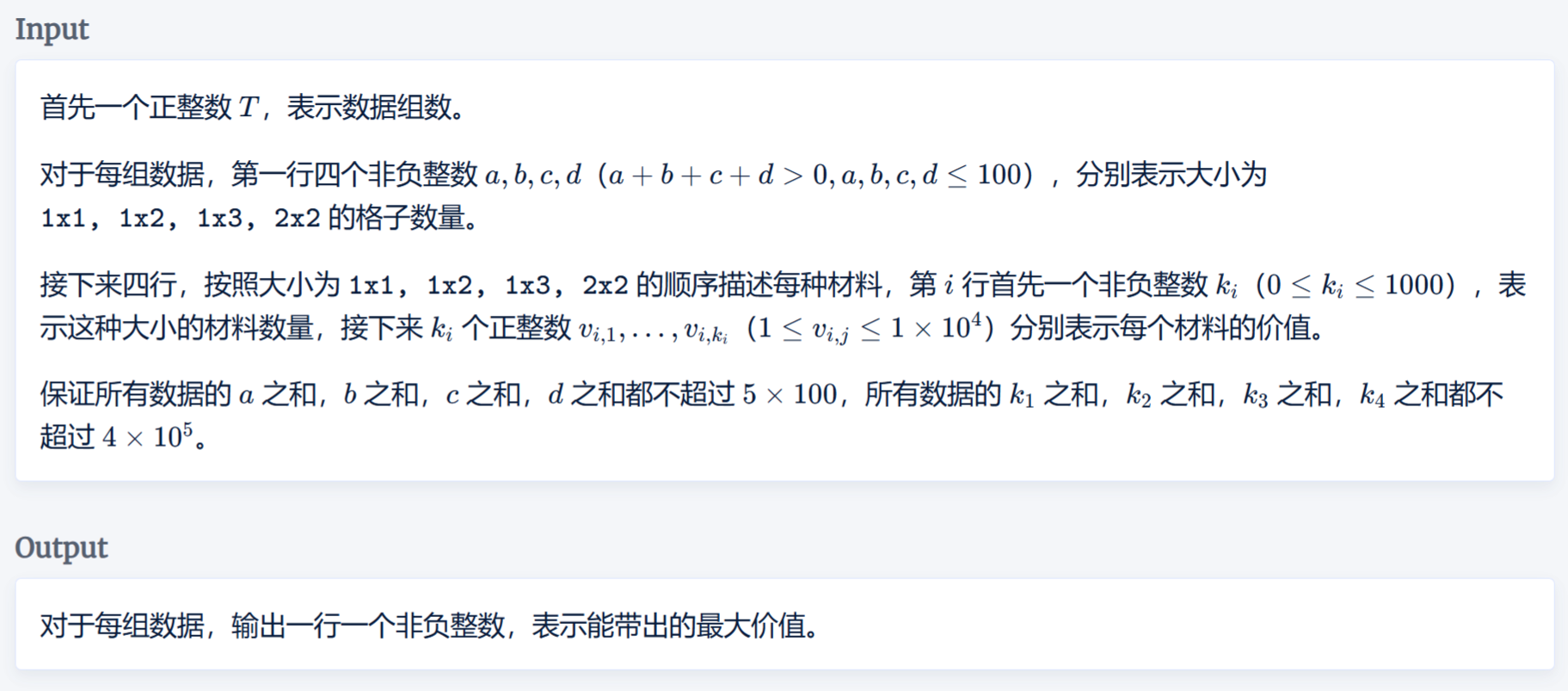
四角洲行动
dfs #枚举
题目

思路
记\(A,B,C,D\)分别为\(1\times1\ ,1\times 2\ ,1\times 3\ ,2\times 2\)这四种材料
则可以列出:
- 以\(2\times 2\)为例,\(D\)材料共有\(d\)个,每个\(D\)有三种分配方案,所以可以对这\(d\)个材料划分成三部分,分别选取对应的分配方案
- 因此想到了隔板法,放置两块可以重叠的隔板,分割出来的三个部分去选择对应的分配方案即可
- 创建两个指针\(d_{1},d_{2}\),\(1\sim d_{1}\)选\(4\times A\)的方案,\(d_{1}+1\sim d_{2}\)选\(2\times A+1\times B\)的方案,\(d_{2}\sim d\)选\(1\times D\)的方案,复杂度为\(o(d^2)\)
- 其他三个材料的选取与上述差不多,\(C\)的也是两个指针\(o(c^2)\)枚举,\(B\)的一个指针\(o(b)\)枚举,\(A\)的\(o(1)\)枚举
- 我的代码中写的是迭代版dfs,只需要在循环的结尾将当前更新进去的值撤销掉就可以实现dfs回溯的功能
- 接下来就算出来了当前情况下四个材料的使用次数,假如材料\(D\)选出了\(num\)个,那么就挑选材料\(D\)中价值前\(num\)大的进行求和即可,那么预处理一下前缀和即可
代码实现
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<cmath>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
#define rep(i, a, b) for(ll i = (a); i <= (b); i ++)
#define per(i, a, b) for(ll i = (a); i >= (b); i --)
//#define see(stl) for(auto&ele:stl)cout<<ele<<" "; cout<<'\n';
const ll inf = 1e7 + 5;
#define int ll
int num[4][1005],pre[4][1005];
void eachT() {
int a,b,c,d;cin>>a>>b>>c>>d;
rep(i,0,3){
int k;cin>>k;
rep(j,1,k)cin>>num[i][j];
sort(num[i]+1,num[i]+1+k);
rep(j,1,k)pre[i][j]=pre[i][j-1]+num[i][k-j+1];
rep(j,k+1,1000)pre[i][j]=pre[i][j-1];
}
int A=0,B=0,C=0,D=0;
ll ans=0;
rep(d1,0,d){
rep(d2,d1,d){//d
rep(d3,d2,d){
A+=4*d1+2*(d2-d1),B+=d2-d1+2*(d3-d2),D+=d-d3;
rep(lc,0,c){
rep(rc,lc,c){//c
A+=3*lc+(rc-lc),B+=rc-lc,C+=c-rc;
rep(i,0,b){//b
A+=2*i,B+=b-i;
A+=a;//a
ll now=pre[0][A]+pre[1][B]+pre[2][C]+pre[3][D];
ans=max(ans,now);
A-=a;
A-=2*i,B-=b-i;
}
A-=3*lc+(rc-lc),B-=rc-lc,C-=c-rc;
}
}
A-=4*d1+2*(d2-d1),B-=d2-d1+2*(d3-d2),D-=d-d3;
}
}
}
cout<<ans<<'\n';
}
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
ll t = 1;
cin >> t;
while (t--) { eachT(); }
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号