Tinkoff Challenge - Final Round (Codeforces Round #414, rated, Div. 1 + Div. 2) 继续跪一把
这次的前三题挺简单的,可是我做的不快也不对。

A robber has attempted to rob a bank but failed to complete his task. However, he had managed to open all the safes.
Oleg the bank client loves money (who doesn't), and decides to take advantage of this failed robbery and steal some money from the safes. There are many safes arranged in a line, where the i-th safe from the left is called safe i. There are n banknotes left in all the safes in total. The i-th banknote is in safe xi. Oleg is now at safe a. There are two security guards, one of which guards the safe b such that b < a, i.e. the first guard is to the left of Oleg. The other guard guards the safe c so that c > a, i.e. he is to the right of Oleg.
The two guards are very lazy, so they do not move. In every second, Oleg can either take all the banknotes from the current safe or move to any of the neighboring safes. However, he cannot visit any safe that is guarded by security guards at any time, becaues he might be charged for stealing. Determine the maximum amount of banknotes Oleg can gather.
The first line of input contains three space-separated integers, a, b and c (1 ≤ b < a < c ≤ 109), denoting the positions of Oleg, the first security guard and the second security guard, respectively.
The next line of input contains a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105), denoting the number of banknotes.
The next line of input contains n space-separated integers x1, x2, ..., xn (1 ≤ xi ≤ 109), denoting that the i-th banknote is located in the xi-th safe. Note that xi are not guaranteed to be distinct.
Output a single integer: the maximum number of banknotes Oleg can take.
5 3 7
8
4 7 5 5 3 6 2 8
4
6 5 7
5
1 5 7 92 3
0
In the first example Oleg can take the banknotes in positions 4, 5, 6 (note that there are 2 banknotes at position 5). Oleg can't take the banknotes in safes 7 and 8 because he can't run into the second security guard. Similarly, Oleg cannot take the banknotes at positions 3and 2 because he can't run into the first security guard. Thus, he can take a maximum of 4 banknotes.
For the second sample, Oleg can't take any banknotes without bumping into any of the security guards.
A题就是给n个数判定有几个数在b和c之间,早都打出来了,不敢交。交完AC但是感觉没有关输入输出流会被FST就又再交了一次,谁知道扣了我那么多分,罪过啊。2333,又去试了下,确实没卡,忧伤。

#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); int a,b,c; cin>>a>>b>>c; int n; cin>>n; int num=0; int p; for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ cin>>p; if(p>b&&p<c) num++;} printf("%d\n",num); return 0; }
Igor the analyst has adopted n little bunnies. As we all know, bunnies love carrots. Thus, Igor has bought a carrot to be shared between his bunnies. Igor wants to treat all the bunnies equally, and thus he wants to cut the carrot into n pieces of equal area.
Formally, the carrot can be viewed as an isosceles triangle with base length equal to 1 and height equal to h. Igor wants to make n - 1cuts parallel to the base to cut the carrot into n pieces. He wants to make sure that all n pieces have the same area. Can you help Igor determine where to cut the carrot so that each piece have equal area?
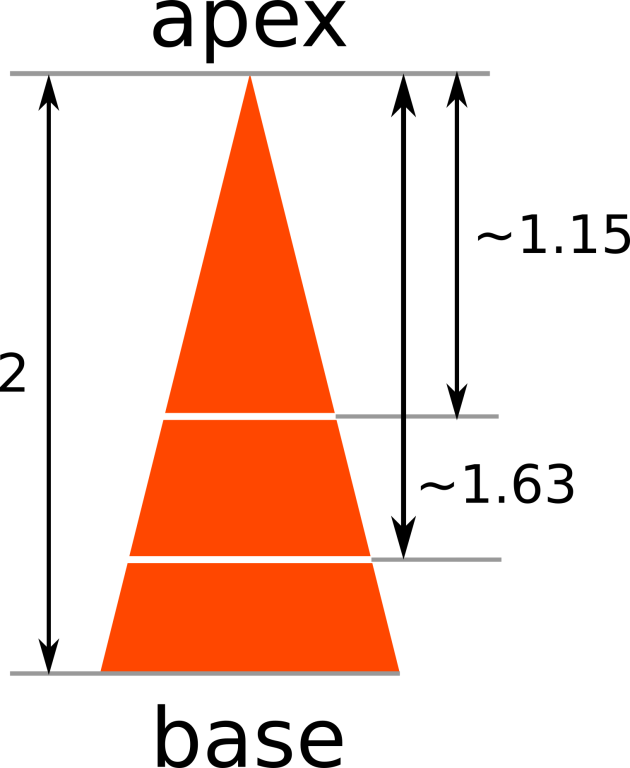 Illustration to the first example.
Illustration to the first example.The first and only line of input contains two space-separated integers, n and h (2 ≤ n ≤ 1000, 1 ≤ h ≤ 105).
The output should contain n - 1 real numbers x1, x2, ..., xn - 1. The number xi denotes that the i-th cut must be made xi units away from the apex of the carrot. In addition, 0 < x1 < x2 < ... < xn - 1 < h must hold.
Your output will be considered correct if absolute or relative error of every number in your output doesn't exceed 10 - 6.
Formally, let your answer be a, and the jury's answer be b. Your answer is considered correct if  .
.
3 2
1.154700538379 1.632993161855
2 100000
70710.678118654752
B题很简单啊,我推对了,可是程序写错了,毕竟我手算不出来这些数啊,尴尬,推了好几遍,但是这个是真的简单啊。还以为会真的卡精度,也没有,自己想太多。
拿n-1条平行于底边的线,使每个封闭图形面积相等

#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int main() {ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); int n,m; cin>>n>>m; double c=n*1.0; for(int i=1;i<n;i++){ printf("%.12f\n",sqrt(double(i)/c)*m); } return 0; }
Oleg the client and Igor the analyst are good friends. However, sometimes they argue over little things. Recently, they started a new company, but they are having trouble finding a name for the company.
To settle this problem, they've decided to play a game. The company name will consist of n letters. Oleg and Igor each have a set of nletters (which might contain multiple copies of the same letter, the sets can be different). Initially, the company name is denoted by nquestion marks. Oleg and Igor takes turns to play the game, Oleg moves first. In each turn, a player can choose one of the letters c in his set and replace any of the question marks with c. Then, a copy of the letter c is removed from his set. The game ends when all the question marks has been replaced by some letter.
For example, suppose Oleg has the set of letters {i, o, i} and Igor has the set of letters {i, m, o}. One possible game is as follows :
Initially, the company name is ???.
Oleg replaces the second question mark with 'i'. The company name becomes ?i?. The set of letters Oleg have now is {i, o}.
Igor replaces the third question mark with 'o'. The company name becomes ?io. The set of letters Igor have now is {i, m}.
Finally, Oleg replaces the first question mark with 'o'. The company name becomes oio. The set of letters Oleg have now is {i}.
In the end, the company name is oio.
Oleg wants the company name to be as lexicographically small as possible while Igor wants the company name to be as lexicographically large as possible. What will be the company name if Oleg and Igor always play optimally?
A string s = s1s2...sm is called lexicographically smaller than a string t = t1t2...tm (where s ≠ t) if si < ti where i is the smallest index such that si ≠ ti. (so sj = tj for all j < i)
The first line of input contains a string s of length n (1 ≤ n ≤ 3·105). All characters of the string are lowercase English letters. This string denotes the set of letters Oleg has initially.
The second line of input contains a string t of length n. All characters of the string are lowercase English letters. This string denotes the set of letters Igor has initially.
The output should contain a string of n lowercase English letters, denoting the company name if Oleg and Igor plays optimally.
tinkoff
zscoder
fzfsirk
xxxxxx
xxxxxx
xxxxxx
ioi
imo
ioi
One way to play optimally in the first sample is as follows :
- Initially, the company name is ???????.
- Oleg replaces the first question mark with 'f'. The company name becomes f??????.
- Igor replaces the second question mark with 'z'. The company name becomes fz?????.
- Oleg replaces the third question mark with 'f'. The company name becomes fzf????.
- Igor replaces the fourth question mark with 's'. The company name becomes fzfs???.
- Oleg replaces the fifth question mark with 'i'. The company name becomes fzfsi??.
- Igor replaces the sixth question mark with 'r'. The company name becomes fzfsir?.
- Oleg replaces the seventh question mark with 'k'. The company name becomes fzfsirk.
For the second sample, no matter how they play, the company name will always be xxxxxx.
这个题我要不是wa4,要不就wa6,要不就wa5.总之各种wa,事后群里人说才知道自己的贪心不对,两个人都是要选择,放字符到前面还是后面的。还以为sort也会超时,用了优先队列,好像无关紧要,不过熟悉了一把pq

#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; char s[300005],s1[150005],s2[150005]; struct cmp { char c; friend bool operator < (cmp x,cmp y) { return x.c > y.c; } }; struct cmp1 { char c; friend bool operator < (cmp1 x,cmp1 y) { return x.c<y.c; } }; int main() { gets(s); int n=0; priority_queue<cmp>qu; for(int i=0; s[i]; i++) { n++; cmp a; a.c=s[i]; qu.push(a); } priority_queue<cmp1>qu1; gets(s); for(int i=0; s[i]; i++) { cmp1 a; a.c=s[i]; qu1.push(a); } int f1=0,f2=0; for(int i=0; i<n; i++) { if(i%2){ s2[f1++]=qu1.top().c; qu1.pop(); } else{ s1[f2++]=qu.top().c; qu.pop(); } } int l1 = 0; int r1 = f2-1; int l2 = 0; int r2 = f1-1; int l = 0; int r = n - 1; for (int i = 0, first = 1; i < n; ++i, first = 1 - first) { if (first) { if (s1[l1] < s2[l2]) { s[l] = s1[l1]; ++l1; ++l; } else { s[r] = s1[r1]; --r1; --r; } } else { if (s2[l2] > s1[l1]) { s[l] = s2[l2]; ++l2; ++l; } else { s[r] = s2[r2]; --r2; --r; } } } s[n]=0; printf("%s",s); return 0; }
本文来自博客园,作者:暴力都不会的蒟蒻,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/BobHuang/p/6850222.html



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号