计算机视觉——匹配地理标记图像
什么是图像分类
图像分类的任务就是给定一个图像,正确给出该图像所属的类别。对于超级强大的人类视觉系统来说,判别出一个图像的类别是件很容易的事,但是对于计算机来说,并不能像人眼那样一下获得图像语义信息,计算机能看到的只是一个个像素的数值,对于一个RGB图像来说,假设图像的尺寸是32*32,那么机器看到的就是一个形状为3*32*32的矩阵,或者更正式的称其为“张量”(“张量”简单来说就是高维的矩阵),那么机器的任务其实也就是寻找一个函数关系,这个函数关系能够将这些像素的数值映射到一个具体的类别(类别可以用某个数值表示)
图片地理标记即图像分类,可以实现多张图片进行特定夫人标志性物体分类。主要步骤需要对图像提取局部表述算子,一般情况都是SIFT特征描述算子。然后通过判断图像是否具有匹配的局部描述算子来定义图像之间的连接,实现图像可视化连接,图的边代表连接,在现实图像的连接将会使用pydot工具包,该工具包是功能强大的GraphViz图形库的Python接口
局部图像描述子
Harris角点检测算法(也称Harris&Stephens角点检测器)是一个极为简单的角点检测算法。该算法的主要思想是,如果像素周围显示存在多于一个方向的边,我们认为该点为兴趣点。该点就称为角点。
我们把图像域中点x上的对称半正定矩阵MI=MI(x)定义为:

其中∇I为包含导数Ix和Iy的图像梯度。由于该定义,M~I~的秩为1,特征值为λ~1~=|∇I|^2^和λ~2~=0。现在对于图像的每个像素,我们可以计算出该矩阵。
选择权重矩阵W(通常为高斯滤波器G~σ~),我们可以得到卷积:
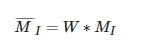
该卷积的目的是得到M~I~在周围像素上的局部平均。计算出的矩阵M~I~^-^有称为Harris矩阵。W的宽度决定了在像素x周围的感兴趣区域。像这样在区域附近对矩阵M~I~^-^取平均的原因是,特征值会依赖于局部图像特性而变化。如果图像梯度在该区域变化,那么M~I~^-^的第二个特征值将不再为0.如果图像的梯度没有变换,M~I~^-^的特征值也不会变化。
取决于该区域∇I的值,Harris矩阵M~I~^-^的特征值有三种情况: 1)如果λ~1~和λ~2~都是很大的正数,则该x点为角点; 2)如果λ~1~很大,λ~2~≈0,则该区域内存在一个边,该区域内的平均M~I~^-^的特征值不会变化太大; 3)如果λ~1~≈λ~2~≈0,则该区域为空。
在不需要实际计算特征值的情况下,为了把重要的情况和其他情况分开,Harris和Stephens在文献中引入了指示函数:
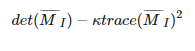
为了去除加权常数κ,我们通常使用商数:
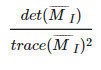
在图像中寻找对应点
Harris角点检测器仅仅能够检测出图像中的兴趣点,但没有给出通过比较图像间的兴趣点来寻找匹配角点的方法。我们需要在每个点上加入描述子信息,并给出一个比较这些描述子的方法。
兴趣点描述子是分配给兴趣点的一个向量,描述该点附近的图像的表现信息。描述子越好,寻找到的对应点越好。我们用对应点或者点的对应来描述相同物体和场景点在不同图像上形成的像素点。
Harris角点的描述子通常是由周围图像像素块的灰度值,以及用于比较的归一化互相关矩阵构成的。图像的像素块由以该像素点为中心的周围矩形部分图像构成。
通常,两个(相同大小)像素块I~1~(x)和I~2~(x)的相关矩阵定义为: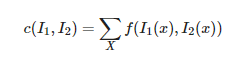
,I2(x))其中,函数f随着相关方法的变化而变化。上式取像素块中所有像素位置x的和。对于互相关矩阵,函数f(I~1~,I~2~)=I~1~I~2~,因此,c(I~1~,I~2~)=I~1~·I~2~,其中·表示向量乘法。c(I~1~,I~2~)的值越大,像素块I~1~和I~2~的相似度越高。
归一化的互相关矩阵是互相关矩阵的一种变形,可以定义为:
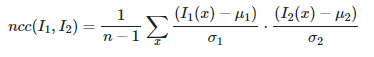
其中,n为像素块中像素的数目,μ~1~和μ~2~表示每个像素块中平均像素值强度,σ~1~和σ~2~分别表示每个像素块中的标准差。通过减去均值和除以标准差,该方法对图像亮度变化具有稳健性。
SIFT(尺度不变特征变换)
David Lowe提出的SIFT(Scale-Invariant Feature Transform,尺度不变特征变化)是过去十年中最成功的图像局部描述子之一。SIFT特征包括兴趣点检测器和描述子。SIFT描述子具有非常强的稳定性,这也是SIFT特征能够成功和流行的主要原因。SIFT特征对于尺度、旋转和亮度都具有不变性,因此,它可以用于三维视角和噪声的可靠匹配。
兴趣点
SIFT特征使用高斯差分函数来定位兴趣点:
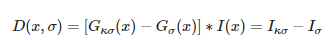
其中,G~σ~是二维高斯核,I~σ~是使用G~σ~模糊的灰度图像,κ是决定相差尺度的常熟。兴趣点是在图像位置和尺度变换下D(x,σ)的最大值和最小值点。这些候选位置通过滤波去除不稳定点。基于一些准则,比如认为低对比度和位于边上的点不是兴趣点,我们可以去除一些候选兴趣点。
描述子
上面讨论的兴趣点(关键点)位置描述子给出了兴趣点的位置和尺度信息。为了实现旋转不变性,基于每个点周围图像梯度的方向和大小,SIFT描述子又引入了参考方向。SIFT描述子使用主方向描述参考方向。主方向使用方向直方图(以大小为权重)来度量。
匹配描述子
对于将一幅图像中的特征匹配到另一幅图像的特征,一种稳健的准则(同样是由Lowe提出的)是使用者两个特征距离和两个最匹配特征距离的比率。相比于图像中的其他特征,该准则保证能够找到足够相似的唯一特征。使用该方法可以使错误的匹配数降低。
(二)图片分类实现
具体实现时,要先创建一个sift.py文件,然后把要分类的图片都存在该项目下(注意:所有图片之间像素不要相差太大,最好可以用美图秀秀批处理进行以同一宽度自适应高度生成图片),就可以直接运行一下代码:
from pylab import *
from PIL import Image
from numpy import *
import os
def process_image(imagename, resultname, params="--edge-thresh 10 --peak-thresh 5"):
"""处理一幅图像,然后将结果保存在文件中"""
if imagename[-3:] != 'pgm':
# 创建一个pgm文件
im = Image.open(imagename).convert('L')
im.save('tmp.pgm')
imagename = 'tmp.pgm'
cmmd = str("sift " + imagename + " --output=" + resultname + " " + params)
os.system(cmmd)
print('processed', imagename, 'to', resultname)
def read_features_from_file(filename):
"""读取特征值属性值,然后将其以矩阵形式返回"""
f = loadtxt(filename)
return f[:, :4], f[:, 4:] # 特征位置,描述子
def plot_features(im, locs, circle=False):
"""显示带有特征的图像
输入:im(数组图像),locs(每个特征的行、列、尺度和方向角度)"""
def draw_circle(c,r):
t = arange(0,1.01,.01)*2*pi
x = r*cos(t) + c[0]
y = r*sin(t) + c[1]
plot(x,y,'b',linewidth=2)
imshow(im)
if circle:
for p in locs:
draw_circle(p[:2],p[2])
else:
plot(locs[:,0],locs[:,1],'ob')
axis('off')
return
def match(desc1, desc2):
"""对于第一幅图像的每个描述子,选取其在第二幅图像中的匹配
输入:desc1(第一幅图像中的描述子),desc2(第二幅图像中的描述子)"""
desc1 = array([d/linalg.norm(d) for d in desc1])
desc2 = array([d/linalg.norm(d) for d in desc2])
dist_ratio = 0.6
desc1_size = desc1.shape
matchscores = zeros((desc1_size[0],1), 'int')
desc2t = desc2.T #预先计算矩阵转置
for i in range(desc1_size[0]):
dotprods = dot(desc1[i,:], desc2t) #向量点乘
dotprods = 0.9999*dotprods
# 反余弦和反排序,返回第二幅图像中特征的索引
index = argsort(arccos(dotprods))
# 检查最近邻的角度是否小于dist_ratio乘以第二近邻的角度
if arccos(dotprods)[index[0]] < dist_ratio * arccos(dotprods)[index[1]]:
matchscores[i] = int(index[0])
return matchscores
def match_twosided(desc1,decs2):
"""双向对称版本的match"""
matches_12 = match(desc1, decs2)
matches_21 = match(decs2, decs2)
ndx_12 = matches_12.nonzero()[0]
# 去除不对称匹配
for n in ndx_12:
if matches_21[int(matches_12[n])] != n:
matches_12[n] = 0
return matches_12
def appendimages(im1, im2):
"""返回将两幅图像并排拼接成的一幅新图像"""
# 选取具有最少行数的图像,然后填充足够的空行
row1 = im1.shape[0]
row2 = im2.shape[0]
if row1 < row2:
im1 = concatenate((im1,zeros((row2-row1,im1.shape[1]))), axis=0)
elif row1 > row2:
im2 = concatenate((im2,zeros((row1-row2,im2.shape[1]))), axis=0)
# 如果这些情况都没有,那么他们的行数相同,不需要进行填充
return concatenate((im1,im2), axis=1)
def plot_matches(im1, im2, locs1, locs2, matchscores, show_below=True):
"""显示一幅带有连接匹配之间连线的图片
输入:im1,im2(数组图像),locs1,locs2(特征位置),matchscores(match的输出),
show_below(如果图像应该显示再匹配下方)"""
im3 = appendimages(im1,im2)
if show_below:
im3 = vstack((im3,im3))
imshow(im3)
cols1 = im1.shape[1]
for i in range(len(matchscores)):
if matchscores[i] > 0:
plot([locs1[i, 0], locs2[matchscores[i, 0], 0] + cols1], [locs1[i, 1], locs2[matchscores[i, 0], 1]], 'c')
axis('off')
if __name__ == '__main__':
# imname = 'raccoon.jpg'
# im1 = array(Image.open(imname).convert('L'))
# process_image(imname, 'raccoon.sift')
# l1, d1 = read_features_from_file('raccoon.sift')
#
# figure()
# gray()
# plot_features(im1, l1, circle=True)
# show()
im1f = r'C:\Users\Yangs\PycharmProjects\SIFT\sift1\raccoon.jpg'
im2f = r'C:\Users\Yangs\PycharmProjects\SIFT\sift1\raccoon.jpg'
im1 = array(Image.open(im1f))
im2 = array(Image.open(im2f))
process_image(im1f, 'out_sift_1.txt')
l1, d1 = read_features_from_file('out_sift_1.txt')
figure()
gray()
subplot(121)
plot_features(im1, l1, circle=False)
process_image(im2f, 'out_sift_2.txt')
l2, d2 = read_features_from_file('out_sift_2.txt')
subplot(122)
plot_features(im2, l2, circle=False)
matches = match_twosided(d1, d2)
print('{} matches'.format(len(matches.nonzero()[0])))
figure()
gray()
plot_matches(im1, im2, l1, l2, matches, show_below=True)
show()
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import json
import os
import urllib
from pylab import *
from PIL import Image
from PCV.localdescriptors import sift
from PCV.tools import imtools
import pydot
if __name__ == '__main__':
download_path = "D:\\image"
path = "D:\\image"
imlist = imtools.get_imlist(download_path)
nbr_images = len(imlist)
featlist = [imname[:-3] + 'sift' for imname in imlist]
for i, imname in enumerate(imlist):
sift.process_image(imname, featlist[i])
matchscores = zeros((nbr_images, nbr_images))
for i in range(nbr_images):
for j in range(i, nbr_images): # only compute upper triangle
print('comparing ', imlist[i], imlist[j])
l1, d1 = sift.read_features_from_file(featlist[i])
l2, d2 = sift.read_features_from_file(featlist[j])
matches = sift.match_twosided(d1, d2)
nbr_matches = sum(matches > 0)
print('number of matches = ', nbr_matches)
matchscores[i, j] = nbr_matches
# copy values
for i in range(nbr_images):
for j in range(i + 1, nbr_images): # no need to copy diagonal
matchscores[j, i] = matchscores[i, j]
# 可视化
threshold = 2 # min number of matches needed to create link
g = pydot.Dot(graph_type='graph') # don't want the default directed graph
for i in range(nbr_images):
for j in range(i + 1, nbr_images):
if matchscores[i, j] > threshold:
# first image in pair
im = Image.open(imlist[i])
im.thumbnail((100, 100))
filename = path + str(i) + '.jpg'
im.save(filename) # need temporary files of the right size
g.add_node(pydot.Node(str(i), fontcolor='transparent', shape='rectangle', image=filename))
# second image in pair
im = Image.open(imlist[j])
im.thumbnail((100, 100))
filename = path + str(j) + '.jpg'
im.save(filename) # need temporary files of the right size
g.add_node(pydot.Node(str(j), fontcolor='transparent', shape='rectangle', image=filename))
g.add_edge(pydot.Edge(str(i), str(j)))
g.write_jpg('22.jpg')




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号