Codeforces Round 866 (Div. 2)
ZMY 是唯一的神迹
感觉整场偏简单
A. Yura's New Name
可以直接贪心的在每个后面不是^的_后面加上一个^
#include <iostream>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxN=2*1e5+10;
void solve(){
string str;
cin >> str;
int sum=0;
vector<int> v;
for(int i=0;i<str.length() ;++i){
if(str[i]=='^') v.push_back(i);
}
if(v.empty()){
cout << str.length()+1 << endl;
return;
}
if(v.size()==1&&str.length()==1) {
cout << 1 << endl;
return ;
}
for(int i=0;i<v.size()-1;++i){
if(v[i]==v[i+1]-1) continue ;
else sum+=(v[i+1]-v[i]-2);
}
int k=0;
for(int i=0;i<str.length();++i){
if(str[i]=='_'){
++k;
}
else {
break;
}
}
sum+=k;
k=0;
for(int i=str.length()-1;i>=0;--i){
if(str[i]=='_'){
++k;
}
else {
break;
}
}
sum+=k;
cout << sum << endl;
}
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
int t;
cin >> t;
while(t--){
solve();
}
return 0;
}
B. JoJo's Incredible Adventures
很明显,每一个矩形都对应着原序列中的一个全 1 段,循环会使头部的段和尾部的段拼接在一起
同时,每对一个已经拼好的矩形继续进行移动,并不会改变其的周长,我们为了使其的面积尽量大,需要让其接近一个正方形
代码删了一些头文件,有可能导致无法过编译
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
ll t, i, j, w, n, z = 0, maxx = 0;
char a[200010] = {};
int main() {
scanf("%lld", &t);
while (t--) {
cin >> a;
n = strlen(a) - 1;
bool f = 0;
z = 0;
maxx = 0;
w = 0;
for (i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
if (a[i] == '0' && f == 0) {
f = 1;
w = z;
}
if (a[i] == '0') {
maxx = max(maxx, z);
z = 0;
}
if (a[i] == '1') {
z++;
}
}
maxx = max(maxx, z + w);
maxx++;
if (f == 1)
cout << maxx / 2 * (maxx / 2 + maxx % 2) << endl;
else {
cout << (maxx - 1)*(maxx - 1) << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
C. Constructive Problem
沙币题
但有个更沙币的废物因为读错了题导致没有切
很明显,我们要求使mex加一有两个条件
- 必须有的数要调整到
mex - 所有的等于
mex+1的数都要被出去
那简单了,我们找出一个包含所有mex+1的数的区间,然后把所有的数都调整到mex,看看是否合法就可以了
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <unordered_map>
#define ll long long
#define reg register
#define fo(a,b,c) for(reg ll a=b;a<=c;a++)
#define re(a,b,c) for(reg ll a=b;a>=c;a--)
#define pii pair<ll,ll>
#define fi first
#define se second
#define mod 998244353
using namespace std;
inline ll gi(){
ll x = 0, f = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){
if (ch == '-')
f = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){
x = (x<<1) + (x<<3) + (ch^48);
ch = getchar();
}
return x * f;
}
ll a[200005];
map<ll,ll> mp;
void sol()
{
ll n=gi();
mp.clear();
ll l=0,r=0;
fo(i,1,n)
{
a[i]=gi();
mp[a[i]]++;
}
ll t=0;
while(mp[t]) t++;
ll z=t;
fo(i,1,n)
{
if(a[i]==t+1)
{
if(l==0) l=i;
r=i;
}
}
fo(i,l,r)
{
a[i]=t;
}
mp.clear();
if(l==r&&r==0)
{
if(t!=n)
{
cout<<"YES";
}
else cout<<"NO";
return;
}
fo(i,1,n)
{
mp[a[i]]++;
}
t=0;
while(mp[t]) t++;
if(t==z+1) cout<<"YES";
else cout<<"NO";
}
int main()
{
ll _=gi();
while(_--)
{
sol();
cout<<'\n';
}
return 0;
}
D. The Butcher
这道题吧,其实我觉得真不难,但不知为何,场切的人比较少
首先一个明显的结论,我们这里只有两种构建方案
分别是将最长的h拿出来和把最长的w拿出来
接下来就枚举一遍所有子矩形,若有一条边能与目前的重合,那就证明其一定是和第一次切的是同一类的,我们把它加进去,然后算贡献算到另一维度头上去
接下来,我们在剩余的子矩形中选出一个另一维度最长的矩形,将其的另一维度加入贡献
接下来怎么判合法性呢,这里有一个假的要死的结论,如果这样构造出来的大矩形的面积等于所有子矩形的面积之和,就认为这样是合法的
不得不说 wzh 是真的敢想
这个假的要死的结论通过了system test,但立刻就被Hack了
真正的结论是这样的,我们枚举一个维度,删掉所有与这个维度符合的子矩形,然后减去另一个的贡献,再换到另一个维度去枚举就可以了,等什么时候删掉了0,或者没有子矩形了,就退出,结算一下
具体实现中,使用了两个mulitset,一个以h为关键字,一个以w为关键字,以实现不同维度之间的交换
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define ld long double
#define inf 0x7ffffff
#define pii pair<int,int>
using namespace std;
const int maxN=2*1e5+10;
int t,n;
int vis[maxN];
pii a[maxN];
bool check(int h,int w,int st){
multiset<pii> s[2];
int p[2];
p[0]=h,p[1]=w;
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)
s[0].insert(a[i]),s[1].insert({a[i].second,a[i].first});
for(int i=st;p[1]&&p[0];i^=1){//i=0为h,i=1为w
auto now=*s[i].rbegin();
if(now.first!=p[i])
return false;
while(!s[i].empty()&&s[i].rbegin()->first==p[i]){
auto x=*s[i].rbegin();
s[i].erase(s[i].lower_bound(x));
s[i^1].erase(s[i^1].lower_bound({x.second,x.first}));
p[i^1]-=x.second;
if(p[i^1]<0)
return false;
}
if(s[i].empty()){
if(p[i^1]!=0)
return false;
else return true;
}
}
if(!s[0].empty()){
return false;
}
return true;
}
void solve(){
cin >> n;
int maxh=0,maxw=0,sum=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i){
cin >> a[i].first >> a[i].second;
maxh=max(maxh,a[i].first),maxw=max(maxw,a[i].second);
}
int h=maxh,w=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)
if(a[i].first==h) w+=a[i].second,vis[i]=1;
int temp=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i){
if(vis[i]) continue ;
temp=max(temp,a[i].second);
}
w+=temp;
vector<pii> ans;
if(check(h,w,0))++sum,ans.push_back({h,w});
w=maxw,h=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i) vis[i]=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)
if(a[i].second==w) h+=a[i].first,vis[i]=1;
temp=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i){
if(vis[i]) continue ;
temp=max(temp,a[i].first);
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i) vis[i]=0;
h+=temp;
if(check(h,w,1))++sum,ans.push_back({h,w});
if(sum==2&&ans[0]==ans[1]) ans.pop_back(),sum--;;
cout << sum << endl;
for(pii x:ans)
cout << x.first << " " << x.second << endl;
}
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
cin >> t ;
while(t--){
solve();
}
return 0;
}
E. The Fox and the Complete Tree Traversal
不错的构造
这个条件非常明显,我们可以让一个节点跳到与其距离为 1 的节点上去,同时,我们有一个奇妙的发现:
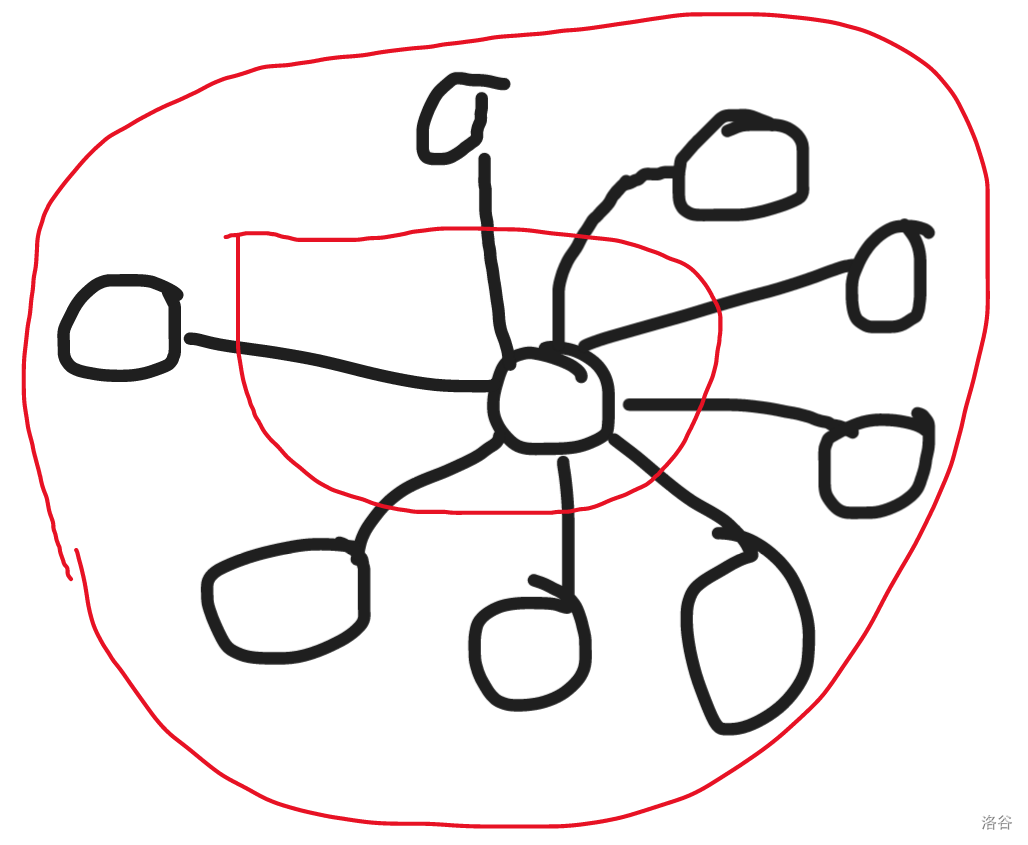
画红圈的这些节点可以相互跳到,这个形式给了我们启发
这里我也不知道怎么过渡了,直接放结论,一颗树有解的充要条件是其删去所有叶子结点之后的节点是一条链
首先,我们来证明其如果有一个三叉的情况,就一定无解
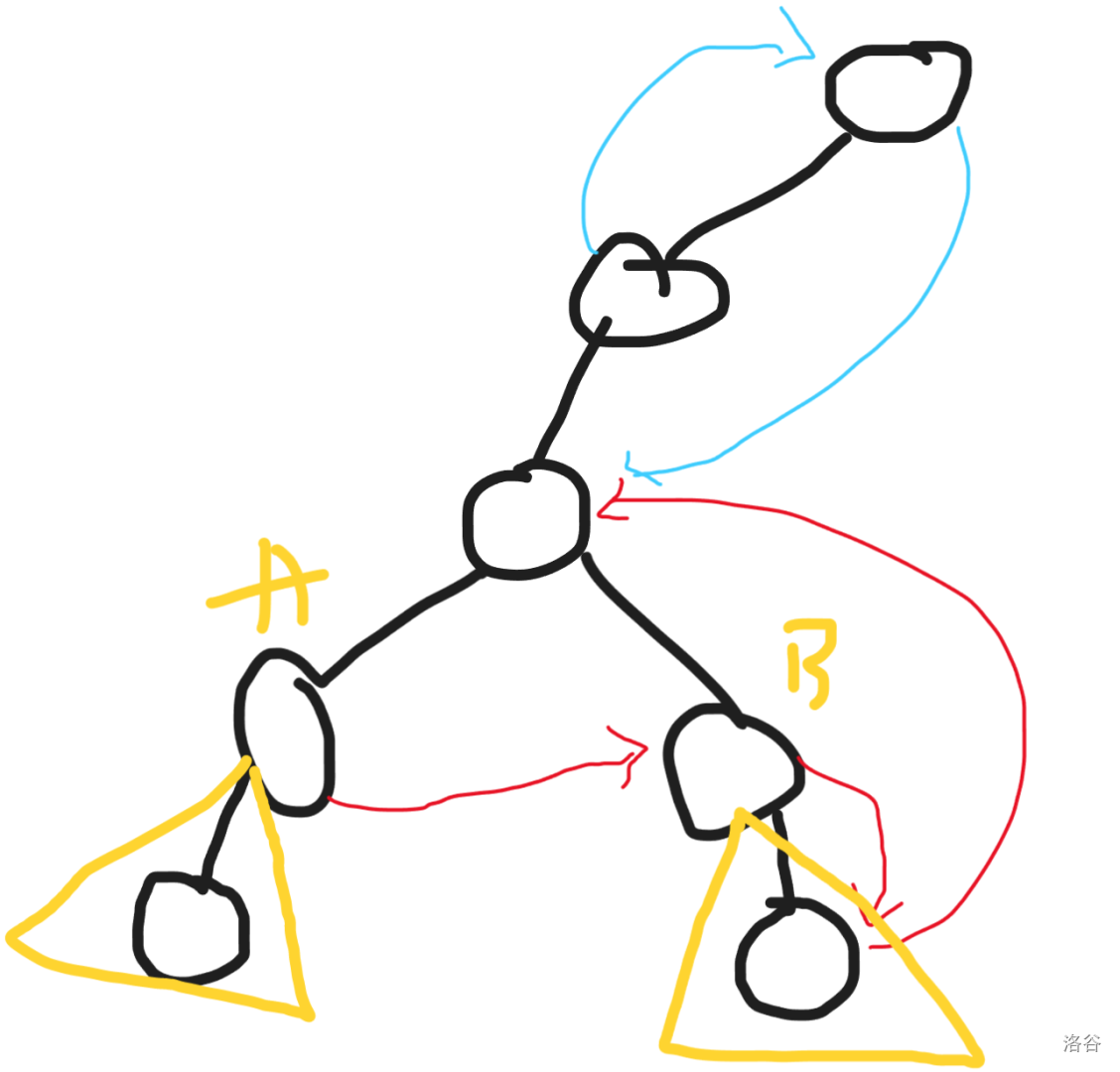
如图所示,显而易见,我们从A开始跳,第一次不能经过中心节点,就要跳到 B 上,当我们跳入 B 的子树的时候,若要再次跳出来,就一定要经过中心节点,明显不符合条件
同时,我们发现,可以通过下面的方法来构造一组答案
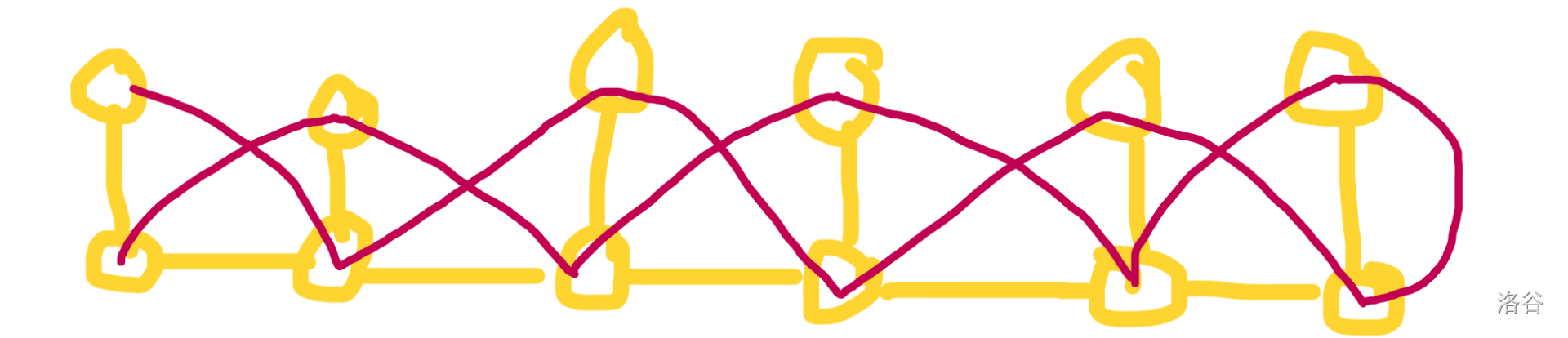
这里上面的节点代表了其挂住的叶结点,由于其叶结点之间是可以相互跳的,所以只用一个节点代替
好的,问题到了这里,就变为了,怎么找出这条路径
我们发现,这条路径一定是整颗无根树的直径,因为如果存在这样的路径,则整颗树可以想象为一个路径上长出了一圈的节点,则我们找出直径,进行构造就可以了
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define ld long double
#define inf 0x7ffffff
using namespace std;
const int maxN=2*1e5+10;
int n,c,w,flag,flag2;
int dep[maxN],siz[maxN];
vector<int>g[maxN],path,leaf[maxN];
void dfs(int now,int f,int &p){
dep[now]=dep[f]+1,siz[now]=1;
if(dep[now]>dep[p]) p=now;
int tot=0;
for(int x:g[now]){
if(x==f) continue ;
dfs(x,now,p);
siz[now]+=siz[x];
if(siz[x]>1) ++tot;
if(!path.empty()){
if(tot>1)flag=1;
if(siz[x]==1) leaf[now].push_back(x);
}
}
}
void dfs2(int now,int f){
path.push_back(now);
for(int x:g[now]){
if(x==f) continue ;
if(x==w){
flag2=1;
return ;
}
dfs2(x,now);
if(flag2) return ;
}
if(flag2) return ;
path.pop_back();
}
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
cin >> n;
for(int i=1;i<n;++i){
int u,v;
cin >> u >> v;
g[u].push_back(v);
g[v].push_back(u);
}
dfs(1,1,c);
memset(dep,0,sizeof(dep));
memset(siz,0,sizeof(siz));
dfs2(c,c);
int temp;
dfs(c,c,temp);
if(flag==1){
cout << "No" << endl;
return 0;
}
cout << "Yes" << endl;
int sy=1;//1为选,0为不选
for(int i=0;i<path.size();++i){
if(sy) cout << path[i] << " ";
else for(int x:leaf[path[i]])
cout << x << " ";
sy^=1;
}
for(int i=path.size()-1;i>=0;--i){
if(sy) cout << path[i] << " ";
else for(int x:leaf[path[i]])
cout << x << " ";
sy^=1;
}cout << endl;
return 0;
}

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号