一、单元测试(Junit单元测试框架)
针对最小的功能单元:方法,编写测试代码对其进行正确性测试
1、优点:
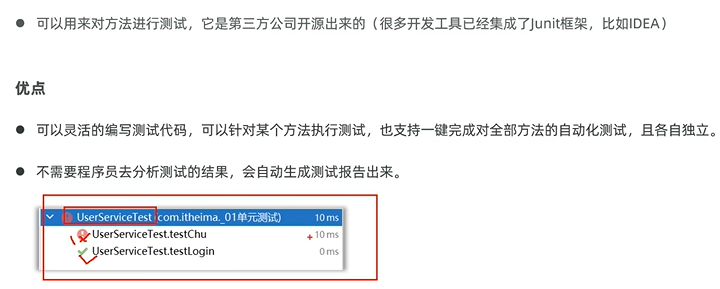
2、操作步骤

注意:导包JUnit4后,重启idea,右键才显示 运行单元测试方法
package com.ithema.junit; /** * 字符串工具类类 */ public class StringUtil { public static void printNumber(String name) { if(name==null){return;} System.out.println("名字长度是" + name.length()); } /** * 获取字符串最大索引 */ public static int getMaxIndex(String data) { if (data == null|| data.isEmpty()) return -1; return data.length()-1; } }
package com.ithema.junit; import org.junit.Assert; import org.junit.Test; /** * 测试类 */ public class StringUtilTest { // 测试方法必须是公共的,不能有参数,不能有返回值 //测试方法上面必须加上@Test注解 @Test public void testPrintNumber() { StringUtil.printNumber("hello world"); StringUtil.printNumber(null); } @Test public void testGetMaxIndex() { int maxIndex = StringUtil.getMaxIndex("hel"); int maxIndex2 = StringUtil.getMaxIndex(""); int maxIndex3 = StringUtil.getMaxIndex(null); //做断言:断言是否和预期结果一样 Assert.assertEquals("本轮测试失败,业务获取最大索引有问题,请检查", 2, maxIndex); Assert.assertEquals("本轮测试失败,业务获取最大索引有问题,请检查", -1, maxIndex2); Assert.assertEquals("本轮测试失败,业务获取最大索引有问题,请检查", -1, maxIndex3); } }
选中方法某处或者类(全部的方法都会运行)
二、反射Reflection

1、认识反射获取类
反射类就是加载类,并允许以编程的方式解剖类中的各种成分(成员变量,方法,构造器等)
(1)获取Class对象的三种方式
- Class c1=类名.Class
- 调用Class提供方法:public static Class forName(String package); Class.forName("com.xx……")
- Object提供的方法:public Class getClass(); Class c3=对象.getClass
package com.ithema.reflect; public class ReflectDemo1 { public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException { //反射第一步,获取类的Class对象(获取类本身) //1、获取类本身 类名.class Class c1 = Student.class; //2、获取类本身 对象.getClass() Student s = new Student(); Class c2 = s.getClass(); //3、Class.forName() Class c3 = Class.forName("com.ithema.reflect.Student"); System.out.println(c1==c2);//true System.out.println(c1==c3); //true 同一份类文件 } }
2、获取类中的成分进行操作
(1)Class提供从类中获取构造器的方法
一般用Declared的

(2)获取类的成员变量

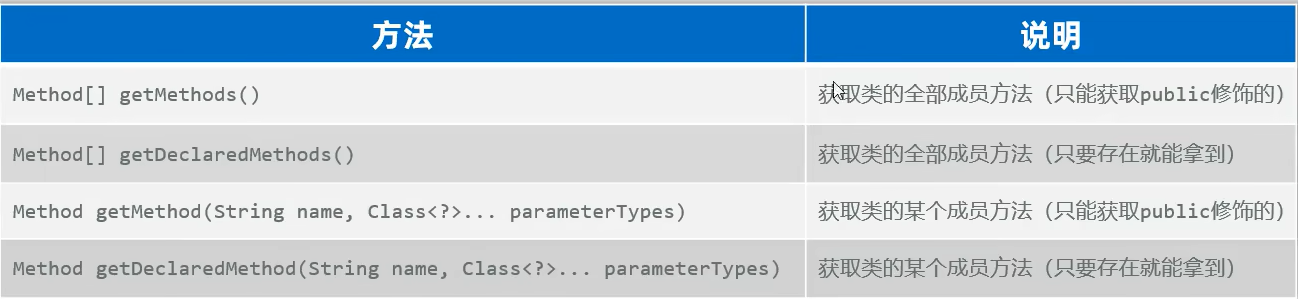
(3)获取类的方法
package com.ithema.reflect; public class Dog { public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public String getHobby() { return hobby; } public void setHobby(String hobby) { this.hobby = hobby; } private String name; private int age; private String hobby; public Dog(String name, int age, String hobby) { this.name = name; this.age = age; this.hobby = hobby; System.out.println("三个参数的有参构造"); } private Dog() { System.out.println("无参构造"); } public Dog(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; System.out.println("两个参数的有参构造"); } private void eat() { System.out.println("无参的吃"); } public String eat(String name) { System.out.println("爱吃" + name); return "谢谢,旺旺"; } @Override public String toString() { return "Dog{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + ", Hobby='" + hobby + '\'' + '}'; } }
package com.ithema.reflect; import org.junit.Test; import java.lang.reflect.Constructor; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException; import java.lang.reflect.Method; public class ReflectDemo2 { @Test public void getClassInfo() { //获取类的信息 //1、获取Class对象 Class c1 = Student.class; System.out.println(c1.getName());//类名的全类名 com.ithema.reflect.Student System.out.println(c1.getSimpleName());//类型Student } //获取类的构造器对象并对其操作 @Test public void constructorInfo() throws Exception { //1、获取Class对象 Class c = Dog.class; //2、获取构造器对象 Constructor[] cons = c.getDeclaredConstructors(); System.out.println("所有的构造器:"); for (Constructor cr : cons) { System.out.println(c.getName() + "参数数量" + cr.getParameterCount()); } //3、获取单个构造器 Constructor con1 = c.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class, int.class, String.class);//有参构造器 System.out.println("单个构造器:" + con1.getName() + con1.getParameterCount()); Constructor con2 = c.getDeclaredConstructor();//无参构造器 System.out.println("无参构造器:" + con2.getName() + con2.getParameterCount()); //4、获取构造器的作用依然是创建对象 Dog d1 = (Dog) con1.newInstance("小王", 18, "游泳"); System.out.println(d1); con2.setAccessible(true);//暴力反射:可以访问私有的属性、方法、构造器 Dog d2 = (Dog) con2.newInstance(); System.out.println(d2); } //获取类的成员变量对象并对其操作 @Test public void getFieldInfo() throws Exception { //1、获取Class对象 Class c = Dog.class; Constructor cr = c.getDeclaredConstructor(); cr.setAccessible(true); Dog dog = (Dog) cr.newInstance(); //2、获取类的成员变量对象 Field[] fileds = c.getDeclaredFields(); for (Field field : fileds) { System.out.println(field.getName() + " " + field.getType()); } //3、获取单个成员变量对象 Field field = c.getDeclaredField("age"); Field field1 = c.getDeclaredField("hobby"); System.out.println(field.getName() + "(" + field.getType() + ")"); System.out.println(field.getName() + "(" + field1.getType() + ")"); //4、获取成员变量的目的是依旧是取值和赋值 field.setAccessible(true);//暴力反射,绕过访问权限直接访问 field.set(dog, 18); field1.setAccessible(true); field1.set(dog,"社交"); System.out.println(dog); } @Test public void getMethodInfo() throws Exception { //1、获取Class对象 Class c = Dog.class; //获取类的构造器对象并实例化 Constructor cr = c.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class, int.class); Dog dog = (Dog) cr.newInstance("小王", 18); //2、获取成员方法对象 Method[] methods = c.getDeclaredMethods(); for (Method method : methods) { System.out.println(method.getName() + "返回类型 " + method.getReturnType()); } //3、获取单个方法对象 Method m1 = c.getDeclaredMethod("eat", String.class);//获取有参的eat方法 Method m2 = c.getDeclaredMethod("eat");//获取的是无参的eat System.out.println(m1.getName() + "(" + m1.getParameterCount() + ")"); System.out.println(m2.getName() + "(" + m2.getParameterCount() + ")"); //4、获取方法对象的目的是调用方法 String result = (String) m1.invoke(dog, "肉骨头"); System.out.println(result); m2.setAccessible(true);//暴力反射 Object result2 = m2.invoke(dog); System.out.println(result2); } }
3、作用、应用场景
(1)反射的作用:
- 可以获取类的全部成分进行操作
- 可以破坏封装性(私有的暴力反射)
- 可以绕过泛型的约束(编译后泛型约束就没有了)
最重要的用途是:适合做java的框架,基本上,主流的框架都会基于反射设计一些通用的功能
package com.ithema.reflect; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; public class ReflectDemo3 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //反射的基本作用 //1、类的全部成分的获取 //2、破坏封装性 //3、可以绕过泛型约束 List<String>list =new ArrayList<>(); list.add("hello"); list.add("world"); Class c=list.getClass(); Method add = c.getMethod("add", Object.class); add.invoke(list,100); add.invoke(list,true); System.out.println(list);// [hello, world, 100, true] } }
//综合
package com.ithema.reflect; import org.apache.commons.io.IOUtils; import java.io.*; import java.lang.reflect.Field; public class SaveObjectFrame { //保存任意对象的静态方法 public static void saveObject(Object obj) throws Exception{ OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("day06-junit-reflect-annotaion-proxy\\src\\obj.txt",true); PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(os); //1、获取Class对象 Class c = obj.getClass(); ps.println("******************"+c.getSimpleName()+"********************"); //2、获取Class对象的所有字段 Field[] fields = c.getDeclaredFields(); //3、遍历所有字段 for (Field field : fields) { field.setAccessible(true); //获取字段的名称和字段的值 ps.println(field.getName() + "=" + field.get(obj) ); } ps.close(); } }
package com.ithema.reflect; public class ReflectDemo4 { //反射的应用场景:框架的通用技术 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Dog dog = new Dog("小黑黑", 2, "吃肉骨头"); SaveObjectFrame.saveObject( dog); Student student = new Student( "小王", 18, "打游戏"); SaveObjectFrame.saveObject( student); Teacher teacher = new Teacher( "张老师", 49, "跳舞、下棋", 5000.0, "四年三班", '男', "12345678901"); SaveObjectFrame.saveObject( teacher); } }
三、注解
1、概述、自定义注解
(1)概述
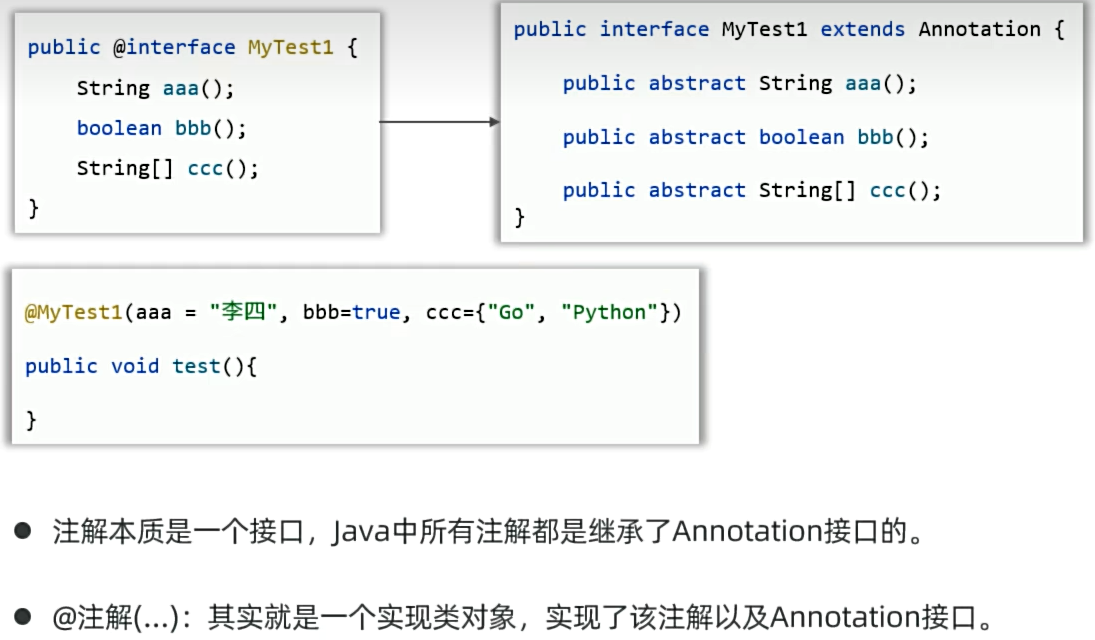
是java的特殊标记,比如@Test @Override等,作用是让其他程序根据注解信息来决定怎么执行该程序。
注解可以用在类上、构造器上、方法上、成员变量上、参数上等位置
(2)自定义注解
public @interface 注解名{
public 属性类型 属性名() default 默认值
}
特殊属性名:value
如果注解中只有一个属性,且是value属性,使用注解时,value名称可以不写
(3)注解的原理
package com.ithema.annotaion; public @interface Mybook { String name();//默认public int age() default 18; String sex() default "男"; String []address(); }
package com.ithema.annotaion; public @interface A { String value();//特殊属性value,在使用时,如果只有一个value属性,可以省略value // String hobby();这个时候value不能省 String hobby() default "小王";//value可省 }
package com.ithema.annotaion; @Mybook( name = "赵颖", age = 18, sex = "女", address = {"北京", "上海"}) @A("del") public class AnnotationDemo1 { public static void main(@A("k") String[] args) { } }
2、元注解
(1)指的是注解注解的注解(vnn)(放在注解上的注解)

(2)元注解:@Target @Retention 如下:
@Target声明被修饰的注解只能在哪些位置使用
@Retention声明注解的保留周期

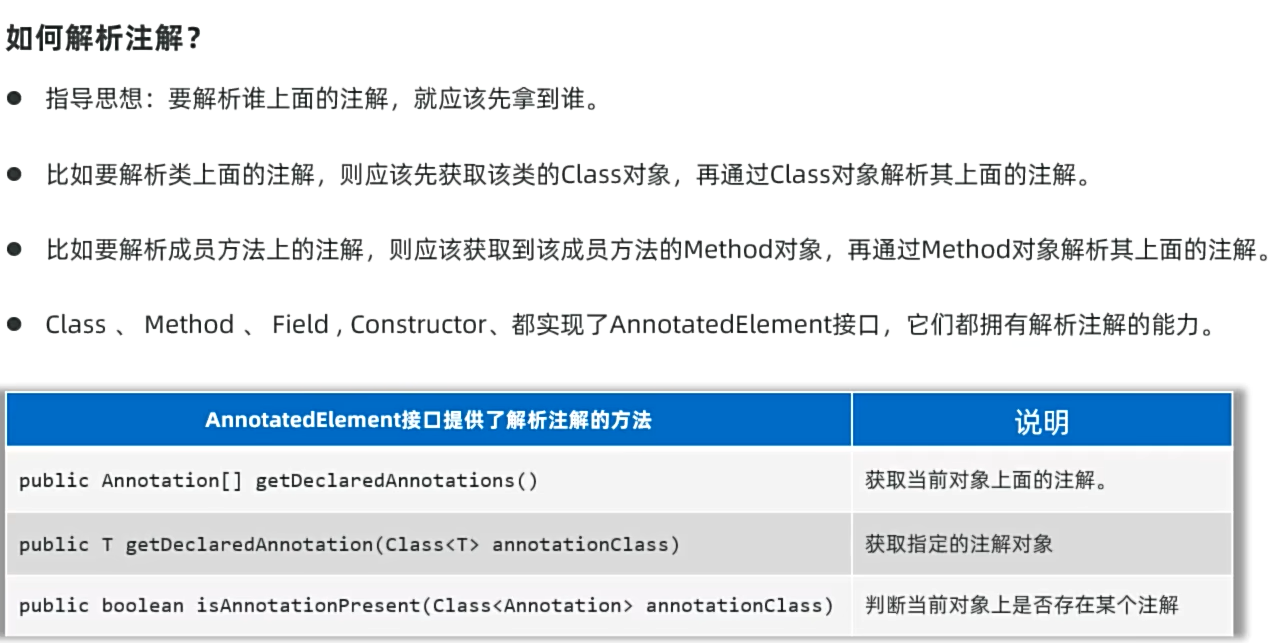
3、注解的解析
就是判断类上、方法上、成员变量上是否存在注解,并把注解里的内容给解析出来
package com.ithema.annotaion; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target; @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target({ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.TYPE}) public @interface Mytest2 { String value(); double price() default 100; String[] city(); }
package com.ithema.annotaion; @Mytest2(value = "华晨宇", price = 400.0, city = {"成都","北京"}) public class Demo { @Mytest2(value = "张靓颖", price = 100.0, city = { "上海","北京"}) public void test(){ System.out.println("test"); } @Mytest2(value = "周深", price = 300.0, city = { "深圳","长沙","沈阳"}) public void test1(String name){ System.out.println("test1"); } }
package com.ithema.annotaion; import org.junit.Test; import java.lang.annotation.Annotation; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.util.Arrays; public class AnnotationDemo3 { @Test public void parsClass() throws Exception { //解析Demo类中的全部注解 Class c = Demo.class; // 判断这个类对象上是否存在某个注解 if (c.isAnnotationPresent(Mytest2.class)) { //获取指定的注解对象 Mytest2 annotation = (Mytest2) c.getAnnotation(Mytest2.class); System.out.println(annotation.value()); System.out.println(annotation.price()); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(annotation.city())); } } @Test public void parsMethod() throws Exception { Class c = Demo.class; Method[] m=c.getDeclaredMethods(); for (Method method : m) { if(method.isAnnotationPresent(Mytest2.class)) { System.out.println(method.getName()); Mytest2 annotation = method.getAnnotation(Mytest2.class); System.out.println(annotation.value()); System.out.println(annotation.price()); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(annotation.city())); System.out.println("--------------------------------"); } } } }
4、作用、应用场景
让其他程序根据注解信息来决定怎么执行该程序
使用注解开发建议的JUnit框架
package com.ithema.annotaion; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target; @Target(ElementType.METHOD) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface Mytest { int count() default 1; }
package com.ithema.annotaion; import java.lang.reflect.Method; public class AnotationDemo4 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //搞清楚注解的应用场景,模拟JUnit框架 //获取类对象 //获取所有方法 //遍历所有方法,判断方法上是否有Test注解,有就执行,没有就不执行 Class c = AnotationDemo4.class; Method[] methods = c.getDeclaredMethods(); // Object o = c.getConstructor().newInstance(); // Constructor constructor = c.getConstructor(); // AnotationDemo4 obj = (AnotationDemo4) constructor.newInstance(); AnotationDemo4 obj = new AnotationDemo4(); for (Method m : methods) { if (m.isAnnotationPresent(Mytest.class)) { Mytest declaredAnnotation = m.getDeclaredAnnotation(Mytest.class); int value = declaredAnnotation.count(); for (int i = 0; i < value; i++) { m.invoke(obj); } } } } //测试方法 public 无参无返回值 @Mytest public void test1() { System.out.println("test1执行了"); } public void test2() { System.out.println("test2执行了"); } @Mytest(count = 3)//执行3次 public void test3() { System.out.println("test3执行了"); } public void test4() { System.out.println("test4执行了"); } }
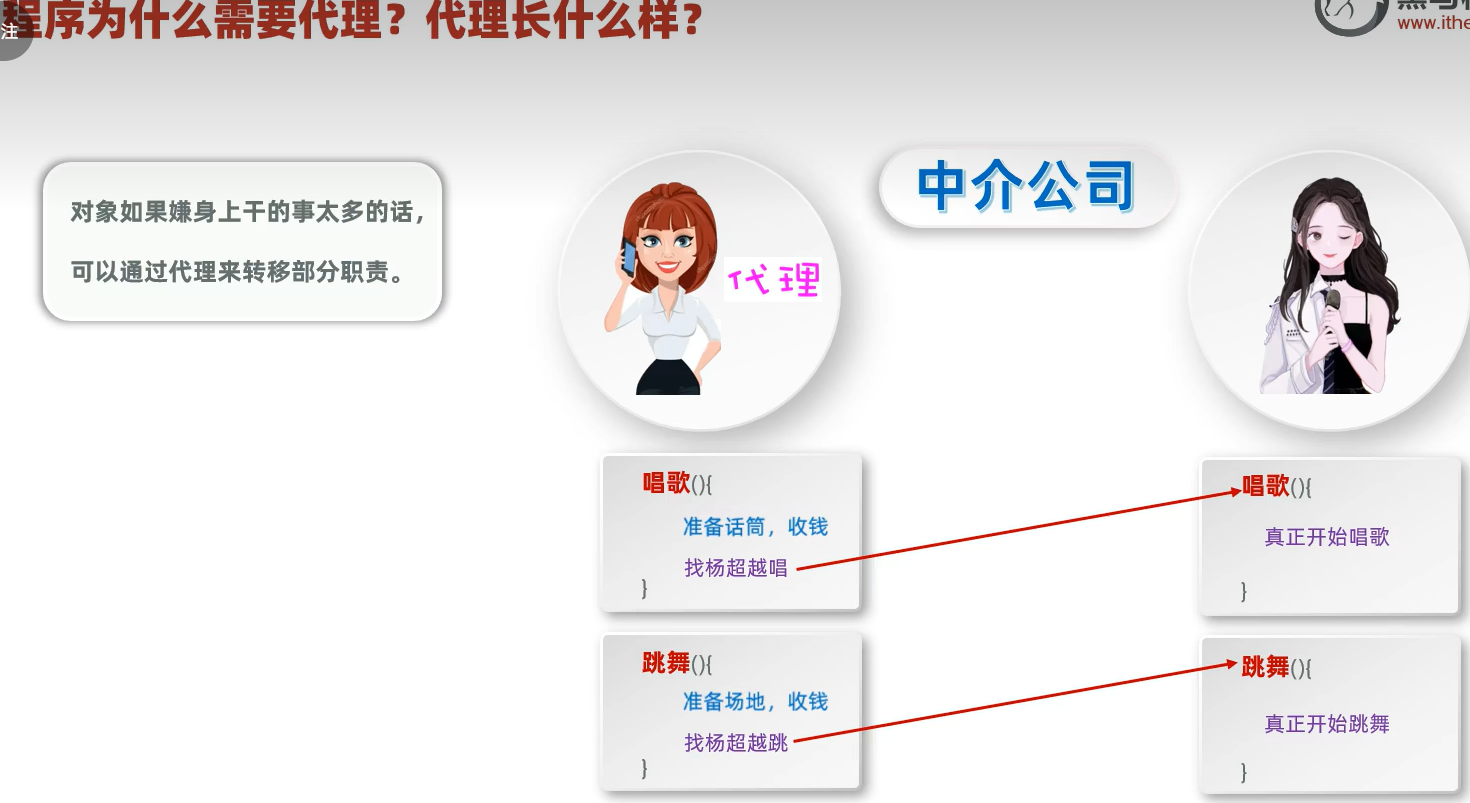
四、动态代理
1、需要代理的原因
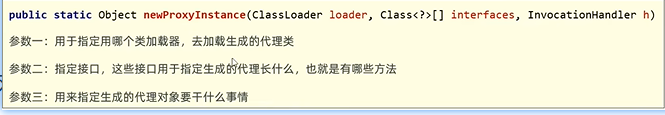
(1)创建代理
java.lang.reflect.Proxy类:提供了为对象产生代理对象的方法:
public static Object newProxy
package com.ithema.proxy; //明星服务接口 public interface StarService { void sing(String name); String dance(); }
package com.ithema.proxy; import lombok.AllArgsConstructor; import lombok.Data; import lombok.NoArgsConstructor; @Data @AllArgsConstructor @NoArgsConstructor public class Star implements StarService { private String name; @Override public void sing(String name) { System.out.println(this.name + "在唱"+ name); } @Override public String dance() { System.out.println(this.name + "在跳pop"); return "谢谢"; } }
package com.ithema.proxy; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; //代理工具类,中介公司,专门负责创建代理对象并返回 public class ProxyUtils { //创建代理对象并返回 public static StarService createProxy(Star star) { /** * 参数一:用于执行用哪个类加载器去加载生成的代理类。哪个类的都行 * 参数二:用于指定代理类需要实现的接口:明星类实现了哪些接口,代理类就实现哪些接口 * 参数三:用于指定代理类需要如何去代理(代理要做的事) */ return (StarService) Proxy.newProxyInstance(ProxyUtils.class.getClassLoader(), star.getClass().getInterfaces(), new InvocationHandler() { @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { //声明代理对象要干的事情 //参数一:proxy接收到代理对象本身(暂时用不到) //参数二:method表示正在被代理的方法 //参数三:args表示正在被代理方法的参数 if("sing".equals(method.getName())) { System.out.println("准备话筒,收钱20w"); }else if("dance".equals(method.getName())){ System.out.println("准备场地,收钱100w"); } //真正干活(把真正的明星对象叫来正式干活) //找真正的明星对象来执行被代理的方法 return method.invoke(star, args); } }); } }
package com.ithema.proxy; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { //1、创建明星类Star Star star = new Star("杨超越"); //为明星创建一个专属的代理对象 StarService proxy = ProxyUtils.createProxy(star); proxy.sing("月亮之上"); System.out.println(proxy.dance()); } }
2、解决实际问题,掌握代理的好处
例如统计每个方法的耗时(AOP切面思想,上下一样,中间不一样)
package com.ithema.proxy2; public interface UserService { void loginUser(String name, String pwd) throws Exception; void deleteUsers() throws Exception; String[] SelectUsers() throws Exception; }
package com.ithema.proxy2; import lombok.AllArgsConstructor; import lombok.Data; import lombok.NoArgsConstructor; @Data @AllArgsConstructor public class UserServiceImp implements UserService { @Override public void loginUser(String name, String pwd) throws Exception { System.out.println("用户"+name+"登录成功"); Thread.sleep(200); } @Override public void deleteUsers() throws Exception{ System.out.println("删除1000哥用户成功"); Thread.sleep(500); } @Override public String[] SelectUsers() throws Exception{ System.out.println("查询到3名用户"); String[]users={"王一博","肖战","杨夏"}; Thread.sleep(100); return users; } }
package com.ithema.proxy2; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; import java.util.logging.Handler; //代理工具类,中介公司,专门负责创建代理对象并返回 public class ProxyUtils { public static <T>T createProxy(T user) { return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(ProxyUtils.class.getClassLoader(), user.getClass().getInterfaces(), new InvocationHandler() { @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); Object obj = method.invoke(user, args); long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println(method.getName()+"耗时:" + (end - start) / 1000.0 + "s"); return obj; } }); } }
package com.ithema.proxy2; import java.util.Arrays; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //使用动态代理解决实际问题,并掌握使用代码的好处 //统计每个方法的 UserService proxy = ProxyUtils.createProxy(new UserServiceImp()); proxy.loginUser("admin","123456"); proxy.deleteUsers(); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(proxy.SelectUsers())); } }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号