第二次作业-个人项目
个人项目
Github连接: https://github.com/sywaaaa/3123004673
| 这个作业属于哪个课程 | 课程链接 |
|---|---|
| 这个作业要求在哪里 | 作业要求 |
| 这个作业的目标 | 任务目标:了解项目开发流程 熟悉git使用方式 熟练模块化开发流程 |
一. PSP
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 20 | 15 |
| Estimate | 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 10 | 10 |
| Development | 开发 | 5 | 5 |
| Analysis | 需求分析(包括学习新技术) | 40 | 50 |
| Design Spec | 生成设计文档 | 25 | 20 |
| Design Review | 设计复审 | 15 | 10 |
| Coding Standard | 代码规范(为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 10 | 10 |
| Design | 具体设计 | 30 | 25 |
| Coding | 具体编码 | 100 | 90 |
| Code Review | 代码复审 | 20 | 15 |
| Test | 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 30 | 40 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 10 | 10 |
| Test Report | 测试报告 | 10 | 10 |
| Size Measurement | 计算工作量 | 5 | 5 |
| Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | 事后总结,并提出过程改进计划 | 10 | 5 |
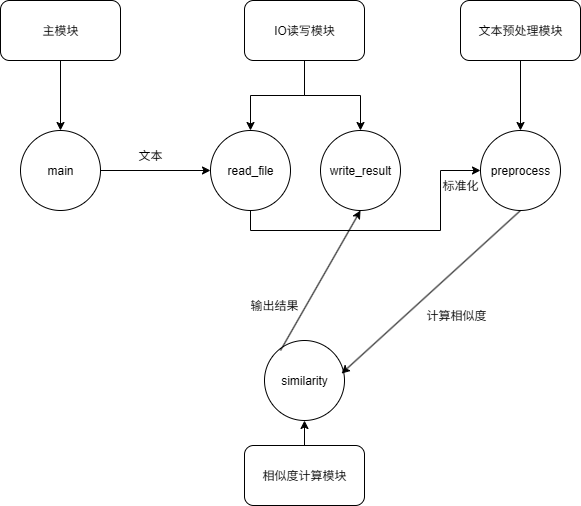
二. 模块接口设计与实现过程
项目结构
project/
│── sim/
│ ├── init.py
│ ├── io.py # 文件读写
│ ├── preprocess.py # 文本预处理
│ └── similarity.py # 相似度计算
|── 测试文本
|── tests/
| |──__init__.py
| |──__test_case__.py #边缘测试样例
│── main.py # 主程序入口
│── test_long_high_similarity.py # 性能测试入口
│── test.py 测试文本测试入口
│── README.md
辅助函数功能介绍
| 函数名 | 模块 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|
main() |
main.py |
程序入口,解析命令行,调用 I/O 与相似度计算 |
read_file(path: str) |
sim.io |
读取文本文件,返回字符串 |
write_result(path: str, rate: float) |
sim.io |
写入相似度结果 |
normalize_text(text: str) |
sim.preprocess |
文本标准化(去空格、小写化等) |
1. 计算模块介绍
- 模块名称:
sim/similarity.py - 职责:计算两段文本的相似度,返回重复率(0~100%)
- 模块特点:核心计算模块,直接处理标准化后的文本,算法需支持大文本且高效。
2. 代码组织设计
本模块采用函数化设计,没有使用类,结构如下:
similarity.py
│
├── duplication_rate(orig_text: str, suspect_text: str) -> float
│ └─ 核心函数,负责:
│ 1. 调用 normalize_text 对文本预处理
│ 2. 调用内部 DP 算法计算编辑距离
│ 3. 返回重复率
│
└── (可选)内部辅助函数
└── normalize_text(text: str) -> str # 如果不在 preprocess 模块
-
关键函数:
duplication_rate:对外接口,模块唯一出口
-
函数关系:
duplication_rate调用preprocess.normalize_text对文本标准化- 模块内部维护局部变量完成计算
- 输出结果作为浮点型重复率返回给主程序或调用方
3. 算法核心(关键点)
-
文本标准化
- 去除空格
- 大小写统一
- 可选去掉标点或特殊符号
-
编辑距离计算
-
采用动态规划(DP)
-
状态定义:
dp[i][j] = 前i个字符和前j个字符的最小编辑距离 -
状态转移:
dp[i][j] = min( dp[i-1][j] + 1, # 删除 dp[i][j-1] + 1, # 插入 dp[i-1][j-1] + cost # 替换 / 不变 ) -
优化思路:
-
滚动数组:只保留两行 DP 数组,空间复杂度 O(m)
-
列数选择短字符串进一步减少内存占用
-
边界处理:
- 空文本对空文本 → 100%
- 空文本对非空文本 → 0%
-
-
-
重复率计算
-
根据公式:
similarity = (1 - distance / max(len(a), len(b))) * 100 -
输出浮点型,保留两位小数
-
4. 算法独到之处
-
大文本优化
- 使用滚动数组显著降低空间复杂度
- 保持算法准确性,在大规模数据下表现良好
-
可扩展接口
- 模块接口为单一函数
duplication_rate - 上层程序无需关心内部 DP 实现
- 模块接口为单一函数
-
边界处理健壮
- 自动处理空文本、单字符文本
- 对中英文混合、标点符号差异具备鲁棒性
5. 模块函数关系图
三. 计算模块接口部分的性能改进
在原先的计算模块使用的是经典版本的动态规划 (DP) 编辑距离:
dp[i][j] = min(
dp[i-1][j] + 1, # 删除
dp[i][j-1] + 1, # 插入
dp[i-1][j-1] + cost # 替换 / 不变
)
- 空间:dp[n+1][m+1] 二维矩阵,复杂度 O(n*m)
- 时间:需要填满整个矩阵,复杂度 O(n*m)
缺点:长文本占用内存大,超过几万字符可能非常慢或内存吃紧
优化策略:滚动数组
# 原来:dp = [[0]*(m+1) for _ in range(n+1)]
# 优化:
prev_row = list(range(m + 1))
curr_row = [0] * (m + 1)
for i in range(1, n + 1):
curr_row[0] = i
for j in range(1, m + 1):
cost = 0 if a[i-1] == b[j-1] else 1
curr_row[j] = min(
prev_row[j] + 1, # 删除
curr_row[j-1] + 1, # 插入
prev_row[j-1] + cost # 替换
)
prev_row, curr_row = curr_row, prev_row # 滚动切换
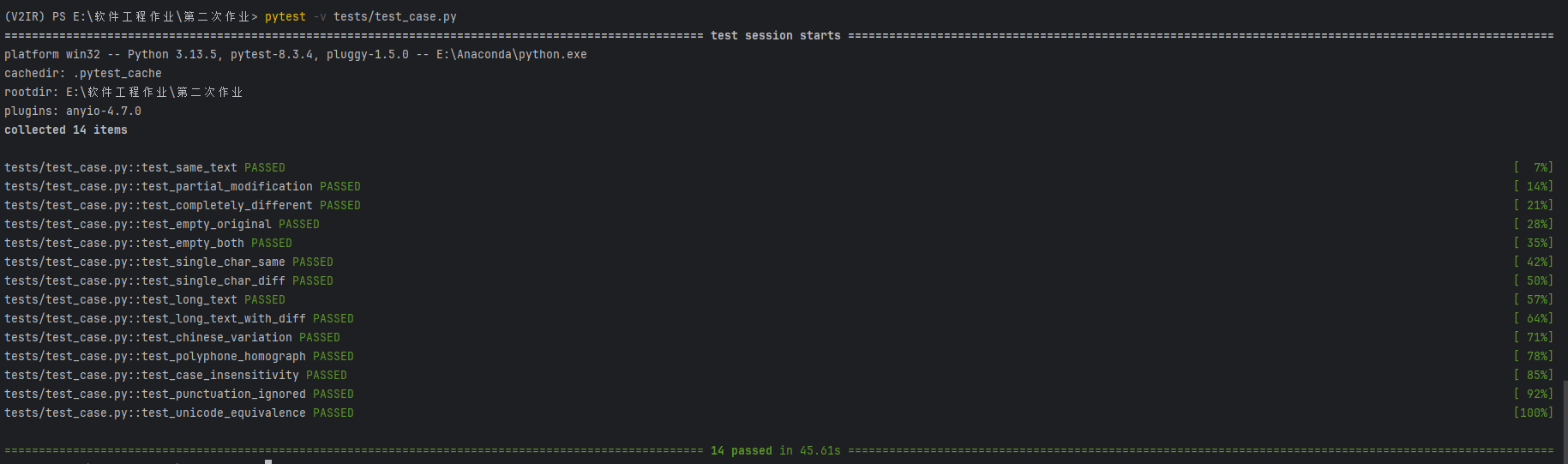
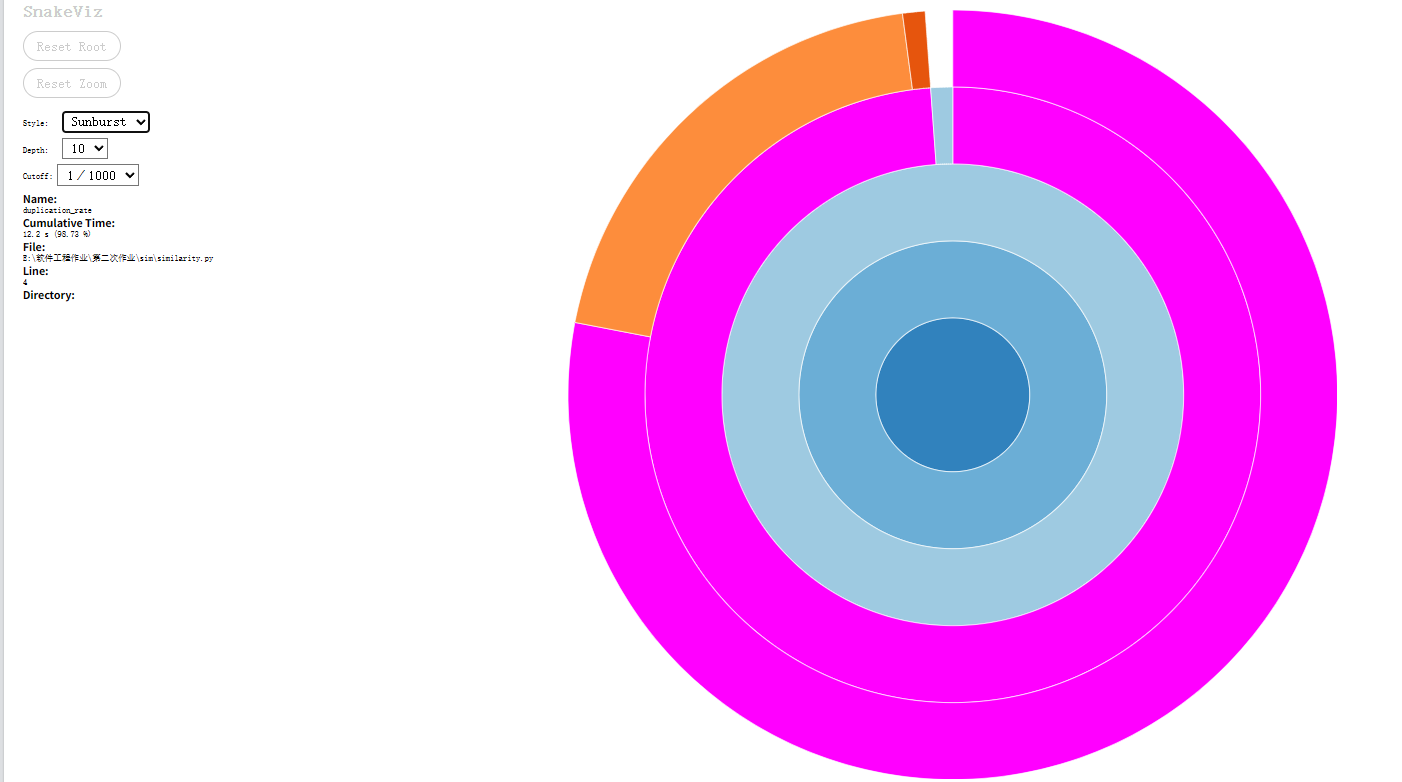
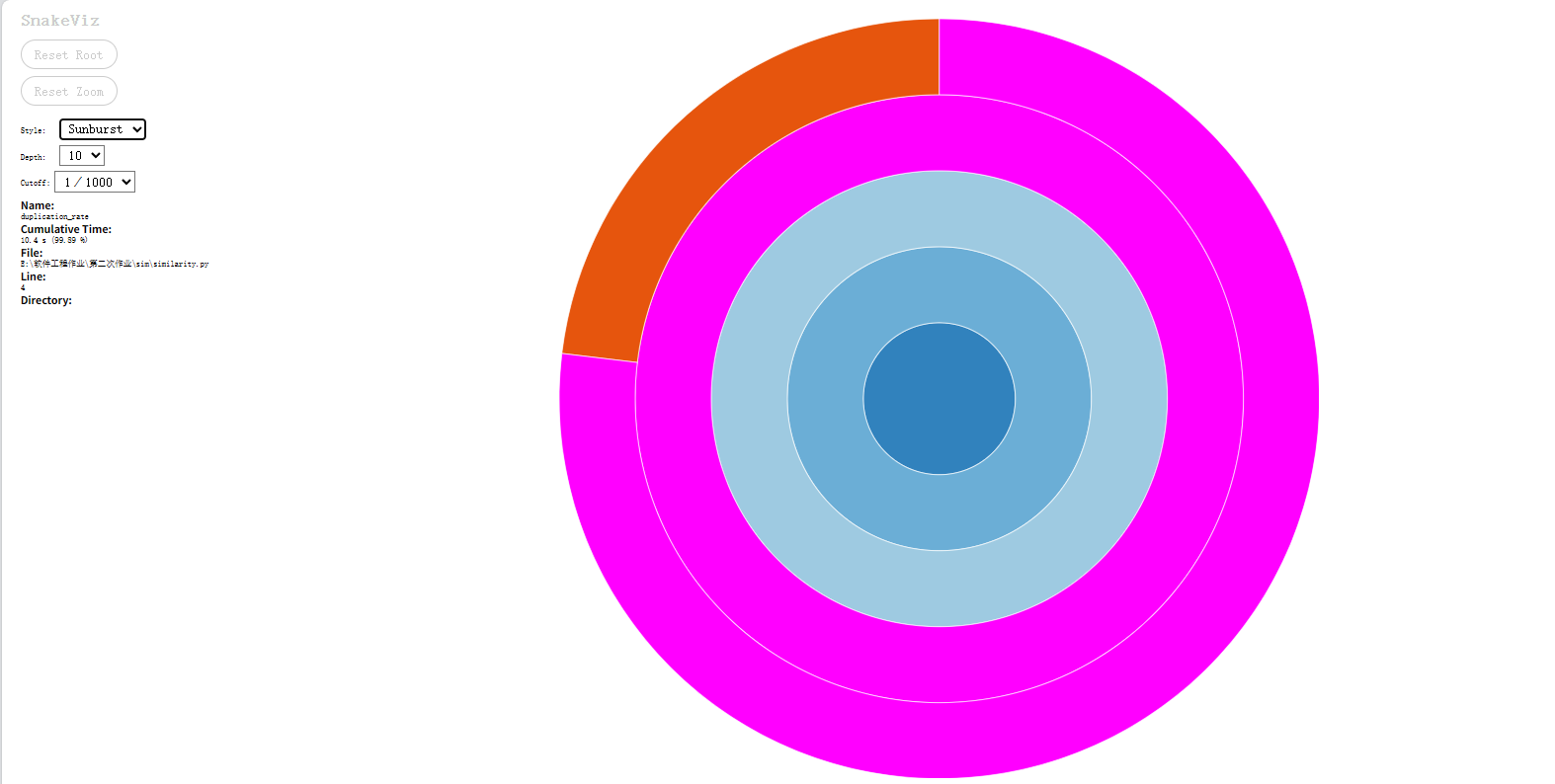
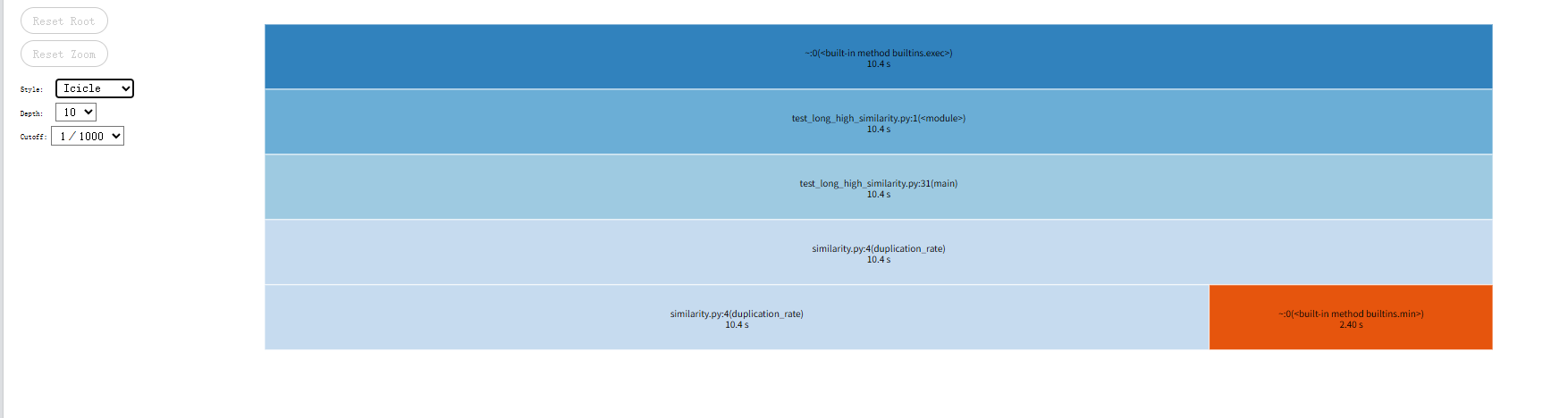
性能对比(cProfile + snakeviz)
-
修改前
![image]()
![image]()
-
修改后
![image]()
![image]()
优化后处理5000字文章从12.2s降至10.4s,实现明显性能提升。
四. 测试样例
边缘测试函数设计
# tests/test_cases.py
import os
from sim.similarity import duplication_rate
def test_same_text():
orig = "今天天气晴朗,适合户外运动。"
plag = "今天天气晴朗,适合户外运动。"
assert round(duplication_rate(orig, plag), 2) == 100.00
def test_partial_modification():
orig = "深度学习需要大量计算资源。"
plag = "机器学习需要大量 GPU 资源。"
rate = duplication_rate(orig, plag)
assert 30 <= rate <= 70
def test_completely_different():
orig = "春天是万物复苏的季节。"
plag = "量子物理研究微观粒子。"
assert round(duplication_rate(orig, plag), 2) == 0.00
def test_empty_original():
orig = ""
plag = "这是一个测试句子。"
assert round(duplication_rate(orig, plag), 2) == 0.00
def test_empty_both():
orig = ""
plag = ""
assert round(duplication_rate(orig, plag), 2) == 100.00
def test_single_char_same():
orig = "A"
plag = "A"
assert round(duplication_rate(orig, plag), 2) == 100.00
def test_single_char_diff():
orig = "A"
plag = "B"
assert round(duplication_rate(orig, plag), 2) == 0.00
def test_long_text():
orig = "abcdefg" * (10000 // 7)
plag = "abcdefg" * (10000 // 7)
assert round(duplication_rate(orig, plag), 2) == 100.00
def test_long_text_with_diff():
orig = "abcdefg" * (10000 // 7)
plag = ("abcdefg" * (9999 // 7)) + "x"
rate = duplication_rate(orig, plag)
assert rate < 100 and rate > 90
def test_chinese_variation():
orig = "“你好,”她说,“今天天气不错。”。"
plag = "“你好!”他说,“今天天气很好。”"
rate = duplication_rate(orig, plag)
assert 70 <= rate <= 85
def test_polyphone_homograph():
orig = "银行行长在银行门口行走。"
plag = "银行行长在银行前行路。"
rate = duplication_rate(orig, plag)
assert 70 <= rate <= 85
def test_case_insensitivity():
orig = "Hello World"
plag = "hello world"
assert round(duplication_rate(orig, plag), 2) == 100.00
def test_punctuation_ignored():
orig = "Hello, world!!!"
plag = "Hello world"
assert round(duplication_rate(orig, plag), 2) == 100.00
def test_unicode_equivalence():
orig = "office"
plag = "office"
assert round(duplication_rate(orig, plag), 2) == 100.00
测试样例说明
| 测试函数 | 测试目的 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
test_same_text |
完全相同文本 | 两个字符串完全一致,检查函数返回 100% 的重复率。 |
test_partial_modification |
部分相似文本 | 原文和改写后的文本有部分词语不同,测试函数能返回一个合理的中间相似度(约 50%)。 |
test_completely_different |
完全不同文本 | 原文和抄袭文完全无关,检查返回 0%。 |
test_empty_original |
原文为空 | 检查空原文与非空文本的相似度,预期为 0%。 |
test_empty_both |
两个空字符串 | 空文本对比空文本,认为完全相同,返回 100%。 |
test_single_char_same |
单字符相同 | 检查最小单位相同的情况,预期 100%。 |
test_single_char_diff |
单字符不同 | 检查最小单位不同的情况,预期 0%。 |
test_long_text |
超长文本完全相同 | 构造 1 万字符的长文本,验证函数在大文本上的正确性和性能。 |
test_long_text_with_diff |
超长文本部分不同 | 超长文本最后一个字符不同,检查函数返回略低于 100%,约 90%-100%。 |
test_chinese_variation |
中文标点和同义词变化 | 测试中文文本中标点和词语轻微变化的相似度,预期约 70-85%。 |
test_polyphone_homograph |
中文多音字/同形字变化 | 测试“行长行走”等词语替换的相似度,预期约 70-85%。 |
test_case_insensitivity |
英文大小写差异 | 测试大小写忽略的情况,期望 100%。 |
test_punctuation_ignored |
英文标点差异 | 测试标点被忽略的情况,期望 100%。 |
test_unicode_equivalence |
Unicode 等效字符 | 测试 Unicode 合字(如 fi)与普通字符组合的等效性,期望 100%。 |
测试结果:全部通过
测试函数设计
import os
import subprocess
# 原文件路径
orig_file = r"E:\软件工程作业\第二次作业\测试文本\orig.txt"
# 需要对比的文件
suspect_files = [
r"E:\软件工程作业\第二次作业\测试文本\orig_0.8_add.txt",
r"E:\软件工程作业\第二次作业\测试文本\orig_0.8_del.txt",
r"E:\软件工程作业\第二次作业\测试文本\orig_0.8_dis_1.txt",
r"E:\软件工程作业\第二次作业\测试文本\orig_0.8_dis_10.txt",
r"E:\软件工程作业\第二次作业\测试文本\orig_0.8_dis_15.txt",
]
# 遍历每个文件并执行 main.py
for suspect in suspect_files:
# ans_file 命名规则(比如 orig_0.8_add_ans.txt)
ans_file = suspect.replace(".txt", "_ans.txt")
cmd = ["python", "main.py", orig_file, suspect, ans_file]
print("运行命令:", " ".join(cmd))
# 执行命令
subprocess.run(cmd, check=True)
print("全部执行完成!")
五. 异常处理
-
文件未找到时
![image]()
-
非utf-8编码时
![image]()
-
命令行不规范时
![image]()
对空文本、文件权限不足、内存爆满等异常也进行了处理,但不常见,此处不展示。
main函数异常处理逻辑实现:
import sys
from sim.io import read_file, write_result
from sim.similarity import duplication_rate
def main():
if len(sys.argv) != 4:
print("请使用: python main.py [orig_file] [suspect_file] [ans_file] 启动程序")
sys.exit(1)
orig_path, suspect_path, ans_path = sys.argv[1], sys.argv[2], sys.argv[3]
try:
orig_text = read_file(orig_path)
suspect_text = read_file(suspect_path)
except Exception as e:
print(f"读取文件出错: {e}")
sys.exit(1)
try:
rate = duplication_rate(orig_text, suspect_text)
except Exception as e:
print(f"计算重复率出错: {e}")
sys.exit(1)
try:
write_result(ans_path, rate)
except Exception as e:
print(f"写入结果文件出错: {e}")
sys.exit(1)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
io函数异常处理实现:
def read_file(path: str) -> str:
"""读取文本文件,加入异常处理"""
try:
with open(path, "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
return f.read()
except FileNotFoundError:
raise FileNotFoundError(f"文件未找到: {path}")
except IOError as e:
raise IOError(f"读取文件出错: {e}")
def write_result(path: str, rate: float):
"""写入结果文件,加入异常处理"""
try:
with open(path, "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write(f"{rate:.2f}%")
except IOError as e:
raise IOError(f"写入文件出错: {e}")






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号