[CSS] Containing Block
Identifying the containing block
The process for identifying the containing block depends entirely on the value of the element's position property:
-
If the
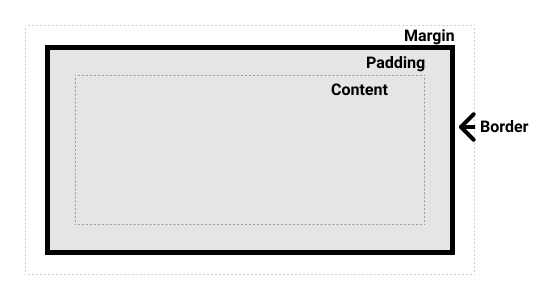
positionproperty isstatic,relative, orsticky, the containing block is formed by the edge of the content box of the nearest ancestor element that is either a block container (such as an inline-block, block, or list-item element) or establishes a formatting context (such as a table container, flex container, grid container, or the block container itself). -
If the
positionproperty isabsolute, the containing block is formed by the edge of the padding box of the nearest ancestor element that has apositionvalue other thanstatic(fixed,absolute,relative, orsticky). -
If the
positionproperty isfixed, the containing block is established by the viewport (in the case of continuous media) or the page area (in the case of paged media). -
If the
positionproperty isabsoluteorfixed, the containing block may also be formed by the edge of the padding box of the nearest ancestor element that has any of the following:- A
filter,backdrop-filter,transform, orperspectivevalue other thannone. - A
containvalue oflayout,paint,strictorcontent(e.g.contain: paint;). - A
container-typevalue other thannormal. - A
will-changevalue containing a property for which a non-initial value would form a containing block (e.g.filterortransform). - A
content-visibilityvalue ofauto.
- A



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号