回文自动机
帕姆
回文自动机是一种方便解决跟回文有关的一种数据结构。
这个东西感觉能干一切 manacher 能干的事,在这个自动机中,一个状态表示的是一个本质不同的回文串,而转移边表示在这个字符串前后在加相同字符变成另一个回文串。
类似后缀自动机,我们定义后缀链接表示最长的后缀使得这个后缀是个回文串。
同时我们定义两个初始节点,分别表示长度为奇数的回文串和长度为偶数的回文串,比如 \(\text{abba}\) 的回文自动机就是:
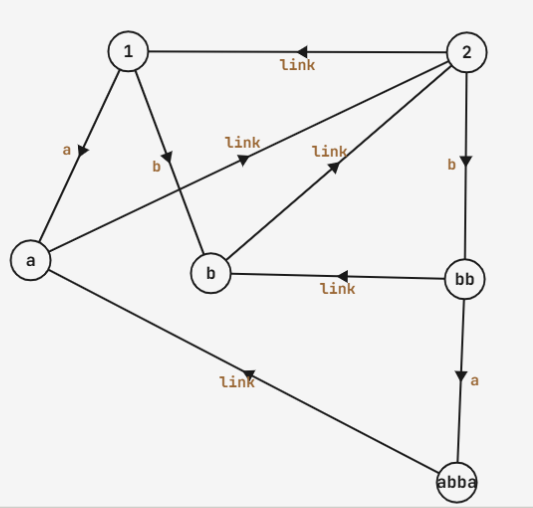
显然的是只保留转移边的图为两棵树。
现在考虑如何构造。
我们考虑每次插入一个字符,然后我们思考一个事情就是每次最多添加 \(1\) 个本质不同的回文串。
为什么呢?
我们画图:
那个黄绿色的是短的绿色的在长的绿色的对称,发现黄绿色的一定之前出现过,证毕。
所以我们的构造方式就是找到是原串后缀的最长的回文串所对应的节点,然后一直跳后缀链接,找到第一个满足这个串前面有我们要添加的字符的节点。
然后我们看是否需要新建节点,如果需要,将新节点的后缀链接设为次长的,这个可以通过之前那个点再次一直跳后缀链接来求出。
【模板】回文自动机
直接求出来在后缀树上的深度就行了。
点击查看代码
//これも運命じゃないか
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define uint unsigned long long
#define double long double
#define Air
namespace io{
inline int read(){
int x; cin >> x; return x;
}
inline void write(int x){
if(x < 0){putchar('-'); x = -x;}
if(x >= 10){write(x / 10);}
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
}
using namespace io;
const int N = 5e5 + 10;
int n;
string s;
struct Pam{
int son[26];
int fa, len;
}pam[N];
int a[N];
int dep[N];
int tot = 2, lst = 2;
void add(int pos, int c){
int p = lst;
while(a[pos - pam[p].len - 1] != c && p) p = pam[p].fa;
if(!pam[p].son[c]){
pam[p].son[c] = ++tot;
pam[tot].len = pam[p].len + 2;
int q = pam[p].fa;
while(a[pos - pam[q].len - 1] != c && q) q = pam[q].fa;
if(!q){
pam[tot].fa = 2;
}
else{
pam[tot].fa = pam[q].son[c];
}
dep[tot] = dep[pam[tot].fa] + 1;
}
lst = pam[p].son[c];
}
signed main() {
#ifndef Air
freopen(".in","r",stdin);
freopen(".out","w",stdout);
#endif
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
cin >> s;
n = s.size();
pam[1].len = -1;
pam[2].len = 0; pam[2].fa = 1;
s = ' ' + s;
int tp = 0;
a[0] = -1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
a[i] = (s[i] - 97 + tp) % 26;
add(i, a[i]);
tp = dep[lst];
cout << tp << ' ';
}
return 0;
}
【APIO2014】 回文串
也是简单题,我们建出来回文自动机后感觉跑个后缀树上 \(\text{dfs}\) 就行了。
点击查看代码
//これも運命じゃないか
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define uint unsigned long long
#define double long double
#define Air
namespace io{
inline int read(){
int f = 1, t = 0; char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') f = -f; ch = getchar();}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){t = t * 10 + ch - '0'; ch = getchar();}
return t * f;
}
inline void write(int x){
if(x < 0){putchar('-'); x = -x;}
if(x >= 10){write(x / 10);}
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
}
using namespace io;
string s;
int n;
const int N = 300010;
struct Pam{
int son[26];
int fa, len;
}pam[N];
int dp[N];
int a[N];
int tot = 2, lst = 2;
void add(int pos, int c){
int p = lst;
while(a[pos - pam[p].len - 1] != c && p) p = pam[p].fa;
if(!pam[p].son[c]){
pam[p].son[c] = ++tot;
pam[tot].len = pam[p].len + 2;
int q = pam[p].fa;
while(a[pos - pam[q].len - 1] != c && q) q = pam[q].fa;
if(!q){
pam[tot].fa = 2;
}
else{
pam[tot].fa = pam[q].son[c];
}
}
lst = pam[p].son[c];
dp[lst] ++;
}
vector<int>e[N];
int ans = 0;
void dfs(int now, int ff){
for(auto y: e[now]){
if(y == ff) continue;
dfs(y, now);
dp[now] += dp[y];
}
ans = max(ans, pam[now].len * dp[now]);
}
signed main() {
#ifndef Air
freopen(".in","r",stdin);
freopen(".out","w",stdout);
#endif
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
cin >> s;
n = s.size();
s = ' ' + s;
pam[1].len = -1;
pam[2].len = 0, pam[2].fa = 1;
a[0] = -1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
a[i] = s[i] - 'a';
add(i, s[i] - 'a');
}
for(int i = 2; i <= tot; i++){
e[pam[i].fa].push_back(i);
}
dfs(1, 0);
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
【SHOI2011】 双倍回文
建出来后缀树后直接用个什么东西维护一下 \(\frac{len}{2}\) 的数量,感觉就做完了。
点击查看代码
//これも運命じゃないか
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define uint unsigned long long
#define double long double
#define Air
namespace io{
inline int read(){
int x; cin >> x; return x;
}
inline void write(int x){
if(x < 0){putchar('-'); x = -x;}
if(x >= 10){write(x / 10);}
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
}
using namespace io;
int n;
const int N = 5e5 + 10;
string s;
struct Pam{
int son[26];
int fa, len;
}pam[N];
int a[N];
int tot = 2, lst = 2;
void add(int pos, int c){
int p = lst;
while(a[pos - pam[p].len - 1] != c && p) p = pam[p].fa;
if(!pam[p].son[c]){
pam[p].son[c] = ++tot;
pam[tot].len = pam[p].len + 2;
int q = pam[p].fa;
while(a[pos - pam[q].len - 1] != c && q) q = pam[q].fa;
if(!q){
pam[tot].fa = 2;
}
else{
pam[tot].fa = pam[q].son[c];
}
}
lst = pam[p].son[c];
}
vector<int>e[N];
unordered_map<int, int> mp;
int ans = 0;
void dfs(int now){
if(pam[now].len % 2 == 0)
mp[pam[now].len] ++;
if(pam[now].len % 2 == 0 && mp[pam[now].len / 2]){
ans = max(ans, pam[now].len);
}
for(auto y: e[now]){
dfs(y);
}
if(pam[now].len % 2 == 0)
mp[pam[now].len] --;
}
signed main() {
#ifndef Air
freopen(".in","r",stdin);
freopen(".out","w",stdout);
#endif
// freopen("dat.txt","r",stdin);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
n = read();
cin >> s;
s = ' ' + s;
pam[1].len = -1;
pam[2].len = 0, pam[2].fa = 1;
a[0] = -1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
a[i] = s[i] - 'a';
add(i, a[i]);
}
for(int i = 2; i <= tot; i++){
e[pam[i].fa].push_back(i);
}
dfs(1);
cout << ans;
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号