后缀自动机
抽象
后缀自动机
后缀自动机,是可以用 \(O(n)\) 的时空复杂度来表示一个字符串中全部子串的一种数据结构。
其中每个节点表示的是一些结束于相同位置的子串,每个子串可以从起始状态出发沿着这个子串对应的的一些边到达对应状态,类似 AC自动机。
那么有什么性质呢:
- 两个子串的结束位置不是包含就是无交
这个感性理解一波是好说的,如果说包含了,表示肯定其中一个是另一个的子串,否则就肯定不会在同一个位置结束。
- 一个节点所表示的子串的长度集合一定是连续的一段自然数。
因为这个节点表示的是结束位置相同的几个点,而他们肯定是有子串关系的,而最短的那个和最长的那个出现在一个节点中,说明中间的那些一定也只会在这个节点中。
那么如何构造呢:
我们考虑现在要构造 \(abcbbc\) 的后缀自动机,
我们先考虑加入 \(a\) 的情况
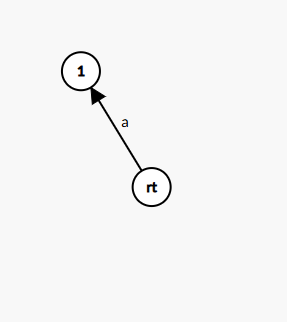
太简单了,对吧,那么考虑加入 \(b\) 呢?
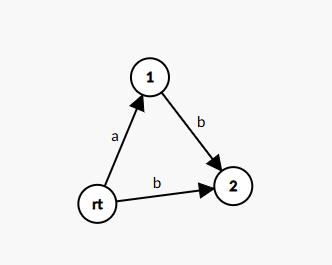
也不难,那么加入 \(c\) 呢?
我们概括一下前三个点,就是找到包含某个后缀的状态,然后向新建的这个状态连边,那么加入 \(b\) 呢?
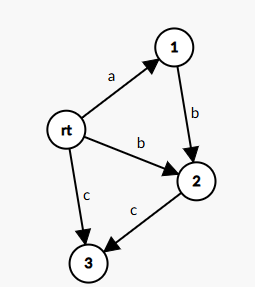
此时我们发现不好直接看出来了,我们定义一种新的边叫 \(fa\) 边,什么含义呢,就是表示这个状态里最短的那个串,去掉首字母所对应的状态,我们试着连一下:
当我们试着加入 \(b\) 的时候,我们先新建一个点,然后原先建出来的点向自己连边,然后往前跳 \(fa\) 边,发现 \(rt\) 节点有 \(b\) 这个边了,怎么办呢?
我们考虑把 \(2\) 拆成两个节点,一个包含我的最大后缀的点,发现这个新点的最大串的长度应该就是 \(rt\) 的长度 \(+1\),并且这个新点有老点的任意一条转移,如图:
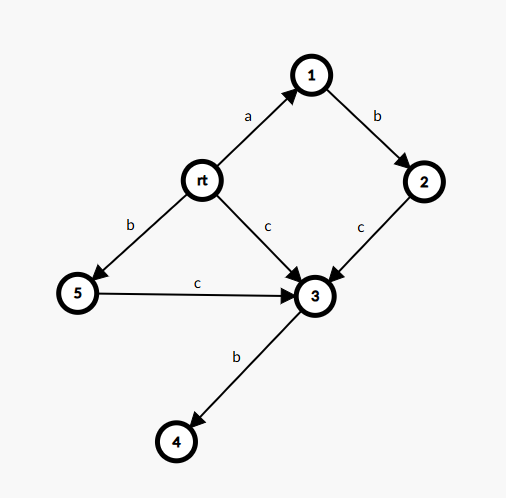
那么 \(fa\) 边的那张图呢?
我们只需要将老点向新点连一条边,新点继承老点的边,最开始新建的那个点向新点连边就行了。
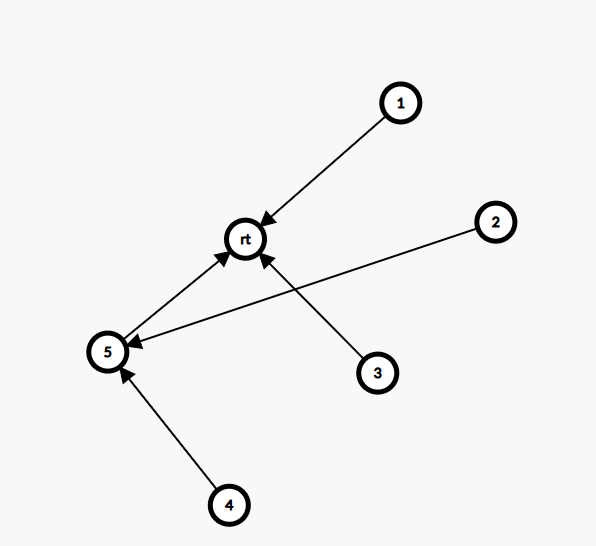
为什么这样是对的呢?
我们发现老点对应的一定是前一段较小的边划分给新点,发现符合 \(fa\) 边的定义,然后我们连一条边,另外我们继承也是好理解的,而我们最开始新建的那个点向新点连边其实就是他是我们的原串的某个后缀加上这个字符链接的,但不过这个子串在之前出现过,所以连一条 \(fa\) 边是对的。
那么接下来再加一个 \(b\),怎么加呢?
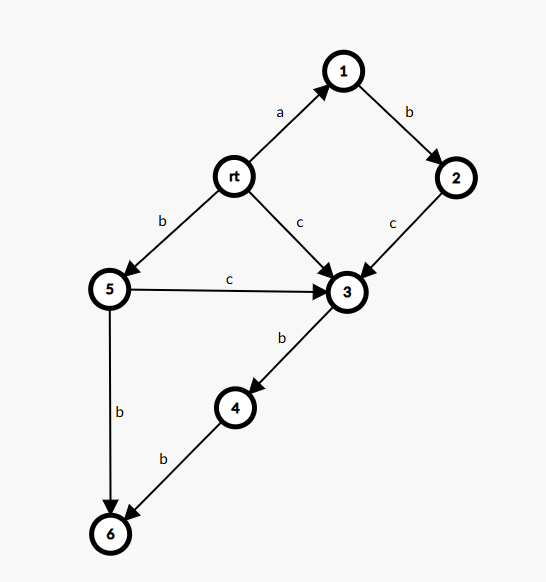
那为什么这次不用拆点了呢?因为 \(5\) 所有的串本来就可以在后面加一个 \(c\) 变成一个新子串,所以直接连边就行了。
同样的,\(6\) 的 \(fa\) 边就指向 \(5\)。
如果要加入一个 \(c\),如图:
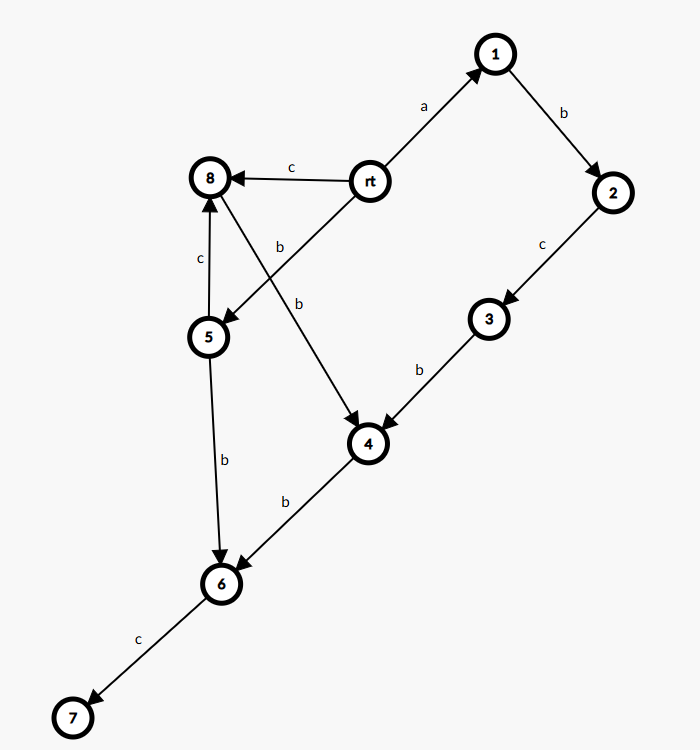
拆点就行了,但是需要注意的是要将我跳 \(fa\) 边中所有通过 \(c\) 连向 \(3\) 的点全部连向 \(8\),感性理解就是拆点得完全拆掉,否则会出现一个节点表示的串的长度不是一段连续的自然数的情况。
到这里相信大家已经会写代码了:
点击查看代码
struct Sam{
int son[26];
int fa;
int len;
}sam[N * 2];
string s;
int tot = 1, lst = 1;
void add(int c){
int p = lst;
int np = ++tot;
lst = tot;
sam[np].len = sam[p].len + 1;
for(; p && !sam[p].son[c]; p = sam[p].fa){
sam[p].son[c] = np;
}
if(!p) {//一路上很顺利,直接加就行了
sam[np].fa = 1;
return ;
}
int q = sam[p].son[c];
if(sam[q].len == sam[p].len + 1){//如果全部的都能连这个字符
sam[np].fa = q;
}
else{
int nq = ++tot;//拆点
sam[nq] = sam[q];
sam[nq].len = sam[p].len + 1;
sam[np].fa = sam[q].fa = nq;
for(; p && sam[p].son[c] == q; p = sam[p].fa){//拆完全
sam[p].son[c] = nq;
}
}
}
P5231
直接建出来 SAM 后暴力匹配之。
点击查看代码
//これも運命じゃないか
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// #define int long long
#define uint unsigned long long
#define double long double
#define Air
namespace io{
inline int read(){
int x; cin >> x; return x;
}
inline void write(int x){
if(x < 0){putchar('-'); x = -x;}
if(x >= 10){write(x / 10);}
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
}
using namespace io;
int n;
const int N = 1e7 + 10;
struct Sam{
int son[4];
int fa;
int len;
}sam[N * 2];
string s;
int tot = 1, lst = 1;
void add(int c){
int p = lst;
int np = ++tot;
lst = tot;
sam[np].len = sam[p].len + 1;
for(; p && !sam[p].son[c]; p = sam[p].fa){
sam[p].son[c] = np;
}
if(!p) {
sam[np].fa = 1;
return ;
}
int q = sam[p].son[c];
if(sam[q].len == sam[p].len + 1){
sam[np].fa = q;
}
else{
int nq = ++tot;
sam[nq] = sam[q];
sam[nq].len = sam[p].len + 1;
sam[np].fa = sam[q].fa = nq;
for(; p && sam[p].son[c] == q; p = sam[p].fa){
sam[p].son[c] = nq;
}
}
}
signed main() {
#ifndef Air
freopen(".in","r",stdin);
freopen(".out","w",stdout);
#endif
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
n = read();
int q = read();
cin >> s;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if(s[i - 1] == 'E'){
add(0);
}
if(s[i - 1] == 'S'){
add(1);
}
if(s[i - 1] == 'W'){
add(2);
}
if(s[i - 1] == 'N'){
add(3);
}
}
while(q--){
cin >> s;
int now = 1;
int m = s.size();
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
int to;
if(s[i - 1] == 'E'){
to = 0;
}
if(s[i - 1] == 'S'){
to = 1;
}
if(s[i - 1] == 'W'){
to = 2;
}
if(s[i - 1] == 'N'){
to = 3;
}
if(!sam[now].son[to]){
now = -1;
cout << i - 1 << '\n';
break;
}
else{
now = sam[now].son[to];
}
}
if(now != -1){
cout << m << '\n';
}
}
return 0;
}
最长公共子串
考虑一个事情就是我们对于第一个串建出来 SAM,然后对于后面的串,我们考虑在 SAM 维护一个信息表示目前这个串所能匹配的最长长度,这个是好做的,然后我们跑完一次之后记得要往上跳祖先去更新,然后维护最小值,就做完了。
点击查看代码
//これも運命じゃないか
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define uint unsigned long long
#define double long double
#define Air
namespace io{
inline int read(){
int x; cin >> x; return x;
}
inline void write(int x){
if(x < 0){putchar('-'); x = -x;}
if(x >= 10){write(x / 10);}
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
}
using namespace io;
int n;
const int N = 1e4 + 10;
struct Sam{
int son[26];
int fa, len;
}sam[N * 2];
int tot = 1, lst = 1;
string s;
void add(int c){
int p = lst;
int np = ++tot;
lst = tot;
sam[np].len = sam[p].len + 1;
for(; p && !sam[p].son[c]; p = sam[p].fa){
sam[p].son[c] = np;
}
if(!p){
sam[np].fa = 1;
return ;
}
int q = sam[p].son[c];
if(sam[q].len == sam[p].len + 1){
sam[np].fa = q;
return ;
}
int nq = ++tot;
sam[nq] = sam[q];
sam[nq].len = sam[p].len + 1;
sam[q].fa = sam[np].fa = nq;
for(; p && sam[p].son[c] == q; p = sam[p].fa){
sam[p].son[c] = nq;
}
}
int ans[N * 2], now[N * 2];
signed main() {
#ifndef Air
freopen(".in","r",stdin);
freopen(".out","w",stdout);
#endif
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
n = read();
cin >> s;
int m = s.size();
s = ' ' + s;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
add(s[i] - 'a');
}
memset(ans, 0x3f, sizeof ans);
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++){
cin >> s;
m = s.size();
s = ' ' + s;
memset(now, 0, sizeof now);
int to = 1, tmp = 0;
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++){
int c = s[j] - 'a';
while(to > 1 && !sam[to].son[c]){
to = sam[to].fa;
tmp = sam[to].len;
}
if(sam[to].son[c]){
to = sam[to].son[c];
tmp++;
}
now[to] = max(now[to], tmp);
}
for(int j = tot; j >= 1; j--){
int p = sam[j].fa;
now[p] = max(now[p], min(now[j], sam[p].len));
}
for(int j = 1; j <= tot; j++){
ans[j] = min(ans[j], now[j]);
}
}
int res = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= tot; i++){
res = max(res, ans[i]);
}
cout << res;
return 0;
}
「SDOI2016」生成魔咒
用 SA 的做法在之前已经写过了,这里 SAM 怎么写呢?
我们考虑直接大力建 SAM,然后每次答案就加上我这个节点所表示的大小。
点击查看代码
//これも運命じゃないか
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define uint unsigned long long
#define double long double
#define Air
namespace io{
inline int read(){
int f = 1, t = 0; char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') f = -f; ch = getchar();}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){t = t * 10 + ch - '0'; ch = getchar();}
return t * f;
}
inline void write(int x){
if(x < 0){putchar('-'); x = -x;}
if(x >= 10){write(x / 10);}
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
}
using namespace io;
int n;
const int N = 200010;
struct Sam{
map<int, int>son;
int fa, len;
}sam[N];
int tot = 1, lst = 1;
int ans = 0;
void add(int c){
int p = lst;
int np = ++tot;
lst = tot;
sam[np].len = sam[p].len + 1;
for(; p && !sam[p].son[c]; p = sam[p].fa){
sam[p].son[c] = np;
}
if(!p){
sam[np].fa = 1;
return ;
}
int q = sam[p].son[c];
if(sam[q].len == sam[p].len + 1){
sam[np].fa = q;
return ;
}
int nq = ++tot;
sam[nq] = sam[q];
sam[nq].len = sam[p].len + 1;
sam[q].fa = sam[np].fa = nq;
for(; p && sam[p].son[c] == q; p = sam[p].fa){
sam[p].son[c] = nq;
}
}
signed main() {
#ifndef Air
freopen(".in","r",stdin);
freopen(".out","w",stdout);
#endif
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
n = read();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
add(read());
ans += sam[lst].len - sam[sam[lst].fa].len;
cout << ans << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
「TJOI2015」弦论
建出来 SAM,然后直接做个 DAG 上 DP 就行了。
点击查看代码
//これも運命じゃないか
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define uint unsigned long long
#define double long double
#define Air
namespace io{
inline int read(){
int x; cin >> x; return x;
}
inline void write(int x){
if(x < 0){putchar('-'); x = -x;}
if(x >= 10){write(x / 10);}
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
}
using namespace io;
int n, m;
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
struct Sam{
int son[26];
int fa, len;
}sam[N];
int dp[N];
string s;
int tot = 1, lst = 1;
void add(int c){
int p = lst;
int np = ++tot;
lst = tot;
sam[np].len = sam[p].len + 1;
dp[np] = 1;
for(; p && !sam[p].son[c]; p = sam[p].fa){
sam[p].son[c] = np;
}
if(!p){
sam[np].fa = 1;
return ;
}
int q = sam[p].son[c];
if(sam[q].len == sam[p].len + 1){
sam[np].fa = q;
return ;
}
int nq = ++tot;
sam[nq] = sam[q];
sam[nq].len = sam[p].len + 1;
sam[np].fa = sam[q].fa = nq;
for(; p && sam[p].son[c] == q; p = sam[p].fa){
sam[p].son[c] = nq;
}
}
vector<int>e[N];
void dfs_dp(int now){
for(auto y: e[now]){
dfs_dp(y);
dp[now] += dp[y];
}
}
int val[N];
ll sum[N];
bool vis[N];
void dfs_sum(int now){
vis[now] = 1;
sum[now] = val[now];
for(int i = 0; i < 26; i++){
int y = sam[now].son[i];
if(!y) continue;
if(!vis[y])
dfs_sum(y);
sum[now] += sum[y];
}
}
vector<int>ans;
void get_ans(int t){
if(sum[1] < t) return ;
int now = 1;
while(1){
if(val[now] >= t) break;
t -= val[now];
for(int i = 0; i < 26; i++){
int y = sam[now].son[i];
if(!y) continue;
if(sum[y] >= t){
now = y;
ans.push_back(i);
break;
}
else{
t -= sum[y];
}
}
}
}
signed main() {
#ifndef Air
freopen(".in","r",stdin);
freopen(".out","w",stdout);
#endif
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
cin >> s;
n = s.size();
s = ' ' + s;
int TPS = read();
m = read();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
add(s[i] - 'a');
}
for(int i = 2; i <= tot; i++){
e[sam[i].fa].push_back(i);
}
dfs_dp(1);
for(int i = 2; i <= tot; i++){
if(TPS) val[i] = dp[i];
else val[i] = 1;
}
dfs_sum(1);
get_ans(m);
if(!ans.size()){
cout << -1 << '\n';
return 0;
}
for(auto y: ans){
cout << (char)(y + 'a');
}
return 0;
}
「BJOI2020」封印
先求出来每个结尾所对应的最小的 \(l\),然后我们二分一波,找到第一个可以包含整个的,然后写个数据结构维护最大值就做完了。
点击查看代码
//これも運命じゃないか
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define uint unsigned long long
#define double long double
#define Air
namespace io{
inline int read(){
int x; cin >> x; return x;
}
inline void write(int x){
if(x < 0){putchar('-'); x = -x;}
if(x >= 10){write(x / 10);}
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
}
using namespace io;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
int n;
int m;
struct Sam{
int son[26];
int fa, len;
}sam[N * 2];
int tot = 1, lst = 1;
void add(int c){
int p = lst;
int np = ++tot;
lst = tot;
sam[np].len = sam[p].len + 1;
for(; p && !sam[p].son[c]; p = sam[p].fa){
sam[p].son[c] = np;
}
if(!p){
sam[np].fa = 1;
return ;
}
int q = sam[p].son[c];
if(sam[q].len == sam[p].len + 1){
sam[np].fa = q;
return ;
}
int nq = ++tot;
sam[nq] = sam[q];
sam[nq].len = sam[p].len + 1;
sam[q].fa = sam[np].fa = nq;
for(; p && sam[p].son[c] == q; p = sam[p].fa){
sam[p].son[c] = nq;
}
return ;
}
string s, t;
int pos[N];
int st[N][30];
int pre[N];
void prework(){
for(int i = 2; i < N; i++){
pre[i] = pre[i / 2] + 1;
}
}
int ask(int l, int r){
if(l > r) return -1e18;
int step = pre[r - l + 1];
return max(st[l][step], st[r - (1ll << step) + 1][step]);
}
signed main() {
#ifndef Air
freopen(".in","r",stdin);
freopen(".out","w",stdout);
#endif
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
prework();
cin >> s;
n = s.size();
s = ' ' + s;
cin >> t;
m = t.size();
t = ' ' + t;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
add(t[i] - 'a');
}
int now = 1, len = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
int c = s[i] - 'a';
while(now > 1 && !sam[now].son[c]){
now = sam[now].fa;
len = sam[now].len;
}
if(sam[now].son[c]){
now = sam[now].son[c];
len ++;
}
pos[i] = i - len + 1;
// pos[i] = max(pos[i], 1ll);
st[i][0] = i - pos[i] + 1;
// cerr << pos[i] << ' ' ;
}
// cerr << '\n';
for(int j = 1; j <= 20; j++){
for(int i = 1; i + (1ll << j) - 1 <= n; i++){
st[i][j] = max(st[i][j - 1], st[i + (1ll << (j - 1))][j - 1]);
}
}
int q = read();
while(q--){
int l = read(), r = read();
int id = lower_bound(pos + l, pos + r + 1, l) - pos;
int ans = ask(id, r);
// cerr << id << '\n';
if(id != l){
ans = max(ans, id - l);
}
cout << ans << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
「AHOI2013」 差异
我们考虑一个事情就是我们通过 \(fa\) 边连出来的树是可以快速求出两个子串的最长公共后缀,然后我们反向字符串,求出的就是 \(\text{LCP}\) 然后就做完了。
点击查看代码
//これも運命じゃないか
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define uint unsigned long long
#define double long double
#define Air
namespace io{
inline int read(){
int f = 1, t = 0; char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') f = -f; ch = getchar();}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){t = t * 10 + ch - '0'; ch = getchar();}
return t * f;
}
inline void write(int x){
if(x < 0){putchar('-'); x = -x;}
if(x >= 10){write(x / 10);}
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
}
using namespace io;
const int N = 500010;
struct Sam{
int son[26];
int fa, len;
}sam[N * 2];
string s;
int n;
int dp[N * 2];
vector<int>e[N * 2];
ll ans;
int tot = 1, lst = 1;
void add(int c){
int p = lst;
int np = ++tot;
lst = tot;
dp[np] = 1;
sam[np].len = sam[p].len + 1;
for(; p && !sam[p].son[c]; p = sam[p].fa){
sam[p].son[c] = np;
}
if(!p){
sam[np].fa = 1;
return ;
}
int q = sam[p].son[c];
if(sam[q].len == sam[p].len + 1){
sam[np].fa = q;
return ;
}
int nq = ++tot;
sam[nq] = sam[q];
sam[nq].len = sam[p].len + 1;
sam[q].fa = sam[np].fa = nq;
for(; p && sam[p].son[c] == q; p = sam[p].fa){
sam[p].son[c] = nq;
}
}
void dfs(int now, int ff){
for(auto y: e[now]){
if(y == ff) continue;
dfs(y, now);
ans -= 2ll * sam[now].len * 1ll * dp[y] * dp[now];
dp[now] += dp[y];
}
}
signed main() {
#ifndef Air
freopen(".in","r",stdin);
freopen(".out","w",stdout);
#endif
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
cin >> s;
n = s.size();
s = ' ' + s;
for(int i = n; i >= 1; i--){
add(s[i] - 'a');
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
ans += i * 1ll * (n - 1);
}
// cerr << ans << '\n';
for(int i = 1; i <= tot; i++){
// for(int j = 0; j < 26; j++){
// if(sam[i].son[j])
// cerr << i << ' ' << sam[i].son[j] << ' ' << (char)(j + 'a') << '\n';
// }
// cerr << sam[i].fa << ' ' << i << '\n';
e[sam[i].fa].push_back(i);
}
dfs(1, 0);
cout << ans << '\n';
return 0;
}
「2017 山东一轮集训 Day5」字符串
考虑每个串建立一个 SAM,然后我们在相邻的 SAM 之间连边,连边注意从后往前就做完了。
点击查看代码
//これも運命じゃないか
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define uint unsigned long long
#define double long double
#define Air
namespace io{
inline int read(){
int x; cin >> x; return x;
}
inline void write(int x){
if(x < 0){putchar('-'); x = -x;}
if(x >= 10){write(x / 10);}
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
}
using namespace io;
int n;
const int N = 2e6 + 10, MOD = 1e9 + 7;
struct Sam{
int son[26];
int fa, len;
}sam[N];
int rt[N];
int lst = 0, tot = 0;
void add(int c, int st){
int p = lst;
int np = ++tot;
lst = tot;
sam[np].len = sam[p].len + 1;
for(; p && !sam[p].son[c]; p = sam[p].fa){
sam[p].son[c] = np;
}
if(!p){
sam[np].fa = st;
return ;
}
int q = sam[p].son[c];
if(sam[q].len == sam[p].len + 1){
sam[np].fa = q;
return ;
}
int nq = ++tot;
sam[nq] = sam[q];
sam[nq].len = sam[p].len + 1;
sam[q].fa = sam[np].fa = nq;
for(; p && sam[p].son[c] == q; p = sam[p].fa){
sam[p].son[c] = nq;
}
}
string s;
int dp[N];
int dfs(int now){
if(dp[now]) return dp[now];
dp[now] = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < 26; i++){
if(!sam[now].son[i]) continue;
int y = sam[now].son[i];
dp[now] += dfs(y);
dp[now] %= MOD;
}
return dp[now];
}
signed main() {
#ifndef Air
freopen(".in","r",stdin);
freopen(".out","w",stdout);
#endif
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
n = read();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
cin >> s;
rt[i] = ++tot;
lst = tot;
int m = s.size();
s = ' ' + s;
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++){
add(s[j] - 'a', rt[i]);
}
}
for(int i = n - 1; i >= 1; i--){
for(int j = rt[i]; j < rt[i + 1]; j++){
for(int k = 0; k < 26; k++){
if(!sam[j].son[k]){
sam[j].son[k] = sam[rt[i + 1]].son[k];
}
}
}
}
cout << dfs(1);
return 0;
}
谢特
建出来后缀自动机后把 \(fa\) 边拿出来做个线段树合并就行了,挺像差异那道题的。
点击查看代码
//これも運命じゃないか
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// #define int long long
#define uint unsigned long long
#define double long double
#define Air
namespace io{
inline int read(){
int x; cin >> x; return x;
}
inline void write(int x){
if(x < 0){putchar('-'); x = -x;}
if(x >= 10){write(x / 10);}
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
}
using namespace io;
const int N = 2e5 + 10, Iinf = 0, Ainf = 262143, Bval = 131072;
int n;
int a[N];
string s;
struct Segment{
int lc, rc;
int dat;
#define lc(x) seg[x].lc
#define rc(x) seg[x].rc
}seg[N * 2 * 20];
int tp = 0;
int rt[N * 2];
void build(int &p){
if(!p) p = ++tp;
}
void change(int p, int l, int r, int x){
seg[p].dat ++;
if(l == r){
return ;
}
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if(x <= mid){
build(lc(p));
change(lc(p), l, mid, x);
}
else{
build(rc(p));
change(rc(p), mid + 1, r, x);
}
}
int merge(int p1, int p2, int l, int r){
if(!p1){
return p2;
}
if(!p2){
return p1;
}
seg[p1].dat += seg[p2].dat;
if(l == r){
return p1;
}
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
lc(p1) = merge(lc(p1), lc(p2), l, mid);
rc(p1) = merge(rc(p1), rc(p2), mid + 1, r);
return p1;
}
int ask(int p, int l, int r, int x, int val){
if(!seg[p].dat){
return -1;
}
if(l == r){
return l;
}
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if(x & val){
if(seg[lc(p)].dat){
return ask(lc(p), l, mid, x, (val >> 1));
}
else{
return ask(rc(p), mid + 1, r, x, (val >> 1));
}
}
else{
if(seg[rc(p)].dat){
return ask(rc(p), mid + 1, r, x, (val >> 1));
}
else{
return ask(lc(p), l, mid, x, (val >> 1));
}
}
}
int get(int p1, int p2, int l, int r){
if(!seg[p1].dat){
return -1e9;
}
if(l == r) {
int val = ask(p2, Iinf, Ainf, l, Bval);
if(val != -1)
return (val ^ l);
else
return -1e9;
}
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
int ans = -1e9;
ans = max(ans, get(lc(p1), p2, l, mid));
ans = max(ans, get(rc(p1), p2, mid + 1, r));
return ans;
}
struct Sam{
int son[26];
int fa, len;
}sam[N * 2];
int tot = 1, lst = 1;
void add(int c){
int p = lst;
int np = ++tot;
lst = tot;
sam[np].len = sam[p].len + 1;
build(rt[np]);
for(; p && !sam[p].son[c]; p = sam[p].fa){
sam[p].son[c] = np;
}
if(!p){
sam[np].fa = 1;
return ;
}
int q = sam[p].son[c];
if(sam[q].len == sam[p].len + 1){
sam[np].fa = q;
return ;
}
int nq = ++tot;
sam[nq] = sam[q];
build(rt[nq]);
sam[nq].len = sam[p].len + 1;
sam[q].fa = sam[np].fa = nq;
for(; p && sam[p].son[c] == q; p = sam[p].fa){
sam[p].son[c] = nq;
}
}
vector<int>e[N * 2];
int ans;
void dfs(int now){
for(auto y : e[now]){
dfs(y);
// cerr << get(rt[now], rt[y], Iinf, Ainf) << '\n';
if(seg[rt[y]].dat > seg[rt[now]].dat){
ans = max(ans, sam[now].len + get(rt[now], rt[y], Iinf, Ainf));
}
else{
ans = max(ans, sam[now].len + get(rt[y], rt[now], Iinf, Ainf));
}
merge(rt[now], rt[y], Iinf, Ainf);
}
}
signed main() {
#ifndef Air
freopen(".in","r",stdin);
freopen(".out","w",stdout);
#endif
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
n = read();
cin >> s;
s = ' ' + s;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
a[i] = read();
}
for(int i = n; i >= 1; i--){
add(s[i] - 'a');
change(rt[lst], Iinf, Ainf, a[i]);
}
for(int i = 2; i <= tot; i++){
e[sam[i].fa].push_back(i);
}
dfs(1);
cout << ans << '\n';
return 0;
}
广义后缀自动机
就是有多个串的后缀自动机。
我们考虑把全部串放到一个 Trie 树上,然后我们 bfs 来构造,每次就记录下这个点插入的点的编号,然后我们构造的时候将 \(\text{lst}\) 赋值为我父亲的记录的编号,可以看看代码。
点击查看代码
//これも運命じゃないか
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define uint unsigned long long
#define double long double
#define Air
namespace io{
inline int read(){
int x; cin >> x; return x;
}
inline void write(int x){
if(x < 0){putchar('-'); x = -x;}
if(x >= 10){write(x / 10);}
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
}
using namespace io;
int n;
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
struct Trie{
int son[26];
}tr[N];
int pos[N];
int tp = 1;
void insert(string s){
int m = s.size();
s = ' ' + s;
int now = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
int c = s[i] - 'a';
if(!tr[now].son[c]){
tr[now].son[c] = ++tp;
}
now = tr[now].son[c];
}
}
struct Sam{
int son[26];
int len, fa;
#define fa(x) sam[x].fa
}sam[N * 2];
int tot = 1;
int add(int c, int lst){
int p = lst;
int np = ++tot;
sam[np].len = sam[p].len + 1;
for(; p && !sam[p].son[c]; p = sam[p].fa){
sam[p].son[c] = np;
}
if(!p){
sam[np].fa = 1;
return np;
}
int q = sam[p].son[c];
if(sam[q].len == sam[p].len + 1){
sam[np].fa = q;
return np;
}
int nq = ++tot;
sam[nq] = sam[q];
sam[nq].len = sam[p].len + 1;
sam[q].fa = sam[np].fa = nq;
for(; p && sam[p].son[c] == q; p = sam[p].fa){
sam[p].son[c] = nq;
}
return np;
}
void bfs(){
queue<int>q;
q.push(1);
pos[1] = 1;
while(q.size()){
int now = q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i = 0; i < 26; i++){
int y = tr[now].son[i];
if(!y) continue;
q.push(y);
pos[y] = add(i, pos[now]);
}
}
}
signed main() {
#ifndef Air
freopen(".in","r",stdin);
freopen(".out","w",stdout);
#endif
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
n = read();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
string s;
cin >> s;
insert(s);
}
// cerr << tp << '\n';
bfs();
ll ans = 0;
for(int i = 2; i <= tot; i++){
ans += sam[i].len - sam[fa(i)].len;
}
cout << ans << '\n' << tot << '\n';
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号