数据采集与融合技术实践第一次作业
作业①:
要求:用requests和BeautifulSoup库方法定向爬取给定网址(http://www.shanghairanking.cn/rankings/bcur/2020 )的数据,屏幕打印爬取的大学排名信息。
输出信息:
排名 学校名称 省市 学校类型 总分
1 清华大学 北京 综合 852.5
2......
代码如下:
import urllib.request
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
# 定义要爬取的网址
url = 'http://www.shanghairanking.cn/rankings/bcur/2020'
# 用urllib.request库发送GET请求
response = urllib.request.urlopen(url)
# 读取网页内容
html = response.read()
# 使用BeautifulSoup解析网页
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'html.parser')
# 找到包含大学排名信息的表格
table = soup.find('table', class_='rk-table')
# 获取N(学号尾数最后2位)
N = 23
# 打印表头
print("{:<6} {:<20} {:<10} {:<8} {:<10}".format("排名", "学校名称", "省市", "学校类型", "总分"))
# 找到表格中的每一行
rows = table.find_all('tr')[1:] # 跳过表头行
for row in rows[:N]: # 只打印前N行
# 找到每一行中的列数据
cols = row.find_all('td')
# 提取排名、学校名称、省市、学校类型和总分
rank = cols[0].get_text().strip()
school_name_with_line_break = cols[1].get_text().strip()
school_name = school_name_with_line_break.split('\n')[0] # 只取换行符前的部分
province_city = cols[2].get_text().strip()
school_type = cols[3].get_text().strip()
total_score = cols[4].get_text().strip()
# 打印排名信息
print("{:<6} {:<20} {:<10} {:<8} {:<10}".format(rank, school_name, province_city, school_type, total_score))
结果截图:
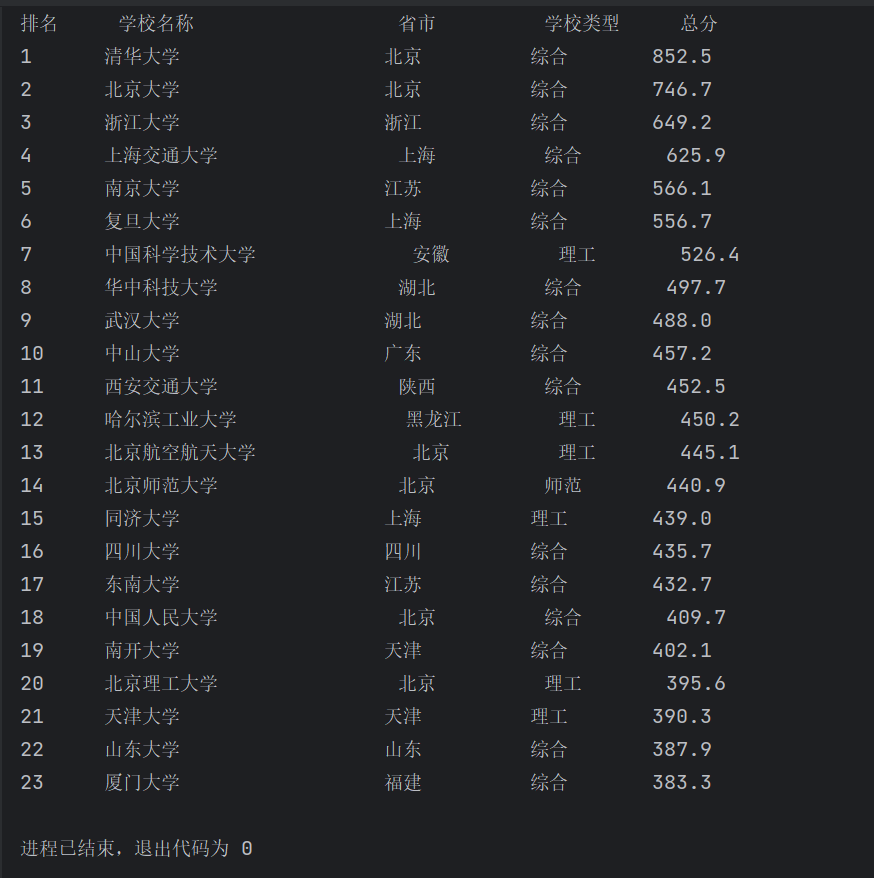
心得体会:
通过该项实践,我对requests和BeautifulSoup库方法有了初步的认识,并能用些基础的方法爬取给定网址的数据,首次体会到爬虫的神奇功能与爬出数据的乐趣。
作业②:
要求:用requests和re库方法设计某个商城(自已选择)商品比价定向爬虫,爬取该商城,以关键词“书包”搜索页面的数据,爬取商品名称和价格。
输出信息:
序号 商品名
1 xxx
2......
代码如下:
import requests
import re
# 发送HTTP请求获取网页内容
def fetch_webpage(url):
response = requests.get(url)
if response.status_code == 200:
return response.text
else:
print("网页请求失败")
return None
# 解析网页内容,提取商品信息
def extract_product_info(html):
# 使用正则表达式匹配商品名称和价格
title = r'<p class="name" name="title" ><a title=" (.*?)".*?>'
price = r'<span class="price_n">¥(.*?)</span>'
pricelist = re.findall(price, html)
titlelist = re.findall(title, html)
i=0
print("{:<3} {:<80} {:<10}".format("序号", "商品名", "价格"))
if pricelist:
for product in pricelist:
product_name = titlelist[i]
product_price = pricelist[i]
print("{:<3} {:<80} {:<10}".format(i+1,product_name,product_price))
i += 1
def main():
keyword = "书包"
url = f"http://search.dangdang.com/?key={keyword}&act=input"
html = fetch_webpage(url)
if html:
extract_product_info(html)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
结果截图:
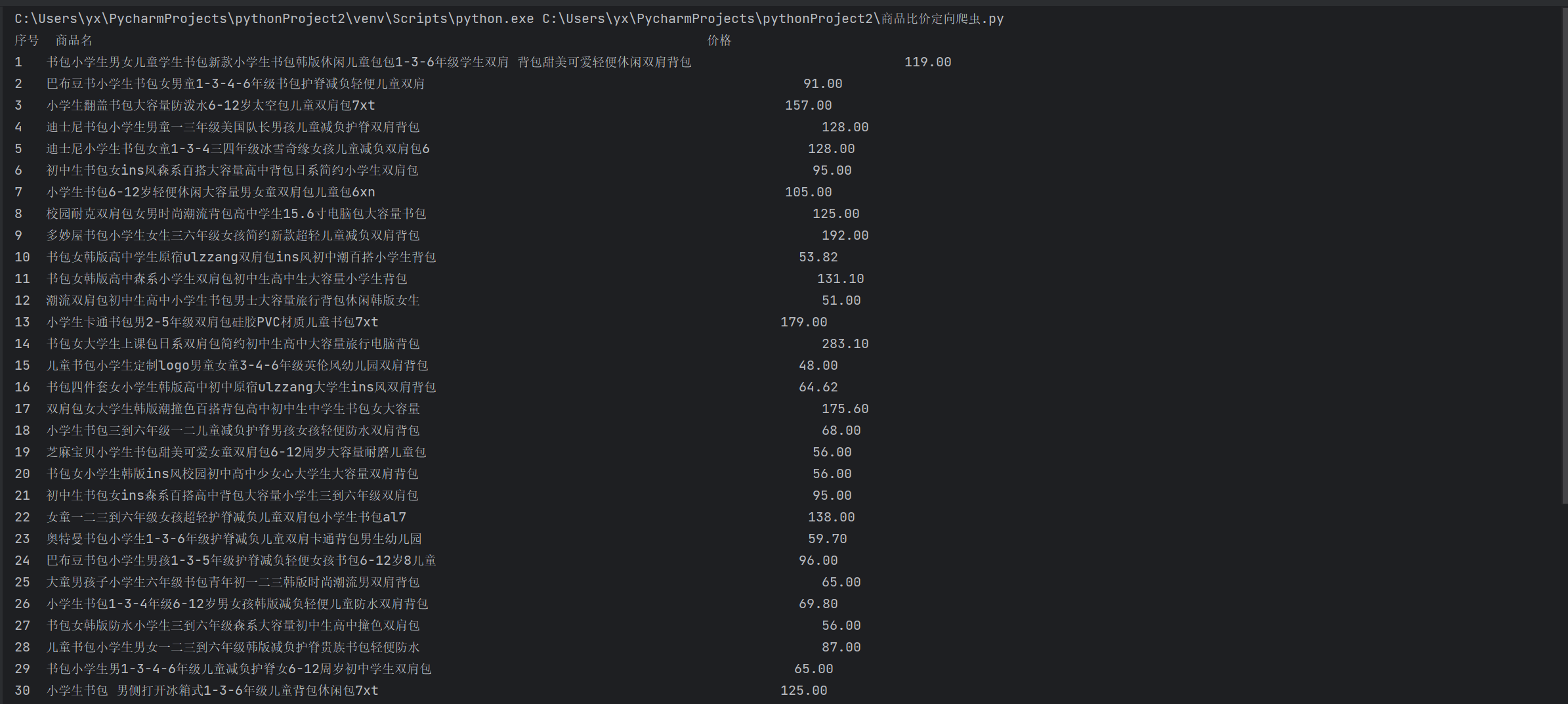
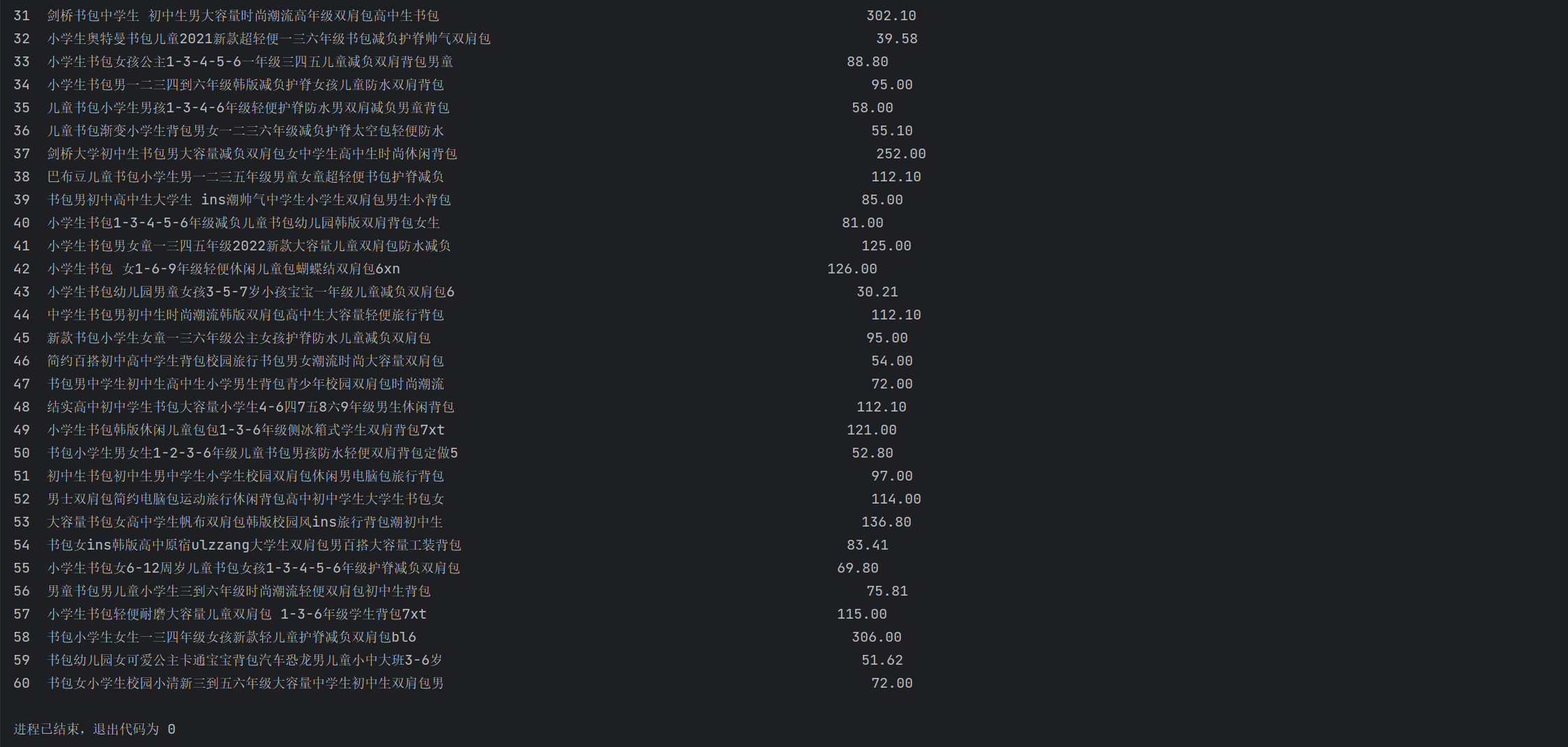
心得体会:
通过该项实践,我对requests和re库方法有了一定的了解,其中不习惯对正则表达式的使用,让我遇到了一些麻烦,花了较长的时间解决。
作业③:
要求:爬取一个给定网页( https://xcb.fzu.edu.cn/info/1071/4481.htm)或者自选网页的所有JPEG和JPG格式文件
输出信息:
将自选网页内的所有JPEG和JPG文件保存在一个文件夹中
代码如下:
import requests
import re
import os
import time
from urllib.parse import urlparse
# 创建一个目录来保存爬取的图片
if not os.path.exists('dangdang_images'):
os.makedirs('dangdang_images')
# 设置搜索关键词
search_keyword = "书包"
# 定义爬取函数
def crawl_dangdang_images(keyword, max_pages):
base_url = "http://search.dangdang.com/?key={}&act=input&page_index={}"
# 总共要爬取的图片数量
total_images = 100 # 前两页共有图片数量
images_downloaded = 0
page = 1
while images_downloaded < total_images and page <= max_pages:
url = base_url.format(keyword, page)
response = requests.get(url)
if response.status_code == 200:
# 使用正则表达式查找图片链接
img_links = re.findall(r'src=["\'](.*?)["\']', response.text)
for img_link in img_links:
# 检查图片链接是否包含协议(http://或https://)
if not img_link.startswith("http:") and not img_link.startswith("https:"):
img_link = "http:" + img_link
# 使用urllib的urlparse检查链接是否有效
parsed_url = urlparse(img_link)
# 排除无效的链接、JS文件和非图片文件
if parsed_url.netloc and not img_link.endswith(('.js', '.css')):
# 检查文件扩展名,只下载常见的图片格式
valid_image_extensions = ('.jpg', '.jpeg', '.png', '.gif', '.bmp')
if img_link.lower().endswith(valid_image_extensions):
# 生成图片的文件名
img_name = os.path.basename(parsed_url.path)
# 下载图片
img_data = requests.get(img_link).content
with open(f'dangdang_images/{img_name}', 'wb') as img_file:
img_file.write(img_data)
print(f"下载图片:{img_name}")
images_downloaded += 1
if images_downloaded >= total_images:
break
# 控制爬取速度,避免对服务器造成过多负担
time.sleep(1)
else:
print(f"无法访问页面:{url}")
page += 1
if __name__ == "__main__":
max_pages_to_crawl = 2 # 只爬取前两页的图片
crawl_dangdang_images(search_keyword, max_pages_to_crawl)
结果截图:
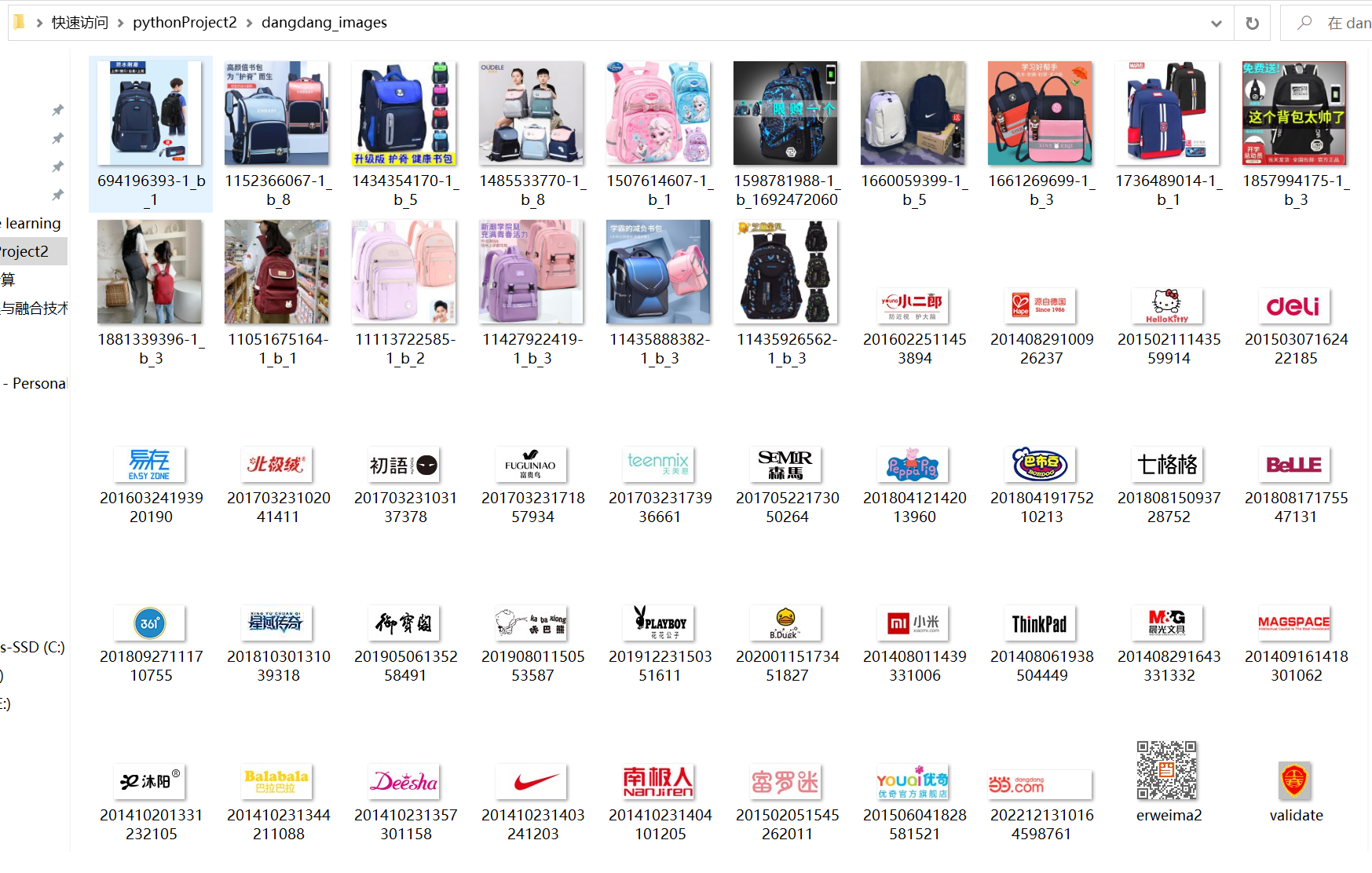
心得体会:
通过该项实践,我对正则表达式有了更深的理解,并学会了如何爬取图片,如何排除干扰。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号