二叉树遍历
深度优先
前序遍历(根-左-右):[a, b, d, g, h, c,e,i,f]
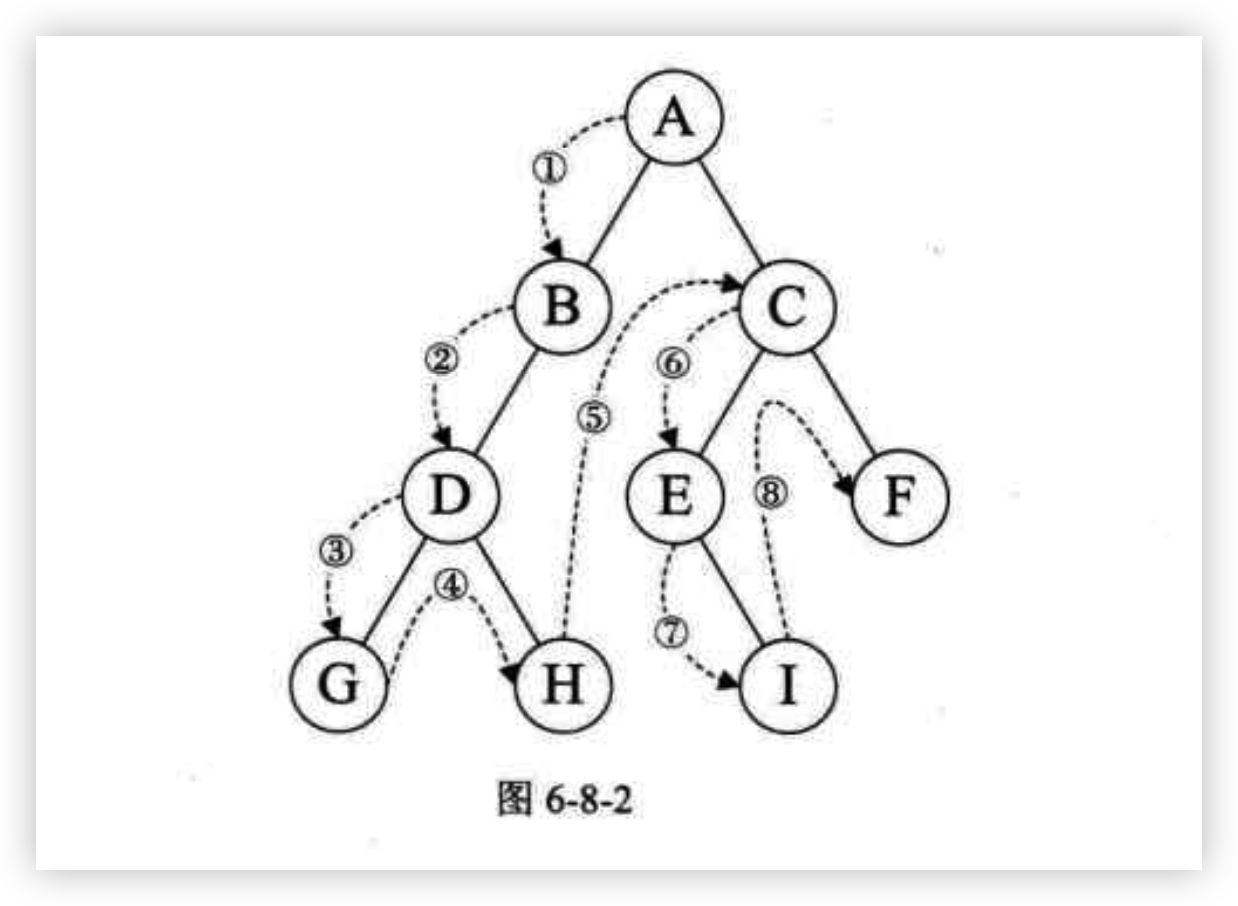
- 访问根节点
- 访问当前节点的左子树
- 若当前节点无左子树,则访问当前节点的右子树
递归版本:
function preorderTraversal(root) { if (root === null) return; // 访问根节点 console.log(root.val); // 遍历左子树 preorderTraversal(root.left); // 遍历右子树 preorderTraversal(root.right); }
优化版本:
function preOrder(root) { // 如果树为空,返回空数组 if (!root) return []; // 用栈来模拟递归的过程 const stack = [root]; // 初始时将根节点压入栈 const result = []; // 存储遍历结果 // 遍历栈中的每个节点 while (stack.length) { const node = stack.pop(); // 弹出栈顶节点 result.push(node.val); // 访问该节点,并将节点值保存到结果数组中 // 由于栈是后进先出,要先访问左节点,所以先将右子节点入栈,再将左子节点入栈 if (node.right) stack.push(node.right); if (node.left) stack.push(node.left); } return result; // 返回遍历结果 } // 测试数据 const tree1 = { val: 1, left: { val: 2, left: { val: 4 }, right: { val: 5 } }, right: { val: 3 } }; console.log('前序遍历 (根 -> 左 -> 右):', preOrder(tree1)); // 预期输出: [1, 2, 4, 5, 3]
中序遍历(左-根-右):[g,d,h,b,a,e,i,c,f]
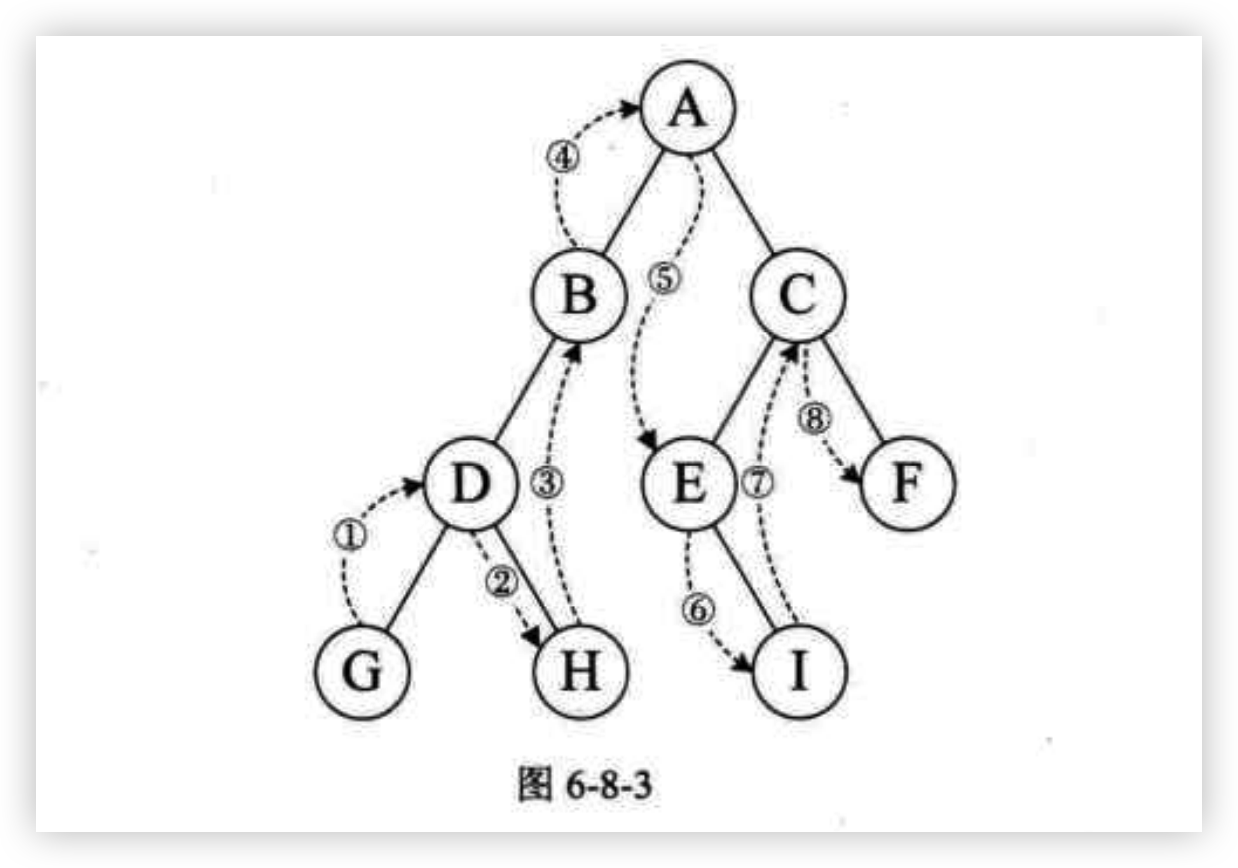
- 访问当前节点的左子树
- 访问根节点
- 访问当前节点的右子树
递归版本:
function inorderTraversal(root) { if (root === null) return; // 遍历左子树 inorderTraversal(root.left); // 访问根节点 console.log(root.val); // 遍历右子树 inorderTraversal(root.right); }
优化版本:
function inOrder(root) { const result = []; // 存储遍历结果 const stack = []; // 用栈来模拟递归的过程 let current = root; // 从根节点开始 // 当当前节点存在或者栈不为空时,继续遍历 while (current || stack.length) { // 一直向左走,将所有左子节点压入栈 while (current) { stack.push(current); // 将当前节点压入栈 current = current.left; // 移动到左子节点 } // 弹出栈顶节点并访问 current = stack.pop(); // 弹出栈顶节点 result.push(current.val); // 访问该节点并将其值保存到结果数组 // 访问完左子树后,转向右子树 current = current.right; } return result; // 返回遍历结果 } // 测试数据 console.log('中序遍历 (左 -> 根 -> 右):', inOrder(tree1)); // 预期输出: [4, 2, 5, 1, 3]
后序遍历:(左-右-根,若有子树,则先访问子树,子树也是左-右-根):[g,h,d,b,i,e,f,c,a]
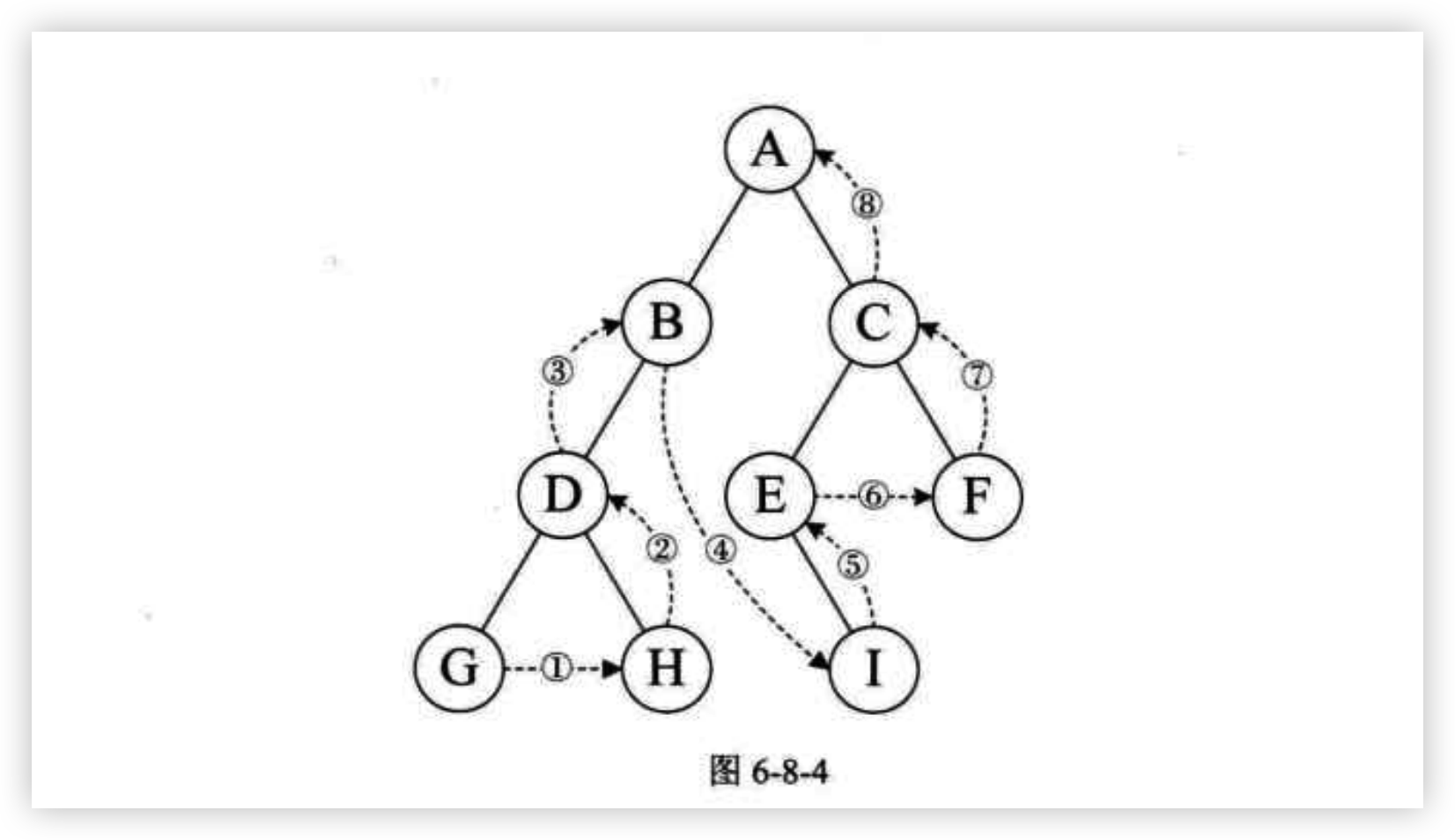
- 访问当前节点的左子树
- 访问当前节点的右子树
- 访问根节点
递归版本:
function postorderTraversal(root) { if (root === null) return; // 遍历左子树 postorderTraversal(root.left); // 遍历右子树 postorderTraversal(root.right); // 访问根节点 console.log(root.val); }
优化版本:
function postOrder(root) { // 如果树为空,返回空数组 if (!root) return []; const stack1 = [root]; // 用栈1来存储节点 const stack2 = []; // 用栈2来反转顺序 const result = []; // 存储遍历结果 // 栈1模拟后序遍历顺序,根 -> 右 -> 左 while (stack1.length) { const node = stack1.pop(); // 弹出栈1的栈顶节点 stack2.push(node); // 将弹出的节点压入栈2 // 先将左子节点入栈,再将右子节点入栈 if (node.left) stack1.push(node.left); // 左子节点压栈 if (node.right) stack1.push(node.right); // 右子节点压栈 } // 将栈2中的节点弹出并访问,得到左 -> 右 -> 根的顺序 while (stack2.length) { const node = stack2.pop(); // 弹出栈2的栈顶节点 result.push(node.val); // 访问并保存节点值 } return result; // 返回遍历结果 } // 测试数据 console.log('后序遍历 (左 -> 右 -> 根):', postOrder(tree1)); // 预期输出: [4, 5, 2, 3, 1]
广度优先
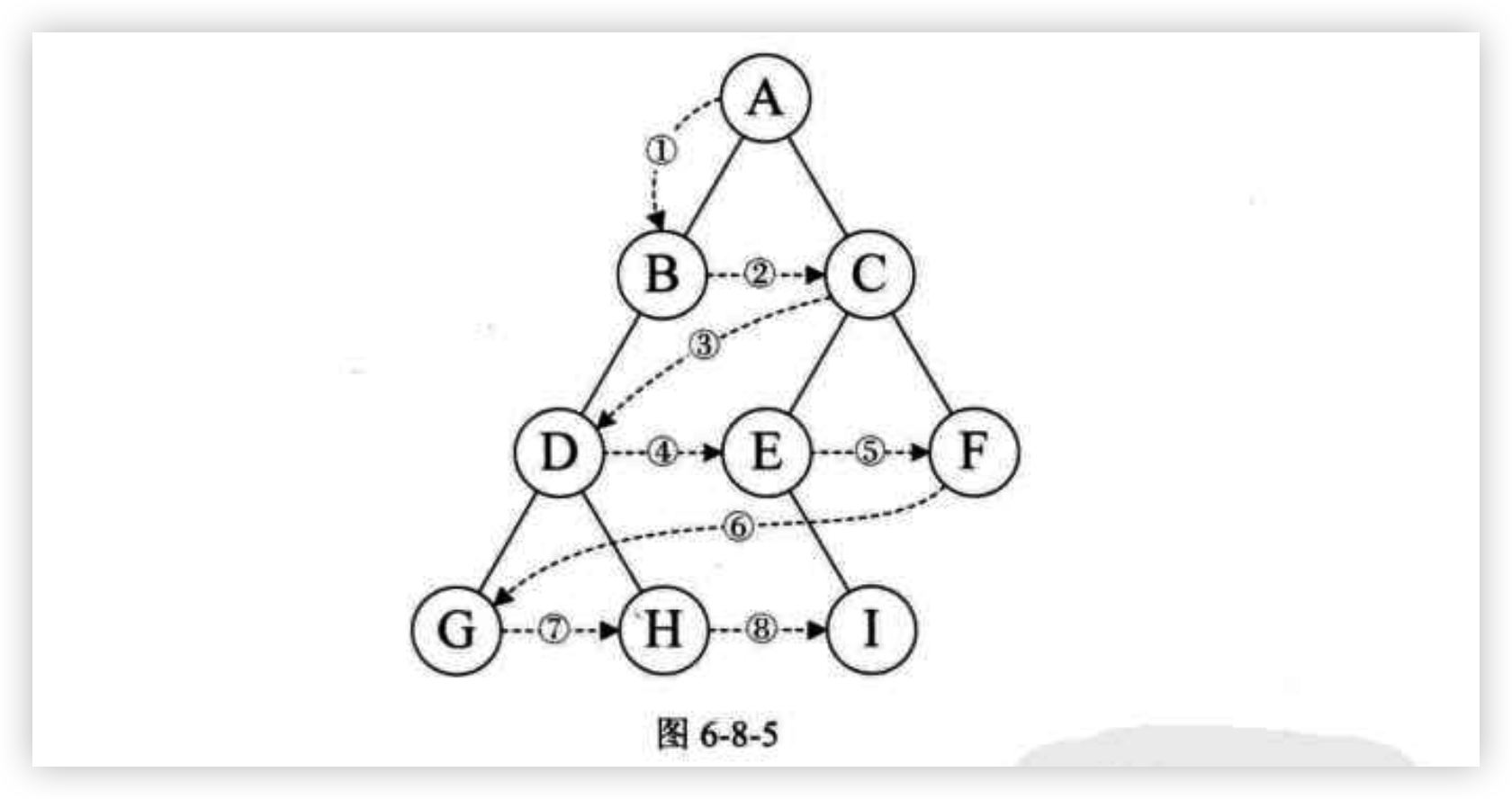
- 从根节点开始,一层一层的遍历
- 同一层,按从左到右的顺序


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号