函数和运算符重载
函数的作用域
在C语言中函数默认都是全局的,使用关键字static可以将函数声明为静态,函数定义为static就意味着这个函数只能在定义这个函数的文件中使用,在其他文件中不能调用,即使在其他文件中声明这个函数都没用。
内部函数
如果在一个源文件中定义的函数只能被本文件中的函数调用,而不能被同一源程序其他文件中的函数调用,这种函数称为内部函数。
内部函数的首部可写为:
static 类型说明符 函数名(形参表)
内部函数也称为静态函数。但此处静态static的含义已经不是存储方式,而是指对函数的调用范围只局限于本文件,因此在不同的源文件中定义的同名的静态函数不会引起混淆。
外部函数
如果在一个源文件中定义的函数既能被本文件中的函数调用,又能被同一源程序其他文件中的函数调用,这种函数称为外部函数
外部函数的首部可写为:
extern 类型说明符 函数名(形参表)
C语言规定,如果在定义函数时省略extern,则隐含为外部函数
外部函数在整个源程序中都有效,如果程序中的其他文件要使用另一文件中定义的函数,就需要在该文件中对该外部函数进行声明。
当被调用函数在另一个文件中时,在主调函数中都必须用extern声明被调用函数是外部函数。
注意:
- 允许在不同的函数中使用相同的变量名,它们代表不同的对象,分配不同的单元,互不干扰。
- 同一源文件中,允许全局变量和局部变量同名,在局部变量的作用域内,全局变量不起作用。
- 所有的函数默认都是全局的,意味着所有的函数都不能重名,但如果是staitc函数,那么作用域是文件级的,所以不同的文件static函数名是可以相同的。
函数占位参数
C++中函数的形参列表里可以有占位参数,用来做占位,调用函数时必须填补该位置
重载函数
C++允许使用同一个函数名定义多个函数,但这些函数的参数个数或参数类型必须有区别,在调用这些函数时,编译器会根据调用这些函数时的参数个数或类型不同调用不同的函数。这就是函数的重载。
作用:函数名可以相同,提高复用性
函数重载满足条件:
- 同一个作用域下
- 函数名称相同
- 函数参数类型不同 或者个数不同 或者顺序不同
注意:函数的返回值不可以作为函数重载的条件
运算符重载
在C++语言中,用户可以重载C++中大部分的内置运算符。使用运算符重载不但可以提高程序代码的可读性,还可以满足泛型算法的应用需求。C++运算符重载可以定义一些以运算符为名称的函数,然后可以在程序中按照使用运算符的方式调用这些函数。运算符重载函数的函数名由关键字operator和其后要重载的运算符符号构成的,运算符重载函数也有返回类型和参数列表。
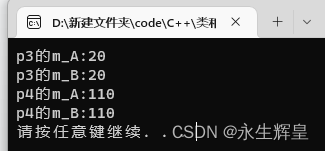
例:+运算符:
运行结果:
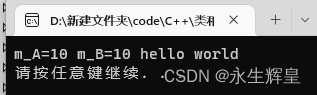
<<运算符:
运行结果:
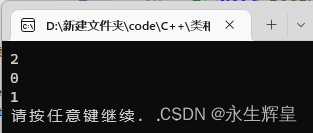
递增运算符:
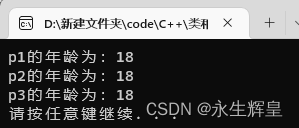
赋值运算符:
关系运算符




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号