代理与负载均衡
一、代理的两种方式
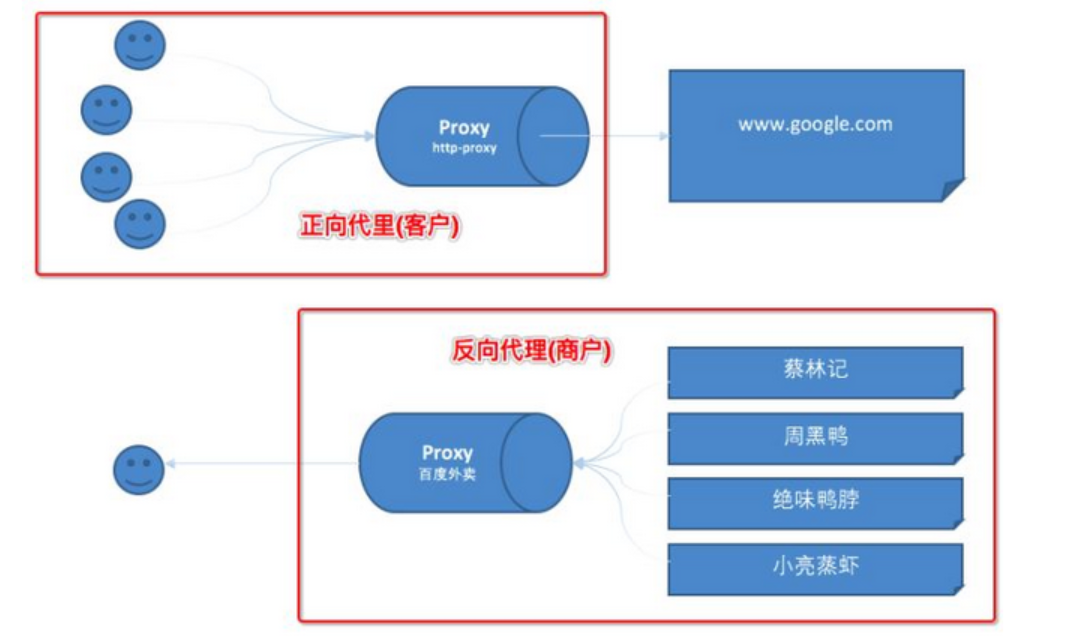
正向代理
正向代理类似一个跳板机,代理访问外部资源,找完代理之后,还需要找服务器。
比如我们国内访问谷歌,直接访问访问不到,我们可以通过一个正向代理服务器,请求发到代理服,代理服务器能够访问谷歌,这样由代理去谷歌取到返回数据,再返回给我们,这样我们就能访问谷歌了
作用:
(1)访问原来无法访问的资源,如google
(2) 可以做缓存,加速访问资源
(3)对客户端访问授权,上网进行认证
(4)代理可以记录用户访问记录(上网行为管理),对外隐藏用户信息
反向代理
反向代理(Reverse Proxy)实际运行方式是指以代理服务器来接受internet上的连接请求,然后将请求转发给内部网络上的服务器,并将从服务器上得到的结果返回给internet上请求连接的客户端,此时代理服务器对外就表现为一个服务器,只需要找代理,不需要找服务器。
作用:
(1)保证内网的安全,阻止web攻击,大型网站,通常将反向代理作为公网访问地址,Web服务器是内网
(2)负载均衡,通过反向代理服务器来优化网站的负载
二、Nginx代理服务支持的协议
| ngx_http_uwsgi_module | Python |
| ngx_http_fastcgi_module | PHP |
| ngx_http_scgi_module | Java |
| ngx_http_v2_module | Golang |
| ngx_http_proxy_module | HTTP |
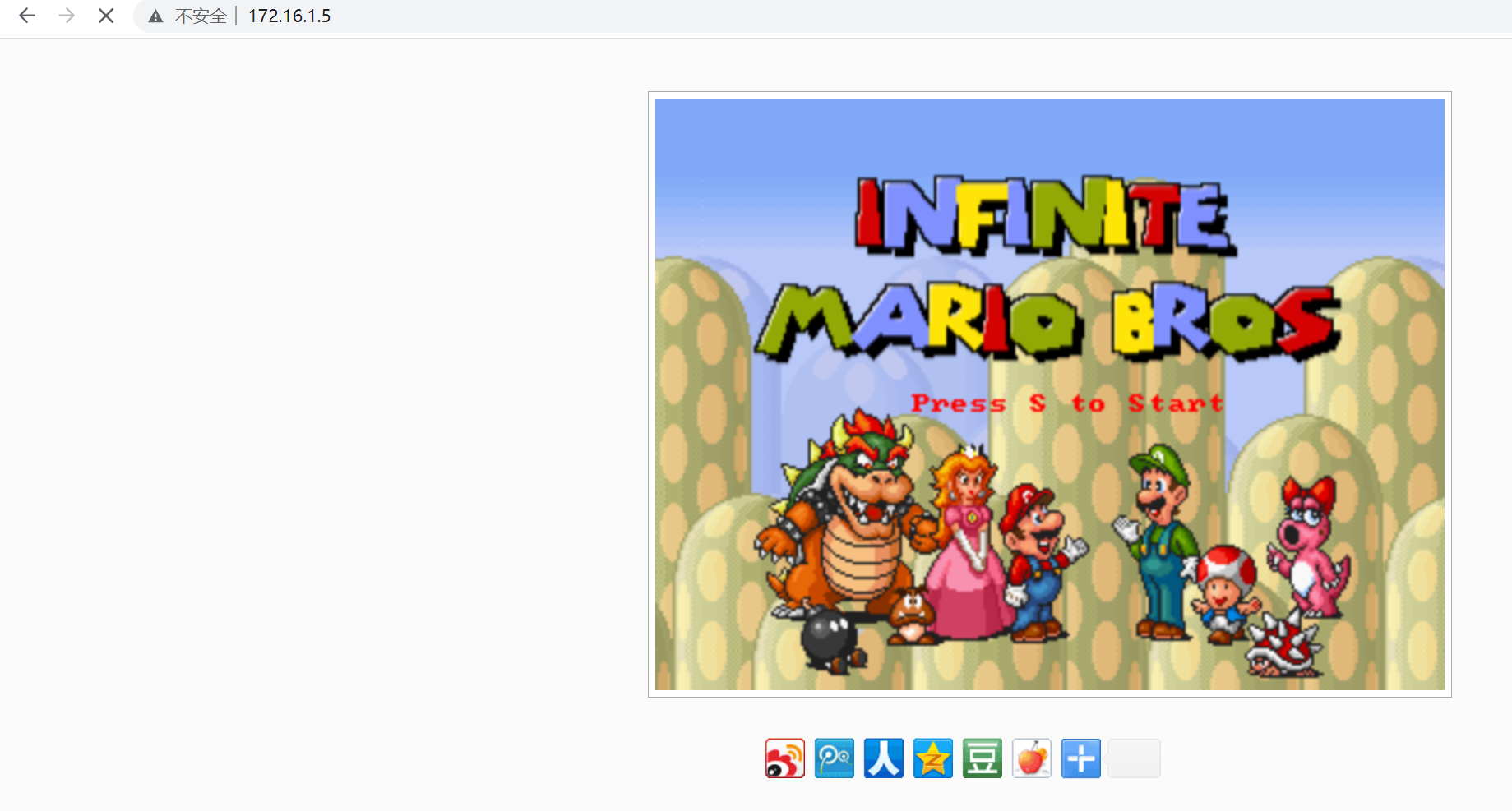
三、实现简易反向代理
部署服务端web01(详细步骤可看之前的博客)
[root@web01 conf.d]# cat game5.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name test.mario.com;
location / {
root /code/html-mario;
index index.html;
}
}
部署代理端lb01
① 编译安装nginx
# 下载Nginx源代码包
[root@lb01 ~]# wget https://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.20.2.tar.gz
# 解压
[root@lb01 ~]# tar -xf nginx-1.20.2.tar.gz
# 进入源代码目录
[root@lb01 ~]# cd nginx-1.20.2
# 安装依赖包
[root@lb01 nginx-1.20.2]# yum install openssl openssl-devel zlib zlib-devel -y
# 设置编译参数
[root@lb01 nginx-1.20.2]# ./configure --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-stream --with-http_ssl_module
# 编译
[root@lb01 nginx-1.20.2]# make
# 安装
[root@lb01 nginx-1.20.2]# make install
# 优化
[root@lb01 nginx]# mkdir /etc/nginx
[root@lb01 nginx]# mv /usr/local/nginx/conf/* /etc/nginx/
[root@lb01 nginx]# mkdir /etc/nginx/conf.d
[root@lb01 nginx]# groupadd www -g 666
[root@lb01 nginx]# useradd www -u 666 -g 666 -M -r -s /sbin/nologin
[root@lb01 nginx]# vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
# For more information on configuration, see:
# * Official English Documentation: http://nginx.org/en/docs/
# * Official Russian Documentation: http://nginx.org/ru/docs/
user www;
worker_processes auto;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
pid /run/nginx.pid;
# Load dynamic modules. See /usr/share/doc/nginx/README.dynamic.
include /usr/share/nginx/modules/*.conf;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;
sendfile on;
tcp_nopush on;
tcp_nodelay on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
types_hash_max_size 4096;
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
# Load modular configuration files from the /etc/nginx/conf.d directory.
# See http://nginx.org/en/docs/ngx_core_module.html#include
# for more information.
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
server_name _;
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
# Load configuration files for the default server block.
include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf;
error_page 404 /404.html;
location = /404.html {
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
}
}
# Settings for a TLS enabled server.
#
# server {
# listen 443 ssl http2;
# listen [::]:443 ssl http2;
# server_name _;
# root /usr/share/nginx/html;
#
# ssl_certificate "/etc/pki/nginx/server.crt";
# ssl_certificate_key "/etc/pki/nginx/private/server.key";
# ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 10m;
# ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
#
# # Load configuration files for the default server block.
# include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf;
#
# error_page 404 /404.html;
# location = /40x.html {
# }
#
# error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
# location = /50x.html {
# }
# }
}
[root@lb01 nginx]# vim /usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service
[Unit]
Description=nginx - high performance web server
Documentation=http://nginx.org/en/docs/
After=network-online.target remote-fs.target nss-lookup.target
Wants=network-online.target
[Service]
Type=forking
PIDFile=/var/run/nginx.pid
ExecStart=/usr/sbin/nginx -c /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
ExecReload=/bin/sh -c "/bin/kill -s HUP $(/bin/cat /var/run/nginx.pid)"
ExecStop=/bin/sh -c "/bin/kill -s TERM $(/bin/cat /var/run/nginx.pid)"
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
[root@lb01 sbin]# ln -s /etc/nginx/nginx.conf /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
[root@lb01 sbin]# mv /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx /usr/sbin/
[root@lb01 sbin]# mkdir /var/log/nginx
[root@lb01 sbin]# systemctl start nginx
[root@lb02 nginx-1.20.2]# systemctl daemon-reload
② 编辑代理配置
[root@lb01 conf.d]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/game.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name _; # _代表本机公网和内网ip都可以登录
location / {
proxy_pass http://172.16.1.7:80; # 服务端的ip
}
}
③ 重启nginx服务
[root@lb01 sbin]# systemctl start nginx
四、配置代理优化文件
① 编辑代理优化配置
[root@lb01 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/proxy_params proxy_set_header Host $http_host; # 用户请求的时候HOST的值是linux.proxy.com, 那么代理服务会像后端传递请求的还是linux.proxy.com proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; # 将$remote_addr的值放进变量X-Real-IP中,$remote_addr的值为客户端的ip proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; # 客户端通过代理服务访问后端服务, 后端服务通过该变量会记录真实客户端地址 proxy_connect_timeout 10s; #设置nginx代理与后端服务器连接超时时间(代理连接超时) proxy_read_timeout 10s; #设置nginx代理等待后端服务器的响应时间 proxy_send_timeout 10s; #设置后端服务器数据回传给nginx代理超时时间 proxy_buffering on; #开启缓冲区,nignx会把后端返回的内容先放到缓冲区当中,然后再返回给客户端,边收边传, 不是全部接收完再传给客户端 proxy_buffer_size 8k; #设置nginx代理保存用户头信息的缓冲区大小 proxy_buffers 8 8k; # 设置有几个缓冲区
② 在nginx配置文件中加载优化文件
[root@lb01 conf.d]# vim game.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name _;
location / {
proxy_pass http://172.16.1.7:80;
include /etc/nginx/proxy_params;
}
}
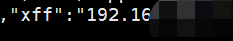 可以在web01服务器中的访问日志中查看修改的信息,如果有便是加载成功了
可以在web01服务器中的访问日志中查看修改的信息,如果有便是加载成功了
五、负载均衡
简介
负载均衡是高可用网络基础架构的关键组件,通常用于将工作负载分布到多个服务器来提高网站、应用、数据库或其他服务的性能和可靠性。
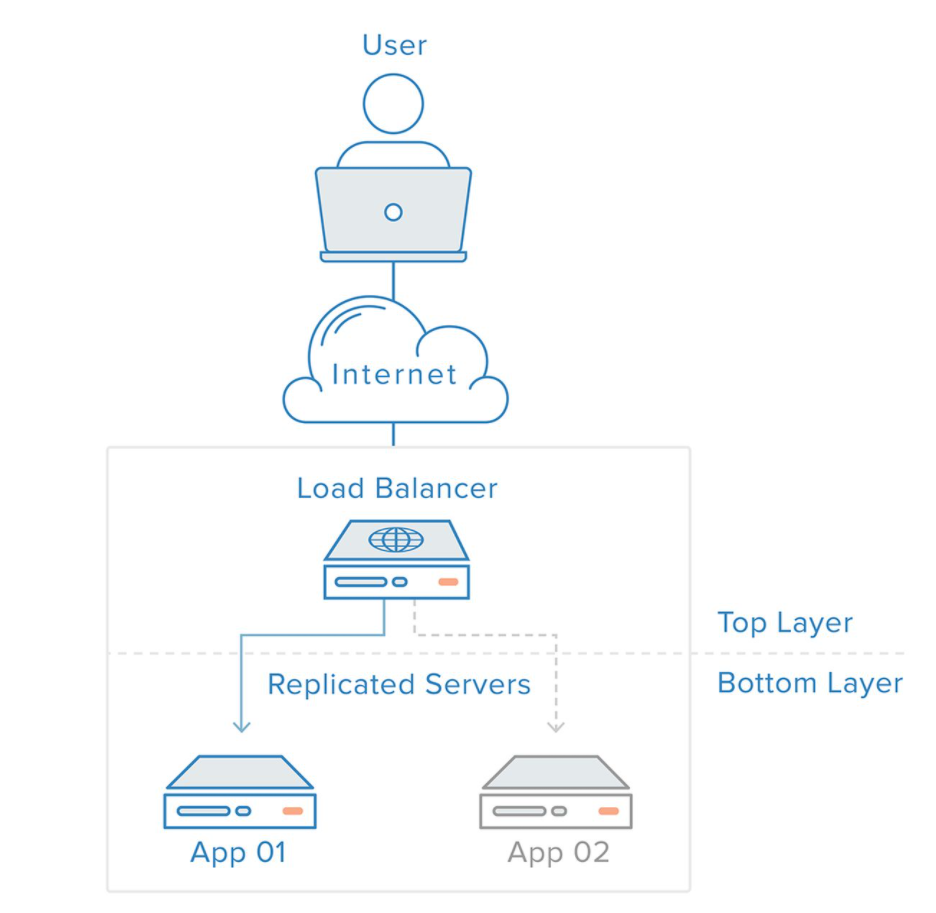
负载均衡的实现
实现负载均衡需要将后端服务打包成一个连接池,然后使用反向代理访问
连接池格式:
upstream [连接池名称] {
server [ip]:[port];
server [ip]:[port];
server [ip]:[port];
}
反向代理格式:
server {
listen 80;
server_name _;
location / {
proxy_pass http://[连接池];
}
}
实例:将三个web服务器作为后端服务,使用lb01当作代理访问
[root@lb01 conf.d]# vim game.conf
upstream mario {
server 172.16.1.7:80;
server 172.16.1.8:80;
server 172.16.1.9:80;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name _;
location / {
proxy_pass http://mario;
include /etc/nginx/proxy_params;
}
}
通过查看每一台后端服务器nginx的访问日志,我们可以发现每一台后端服务器上都会有该代理的访问的记录
tail -f /var/log/nginx/access.log
负载均衡给每台服务器分配的比例
负载均衡分配比例时有三种算法
① 轮询(Nginx负载均衡默认是轮询分配)
upstream supermarie {
server 172.16.1.7:80;
server 172.16.1.8:80;
server 172.16.1.9:80;
}
② 权重 (Nginx中的权重分为0-100,数字越大,分配到的比例越大)
upstream supermarie {
server 172.16.1.7:80 weight=20;
server 172.16.1.8:80 weight=10;
server 172.16.1.9:80 weight=5;
}
③ ip_hash (每一个ip固定访问一个后端)
upstream supermarie {
server 172.16.1.7:80;
server 172.16.1.8:80;
server 172.16.1.9:80;
ip_hash;
}
负载均衡后端状态
| 状态 | 概述 |
|---|---|
| down | 当前的server暂时不参与负载均衡 |
| backup | 预留的备份服务器 |
| max_fails | 允许请求失败的次数 |
| fail_timeout | 经过max_fails失败后, 服务暂停时间 |
down
# nginx配置
[root@lb01 nginx]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/game.conf
upstream mario { server 172.16.1.7:80 down; server 172.16.1.8:80; server 172.16.1.9:80; } server{ listen 80; server_name _; location / { proxy_pass http://mario; include /etc/nginx/proxy_params; } }
通过测试会发现只会有web2和web3的后端服务进行,加上down的服务端停止服务了
backup
# nginx配置
[root@lb01 nginx]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/game.conf
upstream mario { server 172.16.1.7:80 backup; server 172.16.1.8:80; server 172.16.1.9:80; } server{ listen 80; server_name _; location / { proxy_pass http://mario; include /etc/nginx/proxy_params; } }
通过测试发现,只有其他服务器都宕机的情况向下,backup的服务器才会开启服务
max_fail、fail_timeout
这两个状态在使用时必须搭配proxy_next_upstream error timeout invalid_header [错误类型] 使用
错误类型
error # 与服务器建立连接,向其传递请求或读取响应头时发生错误;
timeout # 在与服务器建立连接,向其传递请求或读取响应头时发生超时;
invalid_header # 服务器返回空的或无效的响应;
http_500 # 服务器返回代码为500的响应;
http_502 # 服务器返回代码为502的响应;
http_503 # 服务器返回代码为503的响应;
http_504 # 服务器返回代码504的响应;
http_403 # 服务器返回代码为403的响应;
http_404 # 服务器返回代码为404的响应;
http_429 # 服务器返回代码为429的响应(1.11.13);
non_idempotent # 通常,请求与 非幂等 方法(POST,LOCK,PATCH)不传递到请求是否已被发送到上游服务器(1.9.13)的下一个服务器; 启用此选项显式允许重试此类请求;
off # 禁用将请求传递给下一个服务器。
upstream mario {
server 172.16.1.7:80 max_fails=3 fail_timeout=3s;
server 172.16.1.8:80 max_fails=3 fail_timeout=3s;
server 172.16.1.9:80 max_fails=3 fail_timeout=3s;
}
server{
listen 80;
server_name _;
location / {
proxy_pass http://mario;
proxy_next_upstream error timeout invalid_header http_500 http_502 http_503 http_404;
include /etc/nginx/proxy_params;
}
}
错误请求三次后,该服务就会暂停三秒,proxy_next_upstream会将错误处理掉,之后将请求转给可以运行的服务器上。
六、四层负载均衡
在非HTTP协议的情况下,采用的四层负载均衡的方式负载服务,并且四层负载均衡中不支持域名。
案例1 使用四层负载均衡实现SSH的代理,端口为1122
①修改nginx配置
# 修改nginx配置,增加全局变量
[root@lb01 stream]# vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
stream {
include /etc/nginx/stream/*.conf
② 创建stream目录
[root@lb01 nginx]# mkdir /etc/nginx/stream/
③ 编写mysql连接配置
[root@lb01 stream]# vim /etc/nginx/stream/ssh.conf
server {
listen 1122;
proxy_pass 172.16.1.5:22;
}
④ 重启nginx服务
[root@lb01 stream]# systemctl restart nginx




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号