Android开发--Lesson04--对象传递以及文件存储
一.对象传递
使用Intent传递对象的时候需要注意到,被传递的对象必须是实现了Serialzable接口的对象,即被传递的对象必须要是可序列化的
public class Student implements Serializable { private String id; private String name; public void setId(String id) { this.id = id; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } @Override public String toString() { return "Student{" + "id='" + id + '\'' + ", name='" + name + '\'' + '}'; } }
MainActivity:
Button bt1 = findViewById(R.id.bt1); bt1.setOnClickListener((v)->{ Intent intent = new Intent(demo3.this, toActivity.class); Student student = new Student(); student.setName("maing"); student.setId("18"); intent.putExtra("stu",student); startActivity(intent); });
接收的Activity:
TextView tv = findViewById(R.id.tv1); Intent intent = getIntent(); Student stu = (Student)intent.getSerializableExtra("stu"); tv.setText(stu.toString());
页面结果展示:

参数回传
在 Android 开发中,Activity 的参数回传指的是从一个 Activity (我们称之为第二个 Activity) 返回到启动它的 Activity (我们称之为第一个 Activity) 时传递数据的过程。这个机制通常用于当第二个 Activity 完成某些任务或用户交互后,需要将结果数据返回给第一个 Activity 使用。
实现参数回传的主要步骤如下:
-
启动第二个 Activity 并等待结果:在第一个 Activity 中使用
startActivityForResult()方法(对于较新的 Android 版本,使用ActivityResultLauncher和registerForActivityResult()来兼容新旧版本)来启动第二个 Activity,并指定一个请求码(request code),以便识别返回的结果来自哪个启动操作。 -
设置返回数据:在第二个 Activity 中,通过创建一个新的 Intent 对象并调用
setResult()方法来设置返回的数据。然后调用finish()方法关闭当前 Activity,从而返回到第一个 Activity。 -
处理返回的数据:在第一个 Activity 中实现
onActivityResult()方法(或者使用新的ActivityResultCallback接口),以处理由第二个 Activity 返回的数据。该方法会接收请求码、结果码(如RESULT_OK或RESULT_CANCELED)和包含数据的 Intent。
mainActivity:
// 获取按钮bt1 Button bt1 = findViewById(R.id.bt1); // 获取输入框et EditText et = findViewById(R.id.et); // 获取文本框tv TextView tv = findViewById(R.id.tv); // 注册一个ActivityResultLauncher,用于启动toActivity ActivityResultLauncher<Intent> msg = registerForActivityResult(new ActivityResultContracts.StartActivityForResult(), (o) -> { // 如果返回码为2,则将返回的数据设置到输入框et中 if (o.getResultCode() == 2) { et.setText(o.getData().getStringExtra("msg")); } }); // 为按钮bt1设置点击事件 bt1.setOnClickListener((v)->{ // 创建一个Intent,启动toActivity Intent intent = new Intent(demo3.this, toActivity.class); // 启动toActivity msg.launch(intent); });
跳转的Activity:
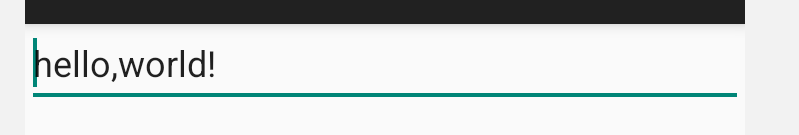
// 获取按钮tbt1 Button tbt1 = findViewById(R.id.tbt1); // 设置按钮tbt1的点击事件 tbt1.setOnClickListener((v)->{ // 创建Intent对象 Intent intent = new Intent(); // 向Intent中添加数据 intent.putExtra("msg","hello,world!"); // 设置返回结果 setResult(2,intent); // 结束当前Activity finish(); });
最后数据回传结果:
二.动态加载Fragment
在 Android 开发中,Fragment 是一种可以嵌入到 Activity 中的 UI 片段。它可以让开发者在一个 Activity 中构建灵活的用户界面,并且可以在多个 Activity 之间重用这些片段。Fragment 必须总是被嵌入在一个 Activity 中,其生命周期直接与宿主 Activity 的生命周期相关联。这意味着当 Activity 被销毁或重建时,其内部的所有 Fragment 也会经历相同的过程。
Fragment 的主要特性
- 模块化布局:允许你在不同的屏幕尺寸上使用更加灵活的布局设计。例如,在平板设备上,你可能希望同时显示两个 Fragment,而在手机设备上,则是分别显示。
- 可复用性:Fragment 可以在多个 Activity 中复用。
- 适配多屏幕:通过在不同的屏幕上动态地添加、移除或者替换 Fragment,可以更容易地实现不同屏幕尺寸和方向的适应。
如果需要使用Fragment嵌入到Activity到活动窗口,首先需要在Android之中创建Fragment
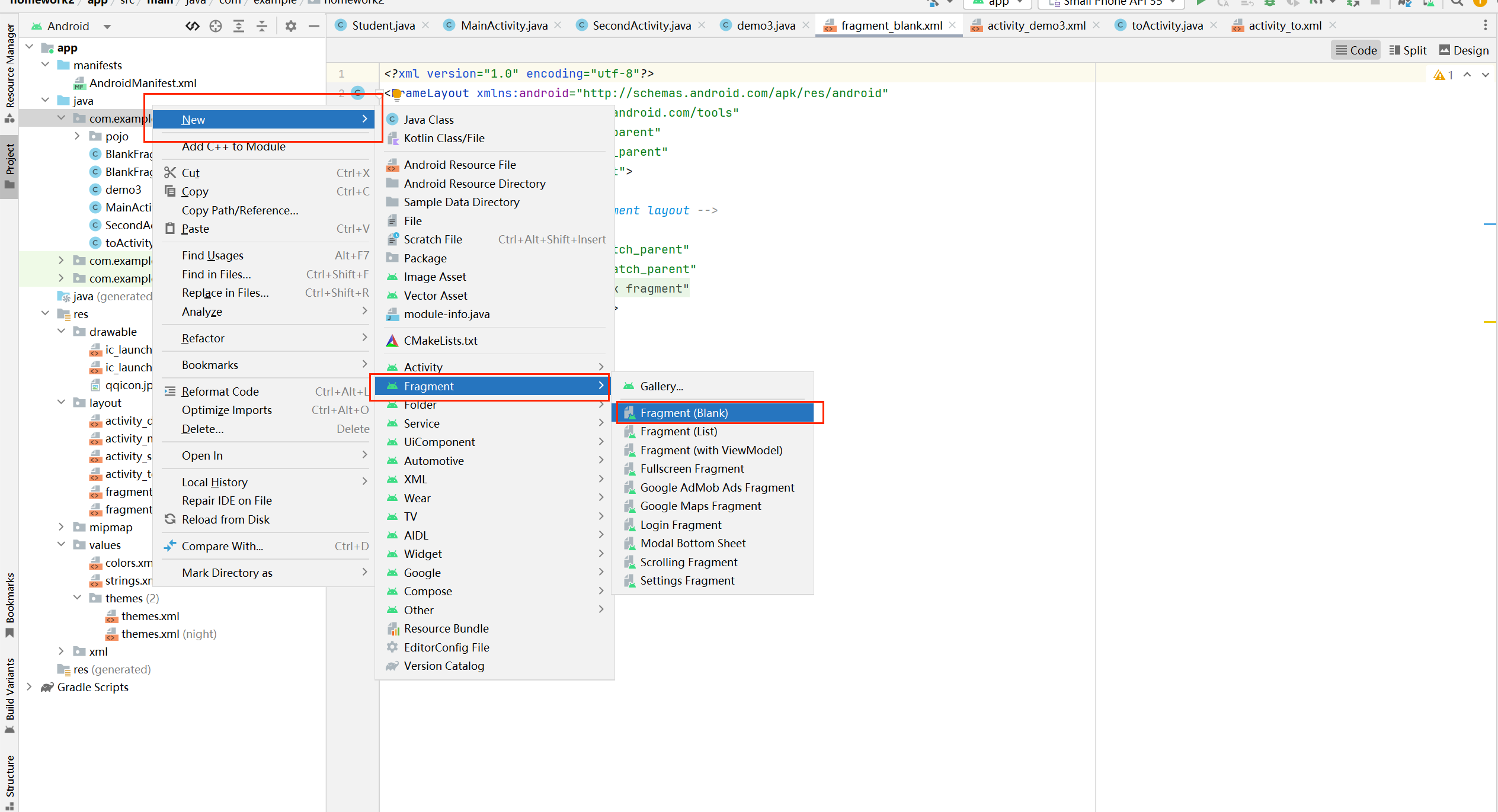
点击创建的方式和Activity一样都是,创建之后,它和普通的Activity其实本质上是差不多的,但是我们需要注意的是,Fragment是碎片,它依赖于Activity才能存活,Activity销毁,它也会被销毁
mainActivity:
// 获取id为fmb1的按钮 Button bt1 = findViewById(R.id.fmb1); // 获取id为fmb2的按钮 Button bt2 = findViewById(R.id.fmb2); // 为按钮bt1设置点击事件 bt1.setOnClickListener(v->{ // 创建BlankFragment对象 BlankFragment bf = new BlankFragment(); // 获取FragmentManager对象 FragmentManager fm = getSupportFragmentManager(); // 创建FragmentTransaction对象 FragmentTransaction ft = fm.beginTransaction(); // 将BlankFragment对象替换到id为fl的布局中 ft.replace(R.id.fl,bf); // 提交事务 ft.commit(); }); // 为按钮bt2设置点击事件 bt2.setOnClickListener(v->{ // 创建BlankFragment2对象 BlankFragment2 bf2 = new BlankFragment2(); // 获取FragmentManager对象 FragmentManager fm = getSupportFragmentManager(); // 创建FragmentTransaction对象 FragmentTransaction ft = fm.beginTransaction(); // 将BlankFragment2对象替换到id为fl的布局中 ft.replace(R.id.fl,bf2); // 提交事务 ft.commit(); });
mainActivity.XML
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:id="@+id/main" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_marginTop="20dp" tools:context=".demo3"> <Button android:id="@+id/fmb1" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="开启第一个Fragment"/> <Button android:id="@+id/fmb2" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="开启第二个Fragment"/> <FrameLayout android:id="@+id/fl" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"/> </LinearLayout>
在嵌入Fragment使用的就是帧布局,使用帧布局的优势就是可以重叠Fragment,是的动态加载碎片的时候可以不断的覆盖
结果截图展示:

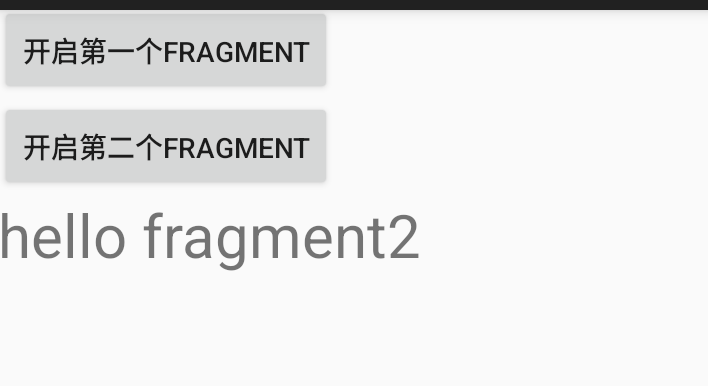
如上图:实际上是加载了两次Fragment的效果,使用两个按钮加载了两次碎片,由于是帧布局,覆盖了上一个
三.文件存储
在Android开发中,文件存储是用来保存应用数据的一种方式。根据数据的性质和使用场景的不同,可以将数据存储到设备的内部存储或者外部存储(如SD卡)。文件存储适用于那些需要以文件形式保存的数据,比如文本文件、图片、音频文件等。
内部存储
特点:只有你的应用能够访问这些文件,当用户卸载应用时,这些文件也会被删除。
操作方法:
写入文件:使用openFileOutput(String name, int mode)方法获取一个FileOutputStream对象,然后写入数据。
读取文件:使用openFileInput(String name)方法获取一个FileInputStream对象来读取数据。
我们默认的文件的存储方式就是读写文件,和Java的流操作是差不多的,都是使用I/O操作读写文件流
案例:
mainActivity.Java
// 获取按钮bt1
Button bt1 = findViewById(R.id.bt1);
// 获取输入框et
EditText et = findViewById(R.id.et);
// 获取文本框tv
TextView tv = findViewById(R.id.tv);
bt1.setOnClickListener(v->{
// 创建文件输出流
FileOutputStream fas = null;
try {
// 打开文件输出流
fas = openFileOutput("data.txt",MODE_PRIVATE);
// 将EditText中的文本写入文件
fas.write(et.getText().toString().getBytes());
}catch (IOException io){
// 打印异常信息
io.printStackTrace();
// 输出异常信息
System.out.println("文件异常");
}finally {
// 关闭文件输出流
if (fas != null){
try {
fas.close();
// 创建文件输入流
FileInputStream fis = openFileInput("data.txt");
// 创建字节数组,用于存储文件内容
byte[] bytes = new byte[fis.available()];
// 读取文件内容
fis.read(bytes);
// 将文件内容设置为TextView的文本
tv.setText(new String(bytes));
// 关闭文件输入流
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// 打印异常信息
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
});
如上图使用的就是InputStream流讲文本写入到data.txt中,然后再关闭写入流的时候顺便将文件使用读取流再次读取出来
截图展示:
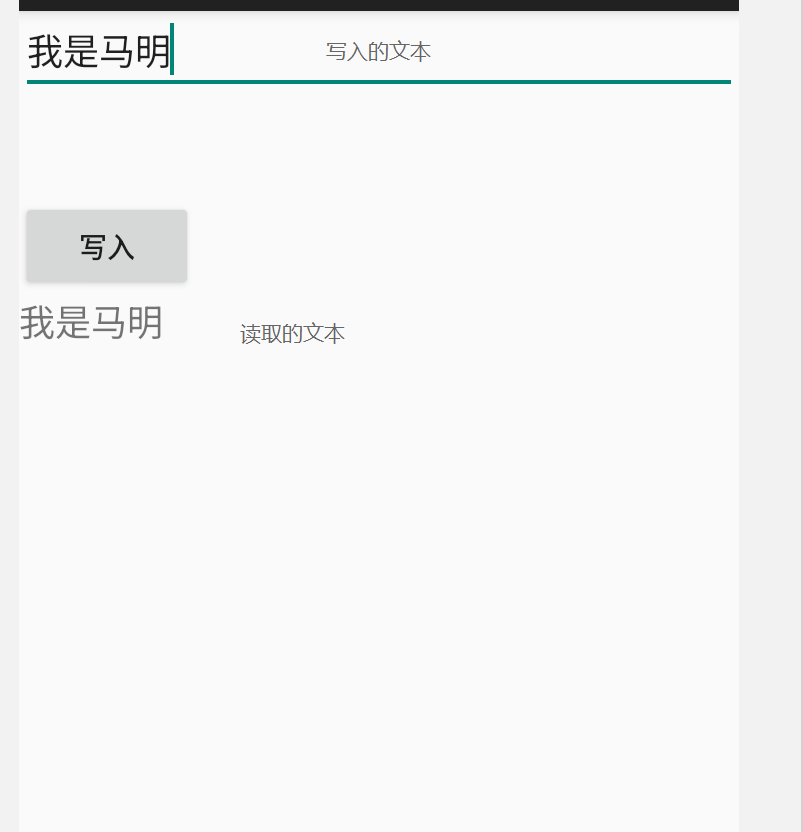
我们可以再项目里面找到写的文件在哪里,需要使用到Device Eplorer,然后查看文件目录结构
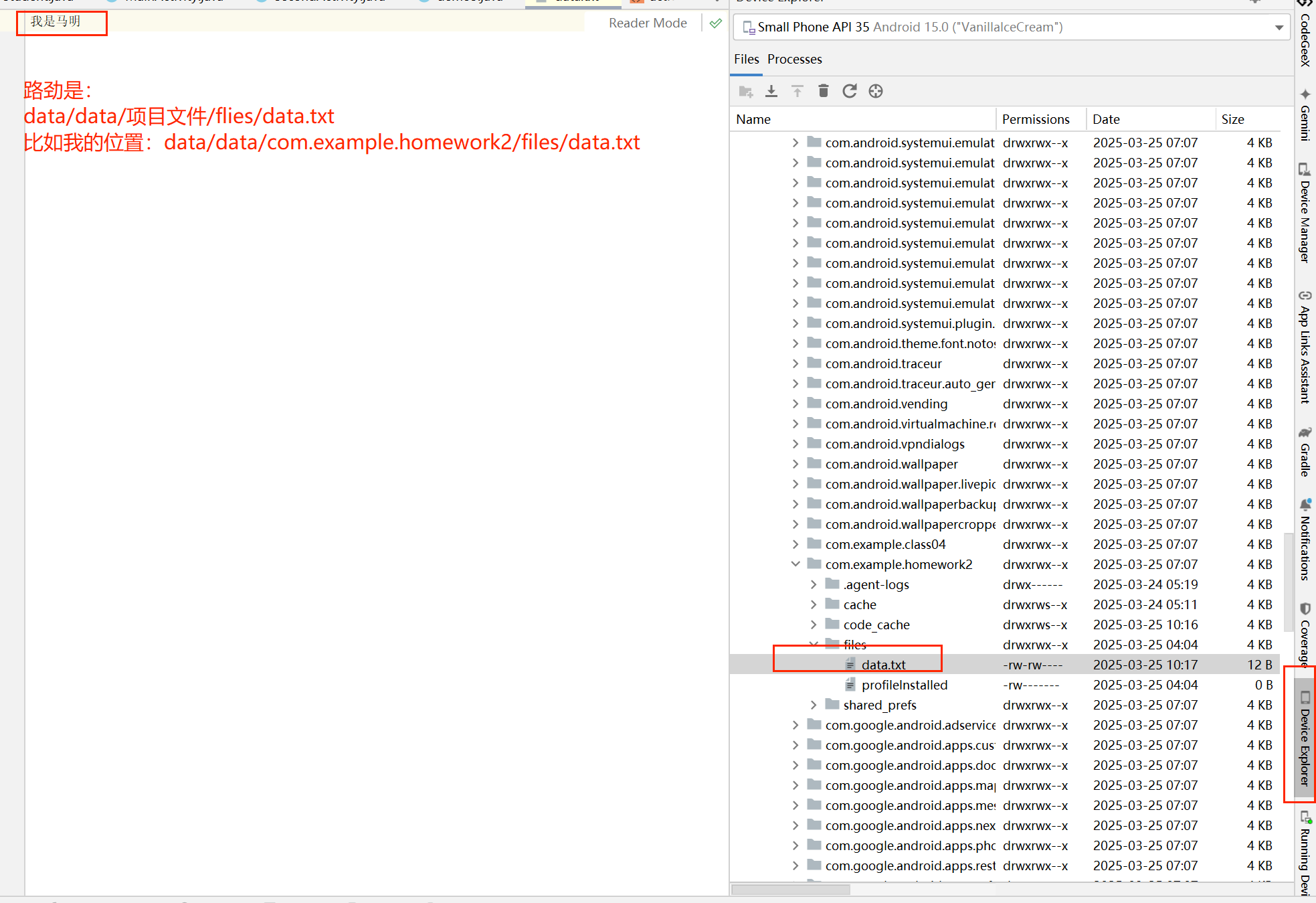
SharedPreferences存储
在Android开发中,SharedPreferences 是一种轻量级的存储方式,用于保存应用的简单配置数据或用户偏好设置。它以键值对(Key-Value)的形式存储数据,并且支持多种数据类型(如 boolean、int、float、long 和 String)。SharedPreferences 存储的数据是持久化的,即使应用关闭或设备重启,数据仍然保留。
使用场景
- 保存用户的登录状态。
- 保存应用的主题设置。
- 保存用户的偏好选项(如音量大小、字体大小等)。
- 保存简单的配置信息。
SharedPreferences 是一种简单、高效的方式,用于存储小规模的配置数据或用户偏好设置。它的使用非常方便,但在处理复杂数据时可能需要结合其他存储方式(如数据库或文件存储)。合理选择存储方式,可以提高应用的性能和用户体验。
mainActivity.Java
// 获取名为"data"的SharedPreferences对象 SharedPreferences data = getSharedPreferences("data", MODE_PRIVATE); // 获取SharedPreferences对象的编辑器 SharedPreferences.Editor edit = data.edit(); // 将"name"键的值设置为"maming" edit.putString("name","maming"); // 将"id"键的值设置为18 edit.putInt("id",18); // 提交修改 edit.commit(); // 将"name"键的值设置为TextView的文本 tv.setText(data.getString("name",null));
上面的例子是在一个Activity中拿取和展示,故而打开页面会直接有name的属性值输出到屏幕山:

--------


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号