实验三
3.1

1 #include<stdlib.h> 2 3 char score_to_grade(int score); // 函数声明 4 5 int main() { 6 int score; 7 char grade; 8 9 while(scanf("%d", &score) != EOF) { 10 grade = score_to_grade(score); // 函数调用 11 printf("分数: %d, 等级: %c\n\n", score, grade); 12 } 13 14 return 0; 15 } 16 17 // 函数定义 18 char score_to_grade(int score) { 19 char ans; 20 21 switch(score/10) { 22 case 10: 23 case 9: ans = 'A'; break; 24 case 8: ans = 'B'; break; 25 case 7: ans = 'C'; break; 26 case 6: ans = 'D'; break; 27 default: ans = 'E'; 28 } 29 30 return ans; 31 }
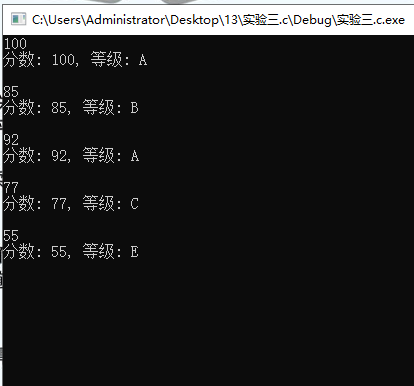
问题1:score_to_grade的功能是将输入的整数分数转化为对应的等级ABCD,形参类型是int,返回值类型是char
问题2:代码在输入相应等级后,不会直接跳出switch分支,而是一直执行到底
3.2

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 3 int sum_digits(int n); // 函数声明 4 5 int main() { 6 int n; 7 int ans; 8 9 while(printf("Enter n: "), scanf("%d", &n) != EOF) { 10 ans = sum_digits(n); // 函数调用 11 printf("n = %d, ans = %d\n\n", n, ans); 12 } 13 14 return 0; 15 } 16 17 // 函数定义 18 int sum_digits(int n) { 19 int ans = 0; 20 21 while(n != 0) { 22 ans += n % 10; 23 n /= 10; 24 } 25 26 return ans; 27 }
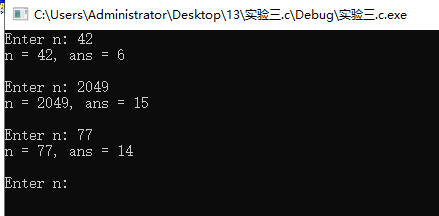
问题1:对输入数值的各位数字求和
问题2:能实现,原代码利用循环条件将各位数字分离出来并用除法将已分离的个位数字去除直到整数变为零,第二种方式是利用递归思想将数值拆分为个位数字和其他数字,直到数值变为个位数字再跳出递归对得到的个位数字求和
3.3

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 3 int power(int x, int n); // 函数声明 4 5 int main() { 6 int x, n; 7 int ans; 8 9 while(printf("Enter x and n: "), scanf("%d%d", &x, &n) != EOF) { 10 ans = power(x, n); // 函数调用 11 printf("n = %d, ans = %d\n\n", n, ans); 12 } 13 14 return 0; 15 } 16 17 // 函数定义 18 int power(int x, int n) { 19 int t; 20 21 if(n == 0) 22 return 1; 23 else if(n % 2) 24 return x * power(x, n-1); 25 else { 26 t = power(x, n/2); 27 return t*t; 28 } 29 }
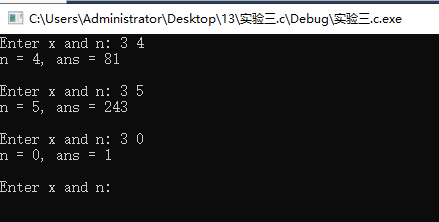
问题1:计算x的n次幂
问题2:是

3.4

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 int is_prime(int n); 4 5 int main(){ 6 int i,c=0; 7 printf("100以内的孪生素数:\n"); 8 for(i=1;i<=100;++i){ 9 if (is_prime(i)){ 10 if (is_prime(i+2)){ 11 printf("%d %d\n",i,i+2); 12 c+=1; 13 } 14 } 15 } 16 printf("100以内的孪生素数共有%d个\n",c); 17 system("pause"); 18 return 0; 19 } 20 21 int is_prime(int n){ 22 int i,f=1; 23 if (n==1) 24 f=0; 25 for(i=2;i<=n/2;++i){ 26 if (n%i==0){ 27 f=0; 28 break; 29 } 30 } 31 return f; 32 }

3.5

1 #include<stdio.h> 2 int s=0; 3 void hanoi(unsigned int n,char from,char temp,char to); 4 void moveplate(unsigned int n,char from,char to); 5 int main(){ 6 7 unsigned int n; 8 while(scanf("%u",&n)!=EOF){ 9 s=0; 10 hanoi(n,'A','B','C'); 11 printf("\n"); 12 printf("一共移动了%d次\n",s); 13 } 14 15 return 0; 16 } 17 void hanoi(unsigned int n,char from,char temp,char to){ 18 19 if(n==1) 20 moveplate(n,from,to); 21 else{ 22 hanoi(n-1,from,to,temp); 23 moveplate(n,from,to); 24 hanoi(n-1,temp,from,to); 25 } 26 } 27 void moveplate(unsigned int n,char from,char to){ 28 29 printf("%u:%c-->%c\n",n,from,to); 30 s++; 31 32 }
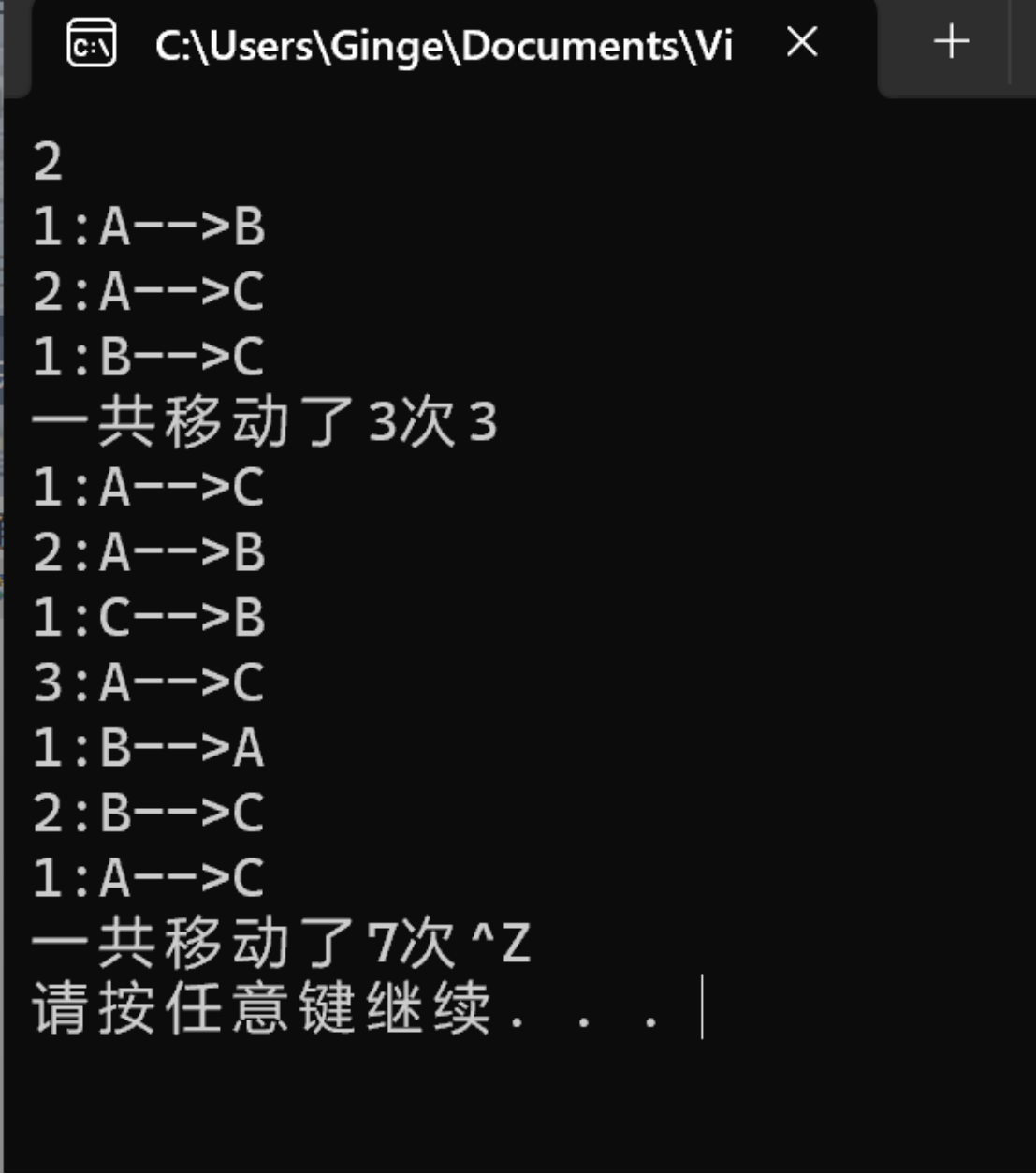
3.6.1

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 int func(int n, int m); // 函数声明 4 5 int main() { 6 int n, m; 7 int ans; 8 9 while(scanf("%d%d", &n, &m) != EOF) { 10 ans = func(n, m); // 函数调用 11 printf("n = %d, m = %d, ans = %d\n\n", n, m, ans); 12 } 13 system("pause"); 14 return 0; 15 } 16 int func(int n, int m) 17 { 18 int i,j,h=1,l=1; 19 for(i=1;i<=m;i++) 20 l*=i; 21 for(j=n-m+1;j<=n;j++) 22 h*=j; 23 return h/l; 24 }
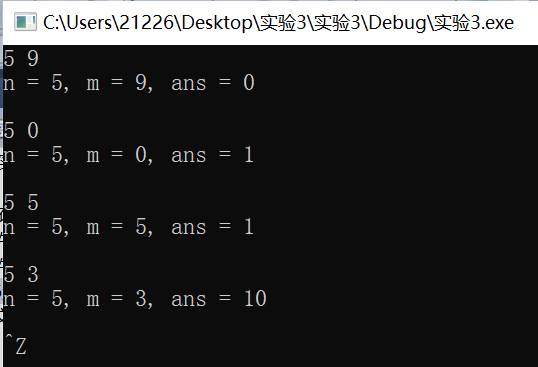
3.6.2

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 int func(int n, int m); // 函数声明 4 5 int main() { 6 int n, m; 7 int ans; 8 9 while(scanf("%d%d", &n, &m) != EOF) { 10 ans = func(n, m); // 函数调用 11 printf("n = %d, m = %d, ans = %d\n\n", n, m, ans); 12 } 13 system("pause"); 14 return 0; 15 } 16 int func(int n, int m) 17 { 18 if(n==m) 19 return 1; 20 if(n<m) 21 return 0; 22 if(m==0) 23 return 1; 24 return func(n-1,m)+func(n-1,m-1); 25 }
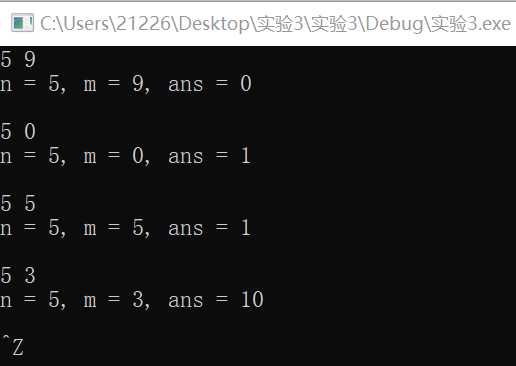
3.7

1 #include<stdio.h> 2 3 int gcd(int a,int b,int c); 4 5 int main(){ 6 int a,b,c; 7 int ans; 8 9 while(scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c)!=EOF){ 10 ans=gcd(a,b,c); 11 printf("最大公约数:%d\n\n",ans); 12 } 13 14 return 0; 15 } 16 17 int gcd(int a, int b, int c) { 18 int i = a; 19 if (i > b) 20 i = b; 21 if (i > c) 22 i = c; 23 for (i; i >= 1; --i) { 24 if (a % i == 0 && b % i == 0 && c % i == 0) 25 return i; 26 27 }return 1; 28 }





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号