@Indexed 注解
本文转载自:https://www.cnblogs.com/aflyun/p/11992101.html
最近在看 SpringBoot 核编程思想(核心篇),看到走向注解驱动编程这章,里面有讲解到:在SpringFramework 5.0 引入了一个注解@Indexed ,它可以为 Spring 的模式注解添加索引,以提升应用启动性能。
在往下阅读的时候,请注意一些模式注解:
| Spring注解 | 场景说明 |
|---|---|
| @Repository | 数据仓库模式注解 |
| @Component | 通用组件模式注解 |
| @Service | 服务模式注解 |
| @Controller | Web控制器模式注解 |
| @Configuration | 配置类模式注解 |
使用场景
在应用中使用@ComponentScan扫描 package 时,如果 package 中包含很多的类,那么 Spring 启动的时候就会变慢。
提升性能的一个方案就是提供一个 Component 的候选列表,Spring 启动时直接扫描注入这些列表就行了,而不需要一个个类去扫描,再筛选出候选 Component。
需要注意的是:在这种模式下,所有组件扫描的目标模块都必须使用这种机制——大白话将就所有的 Component 组件都必须生成到列表文件中去。
While classpath scanning is very fast, it is possible to improve the startup performance of large applications by creating a static list of candidates at compilation time. In this mode, all modules that are target of component scan must use this mechanism.
使用方式
在项目中使用的时候需要导入一个spring-context-indexer jar包。
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context-indexer</artifactId>
<version>xxxx</version>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
然后在代码中,对于使用了模式注解的类上加上@Indexed注解即可。如下:
@Indexed
@Controller
public class HelloController {
}
加了上面的依赖后,项目就会自动使用索引的方式启动Spring。
原理说明
摘自官网:

简单说明一下:在项目中使用了@Indexed之后,编译打包的时候会在项目中自动生成META-INT/spring.components文件。
当Spring应用上下文执行ComponentScan扫描时,META-INT/spring.components将会被CandidateComponentsIndexLoader 读取并加载,转换为CandidateComponentsIndex对象,这样的话@ComponentScan不在扫描指定的package,而是读取CandidateComponentsIndex对象,从而达到提升性能的目的。
知道上面的原理,可以看一下org.springframework.context.index.CandidateComponentsIndexLoader的源码。
ublic final class CandidateComponentsIndexLoader {
public static final String COMPONENTS_RESOURCE_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.components";
public static final String IGNORE_INDEX = "spring.index.ignore";
private static final boolean shouldIgnoreIndex = SpringProperties.getFlag(IGNORE_INDEX);
private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(CandidateComponentsIndexLoader.class);
private static final ConcurrentMap<ClassLoader, CandidateComponentsIndex> cache =
new ConcurrentReferenceHashMap<>();
private CandidateComponentsIndexLoader() {
}
@Nullable
public static CandidateComponentsIndex loadIndex(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
ClassLoader classLoaderToUse = classLoader;
if (classLoaderToUse == null) {
classLoaderToUse = CandidateComponentsIndexLoader.class.getClassLoader();
}
return cache.computeIfAbsent(classLoaderToUse, CandidateComponentsIndexLoader::doLoadIndex);
}
@Nullable
private static CandidateComponentsIndex doLoadIndex(ClassLoader classLoader) {
if (shouldIgnoreIndex) {
return null;
}
try {
Enumeration<URL> urls = classLoader.getResources(COMPONENTS_RESOURCE_LOCATION);
if (!urls.hasMoreElements()) {
return null;
}
List<Properties> result = new ArrayList<>();
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urls.nextElement();
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(new UrlResource(url));
result.add(properties);
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Loaded " + result.size() + "] index(es)");
}
int totalCount = result.stream().mapToInt(Properties::size).sum();
return (totalCount > 0 ? new CandidateComponentsIndex(result) : null);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unable to load indexes from location [" +
COMPONENTS_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex);
}
}
}
使用注意点
虽然这个@Indexed注解能提升性能,但是在使用的时候也需要注意下。
假设Spring应用中存在一个包含META-INT/spring.components资源的a.jar,但是 b.jar 仅存在模式注解,那么使用@ComponentScan扫描这两个JAR中的package时,b.jar 中的模式注解不会被识别,请务必注意这样的问题。
举个列子说明下,能够更好的理解。
-
DemoA项目(使用
@Indexed注解)
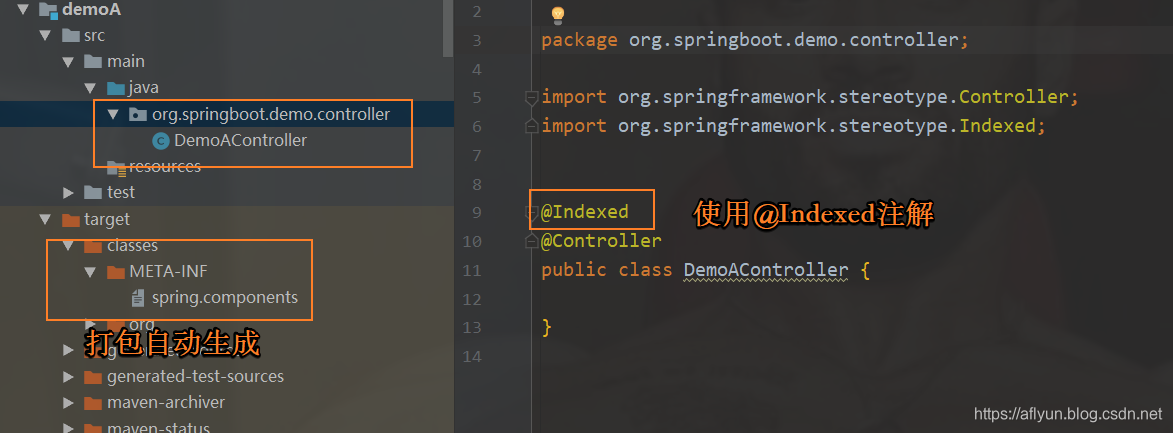
-
DemoB项目(不使用
@Indexed注解)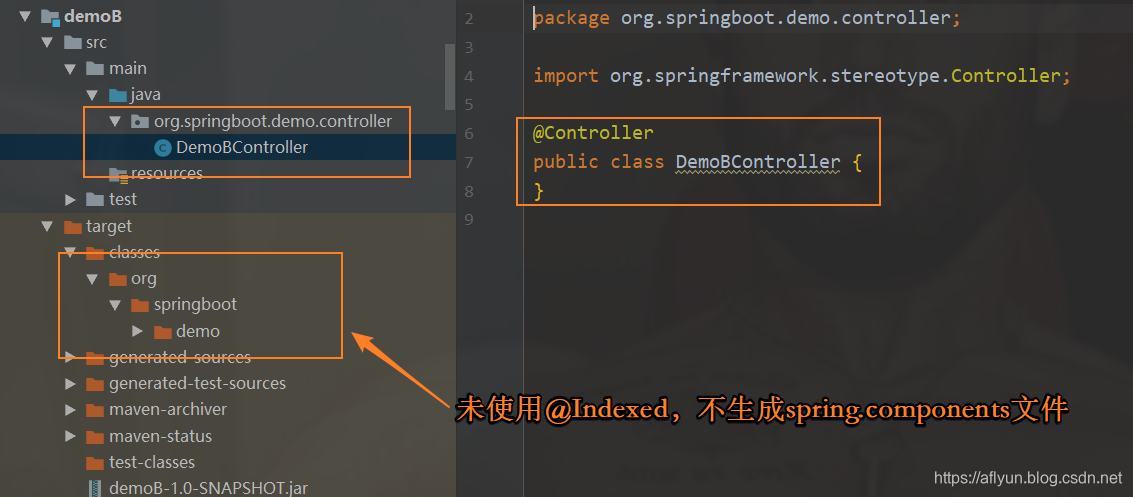
-
SpringBootDemo项目
在此项目中引入DemoA.jar和DemoB.jar。然后进行如下测试,测试代码如下:
配置类,扫描模式注解
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "org.springboot.demo")
public class SpringIndexedConfiguration {
}
测试类:
@Test
public void testIndexedAnnotation(){
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringIndexedConfiguration.class);
System.out.println("获取DemoA Jar中【org.springboot.demo.controller.DemoAController】");
DemoAController demoAController = context.getBean(DemoAController.class);
System.out.println("DemoAController = " + demoAController.getClass());
System.out.println("获取DemoB Jar中【org.springboot.demo.controller.DemoBController】");
DemoBController demoBController = context.getBean(DemoBController.class);
System.out.println("DemoBController = " + demoBController.getClass());
}
结果:
beanDefinitionName = demoAController
获取DemoA Jar中【org.springboot.demo.controller.DemoAController】
DemoAController = class org.springboot.demo.controller.DemoAController
获取DemoB Jar中【org.springboot.demo.controller.DemoBController】
org.springframework.beans.factory.NoSuchBeanDefinitionException: No qualifying bean of type 'org.springboot.demo.controller.DemoBController' available
找不到 DemoBController 。
通过这样一个简单的Demo,验证了上面提到的使用注意点。
对于这种情况,Spring 官网提示了配置相关属性,不再使用index方式启动。要是这样的话,我们完全可以不添加spring-context-indexer 依赖,这样整体就不会使用index模式了。
The index is enabled automatically when a
META-INF/spring.componentsis found on the classpath. If an index is partially available for some libraries (or use cases) but could not be built for the whole application, you can fallback to a regular classpath arrangement (as though no index was present at all) by settingspring.index.ignoretotrue, either as a system property or in aspring.propertiesfile at the root of the classpath.


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号