spring mvc之启动过程源码分析
- 简介
这两个星期都在看spring mvc源码,看来看去还是还是很多细节没了解清楚,在这里把看明白的记录下,欢迎在评论中一起讨论。
一、铺垫
spring mvc是基于servlet的,在正式分析之前,我们来看一下servlet的知识。servlet的生命周期通过三个方法init、service、destory来构建的。
- init():
在Servlet的生命周期中,仅执行一次init()方法。它是在服务器装入Servlet时执行的,负责初始化Servlet对象。可以配置服务器,以在启动服务器或客户机首次访问Servlet时装入Servlet。无论有多少客户机访问Servlet,都不会重复执行init()。
- service():
它是Servlet的核心,负责响应客户的请求。每当一个客户请求一个HttpServlet对象,该对象的Service()方法就要调用,而且传递给这个方法一个“请求”(ServletRequest)对象和一个“响应”(ServletResponse)对象作为参数。在HttpServlet中已存在Service()方法。默认的服务功能是调用与HTTP请求的方法相应的do功能。
- destroy():
仅执行一次,在服务器端停止且卸载Servlet时执行该方法。当Servlet对象退出生命周期时,负责释放占用的资源。一个Servlet在运行service()方法时可能会产生其他的线程,因此需要确认在调用destroy()方法时,这些线程已经终止或完成。
二、spring mvc启动过程
spring mcv的入口是DispatcherServlet,顾名思义就是调度servlet是服务请求调度,它的继承结构如下:

在整合spring mvc时,web.xml有这样配置,相信用过的都知道
<servlet>
<servlet-name>mvc-dispatcher</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:mvc-dispatcher.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>mvc-dispatcher</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.do</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
那根据servlet的知识,在服务器启动,创建dispatcherServlet对象,会执行init方法,根据DispaterServlet的继承关系,找到init方法在HttpServletBean中,下面我们来看一下这个
方法
public final void init() throws ServletException { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Initializing servlet '" + getServletName() + "'"); } // Set bean properties from init parameters. try { /*PropertyValuesz是封装在web.xml配置servlet参数信息 * <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:mvc-dispatcher.xml</param-value> </init-param> */ PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties); BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this); ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext()); bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment())); initBeanWrapper(bw); //将配置的初始化值设置到DispatcherServlet bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true); } catch (BeansException ex) { logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex); throw ex; } //初始化spring mvc容器方法webApplicationContext,由子类的FrameworkServlet来实现 initServletBean(); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Servlet '" + getServletName() + "' configured successfully"); } }
2.1、接下来看FrameworkServlet的initServletBean(),主要调了initWebApplicationContext()方法
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException { getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "'"); if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) { this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization started"); } long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); try { //初始化spring mcv容器 this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext(); initFrameworkServlet(); } catch (ServletException ex) { this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex); throw ex; } catch (RuntimeException ex) { this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex); throw ex; } if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) { long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime; this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization completed in " + elapsedTime + " ms"); } }
2.2、initWebApplicationContext方法
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() { /* 在spring启动过程中,ContextLoaderListener回监听到,实例化IoC容器,并将此容器实例注册到ServletContext中,现在把IOC容器取出来 */ WebApplicationContext rootContext = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext()); WebApplicationContext wac = null; if (wac == null) { //把IOC容器传进去,创建spring mvc自己的容器 wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext); } return wac; if (this.publishContext) { String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName(); //把创建好的spring mcv自己的容器设置到ServletContext容器中 getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac); } }
2.3、createWebApplicationContext方法
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ApplicationContext parent) { /*根据web.xml中的配置决定使用何种WebApplicationContext。默认情况下使用XmlWebApplicationContext web.xml中相关的配置context-param的名称“contextClass” */ Class<?> contextClass = getContextClass(); //获得spring mvc自己容器 ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass); wac.setEnvironment(getEnvironment()); //指定父容器为IOC容器 wac.setParent(parent); //指定spring mcv 核心配置文件的位置classpath:mvc-dispatcher.xml wac.setConfigLocation(getContextConfigLocation()); //spring mcv 容器继续初始化 configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(wac); return wac; }
2.4、配置和刷新spring mvc自己容器方法configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(wac),就是针对spring mcv容器对象一些属性,然后初始化
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac) { //设置ServletContext wac.setServletContext(getServletContext()); //设置ServletConfig wac.setServletConfig(getServletConfig());
postProcessWebApplicationContext(wac);
applyInitializers(wac);
wac.refresh(); }
2.5、接下来,我们看看刷新方法,做了什么事
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { //完成Bean工厂初始化 finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
//完成刷新spring mvc自己的容器功能
finishRefresh();
}
在这里主要看完成BeanFactory初始化工作
2.6、接下来我们看看初始化BeanFactory工作finishBeanFactoryInitialization,主要看到实例化单例对象
protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { //实例化单例对象 beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons(); }
2.7、接下来实例化单例对象方法preInstantiateSingletons()
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException { //获得所有定义好beanNames名称 List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<String>(this.beanDefinitionNames); for (String beanName : beanNames) { RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName); if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) { if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) { final FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName); boolean isEagerInit; if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) { isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Boolean>() { @Override public Boolean run() { return ((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit(); } }, getAccessControlContext()); } else { isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean && ((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit()); } if (isEagerInit) { getBean(beanName); } } else { getBean(beanName); } } } for (String beanName : beanNames) { Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName); if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton) { final SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton = (SmartInitializingSingleton) singletonInstance; if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) { AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() { @Override public Object run() { smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated(); return null; } }, getAccessControlContext()); } else { smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated(); } } } }
这个方法beanNames有以下

是通过getBean(beanName)来实例化对象的,在这里我主要讲spring mvc实例化RequestMappingHandlerMapping做了什么事,不要急,我们先来看一下,RequestMappingHandlerMapping的继承结构
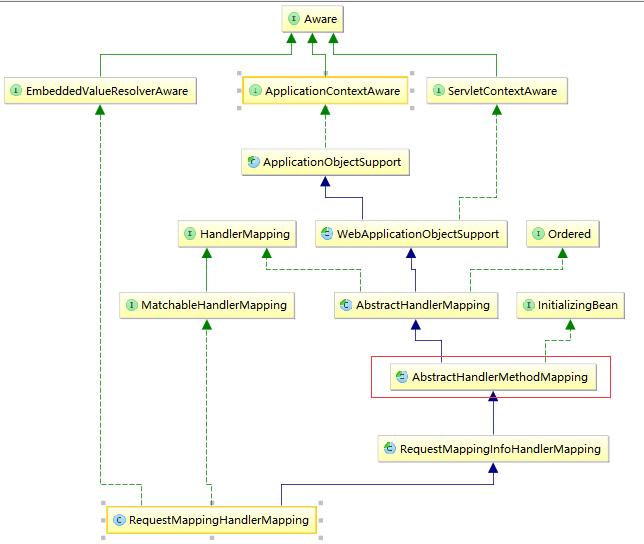
可以看到RequestMappingHandleMapping继承了AbstractHandlerMethodMapping,在初始化的时候,会执行到AbstractHandlerMethodMapping的构造方法,看看
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping这个
实现了InitializingBean,所以这个类在初始化完成时会执行到afterPropertiesSet()方法
2.8、接下来我们看看initHandlerMethods方法到底做了什么事
protected void initHandlerMethods() { //获得所有的beanNames String[] beanNames = (this.detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts ? BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(getApplicationContext(), Object.class) : getApplicationContext().getBeanNamesForType(Object.class)); //遍历取出每个beanName for (String beanName : beanNames) { if (!beanName.startsWith(SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX)) { Class<?> beanType = null; //获得BeanName对应的Class对象 beanType = getApplicationContext().getType(beanName); } //判断这个Class时候否有@Controller和@RequestMapping() if (beanType != null && isHandler(beanType)) { //如果类上含有@Controller和@RequestMapping()注解,执行探测处理器方法
detectHandlerMethods(beanName); } } } handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods()); }
2.9、接下来我们看看detectHandlerMethods(beanName)这个方法到底干了什么事
protected void detectHandlerMethods(final Object handler) { //传进来的handle是个字符串类型的BeanName,首先根据Bean名称创建Class对象 Class<?> handlerType = (handler instanceof String ? getApplicationContext().getType((String) handler) : handler.getClass()); final Class<?> userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType); //获得Controller类对应methods对应的Map Map<Method, T> methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(userType, new MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<T>() { @Override public T inspect(Method method) { return getMappingForMethod(method, userType); } }); //遍历Map,取出Controller类的每一个方法和对应的Mapping for (Map.Entry<Method, T> entry : methods.entrySet()) { Method invocableMethod = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(entry.getKey(), userType); T mapping = entry.getValue(); registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping); } }
下图是Map<Method, T> methods的值
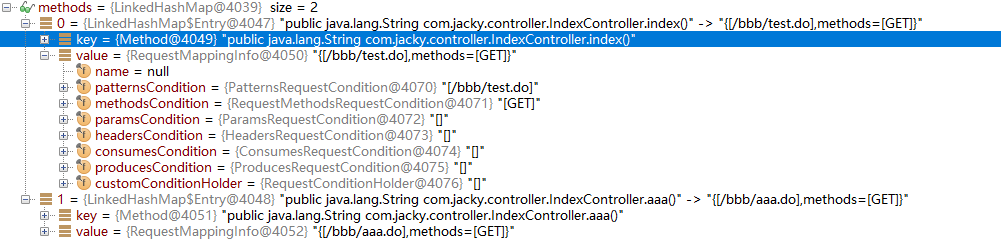
可以看到T封装了Controller类的请求方式,和匹配条件等等数据
2.10、接下来我们来看看spring mvc是怎么注册Controller方法
registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping)
protected void registerHandlerMethod(Object handler, Method method, T mapping) { this.mappingRegistry.register(mapping, handler, method); }
2.11、接下来我们看看mappingRegistry的register方法
public void register(T mapping, Object handler, Method method) { //拿到写锁 this.readWriteLock.writeLock().lock(); try { //根据handler(是你的controller类的类名)和controller的method方法创建handlerMethod对象 HandlerMethod handlerMethod = createHandlerMethod(handler, method); //存储到名称为mappingLookup的Map中 this.mappingLookup.put(mapping, handlerMethod); //然后从mapping中取出请求url List<String> directUrls = getDirectUrls(mapping); for (String url : directUrls) { //然后我们再把url和mapping存储到MultiValueMap类型的urlLookup中,所以我们可以通过url找到mapping,再通过mapping找到handleMethod this.urlLookup.add(url, mapping); } //把mapping和appingRegistration存储到HashMap类型的registry中 this.registry.put(mapping, new AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.MappingRegistration<T>(mapping, handlerMethod, directUrls, name)); } finally { //释放写锁 this.readWriteLock.writeLock().unlock(); } }
这里解释下传进来3个参数 mapping封装了匹配条件,请求方式等数据,handler是我们的controller类名(字符串),method(controller类的方法对象)
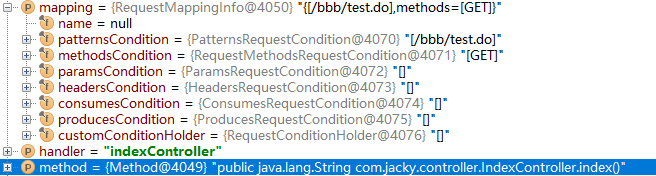
2.12、接下来我们回到的2.8的initHandlerMethods方法
protected void initHandlerMethods() { //获得所有的beanNames String[] beanNames = (this.detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts ? BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(getApplicationContext(), Object.class) : getApplicationContext().getBeanNamesForType(Object.class)); //遍历取出每个beanName for (String beanName : beanNames) { if (!beanName.startsWith(SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX)) { Class<?> beanType = null; //获得BeanName对应的Class对象 beanType = getApplicationContext().getType(beanName); } //判断这个Class时候否有@Controller和@RequestMapping() if (beanType != null && isHandler(beanType)) { //如果类上含有@Controller和@RequestMapping()注解,执行探测处理器方法 detectHandlerMethods(beanName); } } } handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods()); }
执行完了detectHandlerMethods(beanName);方法,继续往下执行handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods())方法,这个方法是个 是个模板 方法,什么都没执行,到这里
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean { @Override public void afterPropertiesSet() { initHandlerMethods(); } }
afterPropertiesSet方法就算执行完了。
2.13、接下来执行继续回到2.7的实例化单例对象方法preInstantiateSingletons();
接下没什么什么好说,preInstantiateSingletons()结束后,finishBeanFactoryInitialization()方法也就结束了,回到了refresh(),继续完成刷新spring mvc自己的容器功能
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { //完成Bean工厂初始化 finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); //完成刷新spring mvc自己的容器功能 finishRefresh(); }
2.14、finishRefresh();这一步会触发一个ApplicationEvent:
protected void finishRefresh() { //其中this是指XmlWebApplicationContext对象 publishEvent(new ContextRefreshedEvent(this));
2.15、接下来解析初始化DispatcherServlet类的各种成员变量
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) { initStrategies(context); }
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) { initMultipartResolver(context); initLocaleResolver(context); initThemeResolver(context); //初始化handlerMappings initHandlerMappings(context); //handlerAdapters initHandlerAdapters(context); initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context); initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context); //初始化视图解析器 initViewResolvers(context); initFlashMapManager(context); }
2.16、接下来回到2.1的FrameworkServlet的initServletBean()方法中,然后initServletBean()执行完之后,HttpServletBean中的init初始化方法也就执行完了,到这里spring mvc启动的源码已经分析完成,
希望你看会有收获。
三、总结
其实分析完spring mvc自己启动的源码会发现,大部分内容都在构建spring mcv自己的容器,构建完成之后将容器放到SevletContext中


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号