java IO流
IO流总结(初级)
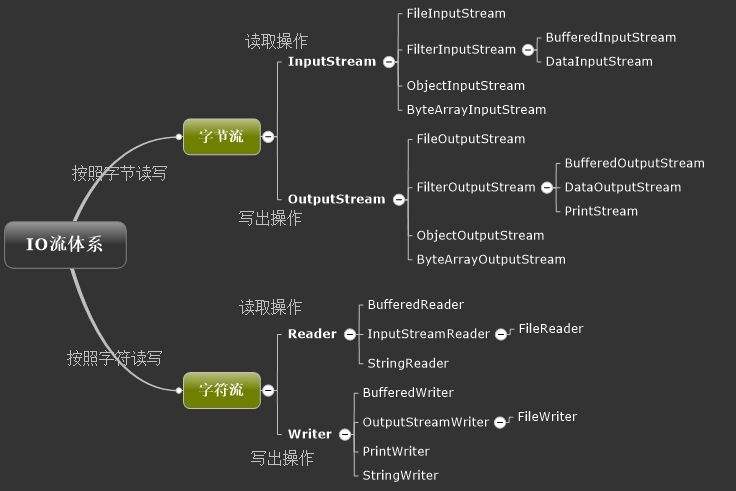
1.继承关系图(Inpustream Outpustream Reader Wrier 均为抽象类)
2.具体使用背景以及案例(含常用方法)
2.1 文件字节流
2.1.1读取文件内容 FileInputStream
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\test.txt");
//得到文件的字节字节数
int count = fis.available();
System.out.println(count);
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\test.txt");
//得到文件的字节大小
int count = fis.available();
System.out.println(count);
//从该输入流读取一个字节的数据。 如果没有输入可用,此方法将阻止。
int read = fis.read();
//第一种
// int buf =0;
// while ((buf = fis.read())!= -1) {
// System.out.println((char) buf );
// }
//第二种
// 从输入流读取一些字节数,并将它们存储到缓冲区b 。 实际读取的字节数作为整数返回。 该方法阻塞直到输入数据可用,检测到文件结束或抛出异常。
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while ((len=fis.read(buf))!=-1){
System.out.println(new String(buf,0,len));
}
fis.close();
}
2.1.2 写内容到文件 FileOutputStream
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\\outtest.txt",true);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
byte [] buf="我要进阿里".getBytes();
fos.write(97);
fos.write(buf);
//与上面一行同效
fos.write(buf,0,buf.length);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
2.1.3 使用文件字节流实现复制
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\test.txt");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\\outtest.txt", true);
//第一种方式
// int len=0;
// while((len=fis.read())!=-1){
// fos.write(len);
// }
// fos.close();
// fis .close();
int len = 0;
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
while ((len = fis.read(buf)) != -1) {
fos.write(buf, 0, len);
//以上等同于fos.write(buf);
}
fos.close();
fis.close();
}
2.2 文件字符流
2.2.1 Reader 读取文件内容
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileReader reader = new FileReader("D:\\test.txt");
int len = 0;
len=reader.read();
System.out.println((char)len);
// char[] cbuf = new char[1024];
// while ((len = reader.read(cbuf)) != -1) {
// System.out.println(new String(cbuf, 0, len));
// }
reader.close();
}
2.2.2 Writer 写内容到文件
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileReader reader = new FileReader("D:\\test.txt");
int len = 0;
len=reader.read();
System.out.println((char)len);
// char[] cbuf = new char[1024];
// while ((len = reader.read(cbuf)) != -1) {
// System.out.println(new String(cbuf, 0, len));
// }
reader.close();
}
2.3 缓冲字节流_缓冲字符流
2.3.1 缓冲字节流 copy文件
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("D:\\test.txt"));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("D:\\outtest.txt"));
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while ((len = bis.read(buf)) != -1) {
bos.write(buf, 0, len);
bos.flush();
}
bos.close();
bis.close();
}
2.3.2 缓冲字符流copy文件 适合纯文本
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader bir= new BufferedReader(new FileReader("D:\\test.txt"));
BufferedWriter bow= new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("D:\\outtest.txt"));
String line=null;
while((line=bir.readLine())!=null){
bow.write(line);
bow.newLine();
bow.flush();
}
bow.close();
bir.close();
}//该方法适合于纯文本copy
2.4 转换流
2.4.1 InputStreamReader OutputStreamWriter 将字节流转换成字符流 (字符流操作文本更方便)
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//数据源是从键盘进入
InputStream is= System.in;
//使用转换流转换
InputStreamReader isr=new InputStreamReader(is,"utf-8");
//提高读取效率
BufferedReader br =new BufferedReader(isr);
BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("D:\\outtesr.txt"),"utf-8"));
String line=null;
while(!"over".equals((line=br.readLine()))){
bw.write(line);
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
bw.close();
br.close();
}
2.5 打印流
2.5.1 PrintStream(通常用于输出文本内容) PrintWriter 打印到文件内 有自动刷新功能(使用 PrintWriter 代替 BufferedWriter 完
成, 更简单 )两者都不抛出IO异常
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// PrintStream ps =System.err;
//无需类型转换 他会制动转换成string 19 在通过Printstrem 就是 '1' '9'
PrintStream ps = System.out;
ps.println(1);
ps.println("偶买噶");
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new FileOutputStream("D:\\god.txt"), true);
pw.println("aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa");
pw.write("baby china");
pw.write(520);
pw.flush();
pw.close();
BufferedWriter br = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("D:\\a.txt"));
br.write("我的baby china");
br.close();
}
2.6 数据流 (提供了读取写入数据类型的能力)
2.6.1 DataInputStream DataOutputStream
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
write();
read();
}
public static void write() throws IOException {
//处理流, 只针对字节流, 二进制文件
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("D:\\data.txt")));
dos.writeInt(520);
dos.writeChar('中');
dos.close();
}
public static void read() throws IOException {
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("D:\\data.txt")));
System.out.println(dis.readInt());;
System.out.println(dis.readChar());
dis.close();
}
2.7 对象流 对象必须实现Serializable接口 才可序列化
public class Person implements Serializable {
private String name;
private int age;
public Person(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
public Person() {
super();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
//以什么格式写进去 就以什么格式读出来
write();
read();
}
public static void write() throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("D:\\object.txt"));
oos.writeObject(new Person());
oos.close();
}
public static void read() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream ois = null;
try {
ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("D:\\object.txt"));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Person p = (Person) ois.readObject();
System.out.println(p);
if(ois!=null){
try {
ois.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
2.8 序列化 与 反序列化 序列化以后的对象可以保存到磁盘上, 也可以在网络上传输, 使得不同的计算机可以共享对象.(序列化的字节序列是平台无关的)
public class Student implements Serializable {
//加了下
private String name;
private int age;
//不愿被序列化的 可以加transient 加 staic 也不会被序列化
private transient String schoolname;
public Student(String name, int age, String schoolname) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.schoolname = schoolname;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getSchoolname() {
return schoolname;
}
public void setSchoolname(String schoolname) {
this.schoolname = schoolname;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", schoolname='" + schoolname + '\'' +
'}';
}
public Student() {
super();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
write();
read();
}
public static void write() throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("D:\\ser.txt"));
oos.writeObject(new Student("小明", 18, "南山实验"));
oos.close();
}
public static void read() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("D:\\ser.txt"));
Student st = (Student) ois.readObject();
System.out.println("st.getName()" + st.getName() + "st.getAge()" + st.getAge() + "st.getSchoolname()" + st.getSchoolname());
}
2.9 文件夹复制
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//copy文件
// File scFile = new File("D:\\国青调研.docx");
// File target = new File("E:\\国青调研.docx");
// copyFile(scFile, target);
//copydir
File scrdir = new File("D:\\scr");
File targetdir = new File("D:\\baby");
copydir(scrdir, targetdir);
}
public static void copydir(File scrDir, File targetDir) throws IOException {
if (!targetDir.exists()) {
targetDir.mkdir();
}
File[] files = scrDir.listFiles();
for (File file : files) {
if (file.isFile()) {
copyFile(new File(scrDir + "\\" + file.getName()), new File(targetDir + "\\" + file.getName()));
} else {
//递归调用
copydir(new File(scrDir + "\\" + file.getName()), new File(targetDir + "\\" + file.getName()));
}
}
}
public static void copyFile(File scFile, File targetFile) throws IOException {
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(scFile));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(targetFile));
int len = 0;
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
while ((len = bis.read(buf)) != -1) {
bos.write(buf, 0, len);
}
bos.close();
bis.close();
}
2.10 字节数组流 数据源或目的地为: 字节数组 只有字节流, 没有字符流 是节点流
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
byte[] buf = buf = write();
read(buf);
}
private static void read(byte[] buf) throws IOException {
ByteArrayInputStream bais = new ByteArrayInputStream(buf);
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(bais);
System.out.println(ois.readChar());
ois.close();
}
private static byte[] write() throws IOException {
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();//创建字节数组流对象 目的地是字节数组 底层次自动创建
//ObjectOutputStream(OutputStream out)
//创建一个写入指定的OutputStream的ObjectOutputStream。
ObjectOutputStream oos = oos = new ObjectOutputStream(baos);
oos.writeChar('a');
oos.close();
return baos.toByteArray();
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号