面向对象程序设计(2)
面向对象程序设计(2)
一:前言
(1):知识点
1:正则表达式
什么是正则表达式:
- 正则表达式,又称规则表达式,通常被用来检索、替换那些符合某个模式(规则)的文本。
- 正则表达式是对字符串操作的一种逻辑公式,就是用事先定义好的一些特定字符、及这些特定字符的组合, 组成一个“规则字符串”,这个“规则字符串”用来表达对字符串的一种过滤逻辑。
正则表达式的三大类:
Pattern 类:
pattern 对象是一个正则表达式的编译表示。Pattern 类没有公共构造方法。要创建一个 Pattern对象,你必须首先调用其公共静态编译方法,它返回一个 Pattern 对象。该方法接受一个正则表达式作为它的第一个参数。
Matcher 类:
Matcher 对象是对输入字符串进行解释和匹配操作的引擎。与Pattern 类一样,Matcher 也没有公共构造方法。你需要调用 Pattern 对象的 matcher 方法来获得一个 Matcher 对象。
PatternSyntaxException类:
PatternSyntaxException 是一个非强制异常类,它表示一个正则表达式模式中的语法错误。
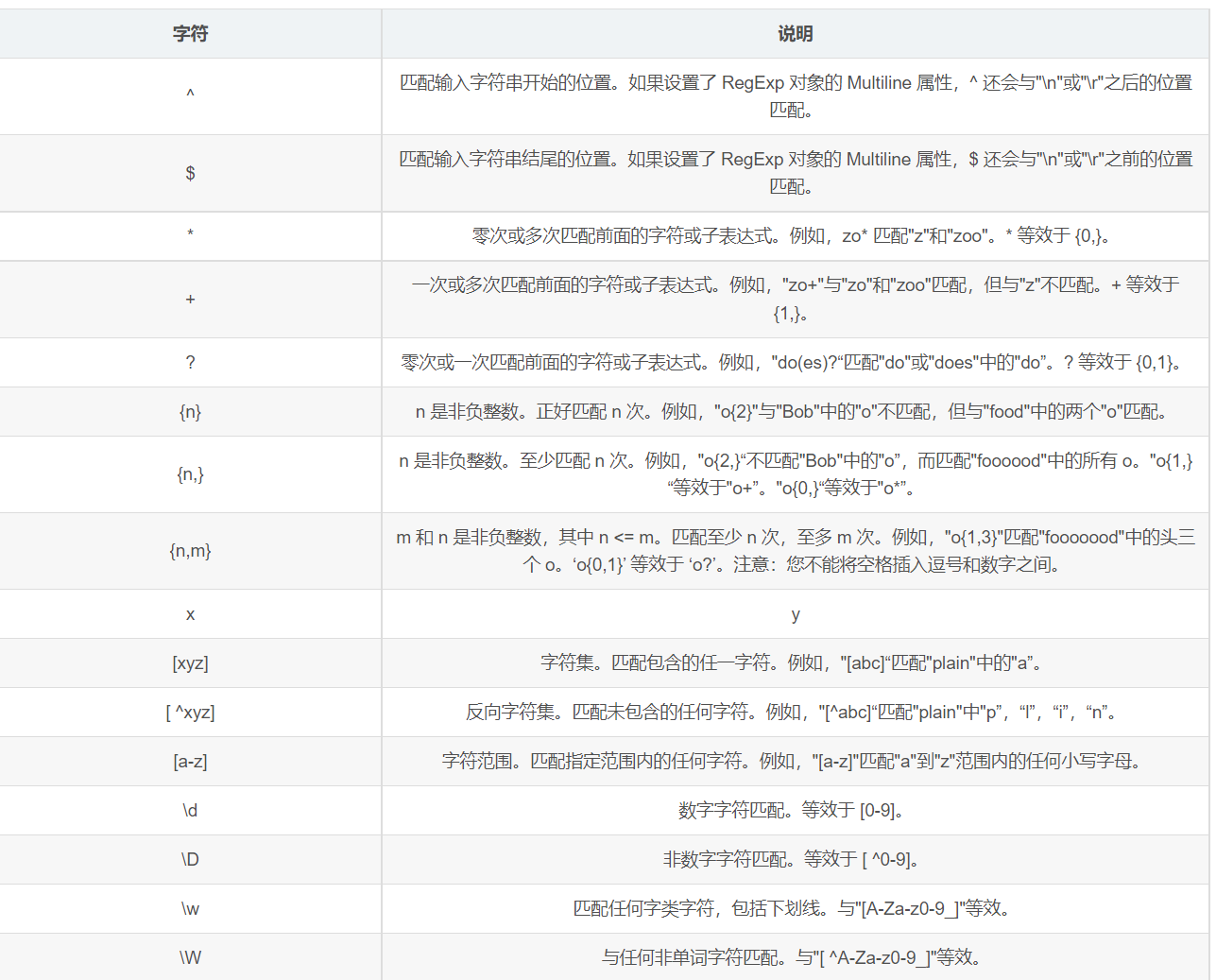
字符说明:
2:动态数组
动态数组:Java动态数组是一种可以任意伸缩数组长度的对象,在Java中比较常用的是ArrayList,ArrayList是javaAPI中自带的java.util.ArrayList。
(1): 什么是数组
同类数据元素的集合,在计算机中以连续的地址存储,编译时确定长度,无法改变。
(2):什么是动态数组
数据结构中顺序表的物理实现,同类数据元素的集合,在计算机中以连续的地址存储,大小在创建时决定,但是可以改变。
(3): 为什么使用动态数组
支持随机访问,查询速度快。但是插入和删除都需要移动元素,比起链表开销较大。如:java集合类中的ArrayList Vector等
3:封装继承多态
Java的三大特性:继承封装多态
(1):封装
封装(Encapsulation)是面向对象方法的重要原则,就是把对象的属性和操作(或服务)结合为一个独立的整体,并尽可能隐藏对象的内部实现细节。
什么是封装:
- 将类的某些信息隐藏在类的内部,不允许外部程序进行直接的访问调用。
- 通过该类提供的方法来实现对隐藏信息的操作和访问。
- 隐藏对象的信息。
- 留出访问的对外接口
封装的特点:
- 对成员变量实行更准确的控制。
- 封装可以隐藏内部程序实现的细节。
- 良好的封装能够减少代码之间的耦合度。
- 外部成员无法修改已封装好的程序代码。
- 方便数据检查,有利于保护对象信息的完整性,同时也提高程序的安全性。
- 便于修改,体高代码的可维护性。
封装的使用:
-
使用private修饰符,表示最小的访问权限。
-
对成员变量的访问,统一提供setXXX,getXXX方法。
(2):继承
什么是继承:
-
使用private修饰符,表示最小的访问权限。
-
对成员变量的访问,统一提供setXXX,getXXX方法。
继承的特点:
提高代码复用性。
父类的属性方法可以用于子类。
可以轻松的定义子类。
使设计应用程序变得简单。
继承的注意事项:
只支持单继承,即一个子类只允许有一个父类,但是可以实现多级继承,及子类拥有唯一的父类,而父类还可以再继承。
子类可以拥有父类的属性和方法。
子类可以拥有自己的属性和方法。
子类可以重写覆盖父类的方法。
继承的使用:
1,在父子类关系继承中,如果成员变量重名,则创建子类对象时,访问有两种方式。
a,直接通过子类对象访问成员变量 等号左边是谁,就优先使用谁,如果没有就向上找。
b,间接通过成员方法访问成员变量该方法属于谁,谁就优先使用,如果没有就向上找。
2,同理:
成员方法也是一样的,创建的对象是谁,就优先使用谁,如果没有则直接向上找。
注意事项:
无论是成员变量还是成员方法,如果没有都是向上父类中查找,绝对不会向下查找子类的。
3,在继承关系中,关于成员变量的使用:
局部成员变量:直接使用
本类成员变量:this.成员变量
父类成员变量:super.父类成员变量
重写和重载:
重写的规则:
1,参数列表必须与被重写方法相同。
2,访问权限不能比父类中被重写的方法的访问权限更低(public>protected>(default)>private)。
3,父类成员的方法只能被它的子类重写。
4,被final修饰的方法不能被重写。
5,构造方法不能
重载的规则:
1,被重载的方法必须改变参数列表(参数个数或者类型不一样)。
2,被重载的方法可以改变返回类型。
3,被重载的方法可以改变访问修饰符。
(3):多态
什么是多态:
多态是同一个行为具有多个不同表现形式或形态的能力。
多态的特点:
1,消除类型之间的耦合关系,实现低耦合。
2,灵活性。
3,可扩充性。
4,可替换性。
4:容器
为什么要引入Java容器?
我们知道,如果定义一个int数组,需要一开始就要制定它的大小。在一些情况下,我们根本不知道它的长度是多少,开辟很大的长度会导致空间浪费。
此外,数组还有很多缺点,例如数组中提供的方法非常有限,对于添加、删除、插入数据等操作,非常不便,同时效率不高。获取数据中实际元素的个数的需求,数组没有现成的属性或方
法可用。数组存储数据的特点:有序、可重复。对于无序、不可重复的需求,不能满足。
为了数组能够更灵活的应用,提出了Java容器的概念。
Java容器基本概念
Java容器类库是用来保存对象的,他有两种不同的概念:
Collection,独立元素的序列,这些元素都服从一条或多条规则。List、Set以及Queue都是Collection的一种,List必须按照顺序保存元素,而Set不能有重复元素,Queue需要按照
排队规则来确定对象的顺序。
Map,Map是键值对类型,允许用户通过键来查找对象。Hash表允许我们使用另一个对象来查找某个对象。
容器接口:
Collection接口
Collection是最基本的集合接口。Java SDK不提供直接继承自Collection的类,Java SDK提供的类都是继承自Collection的“子接口”。所有实现Collection接口的类都必须提供两个标准的构
造函数:无参数的构造函数用于创建一个空的Collection,有一个 Collection参数的构造函数用于创建一个新的Collection,这个新的Collection与传入的Collection有相同的元素。后一个构
造函数允许用户复制一个Collection。
Map接口
Map也是一个接口,一个map不能包含重复的key,每个key只能映射唯一一个value。Map接口是用来取代Dictionary抽象类的。Map接口提供三个集合视图,1.key的集合 2.value的集合
3.key-value的集合。map内元素的顺序取决于Iterator的具体实现,获取集合视图其实是获取一个迭代器,实现对遍历元素细节的隐藏。
同样,map的实现类应该提供两个“标准”构造器,一个无参构造器用来创建一个空map,一个只有一个参数,参数类型是map的构造器,用来创建一个新的和传入参数有一样key-value映射
的map。实际上,后者允许复制任何一个map,这仅仅是一个建议,并没有强制要求,因为接口是无法包含构造器的,不过这个建议在JDK被遵守。
如果一个方法的操作是不被支持的,这个方法指定抛出UnsupportedOperationException异常。如果这个操作对map是没有影响的,那么也可以不抛出UnsupportedOperationException异
常。例如,在一个不能被修改的map调用putAll(Map)方法,如果该map的映射是空的,就不要求抛出UnsupportedOperationException异常。
(2):题量和难度
(1):第四次大作业:
①: 获取每一行的数字并且输出这一行数字的总和
难度不算大,获取数字按照循环累加就可以
②:输入多个点坐标,组成四边形和点线,判断他们构成的各种关系以及完成相对应的要求
难度有点大,四边形被线分割成两个部分最难搞,没有实现
③:银行用户存取款相关业务,要进行封装
不算难,实现功能十分简单,就算要封装,也很简单实现功能
(2):期中考试
给你一个类图,按照类图构造对应函数,其中使用到继承和容器
题量不算大,难度也不算大,类图清晰并且实现的功能不复杂
(3):第五次大作业
五边形的点线面系列,甚至有面和面的关系以及切割成两部分
题量很少,甚至算是只有一题,但是难度我觉得十分高,线切割面积已经很难了,面切割面积,太复杂已经不知道从哪里开始,毫无头绪
2:设计与分析
1.第四/五次大作业
一:获取每一行数字之和
(1):采用str中的split的方法以及正则表达式,获取数字,不断进行累加,最终输出,从而获取结果
没有什么复杂的功能,整个代码就是一路直接下来,只有两个小循环,很
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
Line l = new Line();
Point a = new Point();
Point b = new Point();
double x1,x2,y1,y2;
String str;
x1 = input.nextDouble();
y1 = input.nextDouble();
x2 = input.nextDouble();
y2 = input.nextDouble();
str = input.next();
l.setColor(str);
a.setX(x1);
a.setY(y1);
l.setPoint1(a);
b.setX(x2);
b.setY(y2);
l.setPoint2(b);
l.display();
input.close();
}
}
class Point
{
private double x;
private double y;
public Point()
{
}
public Point(double x,double y)
{
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public double getX()
{
return this.x;
}
public void setX(double x)
{
if(x<=200&&x>0)
this.x = x;
else
{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
public double getY()
{
return this.y;
}
public void setY(double y)
{
if(y<=200&&y>0)
this.y = y;
else
{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
public void display()
{
System.out.printf("(%.2f,%.2f)\n",this.x,this.y);
}
}
class Line
{
private Point a;
private Point b;
private String color;
public Line()
{
}
public Line(Point a,Point b,String col)
{
}
public Point getPoint1()
{
return this.a;
}
public void setPoint1(Point point1)
{
this.a = point1;
}
public Point getPoint2()
{
return this.b;
}
public void setPoint2(Point point2)
{
this.b = point2;
}
public String getColor()
{
return this.color;
}
public void setColor(String str)
{
this.color = str;
}
public double getDistance()
{
double x1,x2,y1,y2,s;
x1 = this.a.getX();
x2 = this.b.getX();
y1 = this.a.getY();
y2 = this.b.getY();
s = Math.sqrt((x1-x2)*(x1-x2)+(y1-y2)*(y1-y2));
return s;
}
public void display()
{
Line l = new Line();
Point a = new Point();
Point b = new Point();
a = this.getPoint1();
System.out.println("The line's color is:"+this.getColor());
System.out.println("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:");
a.display();
b = this.getPoint2();
System.out.println("The line's end point's Coordinate is:");
b.display();
System.out.print("The line's length is:");
System.out.printf("%.2f\n",this.getDistance());
}
}
二:四/五边形点线面系列
(1):四边形的点线面系列,之前出现三角形就已经让我头疼了,这次出现的分割面积还是一样让我头疼,并且出现了一个叫做冗余点的东西,这个我到了五边形也没有系统地解决它,
算是这个系列里的一个败笔吧
(2)类与类之间的关系就出现了比较高的复杂度,有依赖,关联,组合,聚合,主要是关联和组合,由于类的种类比较多,选择里面传参主要是数据,然而实现功能分散在各种点线里
面,所以各种里面组合使用频率最高,而其实继承老师也提过,不过我还没有实现
package PTA51;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
public class PTA51
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
String str = input.nextLine();
Getnumber number = new Getnumber();
Select sel = new Select();
int select;
double[] num = new double[100];
num = number.get_number(str);//获取数字,储存在数组里
select = number.dealnum(num,str);
//select = (int)(str.charAt(0)-48);
switch(select)
{
case 1://选择1
sel.select1(num,select);
break;
case 2:
sel.select2(num, select);
break;
case 3:
sel.select3(num,select);
break;
case 4:
sel.select4(num,select);
break;
case 5:
sel.select5(num,select);
break;
case 6:
sel.select6(num, select);
break;
}
input.close();
}
}
class Getnumber
{
public Getnumber()
{
}
public boolean ifright(String str)
{
boolean flag;
flag = true;
//String pattern = "^[1-5]:(-)?(\\+)?\\d+(.)?(\\d+)?,(-)?(\\+)?\\d+(.)?(\\d+)?( (-)?(\\+)?\\d+(.)?(\\d+)?,(-)?(\\+)?\\d+(.)?(\\d+)?)?( (-)?(\\+)?\\d+(.)?(\\d+)?,(-)?(\\+)?\\d+(.)?(\\d+)?)?( (-)?(\\+)?\\d+(.)?(\\d+)?,(-)?(\\+)?\\d+(.)?(\\d+)?)?( (-)?(\\+)?\\d+(.)?(\\d+)?,(-)?(\\+)?\\d+(.)?(\\d+)?)?( (-)?(\\+)?\\d+(.)?(\\d+)?,(-)?(\\+)?\\d+(.)?(\\d+)?( )?)?";//正则表达式,判断格式
String pattern = "^[1-6]:((\\D)?\\d+(.)?(\\d+)?,(\\D)?\\d+(.)?(\\d+)?( )?){1,}";//正则表达式,判断格式
flag = Pattern.matches(pattern,str);
if(flag)
return true;
return false;
}
// public boolean ifright(String str,int select)
// {
// int i;
// Getnumber g = new Getnumber();
// if(!str.matches("[0-6]:.+"))
// return false;
// select = g.getrightnum(select)/2;
//// for(i = 0;i<select;i++) {
// if (!str.matches("(-)?(\\\\+)?\\\\d+(.)?(\\\\d+)?,(-)?(\\\\+)?\\\\d+(.)?(\\\\d+)?( )?")) {
// return false;
//// }
// }
// return true;
// }
//获取数字
public double[] get_number(String s)
{
int i,k,n,m,count,f;
f = 1;
m = 1;
double num,j;
double[] number = new double[100];
for(i = 2;i < s.length();i+=(count+1))
{
num = 0.0;
j = 0.1;
k = 0;
n = 1;
f = 1;
count = 0;
for(n = i;n<s.length()&&s.charAt(n)!=','&&s.charAt(n)!=' ';n++)
{
count++;
if(s.charAt(n)=='-')
{
f = 0;
}
if(s.charAt(n)!='.'&& k==0&&s.charAt(n)>='0'&&s.charAt(n)<='9')
{
num = s.charAt(n)-48 + num *10;//小数点之前获取整数
}
if(s.charAt(n)=='.')
{
k = 1;//读取到小数点
}
if(k == 1&&s.charAt(n)>='0'&&s.charAt(n)<='9')
{
num = num + (s.charAt(n)-48) * j;//获取小数点之后
j = j * 0.1;
}
}
if(f==0)
{
number[m] = -num;
}
else number[m] = num;
m++;
}
number[0] = m-1;//第一个数字储存数字个数
return number;
}
//判断输入数字个数是否正确,数字正确返回“true”,不正确“false”
public boolean ifRnum(double m,int n)
{
int x,y;
y = 0;
x = (int)m;
if(n==1||n==2)
y = 10;
if(n == 3)
y = 14;
if(n == 4||n==5)
y = 20;
if(n==6)
y = 12;
if(x==y)
return true;
return false;
}
//是否有点重合
public boolean isnotsame1(Point a,Point b,Point c,Point d)
{
boolean f1,f2,f3,f4,f5,f6;
f1 = a.pointsame(a, b);
f2 = a.pointsame(a, c);
f3 = a.pointsame(a, d);
f4 = a.pointsame(b, c);
f5 = a.pointsame(d, b);
f6 = a.pointsame(c, d);
if(f1&&f2&&f3&&f4&&f5&&f6)
return false;
return true;
}
//处理数字出现各种错误,如果没错返回选择
public int dealnum(double[] num,String str)
{
Getnumber ber = new Getnumber();
boolean f1,f2,f3;
int select;
select =(int)(str.charAt(0)-48);
f1 = ber.ifright(str);
f2 = ber.ifRnum(num[0],select);
if(!f1)
{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
if(!f2)
{
System.out.println("wrong number of points");
System.exit(0);
}
return select;
}
//判断应该出现多少个数字
public int getrightnum(int n)
{
if(n==1||n==2)
return 10;
if(n==3)
return 14;
if(n==4||n==5)
return 20;
if(n==6)
return 12;
return 0;
}
//输出格式处理
public void output(double m)
{
//出现2.99999999转成2
//****************
int n1,n2;
n1 = (int)m;
n2 = (int)m+1;
if(Math.abs(m-n1)<1e-5||Math.abs(m-n2)<1e-5)
System.out.printf("%.1f",m);
else
System.out.printf("%.3f",m);
}
//除去重复的点
public Point[] dealsamepoint(double[] num ,int n)
{
Point[] aa = new Point[20];
Point a = new Point();
int i,j,k;
aa = a.sumpoint(num, n);
for(i = 0;i < n;i++){
for(j = i+1;j < n;j++){
if(!a.pointsame(aa[i], aa[j])) {//当出现相同点,后面的取代前面的
for(k = j;k<n;k++) {
aa[k] = aa[k+1];
j--;
}
}
}
}
return aa;
}
//处理冗余点 传回剩余的点
public Point[] dealmore(double[] num ,int n)
{
Point[] all = new Point[20];
Point a = new Point();
Line l = new Line();
Getnumber g = new Getnumber();
int i,j,k,m;
m = g.getrightnum(n)/2;
all = a.sumpoint(num, n);
all = g.dealsamepoint(num, n);
for(i = 0;i<m;i++) {
for(j = i+1;j<m;j++) {
for(k = j+1;k<m;k++) {//如果在一条直线上
if(!l.ifnotsameline(all[i], all[j], all[k])) {
//如果all[j]在x y中间
if((all[k].x>all[j].x&&all[j].x>all[i].x)||(all[k].x<all[j].x&&all[j].x<all[i].x)) {
all[j] = all[k];
}
all = g.dealsamepoint(num, n);//好像看到这里是空的
}
}
}
}
return all;
}
}
class Point
{
double x;
double y;
public Point()
{
}
//构造点
public Point(double a,double b)
{
this.x = a;
this.y = b;
}
//判断点是否重合,重合返回“false”,不重合返回“true”
public boolean pointsame(Point a,Point b)
{
if(a.x==b.x&&a.y==b.y)
return false;
return true;
}
//获取了两个点中x坐标更大的点的坐标
public double getxmax(Point a,Point b)
{
if(a.x>b.x)
return a.x;
else return b.x;
}
//获取了两个点中y坐标更大的点的坐标
public double getymax(Point a,Point b)
{
if(a.y>b.y)
return a.y;
else return b.y;
}
//获取了两个点中x坐标更小的点的坐标
public double getxmin(Point a,Point b)
{
if(a.x>b.x)
return b.x;
else return a.x;
}
//获取了两个点中y坐标更小的点的坐标
public double getymin(Point a,Point b)
{
if(a.y>b.y)
return b.y;
else return a.y;
}
//将点放在点的数组中去
public Point[] sumpoint(double[] sum,int n)
{
Point[] allpoint = new Point[20];
int i,j,m;
j = 0;
Getnumber num = new Getnumber();
m = num.getrightnum(n);
for(i = 1;i < m;i+=2)
{
Point a = new Point(sum[i],sum[i+1]);
allpoint[j] = a;
j++;
}
return allpoint;
}
}
//有关线的类
class Line
{
int f;//斜率是否存在
double A;//斜率
double B;//常数项
Point a3;//表示两点向量方向的点
Point a1,a2;//线上两个点
double x;//两点之间距离
public Line()
{
}
//构造函数,与此同时计算斜率等
public Line(Point a,Point b)
{
this.f = 1;
//保证第一个数是x更小的数
Point c = new Point(0,0);
if(a.x<b.x)
{
this.a1 = a;
this.a2 = b;
//**********
//这里之前a3没有赋值,导致后面程序没有办法进行
this.a3 = c;
}
else
{
this.a1 = b;
this.a2 = a;
this.a3 = c;
}
this.a3.x = a1.x-a2.x;
this.a3.y = a1.y-a2.y;
if(a.x==b.x)//斜率不存在
this.f = 0;
else//求出斜率
{
this.f = 1;
this.A = (a.y-b.y)/(a.x-b.x);
this.B = this.A*(-b.x)+b.y;
}
this.x = Math.sqrt((a.x-b.x)*(a.x-b.x)+(a.y-b.y)*(a.y-b.y));
}
//判断三点是否不在一条直线上,在一条直线上返回“false”,不在返回“true”
public boolean ifnotsameline(Point a,Point b,Point c)
{
Line l = new Line( a, b);
if(l.f==0)
{
if(c.x==a.x)
return false;
return true;
}
if(l.A*c.x+l.B-c.y==0)
return false;
return true;
}
//判断两条直线是否重合,重合返回“true”,不重合返回“false”
public boolean issameline(Line l1,Line l2)
{
if(l1.f!=l2.f)
{
return false;
}
if(l1.f==0&&l2.f==0)
{
if(l1.a1.x==l2.a1.x)
return true;
}
if(l1.A==l2.A&&l1.B==l2.B)
return true;
return false;
}
//点在直线两侧,在两侧返回“true”,不在返回“false”
public boolean difline(Point a,Point b,Line l)
{
double m,n;
if(l.f==0)//斜率不存在
{
if((a.x-l.a1.x)*(b.x-l.a1.x)>0)
return false;
}
m = l.A*a.x+l.B-a.y;
n = l.A*b.x+l.B-b.y;
if(m*n>0)
return false;
return true;
}
//线段有交点“true”,没交点“false”
public boolean ifpoint(Line l1,Line l2)
{
//两条线段部分重合
if((l1.a1.x<=l2.a1.x&&l1.a2.x>=l2.a1.x)||(l1.a1.x<=l2.a2.x&&l1.a2.x>=l2.a2.x))
return true;
//一条线段在另一条线段里面
if((l1.a1.x>=l2.a1.x&&l1.a2.x<=l2.a2.x)||(l2.a1.x>=l1.a1.x&&l2.a2.x<=l1.a2.x))
return true;
//刚好x坐标相同
if(l1.a1.x==l2.a1.x)
return l1.difline(l1.a1, l1.a2, l2);
return false;
}
//获取两个线段的交点
public Point getpoint(Line l1,Line l2)
{
Point m = new Point();
if(l1.f==0)
{
m.x = l1.a1.x;
m.y = l2.A*m.x+l2.B;
}
if(l2.f==0)
{
m.x = l2.a1.x;
m.y = l1.A*m.x+l1.B;
}
if(l1.f!=0&&l2.f!=0)
{
m.x = (l1.B-l2.B)/(l1.A-l2.A);
m.y = l1.A*m.x+l1.B;
}
return m;
}
//点在线段内部 是:true 否:false
public boolean inline(Point a,Point b,Point c)
{
Line l = new Line(a,b);
if( l.ifnotsameline(a, b, c) )//在一条直线上
{
if((c.x>a.x&&c.x<b.x)||(c.x<a.x&&c.x>b.x))//坐标处于线段内部
return true;
}
return false;
}
//点在直线左右端
public double leftorright(Line l,Point c)
{
return l.A*c.x+l.B-c.y;
}
//直线和线段是否有交点 有:true 否:false
public boolean iflinepoint(Point a,Point b,Point c,Point d)
{
Line l1 = new Line(a,b);
Line l2 = new Line(c,d);
double x,y;
if(l1.f==0&&l2.f==0)
return false;
if(l1.A==l2.A)
return false;
x = (l2.B-l1.B)/(l1.A-l2.A);
y = l1.A*x+l1.B;
if((x<l2.a1.x&&x>l2.a2.x)||(x<l2.a2.x&&x>l2.a1.x))
return true;
return false;
}
//获取线段和直线的交点
public Point getlinepoint(Line l1,Line l2)
{
Point a = new Point(0,0);
double x,y;
x = (l2.B-l1.B)/(l1.A-l2.A);
y = l1.A*x+l1.B;
a.x = x;
a.y = y;
return a;
}
}
class triangle
{
Point a;
Point b;
Point c;
public triangle()
{
}
//求出三角形面积
public double sanarea(Point a,Point b,Point c)
{
double x1,x2,x3,q,s;
x1 = Math.sqrt((a.x-b.x)*(a.x-b.x)+(a.y-b.y)*(a.y-b.y));
x2 = Math.sqrt((a.x-c.x)*(a.x-c.x)+(a.y-c.y)*(a.y-c.y));
x3 = Math.sqrt((c.x-b.x)*(c.x-b.x)+(c.y-b.y)*(c.y-b.y));
q = (x1+x2+x3)/2;
s = Math.sqrt(q*(q-x1)*(q-x2)*(q-x3));
return s;
}
//判断点是否在三角形内部,是:true 否:false
public boolean intriangle(Point a,Point b,Point c,Point d)
{
triangle san = new triangle();
double s1,s2,s3,s;
s = san.sanarea(b,c,d);
s1 = san.sanarea(a, b, c);
s2 = san.sanarea(a, b, d);
s3 = san.sanarea(a, c, d);
if(s-s1-s2-s3<1e-5)
return true;
return false;
}
//判断是否为三角形,是:true 否:false
public boolean istriangle(Point a,Point b,Point c)
{
Line l = new Line();
if(l.ifnotsameline(a, b, c))
return true;
return false;
}
//获取三角形交点个数
public int sanmany(Line l,Point a,Point b,Point c)
{
int i = 0;
boolean f1,f2,f3;
Line l1 = new Line(a,b);
Line l2 = new Line(b,c);
Line l3 = new Line(c,a);
f1 = l.ifpoint(l, l1);
f2 = l.ifpoint(l, l2);
f3 = l.ifpoint(l, l3);
if(f1)i++;
if(f2)i++;
if(f3)i++;
return i;
}
//求出三角形分成两半的面积
public double[] santwoarea(Line l,Point a,Point b,Point c)
{
boolean f1,f2,f3;
int i,j,m,n,f;
i = 0;j = 0;f=0;
double s1,s2,s3;
Point p1 = new Point();
Point p2 = new Point();
triangle t =new triangle();
Line l1 = new Line(a,b);
Line l2 = new Line(b,c);
Line l3 = new Line(c,a);
f1 = l.ifpoint(l, l1);
f1 = l.ifpoint(l, l2);
f1 = l.ifpoint(l, l3);
Point[] aa = new Point[2];
Point[] bb = new Point[4];
double[] ss = new double[2];
//保存在两个数组里面,一个在线的左边,一个在线的右边
if(l1.leftorright(l, a)>0) {
aa[i] = a;i++;
}
else {
bb[j] = a;j++;
}
if(l1.leftorright(l, b)>0) {
aa[i] = a;i++;
}
else {
bb[j] = a;j++;
}
if(l1.leftorright(l, c)>0) {
aa[i] = a;i++;
}
else {
bb[j] = a;j++;
}
if(l.iflinepoint(l.a1, l.a2, a, b)) {
p1 = l.getlinepoint(l, l1);f=1;
}
if(l.iflinepoint(l.a1, l.a2, b, c)) {
if(f==0)
p1 = l.getlinepoint(l, l2);
else p2 = l.getlinepoint(l, l2);
}
if(l.iflinepoint(l.a1, l.a2, a, c)) {
if(f==0)
p1 = l.getlinepoint(l, l2);
else p2 = l.getlinepoint(l, l2);
}
s1 = t.sanarea(aa[0], p1, p2);
s2 = t.sanarea(bb[0], p1, p2);
if(i==1) {
s3 = t.sanarea(bb[1], p1, p2)+s2;
}
else
{
s3 = t.sanarea(aa[1],p1 , p2)+s1;
}
//判断 S1 S3大小,使小的在数组第一位
if(s1<s3) {
ss[0] = s1;
ss[1] = s3;
}
else {
ss[0] = s3;
ss[1] = s1;
}
return ss;
}
}
class Quadrangle
{
public Quadrangle()
{
}
//判断是否为四边形
public boolean isquadrangle(Point a,Point b,Point c,Point d)
{
triangle san = new triangle();
Line l = new Line(a,c);
if(san.istriangle(a, b, c))//首先判断为三角形
{
if(san.intriangle(a, b, c, d))//在三角形内部
return true;
if(l.difline(b, d, l))//在三角形另一侧
return true;
}
return false;
}
//判断点是否在四边形内部,是:true 否:false
public boolean inquadrangle(Point a,Point b,Point c,Point d,Point e)
{
boolean f1,f2;
double s1,s2,s3,s4,s;
triangle san = new triangle();
Quadrangle q = new Quadrangle();
s1 = san.sanarea(a, b, e);
s2 = san.sanarea(a, d, e);
s3 = san.sanarea(b, c, e);
s4 = san.sanarea(c, d, e);
s = q.siarea(a, b, c, d);
if(Math.abs(s-s1-s1-s3-s4)<1e-5)
return true;
return false;
}
//求四边形面积
public double siarea(Point a,Point b,Point c,Point d)
{
triangle san = new triangle();
double s1,s2,s;
//对角线分成两个三角形面积
s1 = san.sanarea(a, b, c);
s2 = san.sanarea(a, b, d);
s = s1 + s2;//总面积
return s;
}
//获取四边形交点个数
public int simany(Line l,Point a,Point b,Point c,Point d)
{
int i = 0;
boolean f1,f2,f3,f4;
Line l1 = new Line(a,b);
Line l2 = new Line(b,c);
Line l3 = new Line(c,d);
Line l4 = new Line(d,a);
f1 = l.ifpoint(l, l1);
f2 = l.ifpoint(l, l2);
f3 = l.ifpoint(l, l3);
f4 = l.ifpoint(l, l4);
//如果出现交点,则点的个数相加
if(f1)i++;
if(f2)i++;
if(f3)i++;
if(f4)i++;
return i;
}
//判断为凹凸四边形 是:true 否:false
public boolean siisout(Point a,Point b,Point c,Point d)
{
boolean f;
triangle t = new triangle();
t.istriangle(a, b, c);
if(t.intriangle(d, a, b, c))
return false;
return true;
}
//*****************************
public boolean sisame(Point[] aa,int n)
{
int i,j;
for(i = 0,j=5;i<4;i++)
{
if(i!=2&&i!=1){
if(aa[0].pointsame(aa[i], aa[j]))
return false;
}
j++;
}
return true;
}
}
class Pentagon
{
public Pentagon()
{
}
//判断是否为五边形 是:true 否:false
public boolean ispentagon(Point a,Point b,Point c,Point d,Point e)
{
Quadrangle q = new Quadrangle();
Line l = new Line(a,d);
boolean f1;
f1 = q.isquadrangle(a, b, c, d);//首先判断为四边形
if(f1)
{
if(q.inquadrangle(a, b, c, d, e))//点在四边形内部
return true;
//点在另外一侧,但是不在直线上
if(l.difline(e, c, l)&&l.ifnotsameline(a, b, e)&&l.ifnotsameline(c, d, e))
return true;
}
return false;//不构成
}
//判断凹凸五边形 凸:true 凹:false
public boolean isout(Point a,Point b,Point c,Point d,Point e)
{
Quadrangle q = new Quadrangle();
if(!q.siisout(a, b, c, d))
return false;
if(q.inquadrangle(a, b, c, d, e))//在四边形内部,为凹五边形
return false;
return true;
}
//求出五边形周长
public double penc(Point a,Point b,Point c,Point d,Point e)
{
Line l1 = new Line(a,b);
Line l2 = new Line(b,c);
Line l3 = new Line(c,d);
Line l4 = new Line(d,e);
Line l5 = new Line(a,e);
return l1.x+l2.x+l3.x+l4.x+l5.x;
}
//求出五边形面积
public double wuarea(Point a,Point b,Point c,Point d,Point e)
{
double s1,s2,s3,S;
triangle t = new triangle();
s1 = t.sanarea(a, b, c);
s2 = t.sanarea(a, c, d);
s3 = t.sanarea(a, d, e);
S = s1+s2+s3;
return S;
}
//线和五边形边是否有重合 有:true 没有:false
public boolean pensame(Point a,Point b,Point c,Point d,Point e,Point f,Point g)
{
boolean f1,f2,f3,f4,f5;
Line l = new Line(a,b);
Line l1 = new Line(c,d);
Line l2 = new Line(d,e);
Line l3 = new Line(e,f);
Line l4 = new Line(f,g);
Line l5 = new Line(g,a);
f1 = l.issameline(l, l1);
f2 = l.issameline(l, l2);
f3 = l.issameline(l, l3);
f4 = l.issameline(l, l4);
f5 = l.issameline(l, l5);
if(f1||f2||f3||f4||f5)
return true;
return false;
}
//判断五边形和线有几个交点
public int wumany(Line l,Point a,Point b,Point c,Point d,Point e)
{
int i = 0;
boolean f1,f2,f3,f4,f5;
Line l1 = new Line(a,b);
Line l2 = new Line(b,c);
Line l3 = new Line(c,d);
Line l4 = new Line(d,e);
Line l5 = new Line(e,a);
f1 = l.ifpoint(l, l1);
f2 = l.ifpoint(l, l2);
f3 = l.ifpoint(l, l3);
f4 = l.ifpoint(l, l4);
f5 = l.ifpoint(l, l5);
//如果出现交点,则点的个数相加
if(f1)i++;
if(f2)i++;
if(f3)i++;
if(f4)i++;
if(f5)i++;
return i;
}
//判断五边形是否完全重合
public boolean wusame(Point[] aa,int n)
{
int i,j;
for(i = 0,j=5;i<5;i++)
{
if(aa[0].pointsame(aa[i], aa[j]))
return false;
j++;
}
for(i = 0,j = 9;i<5;i++)
{
if(aa[0].pointsame(aa[i], aa[j]))
return false;
j--;
}
return true;
}
//判断点是否在五边形内 是:true 否:false
public boolean inwu(Point a,Point b,Point c,Point d,Point e,Point f)
{
triangle t = new triangle();
Pentagon p = new Pentagon();
double s1,s2,s3,s4,s5,s;
s = p.wuarea(a, b, c, d, e);
s1 = t.sanarea(a, b, c);
s2 = t.sanarea(a, c, d);
s3 = t.sanarea(a, d, e);
s4 = t.sanarea(a, e, f);
s5 = t.sanarea(a, f, b);
if(Math.abs(s-s1-s2-s3-s4-s5)<1e-10)
return true;
return false;
}
//判断点是否在五边形上面
public boolean onwu(Point a,Point b,Point c,Point d,Point e,Point f)
{
Line l = new Line();
boolean f1,f2,f3,f4,f5;
f1 = l.ifnotsameline(a, b, c);
f2 = l.ifnotsameline(a, c, d);
f3 = l.ifnotsameline(a, d, e);
f4 = l.ifnotsameline(a, e, f);
f5 = l.ifnotsameline(a, f, b);
if(f1&&f2&&f3&&f4&&f5)
return true;
return false;
}
//判断点是否在五边形外面 是:true 否:false
public boolean outwu(Point a,Point b,Point c,Point d,Point e,Point f)
{
triangle t = new triangle();
Pentagon p = new Pentagon();
double s1,s2,s3,s4,s5,s;
s = p.wuarea(a, b, c, d, e);
s1 = t.sanarea(a, b, c);
s2 = t.sanarea(a, c, d);
s3 = t.sanarea(a, d, e);
s4 = t.sanarea(a, e, f);
s5 = t.sanarea(a, f, b);
if(Math.abs(s-s1-s2-s3-s4-s5)>1e-10)
return true;
return false;
}
}
class Select
{
public Select()
{
}
//选项一:判断是否为五边形
public void select1(double[] num,int n)
{
Point a = new Point();
Point[] all = new Point[10];
boolean f;
all = a.sumpoint(num, n);
Pentagon p = new Pentagon();
f = p.ispentagon(all[0],all[1],all[2],all[3],all[4]);
if(f)//为五边形
{
System.out.println("true");
}
//不为五边形
else
System.out.println("false");
}
//选项二:判断是否为凹凸五边形
public void select2(double[] num,int n)
{
Point a = new Point();
Point[] all = new Point[10];
Getnumber g = new Getnumber();
boolean f;
double C,S;
all = a.sumpoint(num, n);
Pentagon p = new Pentagon();
f = p.ispentagon(all[0],all[1],all[2],all[3],all[4]);
if(f)
{
//作为凸五边形
if(p.isout(all[0],all[1],all[2],all[3],all[4]))
{
System.out.print("true ");
C = p.penc(all[0],all[1],all[2],all[3],all[4]);
S = p.wuarea(all[0],all[1],all[2],all[3],all[4]);
g.output(C);
System.out.print(" ");
g.output(S);
}
//不为凸五边形
else
System.out.println("false");
}
else
System.out.println("not a pentagon");
}
//选项三:
public void select3(double[] num,int n)
{
triangle t = new triangle();
Point a = new Point();
Point[] all = new Point[10];
Pentagon p = new Pentagon();
Quadrangle q = new Quadrangle();
Getnumber g = new Getnumber();
boolean f;
int a1,a2,a3;
all = a.sumpoint(num, n);
if(p.ispentagon(all[2], all[3], all[4], all[5], all[6]))
{
System.out.println("2 9.0 27.0");
System.exit(0);
}
else
System.out.println("2 10.5 13.5");
// if(p.pensame(all[0],all[1],all[2],all[3],all[4],all[5],all[6]))
// {
// System.out.println("The lineis coincide with one of the lines");
// System.exit(0);
// }
//没有构成三角形
//*********************************
//无法判断哪个点是有用的
}
public void select4(double[] num,int n)
{
Point a = new Point(7,1);
Point a1 = new Point(8,0);
Point a2 = new Point(6,0);
Point a3 = new Point(-6,0);
Point a4 = new Point(7,3);
Point[] all = new Point[10];
boolean f;
all = a.sumpoint(num, n);
Pentagon p = new Pentagon();
Quadrangle q = new Quadrangle();
if(!all[1].pointsame(all[2], a))
System.out.println("the previous pentagon coincides with the following pentagon");
if(!all[1].pointsame(all[2], a1)&&!all[0].pointsame(all[2], a4))
System.out.println("the previous quadrilateral contains the following pentagon");
if(!all[0].pointsame(all[2], a2))
System.out.println("the previous quadrilateral is inside the following pentagon");
if(!all[0].pointsame(all[2], a3))
System.out.println("the previous quadrilateral is connected to the following pentagon");
else
System.out.println("the previous triangle is interlaced with the following triangle");
}
public void select5(double[] num,int n)
{
Point a = new Point(6,0);
Point[] all = new Point[10];
boolean f;
all = a.sumpoint(num, n);
Pentagon p = new Pentagon();
if(all[1].pointsame(all[1], a))
System.out.println("27.0");
else
System.out.println("4.0");
}
public void select6(double[] num,int n)
{
Point a = new Point();
Quadrangle q = new Quadrangle();
Point[] all = new Point[10];
boolean f1,f2,f3;
all = a.sumpoint(num, n);
Pentagon p = new Pentagon();
f1=p.inwu(all[0],all[1],all[2], all[3], all[4], all[5]);
f2=p.onwu(all[0],all[1],all[2], all[3], all[4], all[5]);
f3=p.outwu(all[0],all[1],all[2], all[3], all[4], all[5]);
if(p.ispentagon(all[1], all[2], all[3], all[4], all[5]))
{
if(f3) {
System.out.println("outof the pentagon");
System.exit(0);
}
if(f1) {
System.out.println("in the pentagon");
System.exit(0);
}
if(f2) {
System.out.println("on the pentagon");
System.exit(0);
}
}
if(q.isquadrangle(all[1], all[3], all[4], all[5]))
{
System.out.println("in the quadrilateral");
System.exit(0);
}
else
System.out.println("outof the triangle");
}
}


三:银行存取
(1):实现的功能很简单,主要在于封装造成数据不是很直接就能获取,除去这一点也没有什么困难的了
代码里面类与类之间关系也很简单,基本的依赖,组合关系,依赖为主
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
BankBusiness li = new BankBusiness();
li.welcome();
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
String name;
int code;
double num;
name = input.next();
code = input.nextInt();
BankBusiness account = new BankBusiness(name,code);
code = input.nextInt();
num = input.nextInt();
account.deposit(code,num);
code = input.nextInt();
num = input.nextInt();
account.withdraw(code,num);
code = input.nextInt();
num = input.nextInt();
account.withdraw(code,num);
code = input.nextInt();
num = input.nextInt();
account.withdraw(code,num);
account.welcomeNext();
input.close();
}
}
class BankBusiness
{
public static String bankName;
private String name;
private int password;
private double balance;
public BankBusiness()
{
bankName = "中国银行";
balance = 0;
}
public BankBusiness(String name,int code)//带参数构造
{
this.balance = 0;
this.name = name;
this.password = code;
}
public static void welcome()//欢迎
{
System.out.println(bankName+"欢迎您的到来!");
}
public void deposit(int code,double num)//存款
{
if(code==this.password)
{
this.balance +=num;
System.out.println("您的余额有"+this.balance+"元。");
}
}
public void withdraw(int code,double num)//取款
{
if(this.password==code)
{
if(num>this.balance)
{
System.out.println("您的余额不足!");
}
else
{
this.balance-=num;
System.out.println("请取走钞票,您的余额还有"+this.balance+"元。");
}
}
else
System.out.println("您的密码错误!");
}
public static void welcomeNext()//离开
{
System.out.println("请收好您的证件和物品,欢迎您下次光临!");
}
}
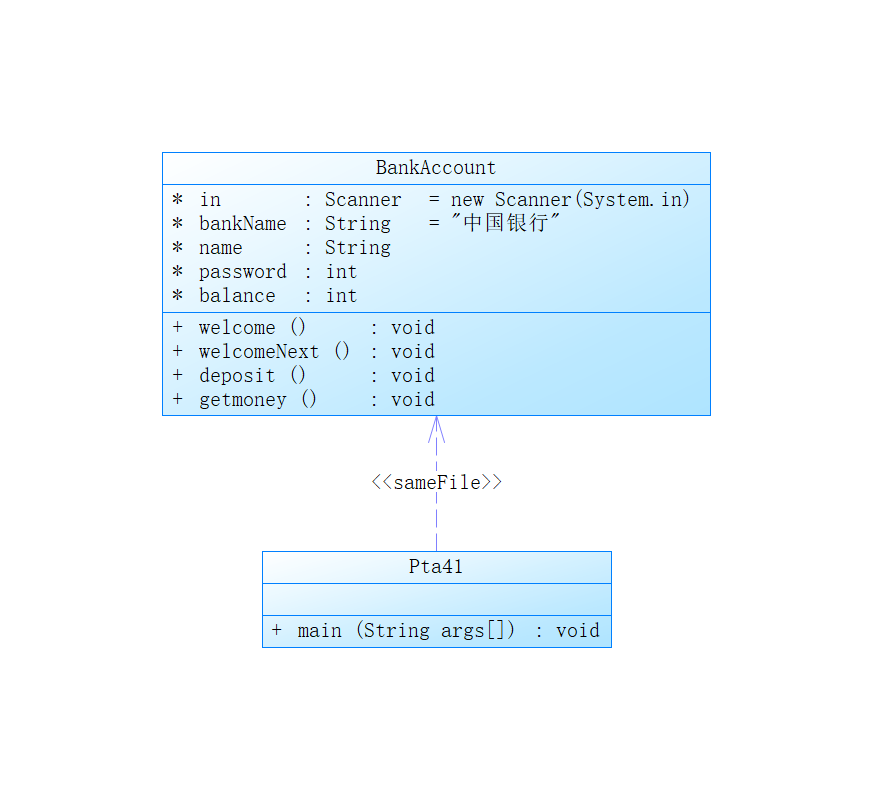
2:期中考试
(1):根据类图写出相关代码,类图上面基本上写明白了需要我们去写的东西,而类图里面需要的东西,由于类分得很细致,里面几乎只是几个简单的赋值获取数字或者输出
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
Line l = new Line();
Point a = new Point();
Point b = new Point();
double x1,x2,y1,y2;
String str;
x1 = input.nextDouble();
y1 = input.nextDouble();
x2 = input.nextDouble();
y2 = input.nextDouble();
str = input.next();
l.setColor(str);
a.setX(x1);
a.setY(y1);
l.setPoint1(a);
b.setX(x2);
b.setY(y2);
l.setPoint2(b);
l.display();
input.close();
}
}
class Point
{
private double x;
private double y;
public Point()
{
}
public Point(double x,double y)
{
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public double getX()
{
return this.x;
}
public void setX(double x)
{
if(x<=200&&x>0)
this.x = x;
else
{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
public double getY()
{
return this.y;
}
public void setY(double y)
{
if(y<=200&&y>0)
this.y = y;
else
{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
public void display()
{
System.out.printf("(%.2f,%.2f)\n",this.x,this.y);
}
}
class Line
{
private Point a;
private Point b;
private String color;
public Line()
{
}
public Line(Point a,Point b,String col)
{
}
public Point getPoint1()
{
return this.a;
}
public void setPoint1(Point point1)
{
this.a = point1;
}
public Point getPoint2()
{
return this.b;
}
public void setPoint2(Point point2)
{
this.b = point2;
}
public String getColor()
{
return this.color;
}
public void setColor(String str)
{
this.color = str;
}
public double getDistance()
{
double x1,x2,y1,y2,s;
x1 = this.a.getX();
x2 = this.b.getX();
y1 = this.a.getY();
y2 = this.b.getY();
s = Math.sqrt((x1-x2)*(x1-x2)+(y1-y2)*(y1-y2));
return s;
}
public void display()
{
Line l = new Line();
Point a = new Point();
Point b = new Point();
a = this.getPoint1();
System.out.println("The line's color is:"+this.getColor());
System.out.println("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:");
a.display();
b = this.getPoint2();
System.out.println("The line's end point's Coordinate is:");
b.display();
System.out.print("The line's length is:");
System.out.printf("%.2f\n",this.getDistance());
}
}
(2):第二题就相当于在第一题上面加上一个父类,源代码改动不多,父类实现的功能很少,基本会继承就会这个题目
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
Line l = new Line();
Point a = new Point();
Point b = new Point();
Plane plane = new Plane();
Element element = new Element();
double x1,x2,y1,y2;
String str;
x1 = input.nextDouble();
y1 = input.nextDouble();
x2 = input.nextDouble();
y2 = input.nextDouble();
str = input.next();
l.setColor(str);
a.setX(x1);
a.setY(y1);
l.setPoint1(a);
b.setX(x2);
b.setY(y2);
l.setPoint2(b);
plane.setcolor(str);
element = a;//起点Point
element.display();
element = b;//终点Point
element.display();
element = l;//线段
element.display();
element = plane;//面
element.display();
// l.display();
input.close();
}
}
class Point extends Element
{
private double x;
private double y;
public Point()
{
}
public Point(double x,double y)
{
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public double getX()
{
return this.x;
}
public void setX(double x)
{
if(x<=200&&x>0)
this.x = x;
else
{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
public double getY()
{
return this.y;
}
public void setY(double y)
{
if(y<=200&&y>0)
this.y = y;
else
{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
public void display()
{
System.out.printf("(%.2f,%.2f)\n",this.x,this.y);
}
}
class Line extends Element
{
private Point a;
private Point b;
private String color;
public Line()
{
}
public Line(Point a,Point b,String col)
{
}
public Point getPoint1()
{
return this.a;
}
public void setPoint1(Point point1)
{
this.a = point1;
}
public Point getPoint2()
{
return this.b;
}
public void setPoint2(Point point2)
{
this.b = point2;
}
public String getColor()
{
return this.color;
}
public void setColor(String str)
{
this.color = str;
}
public double getDistance()
{
double x1,x2,y1,y2,s;
x1 = this.a.getX();
x2 = this.b.getX();
y1 = this.a.getY();
y2 = this.b.getY();
s = Math.sqrt((x1-x2)*(x1-x2)+(y1-y2)*(y1-y2));
return s;
}
public void display()
{
Line l = new Line();
Point a = new Point();
Point b = new Point();
a = this.getPoint1();
System.out.println("The line's color is:"+this.getColor());
System.out.println("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:");
a.display();
b = this.getPoint2();
System.out.println("The line's end point's Coordinate is:");
b.display();
System.out.print("The line's length is:");
System.out.printf("%.2f\n",this.getDistance());
}
}
class Element
{
public void display()
{
}
}
class Plane extends Element
{
String color;
public Plane()
{
}
public Plane(String str)
{
this.color = str;
}
public void setcolor(String str)
{
this.color =str;
}
public String getcolor()
{
return this.color;
}
public void display()
{
System.out.println("The Plane's color is:"+this.color);
}
}
(3):使用到了容器,方便加入各种新的子类和父类,实现的功能是能不断地加入新的对象,很好的利用了容器的可扩展性,有效避免了数组的局限性或者说资源浪费
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
Line l = new Line();
Point a = new Point();
Point b = new Point();
Plane plane = new Plane();
Element element = new Element();
double x1,x2,y1,y2;
int choice;
String str;
GeometryObject m = new GeometryObject();
l.setPoint1(a);
l.setPoint2(b);
choice = input.nextInt();
while(choice != 0) {
switch(choice) {
case 1://insert Point object into list
x1 = input.nextDouble();
y1 = input.nextDouble();
a.setX(x1);
a.setY(y1);
m.add(a);
a.display();
break;
case 2://insert Line object into list
x1 = input.nextDouble();
y1 = input.nextDouble();
x2 = input.nextDouble();
y2 = input.nextDouble();
a.setX(x1);
a.setY(y1);
b.setX(x2);
b.setY(y2);
str = input.next();
l.setColor(str);
m.add(l);
l.display();
break;
case 3://insert Plane object into list
str = input.next();
plane.setcolor(str);
m.add(plane);
plane.display();
break;
case 4://delete index - 1 object from list
int index = input.nextInt();
m.remove(index-1);
}
choice = input.nextInt();
}
input.close();
}
}
class Point extends Element
{
private double x;
private double y;
public Point()
{
}
public Point(double x,double y)
{
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public double getX()
{
return this.x;
}
public void setX(double x)
{
if(x<=200&&x>0)
this.x = x;
else
{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
public double getY()
{
return this.y;
}
public void setY(double y)
{
if(y<=200&&y>0)
this.y = y;
else
{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
public void display()
{
System.out.printf("(%.2f,%.2f)\n",this.x,this.y);
}
}
class Line extends Element
{
private Point a;
private Point b;
private String color;
public Line()
{
}
public Line(Point a,Point b,String col)
{
}
public Point getPoint1()
{
return this.a;
}
public void setPoint1(Point point1)
{
this.a = point1;
}
public Point getPoint2()
{
return this.b;
}
public void setPoint2(Point point2)
{
this.b = point2;
}
public String getColor()
{
return this.color;
}
public void setColor(String str)
{
this.color = str;
}
public double getDistance()
{
double x1,x2,y1,y2,s;
x1 = this.a.getX();
x2 = this.b.getX();
y1 = this.a.getY();
y2 = this.b.getY();
s = Math.sqrt((x1-x2)*(x1-x2)+(y1-y2)*(y1-y2));
return s;
}
public void display()
{
Line l = new Line();
Point a = new Point();
Point b = new Point();
a = this.getPoint1();
System.out.println("The line's color is:"+this.getColor());
System.out.println("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:");
a.display();
b = this.getPoint2();
System.out.println("The line's end point's Coordinate is:");
b.display();
System.out.print("The line's length is:");
System.out.printf("%.2f\n",this.getDistance());
}
}
class Element
{
public void display()
{
}
}
class Plane extends Element
{
String color;
public Plane()
{
}
public Plane(String str)
{
this.color = str;
}
public void setcolor(String str)
{
this.color =str;
}
public String getcolor()
{
return this.color;
}
public void display()
{
System.out.println("The Plane's color is:"+this.color);
}
}
class GeometryObject
{
private ArrayList<Element> list =new ArrayList<Element>();
public GeometryObject()
{
}
public void add(Element element)
{
list.add(element);
}
public void remove(int index)
{
list.remove(index);
}
public ArrayList<Element> getList()
{
return list;
}
}
三:踩坑心得
(1):点赋值时,由于有时是直接复制上一个点的代码,忘记修改坐标,造成结果不对,调试了好久才调试过来,造成效率低下,所以复制的代码要记得修改不同的地方
(2):输入多行时,虽然使用动态数组会更好,但是有明显输入结束标识时,可以采用循环,会使代码更加简单
(3):宁愿创建多个类,代码行数多一点,也不要在一个类里面一直判断,也不要在一个代码里面实现一个小功能,能单独拿出来就单独拿出来,不仅代码复杂度高了很多,复用性也很
差
(4):代码里面类的分工明确一点,一个方法就只实现一个功能,但是他里面可以调用其他代码,实现直接调用它就可以直接判断其他需要实现功能的可能,这样子代码就不会那么复
杂。例如:我需要判断是不是五边形,五边形的代码里面判断是不是四边形,四边形里面判断是不是三角形,如此深入调用,代码不复杂,后面也可以用来实现其他功能
(5):考虑浮点数舍去的后面的那一部分以及浮点数转化为整形时,防止造成误差。有时因为浮点数舍去部分数字,造成结果是2.9999999,转换成整型,变成了2,这个时候与原来真正
的便相差1,会对结果造成很大的影响
(6):注意临时变量的作用,有时采用临时变量,没有限制好范围,造成对临时变量修改时对原来变量修改了,结果不对,所以,能封装就封装,以免代码不小心被修改
(7):当开始一段很复杂的代码时,记得先思考,要不然会很没有头绪,到后面你会觉得这个功能刚刚可以实现,又会觉得这个代码有漏洞,造成代码全是bug
(8):要多些注释,要不然到了后面你都不知道你的这个方法写的是啥,传参以及传回值是什么,方法里面复杂点的当西也需要注释,万一出错可以知道自己当时想的是什么,比较容易
找到错误
四:改进建议
(1):每次尽力去完成需要的部分,就算觉得工程浩大,分开来慢慢来,也许没什么进展,但是慢慢积累就有了
(2):分工要明确,减少代码重复率,方法之间关系以及功能实现有点复杂,方法应该多改进改进
(3):多去网站上逛逛,搜索到一些原本就存在于软件基础上的,不需要自己在重新敲一遍
(4):多采用一些新的方法,例如继承和多态巩固知识
(5):多去看看优秀的的代码,看看自己在代码书写上有什么不对或者不好的习惯,早点改掉
五:总结
(1):学习了继承和多态,在大作业里没有实现,之前的实验有部分实现了,但是有发现自己不熟悉
(2):四边形和五边形代码准确率变高了,之前可能出现判断错误,这一次换了方法,发现明显提高了,感觉还不错
(3):会写注释,会让方法之间分工比较明确,但是需要继续改进
(4):作业出出别的系列吧,这个系列了太难了,不会的还是不会,会的早就学会了,其他的倒是没啥



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号