2022年下学期面向对象程序设计学习总结(二)
一、 前言
(1)部分学习总结:
-
正则表达式
截至目前作业中所涉及到的正则表达式只是一些对于字符串文、本本的处理。
在正则表达式中,我们引入了\的运用(\\ 表示:我要插入一个正则表达式的反斜线,所以其后的字符具有特殊的意义。)在 Java 的正则表达式中,两个 \\ 中第一个\是作为转义标志,后一个代表其他语言中的一个 \,这也就是为什么表示一位数字的正则表达式是 \\d,而表示一个普通的反斜杠是 \\。
System.out.print("\\"); // 输出为 \
System.out.print("\\\\"); // 输出为 \\在正则表达式的学习中,我并没有对java.util.regex 包中的三种类(主要包括以下三个类:Pattern 类:pattern 对象是一个正则表达式的编译表示。Pattern 类没有公共构造方法。要创建一个 Pattern 对象,你必须首先调用其公共静态编译方法,它返回一个 Pattern 对象。该方法接受一个正则表达式作为它的第一个参数。Matcher 类:Matcher 对象是对输入字符串进行解释和匹配操作的引擎。与Pattern 类一样,Matcher 也没有公共构造方法。你需要调用 Pattern 对象的 matcher 方法来获得一个 Matcher 对象。PatternSyntaxException:PatternSyntaxException 是一个非强制异常类,它表示一个正则表达式模式中的语法错误。)进行过多的了解,当前知识层面停留在用变量regex来接受一个正则表达式序列,然后再引入matches匹配一整个需求序列。
正则表达式中还需注意是单个字符匹配原则,在[]中出现的条件只是对一个字符的匹配,不存在对于截取字符串的匹配,用一段字符串的匹配可以用lookingAt去验证一段序列是否是原序列的子序列。
- HashMap
HashMap 是一个散列表,它存储的内容是键值对(key-value)映射。
它的使用是建立在我们import java.util.HashMap;这么一个HashMap类的基础之上的。
其实我觉得形似于python中的字典(Dictionary),同样是可变容器,但是对于弱类型语言python可存储任意类型对象,而在创建一个 HashMap 对象时,我们需要对key和value进行类型的限定例如:
HashMap<Integer, Integer> example = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();- HashSet
HashSet 基于 HashMap 来实现的,很多东西都和HashMap有着一定的相似性。
Set顾名思义就是集合,然后已知集合是不允许有重复元素的无需的,所以HashSet其实就是一个不允许有重复元素的无序的集合。
HashSet 允许有 null 值。
- Lambda表达式
一种函数式的编程思想。
Lambda表达式格式:()->{}
1.小括号中书写的内容和接口中的抽象方法的参数列表一致
2.大括号中书写的内容和实现接口中的抽象方法体一致
3.箭头是固定的
使用条件:1.要存在接口2.有且只有一个接口
- stream
stream() 为集合创建串行流。
| 方法名称 | 方法作用 |
| count | 统计个数 |
| forEach | 逐一处理 |
| filter | 过滤元素 |
| limit | 取用前几个 |
| skip | 跳过前几个 |
| map | 映射每一个元素的结果 |
- JavaFx
是Java中一种可视化设计工具,暂时只学会了创建一个窗口、画一下基本的图形、绘制一个按钮的图标,无法对按钮进行实际的赋予功能。
(2)题量与难度:
|
周数 |
题量 |
难度 |
|
第六周 |
5 |
··· |
|
第七周 |
3 |
······ |
二、设计与分析
PTA:第六周:
踩坑心得:
1、其实在书写代码的过程中要非常注意“ ”双引号中空格的出现,因为这很有可能导致你匹配时无法return正确的布尔值。
2、正则表达式中存在一一对应关系,要注意匹配时的书写。
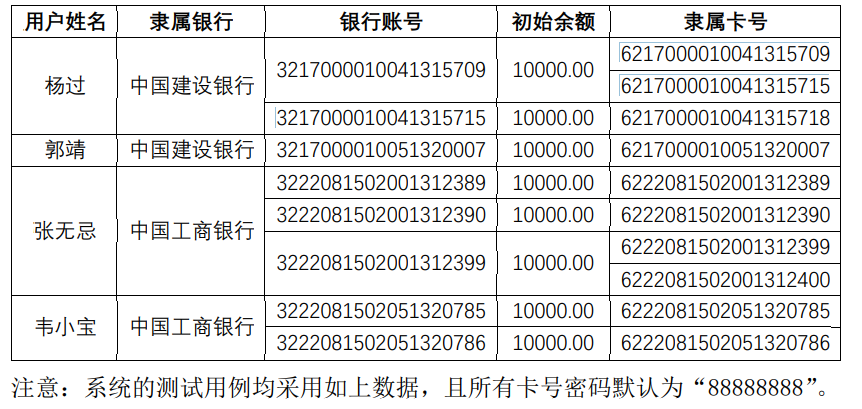
7-5 ATM机类结构设计(一)
设计思路:
根据图中所给我将账户、余额、隶属银行、用户姓名作为账户类属性,再将卡号、账户作为属性归于card类。尝试使用面向对象技术对银行用户在 ATM 机上进行相关操作的模拟系统设
计。
不足点:我将账户和卡号的创建直接写于一个类中,无法正常添加账户或者卡号,代码复用性很弱。
代码如下
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Play play = new Play();
play.inputSome();
}
}
class Play {
private Creat creat = new Creat();
private ATMGUI atmgui = new ATMGUI();
private ATM atm = new ATM();
Play(){}
public void inputSome() {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
String row = in.nextLine();
while (!row.substring(0,1).equals("#")){
if (row.length() == 19){
int index = find(row);
if (index < 0) {
System.out.println("Sorry,this card does not exist.");
System.exit(0);
} else {
atmgui.search(creat.getCards().get(index).getAccount());
}
} else if (row.length() < 19) {
System.out.println("Sorry,this card does not exist.");
System.exit(0);
} else {
String[] deal = row.split("\\s+");
int index = find(deal[0]);
if (index < 0) {
System.out.println("Sorry,this card does not exist.");
System.exit(0);
} else {
if (validateCode(deal[2])) {
if (deal[1].equals(creat.getCards().get(index).getPassword())) {
double deposit = Double.parseDouble(deal[3]);
if (deposit > creat.getCards().get(index).getAccount().getDeposit()) {
System.out.println("Sorry,your account balance is insufficient.");
System.exit(0);
} else {
atm.depositAndWithdrawal(creat.getCards().get(index).getAccount(), deposit, deal[2]);
atmgui.depositAndWithdrawalGUI(creat.getCards().get(index), deposit, deal[2]);
}
} else {
System.out.println("Sorry,your password is wrong.");
System.exit(0);
}
} else {
System.out.println("Sorry,the ATM's id is wrong.");
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
row = in.nextLine();
}
if (row.substring(0,1).equals("#")) {
System.exit(0);
}
}
public int find(String row) {
for (int i = 0;i < creat.getCards().size();i++) {
if (row.equals(creat.getCards().get(i).getCardNum())) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
public boolean validateCode(String code) {
return code.equals("01") || code.equals("02") || code.equals("03") || code.equals("04")
|| code.equals("05") || code.equals("06");
}
}
class Creat {
private ArrayList<Card> cards =new ArrayList<Card>();
Creat() {
//已有账户
Account account1 = new Account("3217000010041315709", "杨过");
Account account2 = new Account("3217000010041315715", "杨过");
Account account3 = new Account("3217000010051320007", "郭靖");
Account account4 = new Account("3222081502001312389", "张无忌");
Account account5 = new Account("3222081502001312390", "张无忌");
Account account6 = new Account("3222081502001312399", "张无忌");
Account account7 = new Account("3222081502051320785", "张无忌");
Account account8 = new Account("3222081502051320786", "张无忌");
//已开户银行卡
Card card1 = new Card("6217000010041315709", "88888888", account1);
Card card2 = new Card("6217000010041315715", "88888888", account1);
Card card3 = new Card("6217000010041315718", "88888888", account2);
Card card4 = new Card("6217000010051320007", "88888888", account3);
Card card5 = new Card("6222081502001312389", "88888888", account4);
Card card6 = new Card("6222081502001312390", "88888888", account5);
Card card7 = new Card("6222081502001312399", "88888888", account6);
Card card8 = new Card("6222081502001312400", "88888888", account6);
Card card9 = new Card("6222081502051320785", "88888888", account7);
Card card10 = new Card("6222081502051320786", "88888888", account8);
cards.add(card1);
cards.add(card2);
cards.add(card3);
cards.add(card4);
cards.add(card5);
cards.add(card6);
cards.add(card7);
cards.add(card8);
cards.add(card9);
cards.add(card10);
}
public ArrayList<Card> getCards() {
return cards;
}
}
class Account {
private String account;
private String bank;
private double deposit;
private String owner;
private ArrayList<String> code = new ArrayList<String>();
Account() {
}
Account(String account, String owner) {
this.account = account;
deposit = 10000.00;
this.bank = judgeBank();
this.owner = owner;
judgeCode();
}
private void judgeCode() {
if (bank.equals("中国建设银行")) {
code.add("01");
code.add("02");
code.add("03");
code.add("04");
} else {
code.add("05");
code.add("06");
}
}
public String judgeBank(){
if (account.matches("[3][2][1][7][0][0][0][0][1][0][0]\\d{8}")) {
return "中国建设银行";
} else {
return "中国工商银行";
}
}
public ArrayList<String> getCode() {
return code;
}
public String getBank() {
return bank;
}
public void setBank(String bank) {
this.bank = bank;
}
public double getDeposit() {
return deposit;
}
public void setDeposit(double deposit) {
this.deposit = deposit;
}
public String getOwner() {
return owner;
}
public void setOwner(String owner) {
this.owner = owner;
}
}
class Card {
private String cardNum;
private String password;
private Account account;
Card() {}
Card(String cardNum, String password, Account account){
this.cardNum = cardNum;
this.password = password;
this.account = account;
}
public Account getAccount() {
return account;
}
public void setAccount(Account account) {
this.account = account;
}
public String getCardNum() {
return cardNum;
}
public void setCardNum(String cardNum) {
this.cardNum = cardNum;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
}
class ATM {
ATM() {}
public void depositAndWithdrawal(Account account, double deposit, String code) {
for (int i = 0;i < account.getCode().size();i++) {
String temp = account.getCode().get(i);
if (temp.equals(code)) {
account.setDeposit(account.getDeposit() - deposit);
return;
}
}
System.out.println("Sorry,cross-bank withdrawal is not supported.");
System.exit(0);
}
}
class ATMGUI {
ATMGUI() {}
public void search(Account account) {
System.out.printf("¥%.2f\n",account.getDeposit());
}
public void depositAndWithdrawalGUI(Card card, double deposit, String code) {
System.out.print(card.getAccount().getOwner() + "在" + card.getAccount().getBank());
if (deposit > 0) {
System.out.printf("的%s号ATM机上取款¥%.2f\n当前余额为¥%.2f\n", code, Math.abs(deposit), card.getAccount().getDeposit());
} else {
System.out.printf("的%s号ATM机上存款¥%.2f\n当前余额为¥%.2f\n", code, Math.abs(deposit), card.getAccount().getDeposit());
}
}
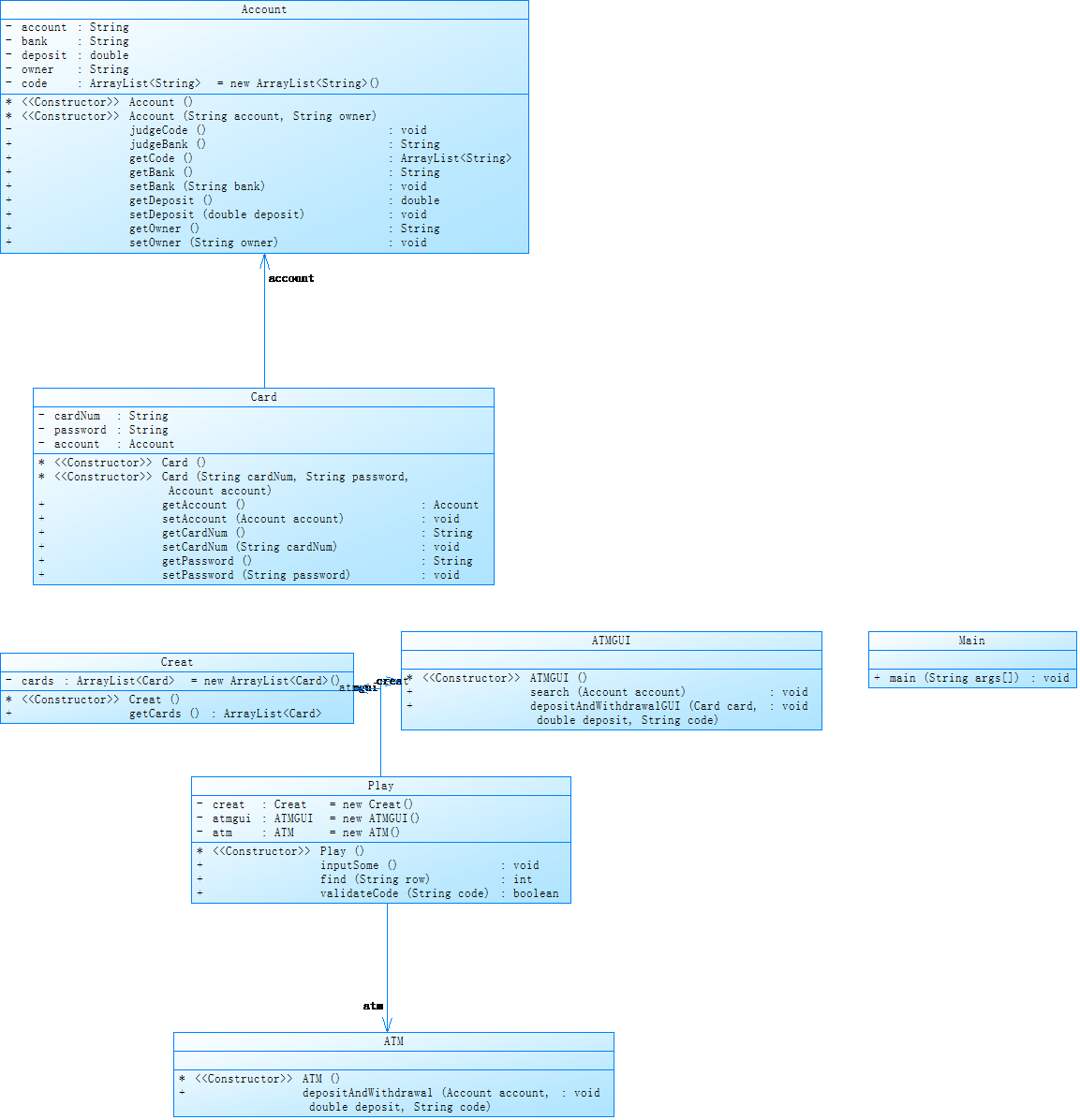
}类图:
复杂度:
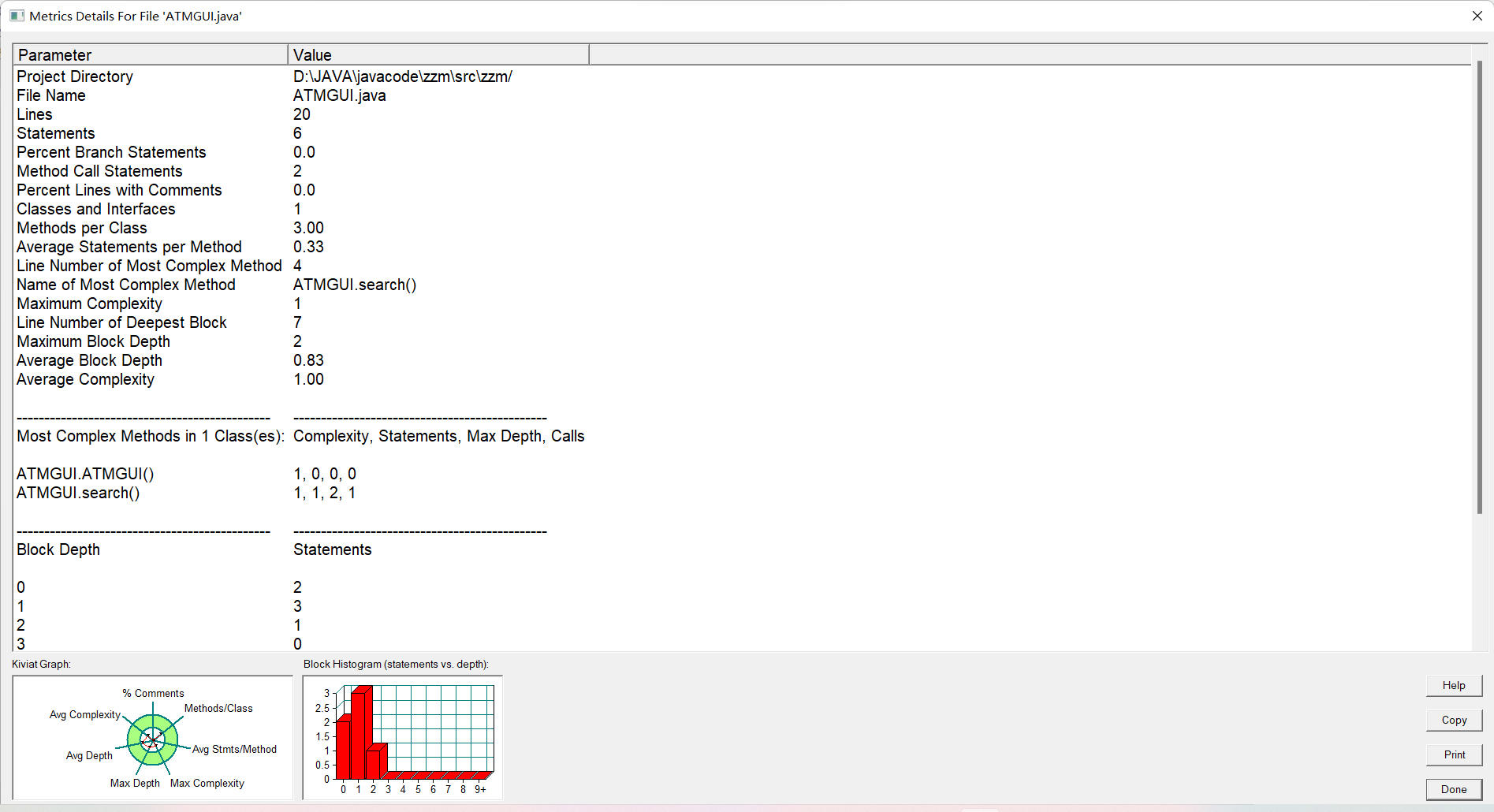
第七周:
以下四边形顶点的坐标要求按顺序依次输入,连续输入的两个顶点是相邻顶点,第一个和最后一个输入的顶点相邻。
选项包括:
1:输入四个点坐标,判断是否是四边形、平行四边形,判断结果输出true/false,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。
2:输入四个点坐标,判断是否是菱形、矩形、正方形,判断结果输出true/false,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。 若四个点坐标无法构成四边形,输出"not a quadrilateral"
3:输入四个点坐标,判断是凹四边形(false)还是凸四边形(true),输出四边形周长、面积,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。 若四个点坐标无法构成四边形,输出"not a quadrilateral"
4:输入六个点坐标,前两个点构成一条直线,后四个点构成一个四边形或三角形,输出直线与四边形(也可能是三角形)相交的交点数量。如果交点有两个,再按面积从小到大输出四边形(或三角形)被直线分割成两部分的面积(不换行)。若直线与四边形或三角形的一条边线重合,输出"The line is coincide with one of the lines"。若后四个点不符合四边形或三角形的输入,输出"not a quadrilateral or triangle"。
后四个点构成三角形的情况:假设三角形一条边上两个端点分别是x、y,边线中间有一点z,另一顶点s:
1)符合要求的输入:顶点重复或者z与xy都相邻,如x x y s、x z y s、x y x s、s x y y。此时去除冗余点,保留一个x、一个y。
2) 不符合要求的输入:z 不与xy都相邻,如z x y s、x z s y、x s z y
5:输入五个点坐标,输出第一个是否在后四个点所构成的四边形(限定为凸四边形,不考虑凹四边形)或三角形(判定方法见选项4)的内部(若是四边形输出in the quadrilateral/outof the quadrilateral,若是三角形输出in the triangle/outof the triangle)。如果点在多边形的某条边上,输出"on the triangle或者on the quadrilateral"。若后四个点不符合四边形或三角形,输出"not a quadrilateral or triangle"。
残缺代码如下
import java.awt.geom.Point2D;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.math.MathContext;
import java.math.RoundingMode;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
String row = in.nextLine();
if (!row.substring(row.length() - 1).equals(" ")) {
row = row + " ";
}
String[] co;
String regexL1 = "[1-3]\\:(([+-]?(([1-9]\\d*)|0)(\\.\\d+)*)[,]([+-]?(([1-9]\\d*)|0)(\\.\\d+)*)\\s){0,3}";
String regex1 = "[1-3]\\:(([+-]?(([1-9]\\d*)|0)(\\.\\d+)*)[,]([+-]?(([1-9]\\d*)|0)(\\.\\d+)*)\\s){4}";
String regexF1 = "[1-3]\\:(([+-]?(([1-9]\\d*)|0)(\\.\\d+)*)[,]([+-]?(([1-9]\\d*)|0)(\\.\\d+)*)\\s){5,}";
String regexL2 = "[4]\\:(([+-]?(([1-9]\\d*)|0)(\\.\\d+)*)[,]([+-]?(([1-9]\\d*)|0)(\\.\\d+)*)\\s){0,5}";
String regex2 = "[4]\\:(([+-]?(([1-9]\\d*)|0)(\\.\\d+)*)[,]([+-]?(([1-9]\\d*)|0)(\\.\\d+)*)\\s){6}";
String regexF2 = "[4]\\:(([+-]?(([1-9]\\d*)|0)(\\.\\d+)*)[,]([+-]?(([1-9]\\d*)|0)(\\.\\d+)*)\\s){7,}";
String regexL3 = "[5]\\:(([+-]?(([1-9]\\d*)|0)(\\.\\d+)*)[,]([+-]?(([1-9]\\d*)|0)(\\.\\d+)*)\\s){0,4}";
String regex3 = "[5]\\:(([+-]?(([1-9]\\d*)|0)(\\.\\d+)*)[,]([+-]?(([1-9]\\d*)|0)(\\.\\d+)*)\\s){5}";
String regexF3 = "[5]\\:(([+-]?(([1-9]\\d*)|0)(\\.\\d+)*)[,]([+-]?(([1-9]\\d*)|0)(\\.\\d+)*)\\s){6,}";
switch (row.substring(0, 1)) {
case "1":
if (row.matches(regex1)) {
co = row.substring(2).split("[\\s\\,\\:]");
ArrayList<BigDecimal> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (String i : co) {
list.add(new BigDecimal(i));
}
Choiceone choiceone = new Choiceone(list);
choiceone.showStatus();
} else if (row.matches(regexF1) || row.matches(regexL1)) {
System.out.println("wrong number of points");
System.exit(0);
} else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
break;
case "2":
if (row.matches(regex1)) {
co = row.substring(2).split("[\\s\\,\\:]");
ArrayList<BigDecimal> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (String i : co) {
list.add(new BigDecimal(i));
}
Choicetwo choicetwo = new Choicetwo(new Choiceone(list));
choicetwo.showStatus();
} else if (row.matches(regexF1) || row.matches(regexL1)) {
System.out.println("wrong number of points");
System.exit(0);
} else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
break;
case "3":
if (row.matches(regex1)) {
co = row.substring(2).split("[\\s\\,\\:]");
ArrayList<BigDecimal> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (String i : co) {
list.add(new BigDecimal(i));
}
Choicethree choicethree = new Choicethree(new Choiceone(list));
choicethree.showStatus();
} else if (row.matches(regexF1)) {
System.out.println("wrong number of points");
System.exit(0);
} else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
break;
case "4":if (row.matches(regex2)) {
co = row.substring(2).split("[\\s\\,\\:]");
double x1 = Double.parseDouble(co[1]);
double y1 = Double.parseDouble(co[2]);
double x2 = Double.parseDouble(co[3]);
double y2 = Double.parseDouble(co[4]);
if (x1 == x2 && y1 == y2) {
System.out.println("points coincide");
System.exit(0);
}
ArrayList<BigDecimal> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (String i : co) {
list.add(new BigDecimal(i));
}
list.remove(0);
list.remove(0);
list.remove(0);
list.remove(0);
Choiceone choiceone = new Choiceone(list);
Choicefour choicefour = new Choicefour();
choicefour.showStatus();
}else if (row.matches(regexF2) || row.matches(regexL2)) {
System.out.println("wrong number of points");
System.exit(0);
} else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}break;
case "5":if (row.matches(regex3)) {
co = row.substring(2).split("[\\s\\,\\:]");
double x1 = Double.parseDouble(co[1]);
double y1 = Double.parseDouble(co[2]);
ArrayList<BigDecimal> list0 = new ArrayList<>();
for (String i : co) {
list0.add(new BigDecimal(i));
}
list0.remove(0);
list0.remove(0);
Choiceone choiceone = new Choiceone(list0);
List<Point2D.Double> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new Point2D.Double(Double.parseDouble(co[2]), Double.parseDouble(co[3])));
list.add(new Point2D.Double(Double.parseDouble(co[4]), Double.parseDouble(co[5])));
list.add(new Point2D.Double(Double.parseDouble(co[6]), Double.parseDouble(co[7])));
list.add(new Point2D.Double(Double.parseDouble(co[8]), Double.parseDouble(co[9])));
Choicefive choicefive = new Choicefive(choiceone,list, new Point2D.Double(x1,y1));
choicefive.showStatus();
}else if (row.matches(regexF3) || row.matches(regexL3)) {
System.out.println("wrong number of points");
System.exit(0);
} else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}break;
default:
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
public static String round(double val) {
BigDecimal bigDecimal = new BigDecimal(val);
bigDecimal = bigDecimal.setScale(3, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP);
bigDecimal = bigDecimal.stripTrailingZeros();
String ret = bigDecimal.toPlainString();
if (!ret.contains(".")) {
ret += ".O";
}
return ret;
}
}
class Vector {
private BigDecimal x;
private BigDecimal y;
Vector() {}
Vector(BigDecimal x, BigDecimal y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public BigDecimal getX() {
return this.x;
}
public BigDecimal getY() {
return this.y;
}
public boolean judgeZero() {
return x.compareTo(BigDecimal.ZERO) == 0 && y.compareTo(BigDecimal.ZERO) == 0;
}
public double getLength() {
return Math.sqrt(Double.parseDouble(x.multiply(x).add(y.multiply(y)).toString()));
}
public boolean parallel(Vector vector) {
int temp = x.multiply(vector.getY()).compareTo(vector.getX().multiply(y));
return temp == 0;
}
public boolean judgeRightAngle(Vector vector) {
return x.multiply(vector.getX()).add(vector.getY().multiply(y)).compareTo(BigDecimal.ZERO) == 0;
}
}
//1:输入四个点坐标,判断是否是四边形、平行四边形,判断结果输出true/false,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。
class Choiceone {
private Vector[] vector = new Vector[6];
Choiceone() {
}
Choiceone(ArrayList<BigDecimal> list) {
vector[0] = new Vector(list.get(2).subtract(list.get(0)), list.get(3).subtract(list.get(0)));
vector[1] = new Vector(list.get(4).subtract(list.get(2)), list.get(5).subtract(list.get(3)));
vector[2] = new Vector(list.get(6).subtract(list.get(4)), list.get(7).subtract(list.get(5)));
vector[3] = new Vector(list.get(0).subtract(list.get(6)), list.get(1).subtract(list.get(7)));
vector[4] = new Vector(list.get(4).subtract(list.get(0)), list.get(5).subtract(list.get(1)));
vector[5] = new Vector(list.get(6).subtract(list.get(2)), list.get(7).subtract(list.get(3)));
}
public Vector[] getVector() {
return vector;
}
public void setVector(Vector[] vector) {
this.vector = vector;
}
public boolean judgeCoincide() {
return vector[0].judgeZero() || vector[1].judgeZero() || vector[2].judgeZero() || vector[3].judgeZero() || vector[4].judgeZero() || vector[5].judgeZero();
}
public boolean judgeParallel() {
return vector[0].parallel(vector[1]) || vector[1].parallel(vector[2]) || vector[2].parallel(vector[3]) || vector[3].parallel(vector[0]);
}
public boolean judgeQuadrangle() {
return !judgeCoincide() && !judgeParallel();
}
public boolean judgeParallelogram() {
return judgeQuadrangle() && vector[0].parallel(vector[2]) && vector[1].parallel(vector[3]);
}
public void showStatus() {
if (judgeCoincide()) {
System.out.println("points coincide");
} else {
System.out.println(judgeQuadrangle() + " " + judgeParallelogram());
}
}
}
// 2:输入四个点坐标,判断是否是菱形、矩形、正方形,判断结果输出true/false,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。 若四个点坐标无法构成四边形,输出"not a quadrilateral"
class Choicetwo {
private Choiceone choiceone;
Choicetwo() {}
Choicetwo(Choiceone choiceone) {
this.choiceone = choiceone;
}
public boolean judgeRhombus() {
if (choiceone.judgeParallelogram()) {
if (choiceone.getVector()[4].judgeRightAngle(choiceone.getVector()[5])) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public boolean judgeRectangle() {
return choiceone.judgeParallelogram() && choiceone.getVector()[0].judgeRightAngle(choiceone.getVector()[1]);
}
public boolean judgeSquare() {
return judgeRectangle() && judgeRhombus();
}
public void showStatus() {
if (choiceone.judgeCoincide()) {
System.out.println("points coincide");
} else if (!choiceone.judgeQuadrangle()) {
System.out.println("not a quadrilateral");
} else {
System.out.println(judgeRhombus() + " " + judgeRectangle() + " " + judgeSquare());
}
}
}
//3:输入四个点坐标,判断是凹四边形(false)还是凸四边形(true),
// 输出四边形周长、面积,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。 若四个点坐标无法构成四边形,输出"not a quadrilateral"
class Choicethree {
private Choiceone choiceone;
Choicethree() {}
Choicethree(Choiceone choiceone) {
this.choiceone = choiceone;
}
public boolean isConvexquadrilateral() {
BigDecimal t1 = choiceone.getVector()[3].getX().multiply(choiceone.getVector()[0].getY()).subtract(choiceone.getVector()[3].getY().multiply(choiceone.getVector()[0].getX()));
BigDecimal t2 = choiceone.getVector()[0].getX().multiply(choiceone.getVector()[1].getY()).subtract(choiceone.getVector()[0].getY().multiply(choiceone.getVector()[1].getX()));
BigDecimal t3 = choiceone.getVector()[1].getX().multiply(choiceone.getVector()[2].getY()).subtract(choiceone.getVector()[1].getY().multiply(choiceone.getVector()[2].getX()));
BigDecimal t4 = choiceone.getVector()[2].getX().multiply(choiceone.getVector()[3].getY()).subtract(choiceone.getVector()[2].getY().multiply(choiceone.getVector()[3].getX()));
if (t1.multiply(t2).multiply(t3).multiply(t4).compareTo(BigDecimal.ZERO) < 0) {
return false;
} else {
return true;
}
}
public double circumference() {
return choiceone.getVector()[0].getLength() + choiceone.getVector()[1].getLength() + choiceone.getVector()[2].getLength() + choiceone.getVector()[3].getLength();
}
public double getArea() {
double S;
if (isConvexquadrilateral()) {
MathContext mc = new MathContext(10);
double s = circumference() / 2.0;
S =Math.sqrt((s - choiceone.getVector()[0].getLength()) * (s - choiceone.getVector()[1].getLength()) * (s - choiceone.getVector()[2].getLength()) * (s - choiceone.getVector()[3].getLength()));
} else {
S = Math.sqrt(4 * Math.pow(choiceone.getVector()[4].getLength(),2) * Math.pow(choiceone.getVector()[5].getLength(),2)
- Math.pow((Math.pow(choiceone.getVector()[0].getLength(),2) - Math.pow(choiceone.getVector()[1].getLength(),2)
+ Math.pow(choiceone.getVector()[2].getLength(),2) - Math.pow(choiceone.getVector()[3].getLength(),2)),2)) / 4;
}
return S;
}
public void showStatus() {
if (choiceone.judgeCoincide()) {
System.out.println("points coincide");
} else if (!choiceone.judgeQuadrangle()) {
System.out.println("not a quadrilateral");
} else {
System.out.println(isConvexquadrilateral() + " " + Main.round(circumference()) +" " + Main.round(getArea()));
}
}
}
class Line {
private double x;
private double y;
Line() {}
Line(double x, double y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public double getX() {
return x;
}
public void setX(double x) {
this.x = x;
}
public double getY() {
return y;
}
public void setY(double y) {
this.y = y;
}
}
class Choicefour {
private Line line;
private Choiceone choiceone;
Choicefour() {}
Choicefour(Line line, Choiceone choiceone) {
this.line = line;
this.choiceone = choiceone;
}
public Line getLine() {
return line;
}
public void setLine(Line line) {
this.line = line;
}
public Choiceone getChoiceone() {
return choiceone;
}
public void setChoiceone(Choiceone choiceone) {
this.choiceone = choiceone;
}
public void showStatus() {
if (choiceone.judgeQuadrangle()) {
System.out.println("The line is coincide with one of the lines");
} else {
System.out.println("not a quadrilateral or triangle");
}
}
}
class Choicefive {
private static final int POLYGON_MIN_SIZE = 3;
private List<Point2D.Double> list;
private Point2D.Double p;
private Choiceone choiceone;
Choicefive() {}
Choicefive(Choiceone choiceone, List<Point2D.Double> list, Point2D.Double p) {
this.p = p;
this.list = list;
this.choiceone = choiceone;
}
public int rayCasting() {
double px = p.x, py = p.y;
boolean flag = false;
//
for (int i = 0, l = list.size(), j = l - 1; i < l; j = i, i++) {
//取出边界的相邻两个点
double sx = list.get(i).x,
sy = list.get(i).y,
tx = list.get(j).x,
ty = list.get(j).y;
// 点与多边形顶点重合
if ((sx == px && sy == py) || (tx == px && ty == py)) {
return 0;
}
// 判断线段两端点是否在射线两侧
//思路:作p点平行于y轴的射线 作s,t的平行线直线 如果射线穿过线段,则py的值在sy和ty之间
if ((sy < py && ty >= py) || (sy >= py && ty < py)) {
// 线段上与射线 Y 坐标相同的点的 X 坐标 ,即求射线与线段的交点
double x = sx + (py - sy) * (tx - sx) / (ty - sy);
// 点在多边形的边上
if (x == px) {
return 0;
}
// 射线穿过多边形的边界
if (x > px) {
flag = !flag;
}
}
}
// 射线穿过多边形边界的次数为奇数时点在多边形内
return flag ? 1 : 2;
}
public void showStatus() {
if (choiceone.judgeQuadrangle()){
if (rayCasting() == 1) {
System.out.println("in the quadrilateral");
} else if (rayCasting() == 0) {
System.out.println("on the quadrilateral");
} else {
System.out.println("outof the quadrilateral");
}
} else {
if (rayCasting() == 1) {
System.out.println("in the triangle");
} else if (rayCasting() == 0) {
System.out.println("on the triangle");
} else {
System.out.println("outof the triangle");
}
}
}
}踩坑心得:
1、相较于上一次的四边形问题,这次我想到了可以运用向量的只是进行代码编写,但是在做之前并没有思考好向量与线段方向思路的优劣,导致在做题时思路混乱。
2、
javafx.geometry.Point2D
+Point2D(x: double,y: double) //用给定的x和y坐标来创建一个Point2D对象
+distance(x: double,y: double): double //返回该点到定点(x,y)的距离
+distance(p: Point2D): double //返回该点到p点的距离
+getX(): double //返回该点的x的坐标
+getY(): double //返回该点的y的坐标
+toString(): String //返回该点的字符串表示
3、求凹凸四边形面积用婆罗摩笈多公式。
s = (a+b+c+d ) / 2.0 S = Math.sqrt((s-a) * (s-b) * (s-c) * (s-d))
4、在程序书写时,我们可以先从反例入手。
类图:
复杂度:
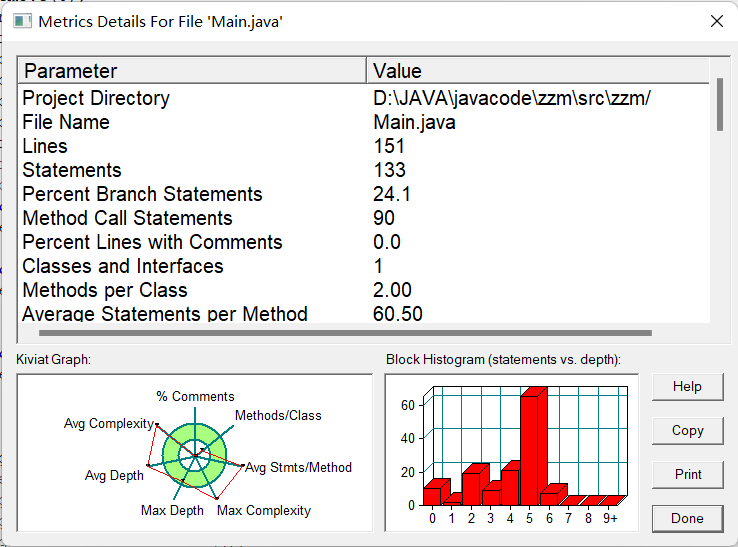
双向链表:
代码如下
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DoubleLinkedListImpl<Integer> list = new DoubleLinkedListImpl<>();
list.add(1);
list.add(3);
list.add(5);
list.add(8);
list.add(9);
list.add(2);
System.out.println(list.getSize());
list.add(2,100);
System.out.println(list.getSize());
list.printList();
list.add(5,101);
System.out.println(list.getSize());
list.printList();
list.add(1,102);
System.out.println(list.getSize());
list.printList();
list.add(9,103);
list.printList();
list.remove();
System.out.println(list.getSize());
list.printList();
list.remove(3);
System.out.println(list.getSize());
list.printList();
System.out.println(list.getFirst());
System.out.println(list.getLast());
}
}
interface DoubleLinkedList<E> {
public boolean isEmpty();
public int getSize();
public E getData(int index);
public void remove();//删除最后一个节点
public void remove(int index);
public void add(int index, E theElement);
public void add(E element);//在链表尾插入节点,插入节点data值为element
public void printList();
public E getFirst();//获取链表第一个节点
public E getLast();//获取链表最后一个节点
}
class DoubleLinkedListImpl<E> implements DoubleLinkedList<E> {
private Node<E> head;
private Node<E> curr;
private Node<E> tail;
private int size;
//所有index都是从1开始
public DoubleLinkedListImpl() {
this.head = new Node<E>();
this.head.setNext(null);
this.head.setPrevious(null);
this.curr = this.tail = null;
this.size = 0;
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.size == 0;
}
@Override
public int getSize() {
return size;
}
@Override
public void add(int index, E theElement) {
if(index < 1 || index > this.size) {
System.out.println("索引坐标错误,请稍后重试");
return ;
}
if (index == 1){
Node<E> temp = new Node<E>(theElement, this.head, null);
this.head.setPrevious(temp);
head = temp;
} else {
curr = this.head;
for(int i = 1; i < index - 1; i++) {
curr = curr.getNext();
}
Node<E> before = curr;
Node<E> after = curr.getNext();
Node<E> temp = new Node<E>(theElement, after, before);
before.setNext(temp);
after.setPrevious(temp);
}
size++;
}
@Override
public void add(E element) {
Node<E> temp = new Node<E>();
temp.setData(element);
if(this.size == 0) {
this.head.setData(element);
this.tail = head;
}else{
this.tail.setNext(temp);
temp.setPrevious(tail);
this.tail = temp;
}
this.size++;
}
@Override
public E getData(int index) {
if(index > this.size || index < 1) {
System.out.println("索引坐标错误,请稍后重试");
return null;
}
curr = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
curr = curr.getNext();
}
return curr.getData();
}
@Override
public void remove() {
if(this.size == 0) {
return;
}
curr = tail.getPrevious();
curr.setNext(null);
tail = curr;
this.size --;
}
@Override
public void remove(int index) {
if(index > this.size || index < 1) {
return ;
}
curr = head;
if(index == 1) {
curr = head.getNext();
}else if (index == this.size) {
remove();
} else {
for(int i = 1; i < index - 1; i++) {
curr = curr.getNext();
}
curr.setNext(curr.getNext().getNext());
}
this.size --;
}
@Override
public E getFirst() {
if(this.size != 0) {
return head.getData();
}
return null;
}
@Override
public E getLast() {
if(this.size != 0) {
return tail.getData();
}
return null;
}
@Override
public void printList() {
curr=head;
if(isEmpty()){
System.out.print("当前链表为空\n");
return;
}
else{
System.out.print(curr.getData()+" ");
curr = curr.getNext();
}
while(curr != null){
System.out.print(curr.getData()+" ");
curr = curr.getNext();
}
System.out.println("");
}
}
class Node<E> {
private E data;
private Node<E> next;
private Node<E> previous;
public Node() {
this.next = null;
}
public Node(E data, Node<E> next, Node<E> previous) {
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
this.previous = previous;
}
public E getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(E data) {
this.data = data;
}
public Node<E> getNext() {
return this.next;
}
public void setNext(Node<E> next) {
this.next = next;
}
public Node<E> getPrevious() {
return this.previous;
}
public void setPrevious(Node<E> previous) {
this.previous = previous;
}
}类图:
踩坑心得:
1、index从1开始计算
2、不管是什么都要双向思考,比如add(Element element) 到底是加在头节点还是尾节点
3、泛型的使用<E>
期中考试:
OOP-1:
设计思路:
-
设计一个类表示平面直角坐标系上的点Point,私有属性分别为横坐标x与纵坐标y,数据类型均为实型数,除构造方法以及属性的getter与setter方法外,定义一个用于显示信息的方法display(),用来输出该坐标点的坐标信息,格式如下:
(x,y),数值保留两位小数。为简化题目,其中,坐标点的取值范围设定为(0,200]。若输入有误,系统则直接输出Wrong Format -
设计一个类表示平面直角坐标系上的线Line,私有属性除了标识线段两端的点point1、point2外,还有一个字符串类型的color,用于表示该线段的颜色,同样,除构造方法以及属性的getter与setter方法外,定义一个用于计算该线段长度的方法getDistance(),还有一个用于显示信息的方法display(),用来输出线段的相关信息,输出格式如下:
The line's color is:颜色值 The line's begin point's Coordinate is: (x1,y1) The line's end point's Coordinate is: (x2,y2) The line's length is:长度值其中,所有数值均保留两位小数,建议可用
String.format("%.2f", data)方法。
题设类图:
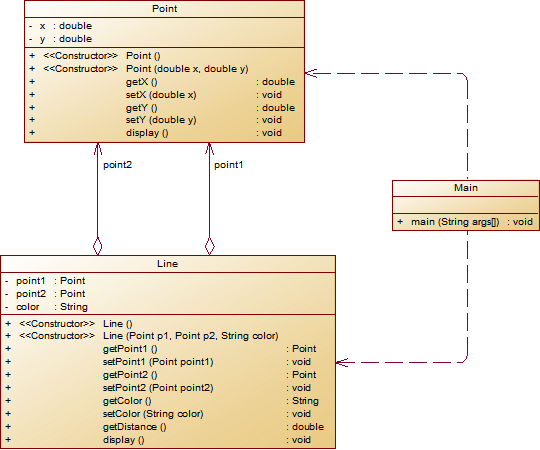
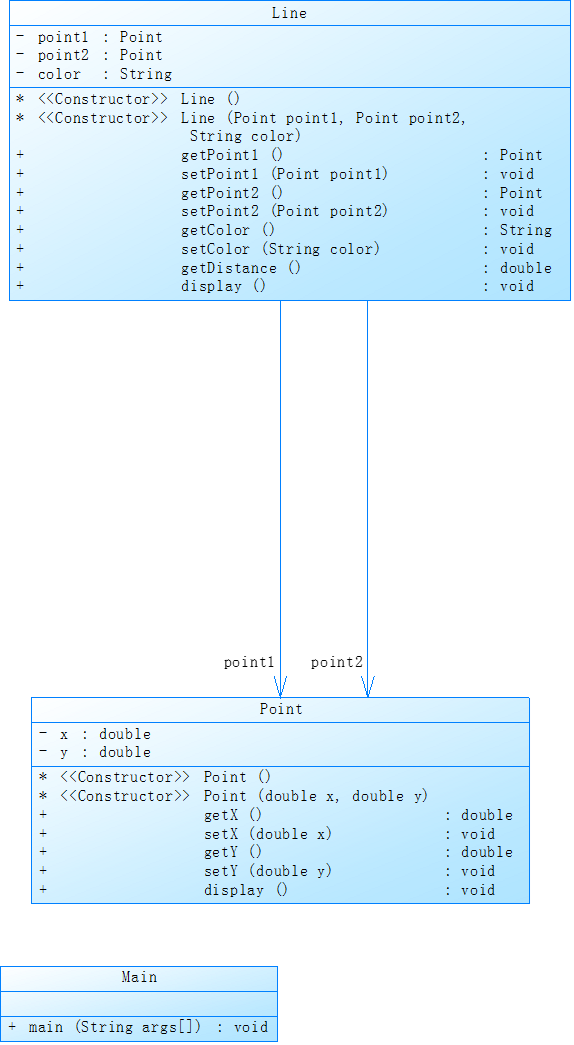
类图:
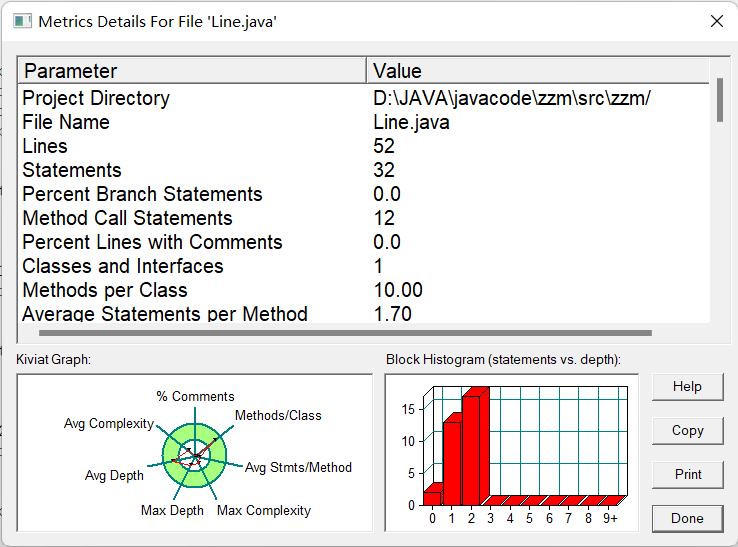
复杂度:
OOP-2:
设计思路:
在“点与线(类设计)”题目基础上,对题目的类设计进行重构,以实现继承与多态的技术性需求。
- 对题目中的点Point类和线Line类进行进一步抽象,定义一个两个类的共同父类Element(抽象类),将display()方法在该方法中进行声明(抽象方法),将Point类和Line类作为该类的子类。
- 再定义一个Element类的子类面Plane,该类只有一个私有属性颜色color,除了构造方法和属性的getter、setter方法外,display()方法用于输出面的颜色,输出格式如下:
The Plane's color is:颜色 - 在主方法内,定义两个Point(线段的起点和终点)对象、一个Line对象和一个Plane对象,依次从键盘输入两个Point对象的起点、终点坐标和颜色值(Line对象和Plane对象颜色相同),然后定义一个Element类的引用,分别使用该引用调用以上四个对象的display()方法,从而实现多态特性。示例代码如下:
element = p1;//起点Point element.display(); element = p2;//终点Point element.display(); element = line;//线段 element.display(); element = plane;//面 element.display();
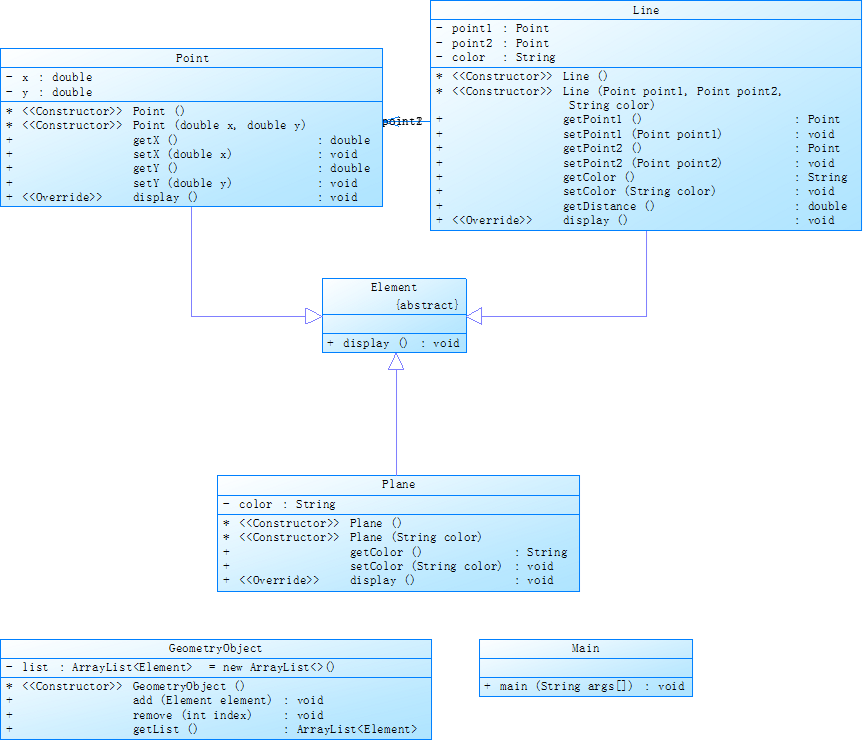
题设类图:
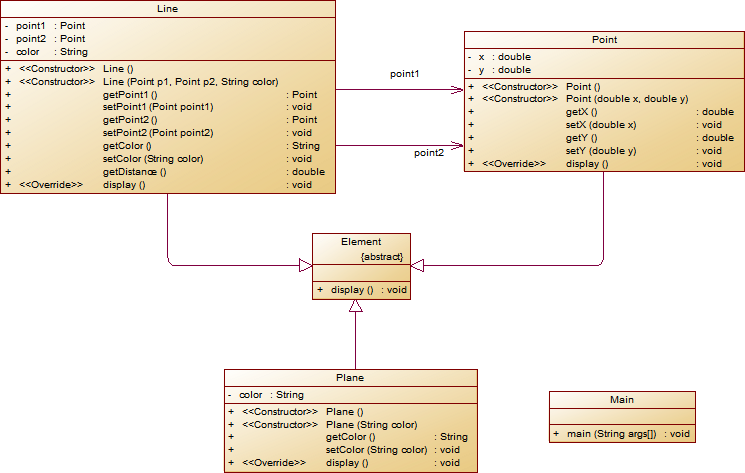
类图:
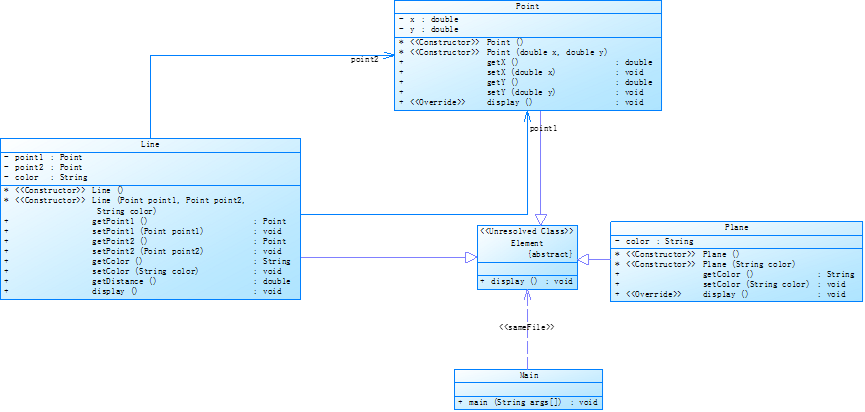
复杂度:
OOP-3:
设计思路:
在“点与线(继承与多态)”题目基础上,对题目的类设计进行重构,增加容器类保存点、线、面对象,并对该容器进行相应增、删、遍历操作。
- 在原有类设计的基础上,增加一个GeometryObject容器类,其属性为
ArrayList<Element>类型的对象(若不了解泛型,可以不使用<Element>) - 增加该类的
add()方法及remove(int index)方法,其功能分别为向容器中增加对象及删除第index - 1(ArrayList中index>=0)个对象 - 在主方法中,用户循环输入要进行的操作(choice∈[0,4]),其含义如下:
- 1:向容器中增加Point对象
- 2:向容器中增加Line对象
- 3:向容器中增加Plane对象
- 4:删除容器中第index - 1个数据,若index数据非法,则无视此操作
- 0:输入结束
题设类图:
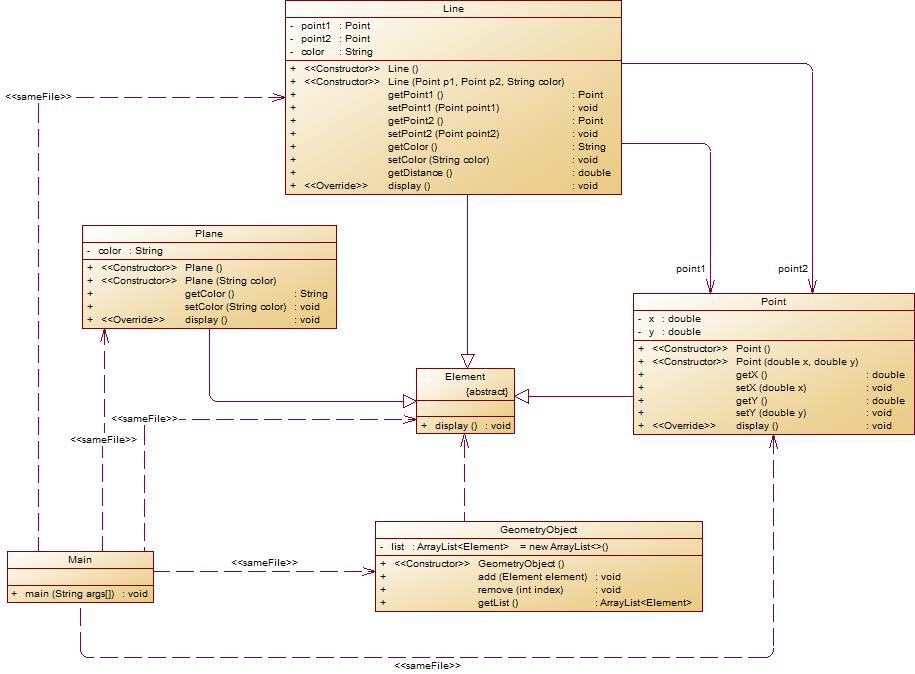
类图:
复杂度:
踩坑心得:1、对输入格式(中间可用一个或多个空格、tab或者回车分隔)处理方法用in.next()接收数据在进行类型转化。
2、容器边界值两边都要考虑。
三、改进建议
1、main里面不要再有冗长的乱如麻的代码,整体逻辑能力有待提高
2、学好数理化走遍天下都不怕,一定好好学数学,不因数学层面知识的欠缺而写不出来题。
3、效率问题。
4、第七次pta不及格。
四、总结
在6-10周的学习过程中,我终于解决了农夫过河的正确解的历史弥留问题。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号