2022年下学期面向对象程序设计学习总结(一)
一、 前言
(1)部分学习总结:
对象是明确的实体,类是具有相同属性和操作的一组对象的集合,是为属于该类的全部对象提供了统一的抽象描述。
作为对象有状态和行为
状态在类中表现为属性,行为在类中表现为方法。
在含有某对象的方法中,我们需要区别这种行为是该对象主动发出的还是被动接受的。
private:私有权限,可用于修饰成员变量,方法,构造方法,但是不能修饰类。
单例模式:一种简单的创建型设计模式。这种模式涉及到一个单一的类,该类负责创建自己的对象,同时确保只有单个对象被创建。这个类提供了一种访问其唯一的对象的方式,可以直接访问,不需要实例化该类的对象。其中就需要将包括成员变量,构造方法用private修饰后,用懒汉式
class Singleton {
private static Singleton instance;
private Singleton (){}
public static Singleton getInstance() {
if (instance == null) {
instance = new Singleton();
}
return instance;
}
}
或者饿汉式
public class Singleton {
private static Singleton instance = new Singleton();
private Singleton (){}
public static Singleton getInstance() {
return instance;
}
}
实现单例模式。
对于封装后的属性,为方便后期对于该类属性的访问与管理,需要引入所有属性对应的getter和setter。
封装:把对象的属性和操作结合成一个独立的系统单位,并尽可能隐藏对象的内部细节。增强代码的维护性和安全性。
在每一个类里头都需要构造方法的存在对属性进行初始化,构造方法可以为空,在有属性的情况下,构造方法不少于两个。
PS:构造方法的方法名和类名一定是相同的(首字母大写)
JAVA无指针,但有reference。
类与类之间的五种关系:(关系,本质为调方法)
1.关联;
2.聚集:分为聚合和组合。两种的实质区别为生存期长短,聚合生存期不一致;组合生存期一致,即同生共死。
3.依赖;
4.继承;
5.实现;
面向对象的七大设计原则:
1.单一职责原则(SRP)一个函数只做一件事情,无法细分
2.迪米特法则(DEMETER):
不要和陌生人说话。
只和你的朋友直接通信。
最少知识原则,知道的越少越好。
3.里氏代换原则:子类的方法父类都要有
4.合成复用原则:
5.依赖倒置原则:依赖于抽象类、接口(只与顶层打交道)
6.接口隔离原则:
Interface即接口,抽象类型,是抽象方法的集合,接口通常以interface来声明。
一个类通过继承接口的方式,从而来继承接口的抽象方法。
实现接口:
class C implements A,B,...{}
继承抽象类实现接口:
class D extends C implements A,B,...{}
接口的继承:
interface C extends A,B,...{}
7.“开-闭”原则:
开放扩展也就是extends
关闭修改也就是modification
继承/复用/泛化:
继承的特点:
1.只支持单继承,即一个子类只允许有一个父类。
2. 子类可以拥有父类的属性和方法。
3. 子类可以拥有自己的属性和方法。
4. 子类可以重写(@Override)覆盖父类的方法。
可以继承父类的public和protected成员变量;不能够继承父类的private成员变量。
访问权限成员变量的时候只有子类和父类在同一个包下才能继承。
子类不能继承父类的构造器。
多态:是指在一般类中定义的属性或操作被特殊类继承之后,可以具有不同的数据类型或表现出不同的行为。
EG:List list = new ArrayList();
final:使用final声明类不能有子类,声明的方法不能被子类所覆写,声明的变量是常量不能修改。
abstract抽象类
abstract class Xxxx{}
抽象类不可以有对象
主要作为父类存在
子类若不重写抽象类方法,子类仍然为抽象类
class Ball extends Cirecle {
public Ball{
}
public Ball(String color, double radius) {
super(color, radius);
}
@Override
public double getArea( ) {
return 4*super.getArea();
}
}
Circle circle = new Circle("red",2.4);
circle.getArea();
Shape shape = new Circle("red",2.4);
System.out.println(shape.getArea());
shape = new Ball("black", 5.4);
System.out.println(shape.getArea());
多态:动态联编、动态绑定 (必须有子类与父类关系)
不同对象接收到同样的消息会产生不同的操作
消息就是方法
EG:
void fun(Shape shape) {
System.out.println(shape.getArea());
}
fun(circle);
fun(ball);
主线:封装 继承 多态
1.整体和部分可以继承(一般不会)
2.大类到小类别的继承
抽象类和接口的区别
1. 抽象类中的方法可以有能实现方法的具体功能方法体,但是接口中不能有方法体。
2. 抽象类中的成员变量不限制类型,而接口中的成员变量只能是 public static final 类型的。
3. 一个类只能继承一个抽象类,而一个类却可以实现多个接口。
Object类是所有类的父类,声明一个Object类的作用就是可以传递任何类型的类来使用。
Object是所有类的父类,它有很多类对象会用到的方法,例如比较常用的toString 、equals。
(2)题量与难度:
|
周数 |
题量 |
难度 |
|
第一周 |
4 |
·· |
|
第二周 |
9 |
·· |
|
第三周 |
3 |
·· |
|
第四周 |
3 |
····· |
|
第五周 |
2 |
··· |
二、设计与分析
PTA:
第一周:
定义一个代表一元二次方程ax2+bx+c=0的类QuadraticEquation,其属性为三个系数a、b、c(均为私有属性),类中定义的方法参考main方法中的代码。main方法源码:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
double a = Double.parseDouble(input.next());
double b = Double.parseDouble(input.next());
double c = Double.parseDouble(input.next());
if(a == 0){
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
//create a QuadraticEquation object
QuadraticEquation equation = new QuadraticEquation(a, b, c);
//get value of b * b - 4 * a * c
double discriminant = equation.getDiscriminant();
System.out.println("a=" + equation.getA() +
",b=" + equation.getB() +
",c=" + equation.getC()+":");
if (discriminant < 0) {
System.out.println("The equation has no roots.");
}
else if (discriminant == 0)
{
System.out.println("The root is " +
String.format("%.2f", equation.getRoot1()));
}
else // (discriminant >= 0)
{
System.out.println("The roots are " +
String.format("%.2f", equation.getRoot1())
+ " and " + String.format("%.2f", equation.getRoot2()));
}
}
}
class QuadraticEquation{
//your code
}注意:须提交完整源码,包括Main类。
代码如下
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
double a = Double.parseDouble(input.next());
double b = Double.parseDouble(input.next());
double c = Double.parseDouble(input.next());
if(a == 0){
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
//create a QuadraticEquation object
QuadraticEquation equation = new QuadraticEquation(a, b, c);
//get value of b * b - 4 * a * c
double discriminant = equation.getDiscriminant();
System.out.println("a=" + equation.getA() +
",b=" + equation.getB() +
",c=" + equation.getC()+":");
if (discriminant < 0) {
System.out.println("The equation has no roots.");
}
else if (discriminant == 0)
{
System.out.println("The root is " +
String.format("%.2f", equation.getRoot1()));
}
else // (discriminant >= 0)
{
System.out.println("The roots are " +
String.format("%.2f", equation.getRoot1())
+ " and " + String.format("%.2f", equation.getRoot2()));
}
}
}
class QuadraticEquation {
private double a;
private double b;
private double c;
QuadraticEquation() {
}
QuadraticEquation(double a, double b, double c) {
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
this.c = c;
}
double getA() {
return a;
}
double getB() {
return b;
}
double getC() {
return c;
}
double getDiscriminant() {
return b * b - 4 * a * c;
}
double getRoot1() {
return (-b + Math.sqrt(b * b - 4 * a * c)) / 2 / a;
}
double getRoot2() {
return (-b - Math.sqrt(b * b - 4 * a * c)) / 2 / a;
}
}7-2 日期类设计 (30 分)
参考题目集二中和日期相关的程序,设计一个类DateUtil,该类有三个私有属性year、month、day(均为整型数),其中,year∈[1820,2020] ,month∈[1,12] ,day∈[1,31] , 除了创建该类的构造方法、属性的getter及setter方法外,需要编写如下方法:
public boolean checkInputValidity();//检测输入的年、月、日是否合法
public boolean isLeapYear(int year);//判断year是否为闰年
public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n);//取得year-month-day的下n天日期
public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n);//取得year-month-day的前n天日期
public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date);//比较当前日期与date的大小(先后)
public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date);//判断两个日期是否相等
public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date);//求当前日期与date之间相差的天数
public String showDate();//以“year-month-day”格式返回日期值应用程序共测试三个功能:
- 求下n天
- 求前n天
- 求两个日期相差的天数
注意:严禁使用Java中提供的任何与日期相关的类与方法,并提交完整源码,包括主类及方法(已提供,不需修改)
程序主方法如下:import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int year = 0;
int month = 0;
int day = 0;
int choice = input.nextInt();
if (choice == 1) { // test getNextNDays method
int m = 0;
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day);
if (!date.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
m = input.nextInt();
if (m < 0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
System.out.print(date.getYear() + "-" + date.getMonth() + "-" + date.getDay() + " next " + m + " days is:");
System.out.println(date.getNextNDays(m).showDate());
} else if (choice == 2) { // test getPreviousNDays method
int n = 0;
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day);
if (!date.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
n = input.nextInt();
if (n < 0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
System.out.print(
date.getYear() + "-" + date.getMonth() + "-" + date.getDay() + " previous " + n + " days is:");
System.out.println(date.getPreviousNDays(n).showDate());
} else if (choice == 3) { //test getDaysofDates method
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherYear = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherMonth = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherDay = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil fromDate = new DateUtil(year, month, day);
DateUtil toDate = new DateUtil(anotherYear, anotherMonth, anotherDay);
if (fromDate.checkInputValidity() && toDate.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println("The days between " + fromDate.showDate() +
" and " + toDate.showDate() + " are:"
+ fromDate.getDaysofDates(toDate));
} else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
else{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
}代码如下
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int year = 0;
int month = 0;
int day = 0;
int choice = input.nextInt();
if (choice == 1) { // test getNextNDays method
int m = 0;
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day);
if (!date.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
m = input.nextInt();
if (m < 0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
System.out.print(date.getYear() + "-" + date.getMonth() + "-" + date.getDay() + " next " + m + " days is:");
System.out.println(date.getNextNDays(m).showDate());
} else if (choice == 2) { // test getPreviousNDays method
int n = 0;
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day);
if (!date.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
n = input.nextInt();
if (n < 0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
System.out.print(
date.getYear() + "-" + date.getMonth() + "-" + date.getDay() + " previous " + n + " days is:");
System.out.println(date.getPreviousNDays(n).showDate());
} else if (choice == 3) { //test getDaysofDates method
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherYear = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherMonth = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherDay = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil fromDate = new DateUtil(year, month, day);
DateUtil toDate = new DateUtil(anotherYear, anotherMonth, anotherDay);
if (fromDate.checkInputValidity() && toDate.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println("The days between " + fromDate.showDate() +
" and " + toDate.showDate() + " are:"
+ fromDate.getDaysofDates(toDate));
} else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
else{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
input.close();
}
}
class DateUtil {
private int year;
private int month;
private long day;
DateUtil() {
}
DateUtil(int year, int month, long day) {
this.year = year;
this.month = month;
this.day = day;
}
public void setYear(int year) {
this.year = year;
}
public int getYear() {
return year;
}
public int getMonth() {
return month;
}
public void setMonth(int month) {
this.month = month;
}
public long getDay() {
return day;
}
public void setDay(long day) {
this.day = day;
}
public boolean checkInputValidity() {//检测输入的年、月、日是否合法
int[] monthDay = {0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31};
if (isLeapYear(year)) {
monthDay[2] = 29;
} else {
monthDay[2] = 28;
}
if (year >= 1820 && year <= 2020 && month <= 12 && month>=1 && day <= monthDay[month] && day >= 1) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
public boolean isLeapYear(int year) {//判断year是否为闰年
if(year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0 || year % 400 == 0) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n) {//取得year-month-day的下n天日期
DateUtil newData = new DateUtil();
int[] monthDay = {0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31};
if (isLeapYear(year)) {
monthDay[2] = 29;
} else {
monthDay[2] = 28;
}
day = day + n;
while (day > monthDay[month]) {
day = day - monthDay[month];
month++;
if (month == 13) {
month = 1;
year++;
if (isLeapYear(year)) {
monthDay[2] = 29;
} else {
monthDay[2] = 28;
}
}
}
newData.month = this.month;
newData.day = this.day;
newData.year = this.year;
return newData;
}
public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n) {//取得year-month-day的前n天日期
DateUtil newData = new DateUtil();
int[] monthDay = {0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31};
if (isLeapYear(year)) {
monthDay[2] = 29;
} else {
monthDay[2] = 28;
}
day = day - n;
while (day < 0) {
month--;
if (month == 0) {
month = 12;
year--;
if (isLeapYear(year)) {
monthDay[2] = 29;
} else {
monthDay[2] = 28;
}
}
day = day + monthDay[month];
}
newData.month = this.month;
newData.day = this.day;
newData.year = this.year;
return newData;
}
public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date) {
if (this.year < date.year)
{
return false;
} else if (this.year > date.year) {
return true;
} else if (this.year == date.year) {
if (this.month > date.month) {
return true;
} else if (this.month == date.month) {
if(this.day > date.day) {
return true;
} else if(this.day < date.day) {
return false;
}
} else if (this.month < date.month) {
return false;
}
}
return false;
}
public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date) {//判断两个日期是否相等
if (this.day == date.day && this.month == date.month && this.year == date.year) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date) {//求当前日期与date之间相差的天数
DateUtil fore = new DateUtil();
DateUtil later = new DateUtil();
int all = 0;
int[] monthDay = {0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31};
if(this.equalTwoDates(date)) {
return 0;
} else if (this.compareDates(date)) {
later.day = this.getDay();
later.month = this.getMonth();
later.year = this.getYear();
fore.day = date.getDay();
fore.month = date.getMonth();
fore.year = date.getYear();
} else {
later.day = date.getDay();
later.month = date.getMonth();
later.year = date.getYear();
fore.day = this.getDay();
fore.month = this.getMonth();
fore.year = this.getYear();
}
for (int i = fore.year + 1; i < later.year;i++) {
if (isLeapYear(i)) {
all += 366;
} else {
all += 365;
}
}
if (fore.year != later.year){
if (isLeapYear(fore.year)) {
monthDay[2] = 29;
} else {
monthDay[2] = 28;
}
for (int i = fore.month;i <= 12;i++) {
if (i == fore.month) {
all += monthDay[i] - fore.day;
} else {
all += monthDay[i];
}
}
if (isLeapYear(later.year)) {
monthDay[2] = 29;
} else {
monthDay[2] = 28;
}
for (int i = 1;i <= later.month;i++) {
if (i == later.month) {
all += later.day;
} else {
all += monthDay[i];
}
}
} else {
if (isLeapYear(later.year)) {
monthDay[2] = 29;
} else {
monthDay[2] = 28;
}
for (int i = fore.month;i <= later.month;i++) {
if (i == later.month) {
all += later.day;
} else if (i == fore.month) {
all += monthDay[i] - fore.day;
} else {
all += monthDay[i];
}
}
}
return all;
}
public String showDate() {
String dataStr = year + "-" + month + "-" + day;
return dataStr;
}
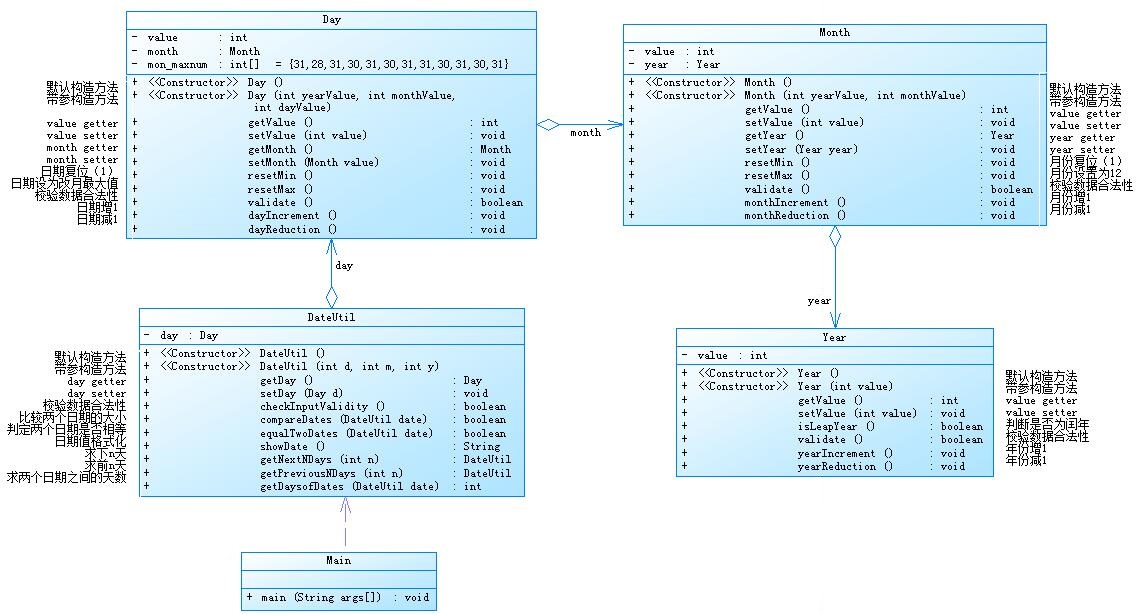
}参考题目7-2的要求,设计如下几个类:DateUtil、Year、Month、Day,其中年、月、日的取值范围依然为:year∈[1900,2050] ,month∈[1,12] ,day∈[1,31] , 设计类图如下:
应用程序共测试三个功能:
- 求下n天
- 求前n天
- 求两个日期相差的天数
注意:严禁使用Java中提供的任何与日期相关的类与方法,并提交完整源码,包括主类及方法(已提供,不需修改)
代码如下import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int year = 0;
int month = 0;
int day = 0;
int choice = input.nextInt();
if (choice == 1) { // test getNextNDays method
int m = 0;
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil date = new DateUtil(day, month, year);
if (!date.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
m = input.nextInt();
if (m < 0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
System.out.println(date.getNextNDays(m).showDate());
} else if (choice == 2) { // test getPreviousNDays method
int n = 0;
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil date = new DateUtil(day, month, year);
if (!date.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
n = input.nextInt();
if (n < 0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
System.out.println(date.getPreviousNDays(n).showDate());
} else if (choice == 3) {
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherYear = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherMonth = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherDay = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil fromDate = new DateUtil(day, month, year);
DateUtil toDate = new DateUtil(anotherDay, anotherMonth, anotherYear);
if (fromDate.checkInputValidity() && toDate.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println(fromDate.getDaysofDates(toDate));
} else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
else{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
input.close();
}
}
class DateUtil {
private Day day;
public DateUtil() {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public DateUtil(int d, int m, int y) {
day = new Day(y, m, d);
}
public Day getDay() {
return day;
}
public void setDay(Day day) {
this.day = day;
}
public boolean checkInputValidity() {
if (day.getMonth().getYear().validate() && day.getMonth().validate() && day.validate()) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date) {
if (day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() < date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue())
{
return false;
} else if (day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() > date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()) {
return true;
} else if (day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() == date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()) {
if (day.getMonth().getValue() > date.getDay().getMonth().getValue()) {
return true;
} else if (day.getMonth() == date.getDay().getMonth()) {
if(day.getValue() > date.getDay().getValue()) {
return true;
} else if(day.getValue() < date.getDay().getValue()) {
return false;
}
} else if (day.getMonth().getValue() < date.getDay().getMonth().getValue()) {
return false;
}
}
return false;
}
public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date) {//判断两个日期是否相等
if (day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() < date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()
&& day.getMonth().getValue() > date.getDay().getMonth().getValue()
&& day.getValue() < date.getDay().getValue()) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
public String showDate() {
String dataStr = day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()
+ "-" + day.getMonth().getValue()
+ "-" + day.getValue();
return dataStr;
}
public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n) {//取得year-month-day的下n天日期
if (day.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) {
day.getMon_maxnum()[1] = 29;
} else {
day.getMon_maxnum()[1] = 28;
}
while (n != 0) {
n--;
day.dayIncrement();
if (day.getValue() > day.getMon_maxnum()[day.getMonth().getValue() - 1]) {
day.getMonth().monthIncrement();
day.resetMin();
if (day.getMonth().getValue() == 13) {
day.getMonth().resetMin();
day.getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement();
if (day.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) {
day.getMon_maxnum()[1] = 29;
} else {
day.getMon_maxnum()[1] = 28;
}
}
}
}
DateUtil newData = new DateUtil(day.getValue(), day.getMonth().getValue(), day.getMonth().getYear().getValue());
return newData;
}
public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n) {//取得year-month-day的前n天日期
if (day.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) {
day.getMon_maxnum()[1] = 29;
} else {
day.getMon_maxnum()[1] = 28;
}
while (n != 0) {
n--;
day.dayReduction();
if (day.getValue() < 1) {
day.getMonth().monthReduction();
if (day.getMonth().getValue() == 0) {
day.getMonth().resetMax();
day.getMonth().getYear().yearReduction();
if (day.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) {
day.getMon_maxnum()[1] = 29;
} else {
day.getMon_maxnum()[1] = 28;
}
}
day.resetMax();
}
}
DateUtil newData = new DateUtil(day.getValue(), day.getMonth().getValue(), day.getMonth().getYear().getValue());
return newData;
}
public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date) {//求当前日期与date之间相差的天数
int all = 0;
DateUtil fore;
DateUtil later;
DateUtil temp;
if (this.equalTwoDates(date)) {
return 0;
} else if(this.compareDates(date)) {
later = this;
fore = date;
} else {
fore = this;
later = date;
}
if (fore.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() != later.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()) {
temp = new DateUtil(fore.getDay().getValue(), fore.getDay().getMonth().getValue(), fore.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue());
fore.getDay().getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement();
while (fore.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() != later.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()) {
if (fore.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) {
all += 366;
} else {
all += 365;
}
fore.getDay().getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement();
}
if (temp.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) {
temp.getDay().getMon_maxnum()[1] = 29;
} else {
temp.getDay().getMon_maxnum()[1] = 28;
}
while(temp.getDay().getMonth().getValue() != 13) {
all += temp.getDay().getMon_maxnum()[temp.getDay().getMonth().getValue() - 1];
temp.getDay().getMonth().monthIncrement();
}
if (later.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) {
later.getDay().getMon_maxnum()[1] = 29;
} else {
later.getDay().getMon_maxnum()[1] = 28;
}
later.getDay().getMonth().monthReduction();
while(later.getDay().getMonth().getValue() != 0) {
all += later.getDay().getMon_maxnum()[later.getDay().getMonth().getValue() - 1];
later.getDay().getMonth().monthReduction();
}
} else {
if (fore.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) {
fore.getDay().getMon_maxnum()[1] = 29;
} else {
fore.getDay().getMon_maxnum()[1] = 28;
}
if (fore.getDay().getMonth().getValue() < later.getDay().getMonth().getValue()){
all += fore.getDay().getMon_maxnum()[fore.getDay().getMonth().getValue() - 1];
fore.getDay().getMonth().monthIncrement();
}
}
all = all -fore.getDay().getValue() + later.getDay().getValue();
return all;
}
}
class Year {
private int value;
public Year() {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public Year(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public boolean isLeapYear() {
if (value % 4 == 0 && value % 100 != 0 || value % 400 == 0) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
public boolean validate() {
if (value >= 1900 && value <=2050) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
public void yearIncrement() {
value++;
}
public void yearReduction() {
value--;
}
}
class Day {
private int value;
private Month month;
private int[] mon_maxnum = {31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31};
public Day() {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public Day(int yearValue, int monthValue, int dayValue) {
this.value = dayValue;
this.month = new Month(monthValue,yearValue);
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public Month getMonth() {
return month;
}
public void setMonth(Month value) {
this.month = value;
}
public void resetMin() {
value = 1;
}
public void resetMax() {
value = mon_maxnum[month.getValue() - 1];
}
public boolean validate() {
if (value <= mon_maxnum[month.getValue() - 1] && value >= 1) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
public int[] getMon_maxnum() {
return mon_maxnum;
}
public void setMon_maxnum(int[] mon_maxnum) {
this.mon_maxnum = mon_maxnum;
}
public void dayIncrement() {
value++;
}
public void dayReduction() {
value--;
}
}
class Month {
private int value;
private Year year;
public Month() {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public Month(int value, int year) {
this.value = value;
this.year = new Year(year);
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public Year getYear() {
return year;
}
public void setYear(Year year) {
this.year = year;
}
public void resetMin() {
value = 1;
}
public void resetMax() {
value = 12;
}
public boolean validate() {
if (value <= 12 && value >= 1) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
public void monthIncrement() {
value++;
}
public void monthReduction() {
value--;
}
}参考题目7-3的要求,设计如下几个类:DateUtil、Year、Month、Day,其中年、月、日的取值范围依然为:year∈[1820,2020] ,month∈[1,12] ,day∈[1,31] , 设计类图如下:
代码如下import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int year = 0;
int month = 0;
int day = 0;
int choice = input.nextInt();
if (choice == 1) { // test getNextNDays method
int m = 0;
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day);
if (!date.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
m = input.nextInt();
if (m < 0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
System.out.print(date.getYear().getValue() + "-" + date.getMonth().getValue() +
"-" + date.getDay().getValue() + " next " + m + " days is:");
System.out.println(date.getNextNDays(m).showDate());
} else if (choice == 2) { // test getPreviousNDays method
int n = 0;
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day);
if (!date.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
n = input.nextInt();
if (n < 0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
System.out.print(date.getYear().getValue() + "-" + date.getMonth().getValue() +
"-" + date.getDay().getValue() + " previous " + n + " days is:");
System.out.println(date.getPreviousNDays(n).showDate());
} else if (choice == 3) { //test getDaysofDates method
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherYear = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherMonth = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherDay = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil fromDate = new DateUtil(year, month, day);
DateUtil toDate = new DateUtil(anotherYear, anotherMonth, anotherDay);
if (fromDate.checkInputValidity() && toDate.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println("The days between " + fromDate.showDate() +
" and " + toDate.showDate() + " are:"
+ fromDate.getDaysofDates(toDate));
} else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
} else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
class DateUtil {
private Day day;
private Month month;
private Year year;
private int[] mon_maxnum = {31, 29, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31};
public DateUtil() {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public DateUtil(int y, int m, int d) {
day = new Day(d);
month = new Month(m);
year = new Year(y);
}
public Day getDay() {
return day;
}
public void setDay(Day day) {
this.day = day;
}
public Month getMonth() {
return month;
}
public void setMonth(Month month) {
this.month = month;
}
public Year getYear() {
return year;
}
public void setYear(Year year) {
this.year = year;
}
public void setDayMin() {
day.setValue(1);
}
public void setDayMax() {
if (year.isLeapYear()) {
mon_maxnum[1] = 29;
} else {
mon_maxnum[1] = 28;
}
day.setValue(mon_maxnum[month.getValue() - 1]);
}
public boolean checkInputValidity() {
if (month.validate() && year.validate() && day.getValue() >= 1 && day.getValue() <= mon_maxnum[month.getValue() - 1]) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date) {
if (year.getValue() < date.getYear().getValue()) {
return false;
} else if (year.getValue() > date.getYear().getValue()) {
return true;
} else if (year.getValue() == date.getYear().getValue()) {
if (month.getValue() > date.getMonth().getValue()) {
return true;
} else if (month.getValue() == date.getMonth().getValue()) {
if(day.getValue() > date.getDay().getValue()) {
return true;
} else if(day.getValue() < date.getDay().getValue()) {
return false;
}
} else if (month.getValue() < date.getMonth().getValue()) {
return false;
}
}
return false;
}
public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date) {//判断两个日期是否相等
if (year.getValue() == date.getYear().getValue()
&& month.getValue() == date.getMonth().getValue()
&& day.getValue() == date.getDay().getValue()) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
public String showDate() {
String dataStr = year.getValue()
+ "-" + month.getValue()
+ "-" + day.getValue();
return dataStr;
}
public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n) {//取得year-month-day的下n天日期
if (year.isLeapYear()) {
mon_maxnum[1] = 29;
} else {
mon_maxnum[1] = 28;
}
while (n != 0) {
n--;
day.dayIncrement();
if (day.getValue() > mon_maxnum[month.getValue() - 1]) {
month.monthIncrement();
setDayMin();
if (month.getValue() == 13) {
month.resetMin();
year.yearIncrement();
if (year.isLeapYear()) {
mon_maxnum[1] = 29;
} else {
mon_maxnum[1] = 28;
}
}
}
}
DateUtil newData = new DateUtil(year.getValue(), month.getValue(), day.getValue());
return newData;
}
public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n) {//取得year-month-day的前n天日期
if (year.isLeapYear()) {
mon_maxnum[1] = 29;
} else {
mon_maxnum[1] = 28;
}
while (n != 0) {
n--;
day.dayReduction();
if (day.getValue() < 1) {
month.monthReduction();
if (month.getValue() == 0) {
month.resetMax();
year.yearReduction();
if (year.isLeapYear()) {
mon_maxnum[1] = 29;
} else {
mon_maxnum[1] = 28;
}
}
setDayMax();
}
}
DateUtil newData = new DateUtil(year.getValue(),month.getValue(), day.getValue());
return newData;
}
public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date) {//求当前日期与date之间相差的天数
int all = 0;
DateUtil fore;
DateUtil later;
DateUtil temp;
if (this.equalTwoDates(date)) {
return 0;
} else if(this.compareDates(date)) {
later = new DateUtil(this.getYear().getValue(), this.getMonth().getValue(), this.getDay().getValue());
fore = new DateUtil(date.getYear().getValue(), date.getMonth().getValue(), date.getDay().getValue());
} else {
fore = new DateUtil(this.getYear().getValue(), this.getMonth().getValue(), this.getDay().getValue());
later = new DateUtil(date.getYear().getValue(), date.getMonth().getValue(), date.getDay().getValue());
}
if (fore.getYear().getValue() != later.getYear().getValue()) {
temp = new DateUtil(fore.getYear().getValue(), fore.getMonth().getValue(), fore.getDay().getValue());
fore.getYear().yearIncrement();
while (fore.getYear().getValue() != later.getYear().getValue()) {
if (fore.getYear().isLeapYear()) {
all += 366;
} else {
all += 365;
}
fore.getYear().yearIncrement();
}
if (temp.getYear().isLeapYear()) {
temp.mon_maxnum[1] = 29;
} else {
temp.mon_maxnum[1] = 28;
}
while(temp.getMonth().getValue() != 13) {
all += temp.mon_maxnum[temp.getMonth().getValue() - 1];
temp.getMonth().monthIncrement();
}
if (later.getYear().isLeapYear()) {
later.mon_maxnum[1] = 29;
} else {
later.mon_maxnum[1] = 28;
}
later.getMonth().monthReduction();
while(later.getMonth().getValue() != 0) {
all += later.mon_maxnum[later.getMonth().getValue() - 1];
later.getMonth().monthReduction();
}
} else {
if (fore.getYear().isLeapYear()) {
fore.mon_maxnum[1] = 29;
} else {
fore.mon_maxnum[1] = 28;
}
if (fore.getMonth().getValue() < later.getMonth().getValue()){
all += fore.mon_maxnum[fore.getMonth().getValue() - 1];
fore.getMonth().monthIncrement();
}
}
all = all -fore.getDay().getValue() + later.getDay().getValue();
return all;
}
}
class Year {
private int value;
public Year() {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public Year(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public boolean isLeapYear() {
if (value % 4 == 0 && value % 100 != 0 || value % 400 == 0) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
public boolean validate() {
if (value >= 1820 && value <=2020) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
public void yearIncrement() {
value++;
}
public void yearReduction() {
value--;
}
}
class Day {
private int value;
public Day() {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public Day(int Value) {
this.value = Value;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public void dayIncrement() {
value++;
}
public void dayReduction() {
value--;
}
}
class Month {
private int value;
public Month() {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public Month(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public void resetMin() {
value = 1;
}
public void resetMax() {
value = 12;
}
public boolean validate() {
if (value <= 12 && value >= 1) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
public void monthIncrement() {
value++;
}
public void monthReduction() {
value--;
}
}踩坑心得:对于年月日的进位一定要注意同时注意平闰年对于二月天数的变化。对于边界的考虑要更加晚上跨年跨月要注意牵动其他数据的变化。
第二周:
体重是反映和衡量一个人健康状况的重要标志之一,过胖和过瘦都不利于健康,BMI(身体质量指数)计算方法:体重(以千克为单位)除以身高(以米为单位)的平方。中国成人正常的BMI应在18.5-24之间,如果小于18.5为体重不足,如果大于等于24为超重,大于等于28为肥胖。请编写程序,测算身体状态。
代码如下import java.util.Scanner;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
double weight = in.nextDouble();
double height = in.nextDouble();
if (weight < 0 || weight > 727 || height < 0 || height > 2.72) {
System.out.println("input out of range");
System.exit(1);
}
double BMI = weight / height / height;
if (BMI < 18.5) {
System.out.println("thin");
} else if (BMI <= 24) {
System.out.println("fit");
} else if (BMI <= 28) {
System.out.println("overweight");
} else {
System.out.println("fat");
}
}
}踩坑心得:
- 题目要认真阅读,认真满足所需要求,但是题目不是所有的都符合事实,符合测试用例。例如:7-1 身体质量指数(BMI)测算中BMI数据的界限范围有误,正确如下:中国成人正常的BMI应在5-24之间,如果小于18.5为体重不足,如果大于24为超重,大于28为肥胖。
- 答案错误时,数据输出精度也可以考虑一下,很多时候都需要强制转换成float再输出。
- 注意equals()和 == 的应用场景。
改进建议:代码复用性不强,可以改进的更加符合MVC模式。
第三周:
踩坑心得:
- 题目要认真阅读,认真满足所需要求,但是题目不是所有的都符合事实,符合测试用例。例如:7-2 串口字符解析奇偶校验是从起始位后一位开始计算到奇偶校验位中1的个数。
第四周:
7-1 点线形系列1-计算两点之间的距离 (10 分)
本体核心:正则表达式:
String regex = "([+-]?(([1-9]\\d*)|0)(\\.\\d+)*)[,]([+-]?(([1-9]\\d*)|0)(\\.\\d+)*)\\s+([+-]?(([1-9]\\d*)|0)(\\.\\d+)*)[,]([+-]?(([1-9]\\d*)|0) (\\.\\d +)*)";踩坑心得:1.要注意判断输入格式等错误的if一定要放在对数据做进一步处理之前完成。
2.
import java.math.BigDecimal;
PS:题目集04 中的第四个选个选项没写。
第五周:
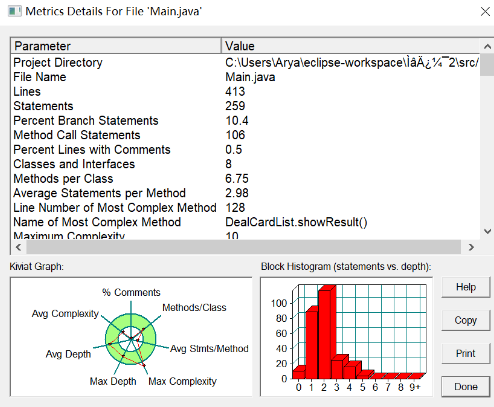
7-1 图形卡片排序游戏 (40 分)
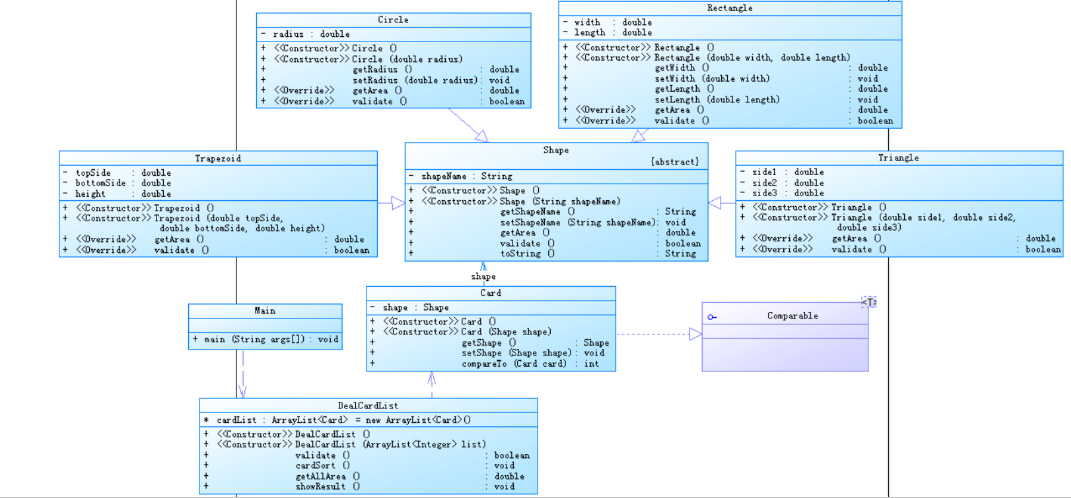
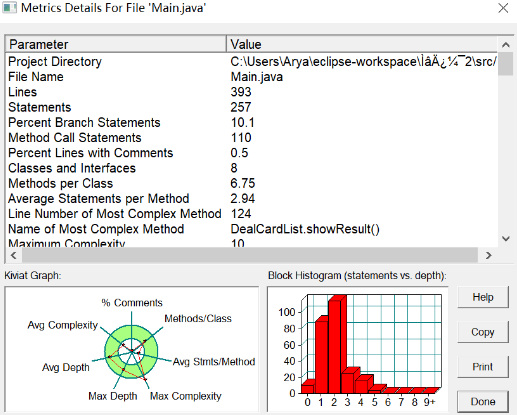
7-2 图形卡片分组游戏 (60 分)
实验:
雨刷器01:本次作业要求用Java,C,Python三种语言对雨刷控制器进行编程模拟,通过简单的交互式菜单,实现司机对雨刷系统的控制及测试,并没有任何设计思维。
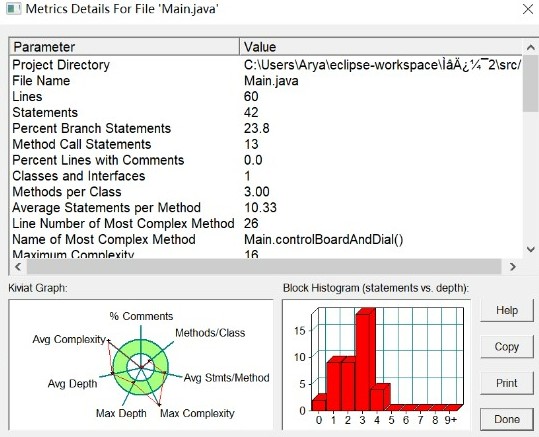
雨刮器02:同上次雨刷问题要求不变,采用面向对象技术,合理设计实体类、业务(控制)类、接口类及各个类之间的关系,务必符合SRP(单一职责原则)。
设计思路:
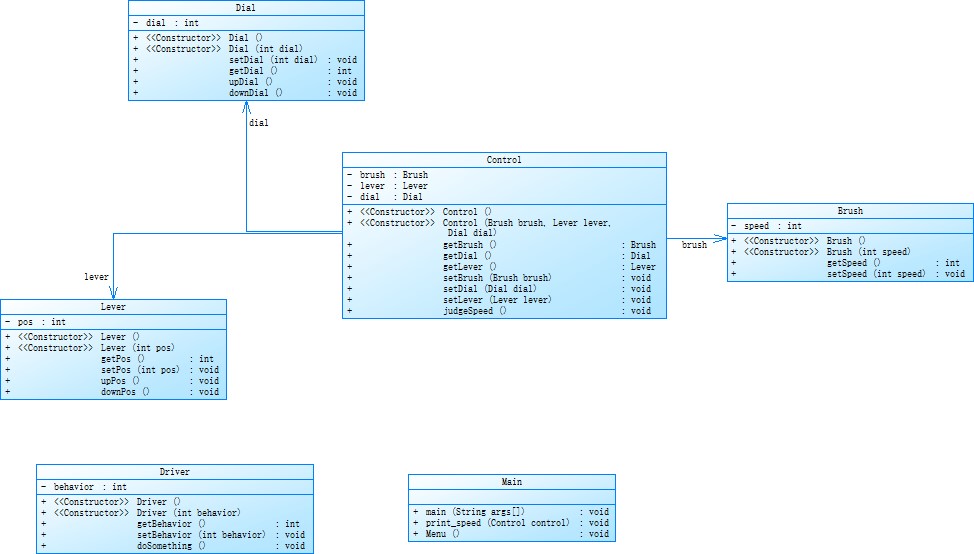
雨刮器03: 重构第二次作业雨刷问题,需求不变,采用面向对象技术,合理设计实体类、业务(控制)类、接口类及各个类之间的关系,务必符合SRP(Single Responsibility Principe,单一职责原则)以及Demeter法则(Law of Demeter)
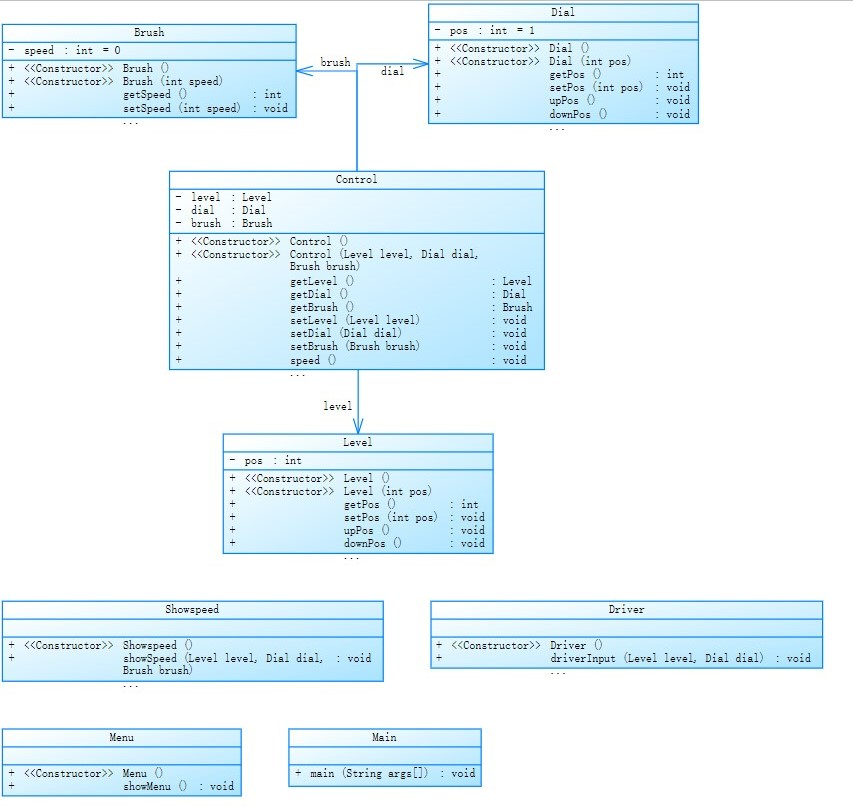
雨刮器04:重构第三次作业雨刷问题,需求不变,采用面向对象技术,再次合理设计实体类、业务(控制)类、接口类及各个类之间的关系,务必符合SRP(Single Responsibility Principe,单一职责原则)、Demeter法则(Law of Demeter)(强制要求)
设计思路: MVC模式为基础框架,并且使用了单例模式。
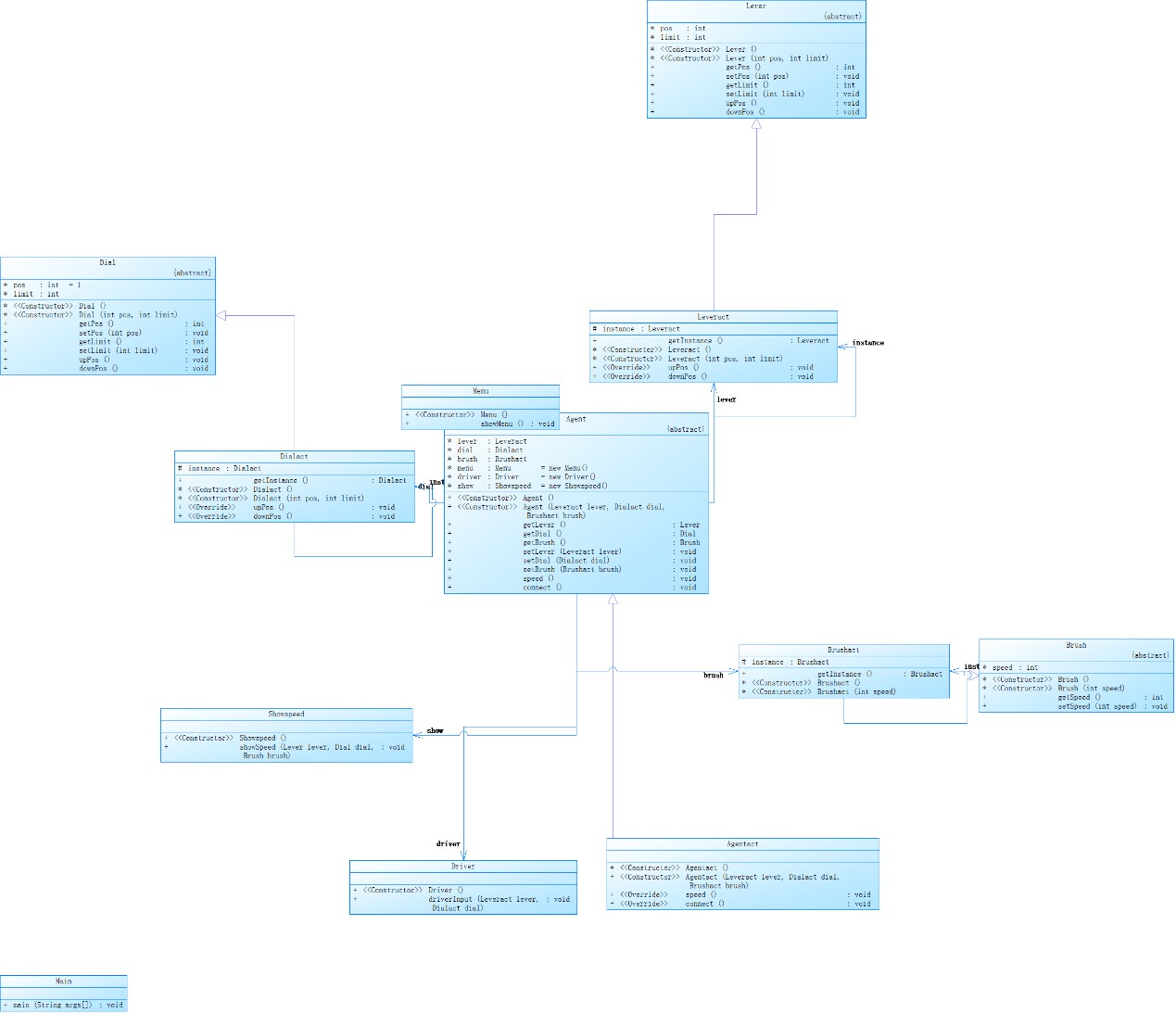
雨刮器05:重构第四次作业雨刷问题,需求变更为该系统可以适用多种雨刷系统,采用面向对象技术,再次合理设计实体类、业务(控制)类、接口类、各个类的抽象父类以及相互的关系,务必符合SRP(Single Responsibility Principe,单一职责原则)、Demeter法则(Law of Demeter)、“开-闭”原则、里氏代换原则、依赖倒转原则以及合成复用原则
设计思路:增添父类,采用顶层设计模式
实验总结:雨刷器设计实体类有雨刷,刻度盘,转速旋钮,接口类有页面交互的GUI,Driver的输入,业务类连接所有的接口 ,负责存储数据到 控制器类,并相应地更新速度。
其实这项实验的每个阶段都是代码逐步完善的过程,可以很明显的感受到自己在思考框架,书写代码,完善代码中的进步。
相较于前三周,对于PTA上的代码属于代码堆积,为完成任务而完成任务(当然有时候如果不向一些学的更加扎实的同学请教有一些细节问题我自己也没有办法解决)这种情况,PTA的题目集04和05有了很大的改善,按类分了,但是还是没有办法符合MVC模式。
有点困惑为啥PTA会有代码行数限制,其实一开始有想过彻底走MVC道路,但是走着走着发现我连getter和setter都没法写全,删删改改才能满足代码行数要求。我哭了(我装的)


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号