//已知2个一维数组:a[]={3,4,5,6,7},b[]={1,2,3,4,5,6,7};把数组a与数组b
//对应的元素乘积再赋值给数组b,如:b[2]=a[2]*b[2];最后输出数组b的元素。
package 数组;
public class Array {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int [] a = { 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 } ;
int [] b = { 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 } ;
int [] c = b ;
int i ;
for ( i = 0 ; i < a.length ; i++)
{
b [ i ] = a [ i ] * c [ i ] ;
System.out.print( b [ i ] + " " ) ;
}
}
}

//找出如下数组中最大的元素和最小的元素,
//a[][]={{3,2,6},{6,8,2,10},{5},{12,3,23}}
package 数组;
public class Array1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int [ ] [ ] a = { { 3 , 2 , 6 } , { 6 , 8 , 10 , } , { 5 } , { 12 , 3 , 23 } } ;
int max = a [ 0 ] [ 0 ] ;
int min = a [ 0 ] [ 0 ] ;
int i ;
int j ;
System.out.println("数组a的元素为: ");
for ( i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++ )
{
if ( i == 2 )//数组a中第三行只有一个元素,分开讨论
{
for ( j = 0 ; j < 1 ; j++)
{
System.out.print( a [ i ] [ j ] + " " ) ;
}
}
else
{
for ( j = 0 ; j < 3 ; j++ )
{
System.out.print( + a [ i ] [ j ] + " " ) ;
if ( a [ i ] [ j ] > max )//比较最大值,不是就将大的那个赋给max
{
max = a [ i ] [ j ] ;
}
else if ( a [ i ] [ j ] < min)//比较最小值,不是就将大的那个赋给min
{
min = a [ i ] [ j ] ;
}
}
}
}
//输出
System.out.println( " \n数组a中的最大值是:" + max ) ;
System.out.println( "数组a中的最小值是:" + min ) ;
}
}

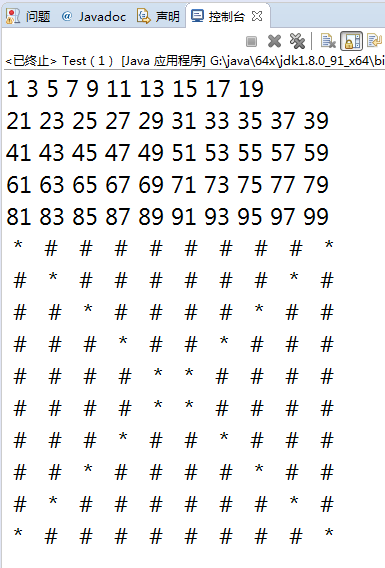
//编写一个名为Test的主类,类中只有一个主方法;
//在主方法中定义一个大小为50的一维整型数组,数组名为x,数组中存放着{1,
//3,5,…,99}输出这个数组中的所有元素,每输出十个换一行;在主方法中定义一
//个大小为10*10的二维字符型数组,数组名为y,正反对角线上存的是‘*’,其余
//位置存的是‘#’;输出这个数组中的所有元素。
package 面向对象;
public class Array
{
int [ ] x = new int [ 50 ] ;
String[][] y = new String [10][10] ;
int i ;
int j ;
void arrayx ( )
{
i = 1 ;
for ( j = 0 ; j < x.length ; j++)
{
x [ j ] = i ;
i = i + 2 ;
if ( j % 10 == 0 && j != 0 )
{
System.out.print( "\n" + x [ j ] + " " ) ;
}
else
{
System.out.print( x [ j ] + " " ) ;
}
}
}
void arrayy ( )
{
for ( i = 0 ; i <10 ; i++ )
{
for ( j = 0 ; j < 10 ; j++ )
{
if ( i == j || ( i + j ) == 9 )
{
y [ i ] [ j ] = " * ";
}
else
{
y [ i ] [ j ] = " # ";
}
System.out.print( y [ i ] [ j ] + " " ) ;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
主类:
package 面向对象;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Array a = new Array ( ) ;
a.arrayx();
System.out.println();
a.arrayy();
}
}





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号