把函数看作对象(python中函数是一等对象)
1.编程语言理论学家将“一等对象”定义为满足以下程序实体:
- 在运行时创建
- 能赋值给变量或数据结构中的元素
- 能做为参数传给函数
- 能作为函数的返回结果
在python中,整数、字符串和字典都是一等对象

def obj(): dic={1:"ff",2:"dfef"} print(type(dic)) #<class 'dict'> print(type(1)) #<class 'int'> print(type(obj)) #<class 'function'> obj()
如上所示,分别是dict 、int、function类型对象
2.高阶函数
接受函数为参数,或者把函数作为返回的函数是高阶函数,如map、filter、reduce等,在python3中引入了列表推导和生成器表达式,这三个函数没有太大用途。下面简单介绍。
2.1map(function,iterable,):返回一个将function应用于iterable中的每一项,其返回输出其结果的迭代器,其中iterable中的迭代对象个数为function函数参数的个数。

def fact(n): '''return n!''' return 1 if n<2 else n*fact(n-1) n=map(fact,(1,2,3,4,5)) print(list(n)) #[1, 2, 6, 24, 120]
2.2filter(function,iterable):用iterable中函数function返回真的那些元素,构建一个新的迭代器。iterable可以是一个序列,一个支持迭代器的容器。
filter(function,iterable)相当于一个生成器表达式,(item for item in iterable if function(item))。

def fact(n): '''return n!''' return 1 if n<2 else n*fact(n-1) def fact_filter(n): if n%2==0: #返回能被2整除的数 return n li=list(map(fact,filter(fact_filter ,range(7)))) #首先返回1~6中能被2整除的数,之后在计算其阶乘 print(li) #[2, 24, 720]
2.3.reduce(function,iterable):函数必须为两个参数,下面是计算两个参数的和相加(该reduce不止可以计算和,取决于function类型)。

from functools import reduce def avg(n,m): return (n+m)/2 print(reduce(avg,[1,2,3,4]))#3.125 结果怎么来的:(1+2)/2=1.5,(1.5+3)/2=2.25,(2.25+4)/2=3.125
3.匿名函数
lambda表达式创建匿名函数,匿名函数一般比较难理解,而且容易引起歧义,所有python中,函数内容较多时一般不用匿名函数。
su=lambda a,b: (a+b) #计算a b两个数之和 print(su(2,3))
#在lambda表达式中函数是运行时绑定,
4.可调用对像
除了用户定义的函数,调用运算符(即())还可以应用到其他对象上,如果想判断对象是否可调用,可以使用内置的callable()函数。python中有7中可调用对象。
- 用户定义的函数:def语句或lambda表达式创建。
- 内置函数:使用CPython中实现的函数,如len、time.strftime等
- 内置方法:使用C语言实现的方法,如dict.get()。
- 方法:在类中定义的函数。
- 类:调用类时会运行类的__new__方法创建一个实例,然后运行__init__方法,初始化实例,并把实例返回个调用方。如__new__被重写那么回有其他表现形式。
- 类的实例:如果类定义了__call__方法,那么类实列可以当作函数调用。
- 生成器函数:使用yield关键字的函数或方法,调用生成器函数返回的是生成器对象。

import random class BingoCage: def __init__(self,items): self._items=list(items) random.shuffle(self._items)#使输入的数随机 def pick(self): try: return self._items.pop() except: raise LookupError('pick from empty BingoCage') def __call__(self): return self.pick() bingo=BingoCage([1,2,3,4,5])#实例化对象 print(bingo.pick()) #函数调用 print(bingo()) #实现了__call__函数,可以将对象视为函数调用 print(callable(bingo)) #True 类中实现__call__函数
5.函数中自定义的属性
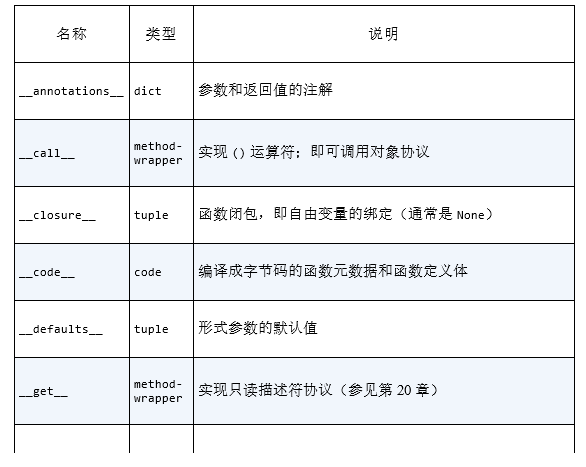
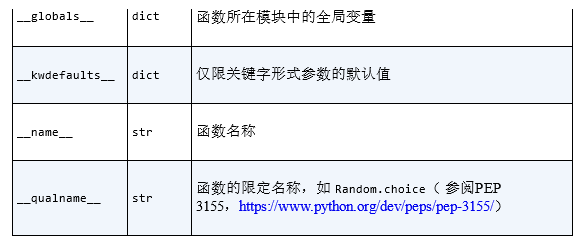
6.函数参数中,参数个数未定情况
在Python可能会见到函数参数列表出现*或**的情况。

def tag(name,*content,cls=None,**attrs): #有一个必选参数,一个默认参数和两个可选参数 '''生成HTML标签''' if cls is not None: attrs['class']=cls #生成类名 if attrs: attr_str=' '.join(" {0}='{1}'".format(attr,value) for attr,value in sorted(attrs.items())) #生成属性名和属性值 else: attr_str='' #若属性未传值,则默认属性为空 if content: return '\n'.join('<%s%s>%s</%s>'%(name,attr_str,c,name) for c in content) #生成标签内容 else: return '<%s%s/>'%(name,attr_str) print(tag("br")) #<br/> print(tag("p","Hello")) #<p>Hello</p> print(tag("a","Hello"," World!!"))#<a>Hello</a> #<a> World!!</a> print(tag("a","hello",cls="side",id=2)) #<a class='side' id='2'>hello</a> my_tag = {'name': 'img', 'title': 'Sunset Boulevard', 'src': 'sunset.jpg', 'cls': 'framed'} print(tag(**my_tag)) #把字典中的所有元素作为单个参数传入,字典中一定要包含指定必须传入参数为键的键值对。如上面的 'name': 'img' #<img class='framed' src='sunset.jpg' title='Sunset Boulevard'/>
7.在定义函数时,可以获取函数参数的参数信息

def clip(text,max_len=50): '''在max_len前面或后面的第一个空格处截取字符串''' end=None if len(text)>max_len: space_before=text.rfind(" ",0,max_len) if space_before>=0: end=space_before else: space_after=text.rfind(" ",max_len) if space_after>=0: end=space_after if end is None: end=len(text) return text[:end].rstrip() print(clip.__defaults__) #获取参数默认值 (50,) print(clip.__code__.co_varnames) #获取函数中变量名 ('text', 'max_len', 'end', 'space_before', 'space_after') print(clip.__code__.co_argcount) #获取变量个数,不包括前缀为*或**的局部变量 2
8.函数注解:为函数声明中的参数和返回值附加元数据
Python3中提供了一种句法,用于为函数声明中的参数和返回值的附加元数据。函数声明中的各个参数可以在:之后增加注解表达式。如果参数有默认值,注解放在参数名和=之间。如果想注解返回值,在)和函数声明末尾的:之间添加->和一个表达式。注解中常用的类(如str或int)和字符串("int>0")

def clip(text:str,max_len:"int>0"=80)->"ftewqy": '''在max_len前面或后面的第一个空格处截取字符串''' end=None if len(text)>max_len: space_before=text.rfind(" ",0,max_len) if space_before>=0: end=space_before else: space_after=text.rfind(" ",max_len) if space_after>=0: end=space_after if end is None: end=len(text) return text[:end].rstrip() print(clip.__annotations__) #{'text': <class 'str'>, 'max_len': 'int>0', 'return': <class 'str'>}
9.下面介绍支持函数编程的包
主要是operator和functools等包。
9.1operator包:
包含了一些基本数大小判断、计算数的和等。
https://docs.python.org/zh-cn/3.7/library/operator.html
9.2functools
https://docs.python.org/zh-cn/3.7/library/functools.html


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号