前三次oop作业总结
一、前言
第一次作业我认为是倾向于让我们初步的去学会构建类和使用正则表达式,并且这次还给出了设计建议简化了我们的设计难度,但在第一次写时我仍然花费了很长的时间,原因在于不知道怎么去使用类以及对于类的关系没有想清楚,但其实整体还是简单的。
第二次作业我觉得变化很大,但重点是体现在写代码的难度上,类的设计上我只多出来两个类(试卷题目类和答案类),而且是较为容易想到的,回到代码上,我当时完全不知道怎么去处理乱序输出和把信息储存,还是之后问了同学的才知道泛型list之类的。
第三次作业模拟了多张试卷以及信息删除等场景,由于出现了多张并且还需要考虑各种异常输入这就导致难度上升很多,还有这次用了hashmap这个散列表,不知道是不是由于这个列表只能遍历,导致运行慢了很多。
二、设计与分析
单独设置一个用来对输入信息进行正则表达式判断的类
第一次作业
点击查看代码
import java.util.*;
class Topic{
int num;
String content;
String standardAnswer;
public Topic(){
}
public Topic(int num,String content,String standardAnswer){
this.num=num;
this.content=content;
this.standardAnswer=standardAnswer;
}
public int getterNum(){
return num;
}
public void setterNum(int num){
this.num=num;
}
public String getterContent(){
return content;
}
public void setterContent(String content){
this.content=content;
}
public String getterStandardAnswer(){
return standardAnswer;
}
public void setterStandardAnswer(String standardAnswer){
this.standardAnswer=standardAnswer;
}
public boolean judgment(String answer){
return answer.equals(standardAnswer);
}
}
class Paper{
Topic topic;
String standaranswer;
int num;
public Paper(){
}
public void add(Topic topic){
this.topic=topic;
}
public void setStandarAnswer(String standaranswer){
this.standaranswer=standaranswer;
}
public Boolean judgment(AnswerPaper answer){
return standaranswer.equals(answer.getAnswer());
}
public int getterNum() {
return num;
}
public Topic getTopic(){
return topic;
}
}
class AnswerPaper{
Paper paper;
String answer;
public AnswerPaper(){
}
public void setAnswers(String answer){
this.answer=answer;
}
public String getAnswer(){
return answer;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
Topic[] topic=new Topic[n];
Paper[] paper=new Paper[n];
AnswerPaper[] answerpaper=new AnswerPaper[n];
sc.nextLine();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
topic[i]=new Topic();
paper[i]=new Paper();
answerpaper[i]=new AnswerPaper();
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
String line = sc.nextLine();
int num1= Integer.parseInt(line.substring(line.indexOf("#N:") + 3, line.indexOf("#Q:")).trim())-1;
String standardAnswer1= line.substring(line.indexOf("#A:") + 3).trim();
String content1= line.substring(line.indexOf("#Q:") + 3, line.indexOf("#A:")).trim();
paper[num1].add(topic[num1]);
topic[num1].setterContent(content1);
paper[num1].setStandarAnswer(standardAnswer1);}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
String answerInput = sc.next();
String answers = answerInput.substring(3);
answerpaper[i].setAnswers(answers);
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
System.out.println(paper[i].getTopic().getterContent()+"~"+answerpaper[i].getAnswer());
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(i!=n-1){
System.out.print(paper[i].judgment(answerpaper[i])+" ");}
else {
System.out.print(paper[i].judgment(answerpaper[i]));
}
}
}
}
点击查看代码
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
ArrayList<String> N = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<String> T = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<String> S = new ArrayList<>();
//输入所有数据并分类
while(true){
String str=input.nextLine();
if(str.contains("#N:")){
N.add(str);
}
if(str.contains("#T:")){
T.add(str);
}
if (str.contains("#S:")){
S.add(str);
}
if(str.equals("end")){
break;
}
}
//对N进行处理
ArrayList<Question> questions = new ArrayList<>();
String body;
String content = null;
String num = null;
String answer = null;
for (int i = 0; i < N.size(); i++) {
String[] parts = N.get(i).split("#N:|#Q:|#A:");
num = parts[1].trim();
content = parts[2].trim();
answer = parts[3].trim();
questions.add(new Question(num, content, answer));
}
//排序
int maxnum=0;
for(int i=0;i<questions.size();i++){
if(Integer.parseInt(questions.get(i).getNum())>maxnum){
maxnum=Integer.parseInt(questions.get(i).getNum());
}
}
boolean[] judge=new boolean[maxnum];
for(int i=0;i<questions.size();i++){
judge[Integer.parseInt(questions.get(i).getNum())-1]=true;
}
for(int i=0;i<maxnum;i++){
if(!judge[i]){
num = String.valueOf(i);
questions.add(new Question(num, content, answer));
}
}
for(int i = 0;i < questions.size()-1;i++){
for(int j = 0;j < questions.size() - i - 1;j++){
if(Integer.parseInt(questions.get(j).getNum()) > Integer.parseInt(questions.get(j+1).getNum())){
Question temp = questions.get(j);
questions.set(j,questions.get(j+1));
questions.set(j+1,temp);
}
}
}
//对T进行处理
ArrayList<Paper> papers = new ArrayList<>();
String score;
for(int i=0;i<T.size();i++){
String[] parts = T.get(i).split("#T:|\\s+|-");
ArrayList<String> nunOfQuestions = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<String> scoreOfQuestions = new ArrayList<>();
for(int j = 0;j < parts.length - 3;j=j+2){
num=parts[j+2].trim();
score=parts[j+3].trim();
nunOfQuestions.add(num);
scoreOfQuestions.add(score);
}
Paper paper=new Paper(parts[1].trim(),nunOfQuestions,scoreOfQuestions,questions);
papers.add(paper);
}
//对S进行处理
ArrayList<Answerpaper> answerpapers = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<String> myAnswers = new ArrayList<>();
String myAnswer;
for(int i = 0;i < S.size();i++){
String[] parts = S.get(i).split("#S:|#A:");
for(int j=0;j<parts.length-2;j++){
myAnswer=parts[j+2].trim();
myAnswers.add(myAnswer);
}
Answerpaper answerpaper=new Answerpaper(parts[1].trim(),myAnswers,papers);
answerpapers.add(answerpaper);
}
//判断试卷总分
for(int i=0;i<papers.size();i++){
int j=i+1;
if(!papers.get(i).fullScore()) {
System.out.println("alert: full score of test paper" + j + " is not 100 points");
}
}
//输出答卷信息(题目内容加判断正误)
int m=0,n=papers.get(0).getNumOfQuestions().size();
for(int i=0;i<answerpapers.size();i++) {
//先判断答卷是否匹配试卷
int f=0;
for(int j=0;j<papers.size();j++){
if(answerpapers.get(i).getNumOfAnswerpaper().equals(papers.get(j).getNumOfPaper())){
f=1;
break;
}
}
if(f==0){
if (i < papers.size()) {
m += papers.get(i).getNumOfQuestions().size();
}
if (i + 1 < papers.size()) {
n += papers.get(i + 1).getNumOfQuestions().size();
} else if (i < papers.size()) {
n += papers.get(i).getNumOfQuestions().size();
}
System.out.println("The test paper number does not exist");
continue;
}
boolean[] flag = new boolean[papers.get(Integer.parseInt(answerpapers.get(i).getNumOfAnswerpaper()) - 1).getQuestions().size()];
for (int j = m; j < n; j++) {
if (j < answerpapers.get(i).getMyAnswers().size()) {
double t = j / (i + 1.0);
if (t == j / (i + 1) && i > 0) {
t--;
}
System.out.print(questions.get(Integer.parseInt(papers.get(Integer.parseInt(answerpapers.get(i).getNumOfAnswerpaper()) - 1).getNumOfQuestions().get((int) t)) - 1).getContent());
System.out.print("~");
System.out.print(answerpapers.get(i).getMyAnswers().get(j));
System.out.print("~");
if (questions.get(Integer.parseInt(papers.get(Integer.parseInt(answerpapers.get(i).getNumOfAnswerpaper()) - 1).getNumOfQuestions().get((int) t)) - 1).getStandAnswer().equals(answerpapers.get(i).getMyAnswers().get(j))) {
System.out.println("true");
flag[(int) t] = true;
} else {
System.out.println("false");
flag[(int) t] = false;
}
} else
System.out.println("answer is null");
}
if (i < papers.size()) {
m += papers.get(i).getNumOfQuestions().size();
}
if (i + 1 < papers.size()) {
n += papers.get(i + 1).getNumOfQuestions().size();
} else if (i < papers.size()) {
n += papers.get(i).getNumOfQuestions().size();
}
int grade = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < papers.get(Integer.parseInt(answerpapers.get(i).getNumOfAnswerpaper()) - 1).getNumOfQuestions().size(); k++) {
if (k != 0)
System.out.print(" ");
if (flag[k]) {
grade += Integer.parseInt(papers.get(Integer.parseInt(answerpapers.get(i).getNumOfAnswerpaper()) - 1).getScoreOfQuestions().get(k));
System.out.print(papers.get(Integer.parseInt(answerpapers.get(i).getNumOfAnswerpaper()) - 1).getScoreOfQuestions().get(k));
} else
System.out.print("0");
}
System.out.print("~");
System.out.println(grade);
}
}
}
//////////////////////////////// 分界线 ////////////////////////////////
class Question {//题库
private String num;
private String content;
private String StandAnswer;
public void setStandAnswer(String standAnswer) {
this.StandAnswer = standAnswer;
}
public void setContent(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
public void setNum(String num) {
this.num = num;
}
public String getStandAnswer() {
return StandAnswer;
}
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
public String getNum() {
return num;
}
public Question() {
}
public Question(String num, String content, String StandAnswer) {
this.num = num;
this.content = content;
this.StandAnswer = StandAnswer;
}
}
class Paper{//试卷
private String numOfPaper;
private ArrayList<String> numOfQuestions;
private ArrayList<String> scoreOfQuestions;
private ArrayList<Question> questions;
public ArrayList<Question> getQuestions() {
return questions;
}
public ArrayList<String> getScoreOfQuestions() {
return scoreOfQuestions;
}
public ArrayList<String> getNumOfQuestions() {
return numOfQuestions;
}
public String getNumOfPaper() {
return numOfPaper;
}
public Paper(String numOfPaper, ArrayList<String> numOfQuestions, ArrayList<String> scoreOfQuestions, ArrayList<Question> questions) {
this.numOfPaper = numOfPaper;
this.numOfQuestions = numOfQuestions;
this.scoreOfQuestions = scoreOfQuestions;
this.questions = questions;
}
public Paper() {
}
public boolean fullScore(){
int sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<scoreOfQuestions.size();i++)
sum+=Integer.parseInt(scoreOfQuestions.get(i));
if(sum==100)
return true;
else
return false;
}
}
class Answerpaper{//答卷
private String numOfAnswerpaper;
private ArrayList<String> myAnswers;
private ArrayList<Paper> papers;
public ArrayList<Paper> getPapers() {
return papers;
}
public ArrayList<String> getMyAnswers() {
return myAnswers;
}
public String getNumOfAnswerpaper() {
return numOfAnswerpaper;
}
public Answerpaper(String numOfAnswerpaper, ArrayList<String> myAnswers, ArrayList<Paper> papers) {
this.numOfAnswerpaper = numOfAnswerpaper;
this.myAnswers = myAnswers;
this.papers = papers;
}
public Answerpaper() {
}
}
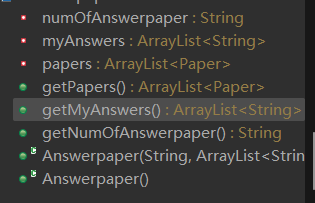
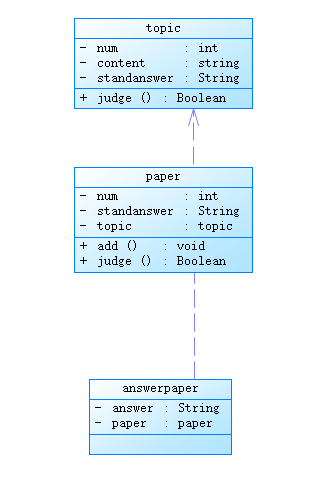
这上面的三张图及代码是我开始类中的设计,也是我后悔的点,类里面的东西太多了,这就导致模板的独立性不高,而且单一职责原则也没有很好的满足,所以重写时新设计了试卷题目类用于保存试卷中的题目信息,这其中考虑的因素有试卷中的题目序号与题目本身的题号不一致,且题目在不同试卷中的分值可能不一样。然后还有新增的答案类这样存储答卷中的答案会更加方便且更改及拓展容易。
这是更改之后的
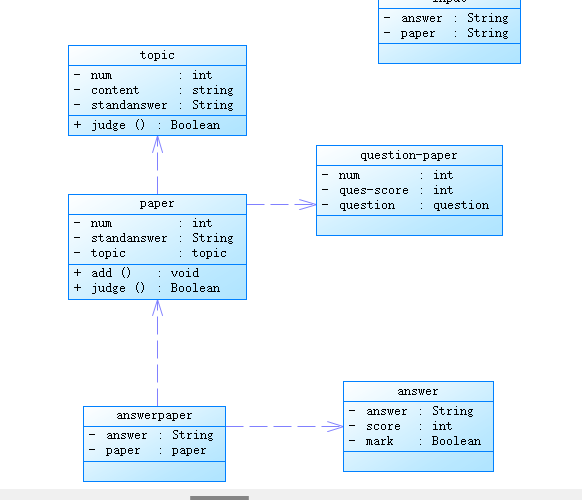
第三次作业
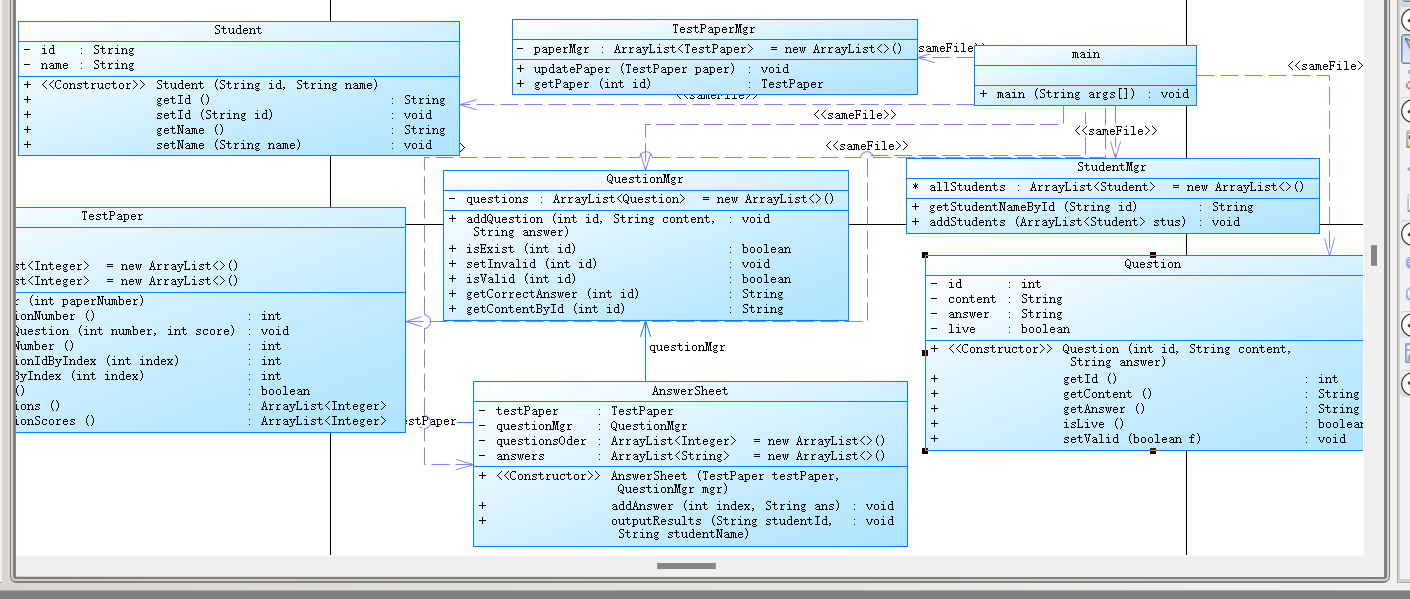
第三次很麻烦需要考虑许多问题,输入试题的信息(编号、题目、标准答案)、试卷引用信息(试卷号、引用的题目号-分值)、答卷信息(试卷号、答案)、学生信息(学号、姓名)、删除题目信息(题号)输出试题每一题的答题、判题信息以及最后每一题的判分结果、总分。输入中出现各类错误时输出对应错误信息。这些是较为具体的点。`import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
import java.util.ArrayList;
class Question {
private int id; //题目编号
private String content;
private String answer;
private boolean live; //是否有效(如果被删除,则无效)
public Question(int id ,String content, String answer) {
this.id = id;
this.content = content;
this.answer = answer;
this.live = true;
}
public int getId(){
return id;
}
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
public String getAnswer() {
return answer;
}
public boolean isLive(){
return live;
}
public void setValid(boolean f){
this.live = f;
}
}
//定义题目管理类,保存所有题目
class QuestionMgr {
private ArrayList
public void addQuestion(int id, String content,String answer){
questions.add(new Question(id,content,answer));
}
//判断题目是否存在
public boolean isExist(int id){
for(int i=0;i<questions.size();i++){
if(questions.get(i).getId() == id)
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 设置题目失效
public void setInvalid(int id){
for(int i=0;i<questions.size();i++){
if(questions.get(i).getId() == id)
questions.get(i).setValid(false);
}
}
//判断题目是否有效
public boolean isValid(int id){
for(int i=0;i<questions.size();i++){
if(questions.get(i).getId() == id)
return questions.get(i).isLive();
}
return false;
}
//根据题目编号获取题目正确答案
public String getCorrectAnswer(int id){
for(int i=0;i<questions.size();i++){
if(questions.get(i).getId() == id)
return questions.get(i).getAnswer();
}
return null; //没有题目id返回空
}
//根据题目编号获取题目内容
public String getContentById(int id){
for(int i=0;i<questions.size();i++){
if(questions.get(i).getId() == id)
return questions.get(i).getContent();
}
return null; //没有题目id返回空
}
}
//保存试卷的所有实体和分值
class TestPaper {
private int paperNumber; //试卷编号
private int questionnumber; //试卷中题目的数量
private ArrayList
private ArrayList
public TestPaper(int paperNumber) {
this.paperNumber = paperNumber;
questionnumber = 0;
}
//获取试卷题目数量
public int getQuestionNumber(){
return questionnumber;
}
//添加一个函数,用来增加试卷题目
public void addPaperQuestion(int number,int score){
paperQuestions.add(number);
paperScore.add(score);
questionnumber++;
}
//获取试卷编号
public int getPaperNumber() {
return paperNumber;
}
// 获取试卷第n题的编号
public int getQuestionIdByIndex(int index){
return paperQuestions.get(index);
}
// 获取试卷第n题的分值
public int getScoreByIndex(int index){
return paperScore.get(index);
}
// 判断试卷是否够100分
public boolean isFulll(){
int sum = 0;
for(int i=0;i<paperScore.size();i++)
sum += paperScore.get(i);
if(sum == 100)
return true;
else
return false;
}
public ArrayList<Integer> getQuestions() {
return paperQuestions;
}
public ArrayList<Integer> getQuestionScores() {
return paperScore;
}
}
// 试卷管理类
class TestPaperMgr{
private ArrayList
//更新试卷
public void updatePaper(TestPaper paper){
for(int i=0;i<paperMgr.size();i++){
if(paperMgr.get(i).getPaperNumber() == paper.getPaperNumber()){
paperMgr.remove(i);
break;
}
}
paperMgr.add(paper);
}
//根据试卷编号获取对应的试卷
public TestPaper getPaper(int id){
for(int i=0;i<paperMgr.size();i++){
if(paperMgr.get(i).getPaperNumber() == id)
return paperMgr.get(i);
}
return null;
}
}
// 学生类
class Student {
private String id;
private String name;
// 其他字段和方法
public Student(String id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
// getter 和 setter 方法
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
// 学生管理类
class StudentMgr{
ArrayList
//根据学号获取学生姓名
public String getStudentNameById(String id){
for(int i=0;i<allStudents.size();i++){
if(allStudents.get(i).getId().equals(id))
return allStudents.get(i).getName();
}
return null;
}
//添加学生信息
public void addStudents(ArrayList<Student> stus){
for(int i=0;i<stus.size();i++)
allStudents.add(stus.get(i));
}
}
class AnswerSheet {
private TestPaper testPaper; //试卷(因为题目限制只有1张试卷,所以,这里直接使用TestPaper实例,没有添加管理类
private QuestionMgr questionMgr; //管理所有试题
private ArrayList
private ArrayList
public AnswerSheet(TestPaper testPaper,QuestionMgr mgr) {
this.testPaper = testPaper;
this.questionMgr = mgr;
}
//添加回答
public void addAnswer(int index,String ans){
questionsOder.add(index);
answers.add(ans);
}
//输出结果
public void outputResults(String studentId, String studentName) {
// 判断是否够100分
if (!testPaper.isFulll()) {
System.out.println("alert: full score of test paper" + testPaper.getPaperNumber() + " is not 100 points");
}
int sumScore = 0; //总得分
int cnt = 0; //答题的数量
String strScore = ""; //判分信息
if(studentName == null)
strScore = studentId + " not found";
else
strScore = studentId+" "+ studentName+":";
ArrayList<String> logs = new ArrayList<>();
int ok = 0,err=0;
//遍历所有的回答
for(int i=0;i<questionsOder.size();i++){
//1.试卷题目序号
int index = questionsOder.get(i);
//2.回答
String ans = answers.get(i);
//3.判断序号是否超出试卷题目个数
if(index > testPaper.getQuestionNumber())
continue;
cnt++; //答题数量+1
//4.根据试题序号获取题目编号
int questionId = testPaper.getQuestionIdByIndex(index-1);
//5.根据试题序号获取题目分值
int questionScore = testPaper.getScoreByIndex(index-1);
//6.判断题目编号对应的题目是否存在
if(!questionMgr.isExist(questionId)){
System.out.println("non-existent question~0");
}else{
//7.判断题目是否已经失效
if(!questionMgr.isValid(questionId)){
String ls = "the question "+ String.valueOf(index) +" invalid~0";
logs.add(ls);
//System.out.println("the question "+ index +" invalid~0");
}else{
//8.根据题目编号获取正确答案
String right = questionMgr.getCorrectAnswer(questionId);
//9.判断答案是否正确
if(right.equals(ans)){
//回答正确
System.out.println(questionMgr.getContentById(questionId)+"~"+ans+"~true");
strScore = strScore +" " + String.valueOf(questionScore);
sumScore += questionScore;
ok++;
}else{
//回答错误
System.out.println(questionMgr.getContentById(questionId)+"~"+ans+"~false");
strScore = strScore +" 0";
err++;
}
}
}//else end
}//for end
for(int i=0;i<logs.size();i++){
strScore = strScore +" 0";
err++;
System.out.println(logs.get(i));
}
for(int i = (ok+err);i<testPaper.getQuestionNumber();i++)
strScore = strScore +" 0";
//10.判断试卷是否全部回答
if(cnt < testPaper.getQuestionNumber())
System.out.println("answer is null");
//11.输出总分
if(studentName == null)
System.out.println(strScore);
else{
strScore = strScore + "~"+String.valueOf(sumScore);
System.out.println(strScore);
}
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
TestPaperMgr paperMgr = new TestPaperMgr(); //管理所有试卷
QuestionMgr questionMgr = new QuestionMgr(); //管理所有试题
StudentMgr stuMgr = new StudentMgr(); //管理所有学生信息
String studentId="";
String studentName = "";
TestPaper currentpaper = null;
AnswerSheet answerSheet = null;
//读取数据开始处理
while (true) {
String line = scanner.nextLine();
//System.out.println(line);
if (line.equals("end")) {
break;
}
Matcher matcher;
if ((matcher = Pattern.compile("#N:(\\d+) #Q:(.*?) #A:(\\d+)").matcher(line)).matches()) {
// Parse #N: section
int number = Integer.parseInt(matcher.group(1));
String questionContent = matcher.group(2); // 获取题目内容
String answer = matcher.group(3);
questionMgr.addQuestion(number, questionContent, answer); // 将题目内容添加到试卷中
} else if ((matcher = Pattern.compile("#T:(\\d+) (.+)").matcher(line)).matches()) {
// Parse #T: section
//#T:(\\d+) (\\d+-\\d+)
int paperNumber = Integer.parseInt(matcher.group(1));
//System.out.println("p1: " + matcher.group(1));
//System.out.println("p2: " + matcher.group(2));
//获取试卷
TestPaper paper = paperMgr.getPaper(paperNumber);
if(paper == null){
paper = new TestPaper(paperNumber);
}
//System.out.println("---------------");
//将试题加入试卷
String[] parts = matcher.group(2).split(" ");
for(int i=0;i<parts.length;i++){
String[] pt = parts[i].split("-");
int questionNumber = Integer.parseInt(pt[0]);
int score = Integer.parseInt(pt[1]);
//System.out.println(" >> "+ questionNumber +" " + score);
paper.addPaperQuestion(questionNumber, score);
}
paperMgr.updatePaper(paper);
//System.out.println( "paper.getQuestionNumber() ="+paper.getQuestionNumber());
} else if ((matcher = Pattern.compile("#X:(\\d+) (.+)").matcher(line)).matches()) {
// Parse #X: section
// 因为这一行可以有多个学生,所以不能直接使用matcher.group(),需要通过-和空格进行分割
int index = line.indexOf(":");
line = line.substring(index+1);
//使用-分隔
String[] parts = line.split("-");
//使用空格分隔
ArrayList<Student> stus = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0;i<parts.length;i++){
String[] stu = parts[i].split(" ");
if(stu.length==2){
stus.add(new Student(stu[0],stu[1]));
}
}
stuMgr.addStudents(stus);
} else if ((matcher = Pattern.compile("#S:(\\d+) (\\d+) (.+)").matcher(line)).matches()) {
//"#S:(\\d+) (\\d+) #A:(\\d+-\\d+)"
// Parse #S: section
/*System.out.println("p0: "+matcher.group(0));
System.out.println("p1: "+matcher.group(1));
System.out.println("p2: "+matcher.group(2));
System.out.println("p3: "+matcher.group(3));
*/
int paperNmb = Integer.parseInt(matcher.group(1)); //获取试卷编号
currentpaper = paperMgr.getPaper(paperNmb); //根据试卷编号找到试卷
if(currentpaper != null){
//获取学生信息
studentId = matcher.group(2);
studentName = stuMgr.getStudentNameById(studentId);
//拆分答案部分
String[] ques = matcher.group(3).split(" ");
//创建答卷
answerSheet = new AnswerSheet(currentpaper,questionMgr);
for(int i=0;i<ques.length;i++){
String ans = ques[i].substring(ques[i].indexOf(":")+1);
String[] pts = ans.split("-");
if (pts.length == 2){
//System.out.println(" >> "+pts[0]);
//System.out.println(" >> "+pts[1]);
int questionNumber = Integer.parseInt(pts[0]);
String answer = pts[1];
answerSheet.addAnswer(questionNumber,answer);
}
}
}
}else if(line.startsWith("#D:N-")){
int index = line.indexOf("-");
if(index < line.length()){
int id = Integer.parseInt(line.substring(index+1));
//System.out.println("Delete "+id);
questionMgr.setInvalid(id);
}
} else {
//格式错误
System.out.println("wrong format:"+line);
}
}
//读取结束,输出结果
if(currentpaper == null){
System.out.println("The test paper number does not exist");
}else {
//判断并输出结果
answerSheet.outputResults(studentId, studentName);
}
}
}
`
说到设计我觉得类的设计是极为重要的,可能就像是电脑中各种硬件的分配,拿我的电脑来说有一个极大的缺陷是容易黑屏,因为电脑中容易发热的硬件及设施大多都放的较为集中,且散热困难,这也是为什么被称为黑屏精灵,我认为这是一个非常典型的在设计方面出现了缺陷,并不是说不能运行,或是设计有问题,而是之间的关系出现了问题,所以我说类间关系也极为关键,再拿单一职责原则和开放-封闭原则来说,一个是说一个类应该只有一个引起它变化的原因,即一个类只负责一项职责,另一个是软件实体应当对扩展开放,对修改封闭。这意味着设计时应当使软件模块易于扩展,但是不需要修改现有代码。应用场景:当需要添加新的功能时,可以通过继承或组合现有类来实现,而不是修改现有类。这些都表明类的设计是很重要的。
三、采坑心得
首先类设计一定要多多考虑,在一开始的思考肯定是想不到所有的问题这也是为什么我们要学会进行补充与拓展
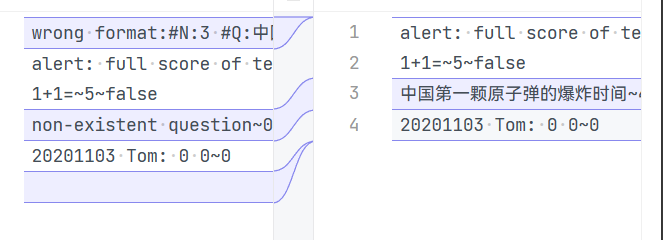
拿这个来举例我发现我的纯字符串类的输入都会显示format,所以我猜测是我的答卷类或题目类错误了,实际上我发现这样的改错并不困难,找到错误的地方才是艰难的,这需要你对于自己代码的理解以及题目的分析,并且我发现在写一些方法类的时候可以多尝试用接口,接口的规范性和拓展性在写这种不断迭代的题是具有非常大的好处的,不然就会像我一样还需要不断的在代码中寻找具体的实现再在调用方法的地方各处修改。
(果然第一次作业写的时候就感觉有点不对劲,导致第二次要推倒重来,好不舍得啊!)
四、改进建议
运行测试点都没全过还可以努力尝试修改,然后就是一些能多建类,确保单一职责也更方便修改及拓展还有在设计系统时,应该依赖于接口或者抽象类,而不是具体实现以及减少对象之间的耦合,提高模块的独立性。
五、总结
首先明确面向对象程序设计所拥有的东西。
一、核心概念
对象:面向对象编程将现实世界中的具体事物抽象成对象,这些对象具有状态(属性)和行为(方法)。
类:类是对具有相同或相似性质的对象的抽象,它定义了对象的属性和方法。
封装性:对象将内部状态和操作封装起来,只向外界暴露必要的接口,以保护数据和隔离复杂性。
继承性:类可以继承其他类的属性和方法,从而实现代码的重用和扩展。
多态性:对象可以根据参数的类型和数量产生不同的操作,同时在不同的环境中有不同的表现。
二、主要特点
抽象性:通过抽象出共性和特性,形成类和对象,减少了对现实世界的直接描述,提高了代码的可重用性和可维护性。
模块化:面向对象编程将程序拆分为多个模块,每个模块负责一个独立的功能,提高了程序的可维护性和可扩展性。
事件驱动:对象可以通过事件触发其他对象的操作,实现程序的动态性和交互性。
三、应用与优势
面向对象程序设计已广泛应用于多个领域,如数据库系统、交互式界面、分布式系统、人工智能等。其优势在于:
提高代码的可重用性:通过继承和多态等特性,可以实现代码的重用,减少重复劳动。
增强程序的可维护性:模块化设计和封装性使得程序更易于理解和修改。
提升开发效率:抽象类和接口等机制可以规范开发过程,提高开发效率。
适应性强:面向对象程序设计可以更好地模拟现实世界,适应复杂多变的需求。
于我们现在所做的则是重点在于设计而非语法,但我们可以更多的学习一些东西,比如正则表达式,能够帮我们大大减少代码量达到需要的效果,还有需要学会优化逻辑优化结构。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号