RMI基础
从 IDEA 断点分析 RMI 通信原理
1. 流程分析总览
首先 RMI 有三部分:
·RMI Registry
·RMI Server
·RMI Client
关于流程图,放在文件里面了
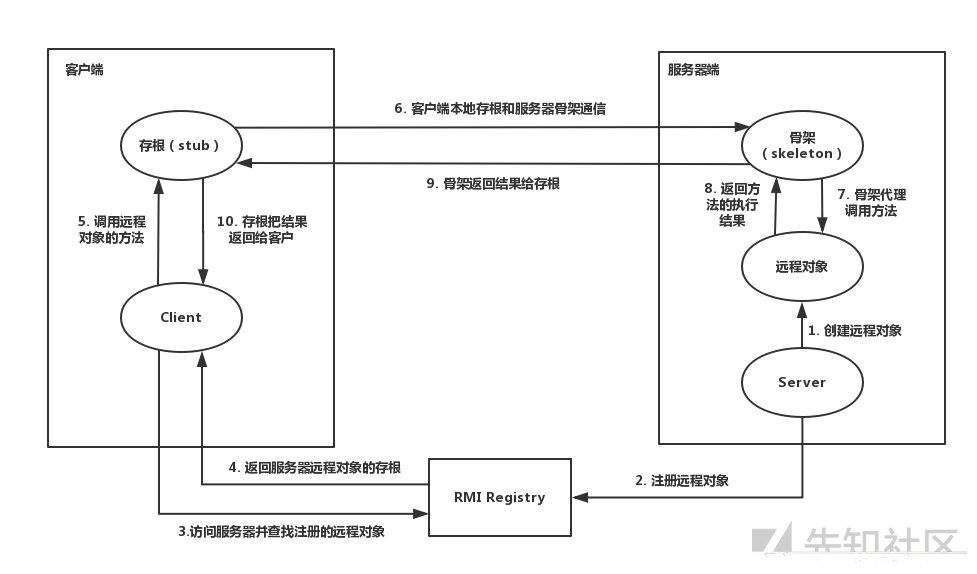
2. 服务注册
① 远程对象创建
RMIServer
public class RMIServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
IRemoteObj remoteObj = new RemoteObjImpl();
// Registry r = LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1099);
// r.bind("remoteObj",remoteObj);
}
}
RemoteObjImpl(Impl接口实现类的意思)
public class RemoteObjImpl extends UnicastRemoteObject implements IRemoteObj {
public RemoteObjImpl() throws RemoteException{
}
public String sayHello(String keywords){
String upKeywords = keywords.toUpperCase();
System.out.println(upKeywords);
return upKeywords;
}
}
我们来研究一下,他是怎么把服务器发到网络上的,在RMIServer的IRemoteObj remoteObj = new RemoteObjImpl();打个断点,开始调试,f7进入,然后shift+f7,再次进入。
protected UnicastRemoteObject() throws RemoteException
{
this(0);
}
RemoteObjImpl 这个类是继承于 UnicastRemoteObject 的,所以先会到父类的构造函数,父类的构造函数这里的 port 传入了 0,它代表一个随机端口,我们f7接着进去。
protected UnicastRemoteObject(int port) throws RemoteException
{
this.port = port;
exportObject((Remote) this, port);
}
然后父类把port赋值为0,远程服务这里如果传入的是 0,它会被发布到网络上的一个随机端口,我们可以继续往下看一看。先 f8 到 exportObject(),再 f7 跳进去看
public static Remote exportObject(Remote obj, int port)
throws RemoteException
{
return exportObject(obj, new UnicastServerRef(port));
}
exportObject() 是一个静态函数,它就是主要负责将远程服务发布到网络上
我们来看这个静态函数,第一个参数是 obj 对象,第二个参数是 new UnicastServerRef(port),第二个参数是用来处理网络请求的。继续往下面跟,去到了 UnicastServerRef 的构造函数。这里跟的操作先 f7,然后点击 UnicastServerRef 跟进
public UnicastServerRef(int port) {
super(new LiveRef(port));
}
跟进去之后UnicastServerRef的构造函数,我们看到它new了一个 LiveRef(port),这个非常重要,它算是一个网络引用的类,跟进this看一看。
public LiveRef(ObjID objID, int port) {
this(objID, TCPEndpoint.getLocalEndpoint(port), true);
}
第一个参数 ID,第三个参数为 true,所以我们重点关注一下第二个参数。
TCPEndpoint 是一个网络请求的类,我们可以去看一下它的构造函数,传参进去一个 IP 与一个端口,也就是说传进去一个 IP 和一个端口,就可以进行网络请求。
public TCPEndpoint(String host, int port) {
this(host, port, null, null);
}
我们进入LiveRef的构造函数
public LiveRef(ObjID objID, Endpoint endpoint, boolean isLocal) {
ep = endpoint;
id = objID;
this.isLocal = isLocal;
}
这时候我们可以看一下一些赋值,发现 host 和 port 是赋值到了 endpoint 里面,而 endpoint 又是被封装在 LiveRef 里面的,所以记住数据是在 LiveRef 里面即可,并且这一LiveRef至始至终只会存在一个。
回到上文那个地方,继续 f7 进入 super 看一看它的父类 UnicastRef,这里就证明整个创建远程服务的过程只会存在一个 LiveRef。
public UnicastRef(LiveRef liveRef) {
ref = liveRef;
}
一路 f7 到一个静态函数 exportObject(),我们后续的操作过程都与 exportObject() 有关,基本都是在调用它,这一段不是很重要,一路 f7 就好了。直到此处出现 Stub,在sun.rmi.server.Util#createProxy()
public Remote exportObject(Remote impl, Object data,
boolean permanent)
throws RemoteException
{
Class<?> implClass = impl.getClass();
Remote stub;
try {
stub = Util.createProxy(implClass, getClientRef(), forceStubUse);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
throw new ExportException(
"remote object implements illegal remote interface", e);
}
if (stub instanceof RemoteStub) {
setSkeleton(impl);
}
Target target =
new Target(impl, this, stub, ref.getObjID(), permanent);
ref.exportObject(target);
hashToMethod_Map = hashToMethod_Maps.get(implClass);
return stub;
}
RMI 先在 Service 的地方,也就是服务端创建一个 Stub,再把 Stub 传到 RMI Registry 中,最后让 RMI Client 去获取 Stub,不过这个取值不是序列化而是传值
我们进去研究一下怎么创建的
public static Remote createProxy(Class<?> implClass,
RemoteRef clientRef,
boolean forceStubUse)
throws StubNotFoundException
{
Class<?> remoteClass;
try {
remoteClass = getRemoteClass(implClass);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex ) {
throw new StubNotFoundException(
"object does not implement a remote interface: " +
implClass.getName());
}
if (forceStubUse ||
!(ignoreStubClasses || !stubClassExists(remoteClass)))
{
return createStub(remoteClass, clientRef);
}
final ClassLoader loader = implClass.getClassLoader();
final Class<?>[] interfaces = getRemoteInterfaces(implClass);
final InvocationHandler handler =
new RemoteObjectInvocationHandler(clientRef);
/* REMIND: private remote interfaces? */
try {
return AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Remote>() {
public Remote run() {
return (Remote) Proxy.newProxyInstance(loader,
interfaces,
handler);
}});
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
throw new StubNotFoundException("unable to create proxy", e);
}
}
这个判断暂时不用管,后续我们会碰到,那个时候再讲,然后这个if是不会通过的,再往下走,我们可以看到这是很明显的类加载的地方
final ClassLoader loader = implClass.getClassLoader();
final Class<?>[] interfaces = getRemoteInterfaces(implClass);
final InvocationHandler handler =
new RemoteObjectInvocationHandler(clientRef);
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Remote>() {
public Remote run() {
return (Remote) Proxy.newProxyInstance(loader,
interfaces,
handler);
第一个参数是 AppClassLoader,第二个参数是一个远程接口,第三个参数是调用处理器,调用处理器里面只有一个 ref,它也是和之前我们看到的 ref 是同一个,创建远程服务当中永远只有一个 ref,此处就把动态代理创建好了。
首先来看一下 RemoteObjectInvocationHandler 这个动态代理,继承 RemoteObject 实现 InvocationHandler,因此这是一个可序列化的、可使用 RMI 远程传输的动态代理类。既然是动态代理类,自然重点关注 invoke 方法,可以看到如果是Object的方法会调用 invokeObjectMethod 方法,其他的则调用 invokeRemoteMethod 方法。
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)
throws Throwable
{
if (! Proxy.isProxyClass(proxy.getClass())) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("not a proxy");
}
if (Proxy.getInvocationHandler(proxy) != this) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("handler mismatch");
}
if (method.getDeclaringClass() == Object.class) {
return invokeObjectMethod(proxy, method, args);
} else if ("finalize".equals(method.getName()) && method.getParameterCount() == 0 &&
!allowFinalizeInvocation) {
return null; // ignore
} else {
return invokeRemoteMethod(proxy, method, args);
}
}
而在invokeRemoteMethod 中实际是委托 RemoteRef 的子类 UnicastRef 的invoke方法执行调用。
public Object invoke(Remote obj,
Method method,
Object[] params,
long opnum)
throws Exception
{
if (clientRefLog.isLoggable(Log.VERBOSE)) {
clientRefLog.log(Log.VERBOSE, "method: " + method);
}
if (clientCallLog.isLoggable(Log.VERBOSE)) {
logClientCall(obj, method);
}
Connection conn = ref.getChannel().newConnection();
RemoteCall call = null;
boolean reuse = true;
boolean alreadyFreed = false;
try {
if (clientRefLog.isLoggable(Log.VERBOSE)) {
clientRefLog.log(Log.VERBOSE, "opnum = " + opnum);
}
// create call context
call = new StreamRemoteCall(conn, ref.getObjID(), -1, opnum);
// marshal parameters
try {
ObjectOutput out = call.getOutputStream();
marshalCustomCallData(out);
Class<?>[] types = method.getParameterTypes();
for (int i = 0; i < types.length; i++) {
marshalValue(types[i], params[i], out);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
clientRefLog.log(Log.BRIEF,
"IOException marshalling arguments: ", e);
throw new MarshalException("error marshalling arguments", e);
}
// unmarshal return
call.executeCall();
try {
Class<?> rtype = method.getReturnType();
if (rtype == void.class)
return null;
ObjectInput in = call.getInputStream();
ref.getChannel().free(conn, true);
return returnValue;
} catch (IOException e) {
clientRefLog.log(Log.BRIEF,
"IOException unmarshalling return: ", e);
throw new UnmarshalException("error unmarshalling return", e);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
clientRefLog.log(Log.BRIEF,
"ClassNotFoundException unmarshalling return: ", e);
throw new UnmarshalException("error unmarshalling return", e);
} finally {
try {
call.done();
} catch (IOException e) {
reuse = false;
}
}
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
if ((call == null) ||
(((StreamRemoteCall) call).getServerException() != e))
{
reuse = false;
}
throw e;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
reuse = false;
throw e;
} catch (Error e) {
reuse = false;
throw e;
} finally {
if (!alreadyFreed) {
if (clientRefLog.isLoggable(Log.BRIEF)) {
clientRefLog.log(Log.BRIEF, "free connection (reuse = " +
reuse + ")");
}
ref.getChannel().free(conn, reuse);
}
}
}
private Object invokeRemoteMethod(Object proxy,
Method method,
Object[] args)
throws Exception
{
try {
if (!(proxy instanceof Remote)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"proxy not Remote instance");
}
return ref.invoke((Remote) proxy, method, args,
getMethodHash(method));
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!(e instanceof RuntimeException)) {
Class<?> cl = proxy.getClass();
try {
method = cl.getMethod(method.getName(),
method.getParameterTypes());
} catch (NoSuchMethodException nsme) {
throw (IllegalArgumentException)
new IllegalArgumentException().initCause(nsme);
}
Class<?> thrownType = e.getClass();
for (Class<?> declaredType : method.getExceptionTypes()) {
if (declaredType.isAssignableFrom(thrownType)) {
throw e;
}
}
e = new UnexpectedException("unexpected exception", e);
}
throw e;
}
}
UnicastRef 的 invoke 方法是一个建立连接,执行调用,并读取结果并反序列化的过程。这里,UnicastRef 包含属性LiveRef,LiveRef 类中的 Endpoint、Channel 封装了与网络通信相关的方法。
ok,创建完这个stub后
if (stub instanceof RemoteStub) {
setSkeleton(impl);
}
先是经过上面这个判断,他的意思是检测 stub 是否是 RemoteStub 的实例,简而言之,就是问他是不是给注册中心的,显然不是,这个实例是搞一个远程对象的,所以不会进入
Target target =
new Target(impl, this, stub, ref.getObjID(), permanent);
继续 f8,到 Target 这里,使用这个 Target 对象封装了我们远程执行方法和生成的动态代理类(Stub)
public Target(Remote impl, Dispatcher disp, Remote stub, ObjID id,
boolean permanent)
{
this.weakImpl = new WeakRef(impl, ObjectTable.reapQueue);
this.disp = disp;
this.stub = stub;
this.id = id;
this.acc = AccessController.getContext();
ClassLoader threadContextLoader =
Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
ClassLoader serverLoader = impl.getClass().getClassLoader();
if (checkLoaderAncestry(threadContextLoader, serverLoader)) {
this.ccl = threadContextLoader;
} else {
this.ccl = serverLoader;
}
this.permanent = permanent;
if (permanent) {
pinImpl();
}
}
f8调用LiveRef#exportObject接着调用 sun.rmi.transport.tcp.TCPEndpoint#exportObject 监听本地端口。
public void exportObject(Target target) throws RemoteException {
synchronized (this) {
listen();
exportCount++;
}
boolean ok = false;
try {
super.exportObject(target);
ok = true;
} finally {
if (!ok) {
synchronized (this) {
decrementExportCount();
}
}
}
}
从这里开始,第一句语句 listen,真正处理网络请求了跟进去。
先获取 TCPEndpoint然后我们继续 f8 往后看,直到 server = ep.newServerSocket();
ServerSocket newServerSocket() throws IOException {
if (TCPTransport.tcpLog.isLoggable(Log.VERBOSE)) {
TCPTransport.tcpLog.log(Log.VERBOSE,
"creating server socket on " + this);
}
RMIServerSocketFactory serverFactory = ssf;
if (serverFactory == null) {
serverFactory = chooseFactory();
}
ServerSocket server = serverFactory.createServerSocket(listenPort);
// if we listened on an anonymous port, set the default port
// (for this socket factory)
if (listenPort == 0)
setDefaultPort(server.getLocalPort(), csf, ssf);
return server;
}
他开了一个socket,已经准备好了,等别人来连接
if (listenPort == 0)
setDefaultPort(server.getLocalPort(), csf, ssf);
若前面端口是0,那么就会给你随机一个端口
我们回到TCPTransport#exportObject,然后我们接着往下走,进入到Transport#exportObject
public void exportObject(Target target) throws RemoteException {
target.setExportedTransport(this);
ObjectTable.putTarget(target);
}
将 Target 实例注册到 ObjectTable 中。ObjectTable 用来管理所有发布的服务实例 Target,进入ObjectTable.putTarget(target)
static void putTarget(Target target) throws ExportException {
ObjectEndpoint oe = target.getObjectEndpoint();
WeakRef weakImpl = target.getWeakImpl();
if (DGCImpl.dgcLog.isLoggable(Log.VERBOSE)) {
DGCImpl.dgcLog.log(Log.VERBOSE, "add object " + oe);
}
synchronized (tableLock) {
if (target.getImpl() != null) {
if (objTable.containsKey(oe)) {
throw new ExportException(
"internal error: ObjID already in use");
} else if (implTable.containsKey(weakImpl)) {
throw new ExportException("object already exported");
}
objTable.put(oe, target);
implTable.put(weakImpl, target);
if (!target.isPermanent()) {
incrementKeepAliveCount();
}
}
}
}
② 注册中心创建
public class RMIServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
IRemoteObj remoteObj = new RemoteObjImpl();
Registry r = LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1099);
r.bind("remoteObj",remoteObj);
}
}
在第二句打上断点,然后进入createRegistry.
public static Registry createRegistry(int port) throws RemoteException {
return new RegistryImpl(port);
}
然后接着f7,到了RegistryImpl
public RegistryImpl(int port)
throws RemoteException
{
if (port == Registry.REGISTRY_PORT && System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
// grant permission for default port only.
try {
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedExceptionAction<Void>() {
public Void run() throws RemoteException {
LiveRef lref = new LiveRef(id, port);
setup(new UnicastServerRef(lref));
return null;
}
}, null, new SocketPermission("localhost:"+port, "listen,accept"));
} catch (PrivilegedActionException pae) {
throw (RemoteException)pae.getException();
}
} else {
LiveRef lref = new LiveRef(id, port);
setup(new UnicastServerRef(lref));
}
}
先判断 port 是否为注册中心的1099,以及是否开启了 SecurityManager,也就是一系列的安全检查。然后就不会进入,他会进入,RegistryImpl 的构造方法中创建LiveRef对象,然后创建 UnicastServerRef 对象,最后调用 setup 进行配置。
LiveRef lref = new LiveRef(id, port);
setup(new UnicastServerRef(lref));
我们目光转向setup
private void setup(UnicastServerRef uref)
throws RemoteException
{
ref = uref;
uref.exportObject(this, null, true);
}
跟进之后发现和之前是一样的,也是先赋值,然后进行 exportObject() 方法的调用。区别在于第三个参数的不同,名为 permanent,第一张是 false,第二张是 true,这代表我们创建注册中心这个对象,是一个永久对象,而之前远程对象是一个临时对象。f7。 在 exportObject 方法中,重要的一步就是使用Util.createProxy()来创建动态代理,
public Remote exportObject(Remote impl, Object data,
boolean permanent)
throws RemoteException
{
Class<?> implClass = impl.getClass();
Remote stub;
try {
stub = Util.createProxy(implClass, getClientRef(), forceStubUse);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
throw new ExportException(
"remote object implements illegal remote interface", e);
}
if (stub instanceof RemoteStub) {
setSkeleton(impl);
}
Target target =
new Target(impl, this, stub, ref.getObjID(), permanent);
ref.exportObject(target);
hashToMethod_Map = hashToMethod_Maps.get(implClass);
return stub;
}
我们到stub = Util.createProxy(implClass, getClientRef(), forceStubUse);看看,之前提到对远程对象使用 RemoteObjectInvocationHandler 来创建,但是之前有一个 stubClassExists 的判断。
public static Remote createProxy(Class<?> implClass,
RemoteRef clientRef,
boolean forceStubUse)
throws StubNotFoundException
{
Class<?> remoteClass;
try {
remoteClass = getRemoteClass(implClass);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex ) {
throw new StubNotFoundException(
"object does not implement a remote interface: " +
implClass.getName());
}
if (forceStubUse ||
!(ignoreStubClasses || !stubClassExists(remoteClass)))
{
return createStub(remoteClass, clientRef);
}
final ClassLoader loader = implClass.getClassLoader();
final Class<?>[] interfaces = getRemoteInterfaces(implClass);
final InvocationHandler handler =
new RemoteObjectInvocationHandler(clientRef);
/* REMIND: private remote interfaces? */
try {
return AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Remote>() {
public Remote run() {
return (Remote) Proxy.newProxyInstance(loader,
interfaces,
handler);
}});
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
throw new StubNotFoundException("unable to create proxy", e);
}
}
首先这里要做一个判断。可以跟进 stubClassExists 进行判断
private static boolean stubClassExists(Class<?> remoteClass) {
if (!withoutStubs.containsKey(remoteClass)) {
try {
Class.forName(remoteClass.getName() + "_Stub",
false,
remoteClass.getClassLoader());
return true;
} catch (ClassNotFoundException cnfe) {
withoutStubs.put(remoteClass, null);
}
}
return false;
}
我们看到这个地方,如果需要创建代理的类在本地有 _Stub 的类,则直接使用 createStub 方法反射调用 stub 类的构造方法创建类实例。是判断是否能获取到 RegistryImpl_Stub 这个类,换句话说,也就是若 RegistryImpl_Stub 这个类存在,则返回 True,反之 False。我们可以找到 RegistryImpl_Stub 这个类是存在的。
这里由于是 RegistryImpl 这个类,系统会找到 RegistryImpl_Stub 这个类并进行实例化,RegistryImpl_Stub 继承了 RemoteStub ,实现了 Registry。这个类实现了 bind/list/lookup/rebind/unbind 等Registry定义的方法,全部是通过序列化和反序列化来实现的。
接着我们进入return createStub(remoteClass, clientRef);
private static RemoteStub createStub(Class<?> remoteClass, RemoteRef ref)
throws StubNotFoundException
{
String stubname = remoteClass.getName() + "_Stub";
try {
Class<?> stubcl =
Class.forName(stubname, false, remoteClass.getClassLoader());
Constructor<?> cons = stubcl.getConstructor(stubConsParamTypes);
return (RemoteStub) cons.newInstance(new Object[] { ref });
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new StubNotFoundException(
"Stub class not found: " + stubname, e);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new StubNotFoundException(
"Stub class missing constructor: " + stubname, e);
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
throw new StubNotFoundException(
"Can't create instance of stub class: " + stubname, e);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new StubNotFoundException(
"Stub class constructor not public: " + stubname, e);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
throw new StubNotFoundException(
"Exception creating instance of stub class: " + stubname, e);
} catch (ClassCastException e) {
throw new StubNotFoundException(
"Stub class not instance of RemoteStub: " + stubname, e);
}
}
这个就是创建一个stub,由服务端给注册中心,然后把ref传进去
因为这个stub是给注册中心的,远程连接的,所以是RemoteStub
if (stub instanceof RemoteStub) {
setSkeleton(impl);
}
继续往下,如果是服务端定义好的,就调用 setSkeleton() 方法,跟进去。
public void setSkeleton(Remote impl) throws RemoteException {
if (!withoutSkeletons.containsKey(impl.getClass())) {
try {
skel = Util.createSkeleton(impl);
} catch (SkeletonNotFoundException e) {
withoutSkeletons.put(impl.getClass(), null);
}
}
}
然后这里有一个 createSkeleton() 方法,其实就是反射实例化 RegistryImpl_Skel这个类并引用在 UnicastServerRef 的 this.skel 中
static Skeleton createSkeleton(Remote object)
throws SkeletonNotFoundException
{
Class<?> cl;
try {
cl = getRemoteClass(object.getClass());
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex ) {
throw new SkeletonNotFoundException(
"object does not implement a remote interface: " +
object.getClass().getName());
}
// now try to load the skeleton based ont he name of the class
String skelname = cl.getName() + "_Skel";
try {
Class<?> skelcl = Class.forName(skelname, false, cl.getClassLoader());
return (Skeleton)skelcl.newInstance();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new SkeletonNotFoundException("Skeleton class not found: " +
skelname, ex);
} catch (InstantiationException ex) {
throw new SkeletonNotFoundException("Can't create skeleton: " +
skelname, ex);
} catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new SkeletonNotFoundException("No public constructor: " +
skelname, ex);
} catch (ClassCastException ex) {
throw new SkeletonNotFoundException(
"Skeleton not of correct class: " + skelname, ex);
}
}
RegistryImpl_Skel 类提供了 dispatch 方法来分发具体的操作。
public void dispatch(Remote var1, RemoteCall var2, int var3, long var4) throws Exception {
if (var4 != 4905912898345647071L) {
throw new SkeletonMismatchException("interface hash mismatch");
} else {
RegistryImpl var6 = (RegistryImpl)var1;
String var7;
Remote var8;
ObjectInput var10;
ObjectInput var11;
switch (var3) {
case 0:
try {
var11 = var2.getInputStream();
var7 = (String)var11.readObject();
var8 = (Remote)var11.readObject();
} catch (IOException var94) {
throw new UnmarshalException("error unmarshalling arguments", var94);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException var95) {
throw new UnmarshalException("error unmarshalling arguments", var95);
} finally {
var2.releaseInputStream();
}
var6.bind(var7, var8);
try {
var2.getResultStream(true);
break;
} catch (IOException var93) {
throw new MarshalException("error marshalling return", var93);
}
case 1:
var2.releaseInputStream();
String[] var97 = var6.list();
try {
ObjectOutput var98 = var2.getResultStream(true);
var98.writeObject(var97);
break;
} catch (IOException var92) {
throw new MarshalException("error marshalling return", var92);
}
case 2:
try {
var10 = var2.getInputStream();
var7 = (String)var10.readObject();
} catch (IOException var89) {
throw new UnmarshalException("error unmarshalling arguments", var89);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException var90) {
throw new UnmarshalException("error unmarshalling arguments", var90);
} finally {
var2.releaseInputStream();
}
var8 = var6.lookup(var7);
try {
ObjectOutput var9 = var2.getResultStream(true);
var9.writeObject(var8);
break;
} catch (IOException var88) {
throw new MarshalException("error marshalling return", var88);
}
case 3:
try {
var11 = var2.getInputStream();
var7 = (String)var11.readObject();
var8 = (Remote)var11.readObject();
} catch (IOException var85) {
throw new UnmarshalException("error unmarshalling arguments", var85);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException var86) {
throw new UnmarshalException("error unmarshalling arguments", var86);
} finally {
var2.releaseInputStream();
}
var6.rebind(var7, var8);
try {
var2.getResultStream(true);
break;
} catch (IOException var84) {
throw new MarshalException("error marshalling return", var84);
}
case 4:
try {
var10 = var2.getInputStream();
var7 = (String)var10.readObject();
} catch (IOException var81) {
throw new UnmarshalException("error unmarshalling arguments", var81);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException var82) {
throw new UnmarshalException("error unmarshalling arguments", var82);
} finally {
var2.releaseInputStream();
}
var6.unbind(var7);
try {
var2.getResultStream(true);
break;
} catch (IOException var80) {
throw new MarshalException("error marshalling return", var80);
}
default:
throw new UnmarshalException("invalid method number");
}
}
}
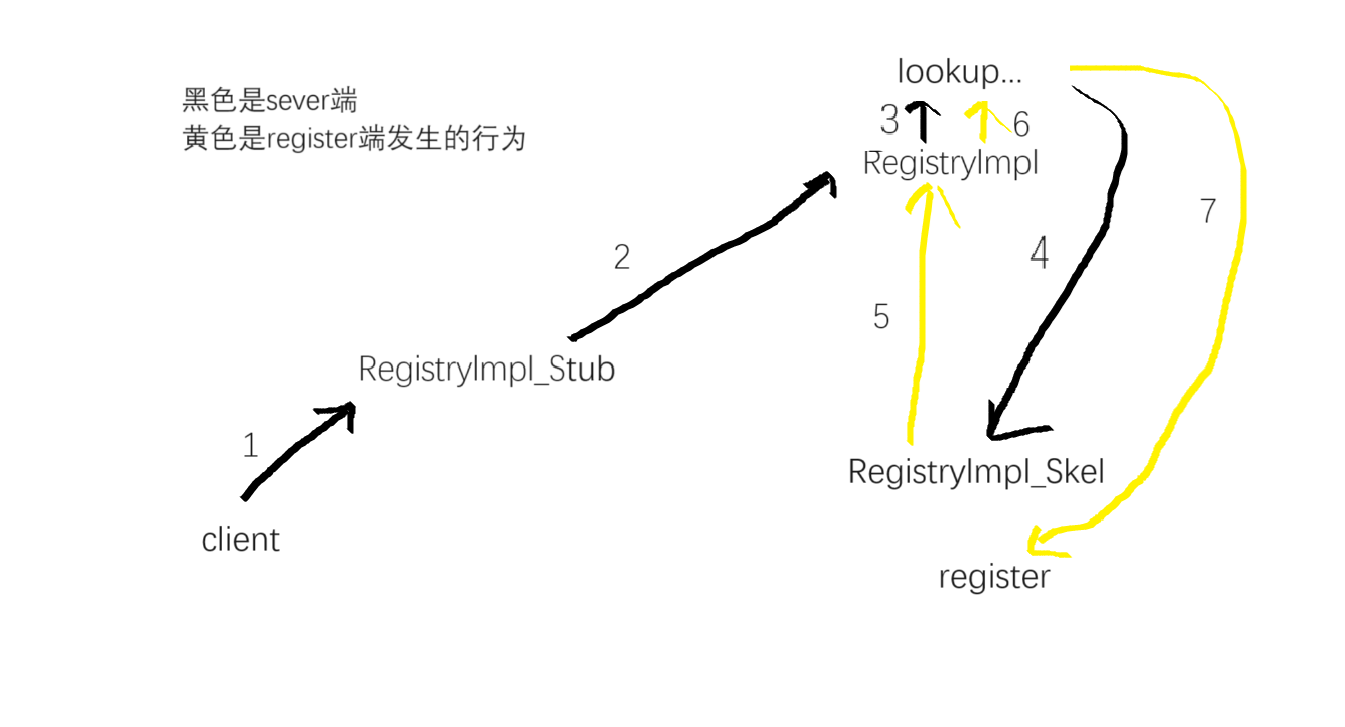
这里要注意一个东西,这个Registrylmpl_Stub是客户端和服务端序列化给注册中心的一个类,Registrylmpl_Skel是注册中心反序列化客户端和服务端给的东西的一个类
后续的 export 流程相同。
③ 服务注册
注册说白了就是 bind 的过程,通常情况下,如果 Server 端和 Registry 在同一端,我们可以直接调用Registry 的 bind 方法进行绑定,具体实现在RegistryImpl的 bind 方法,就是将 Remote 对象和名称 String 放在成员变量 bindings 中,这是一个Hashtable对象。
public void bind(String name, Remote obj)
throws RemoteException, AlreadyBoundException, AccessException
{
checkAccess("Registry.bind");
synchronized (bindings) {
Remote curr = bindings.get(name);
if (curr != null)
throw new AlreadyBoundException(name);
bindings.put(name, obj);
}
}
如果 Server 端和Registry端不在一起,那我们需要先获取 Registry 对象,无论是使用 Naming 或者 LocateRegistry 都是调用 LocateRegistry.getRegistry() 方法来创建 Registry,这部分的创建过程与后面一致的。一些具体的逻辑放在下面服务发现来一起说。
public static Registry getRegistry(String host, int port,
RMIClientSocketFactory csf)
throws RemoteException
{
Registry registry = null;
if (port <= 0)
port = Registry.REGISTRY_PORT;
if (host == null || host.length() == 0) {
// If host is blank (as returned by "file:" URL in 1.0.2 used in
// java.rmi.Naming), try to convert to real local host name so
// that the RegistryImpl's checkAccess will not fail.
try {
host = java.net.InetAddress.getLocalHost().getHostAddress();
} catch (Exception e) {
// If that failed, at least try "" (localhost) anyway...
host = "";
}
}
LiveRef liveRef =
new LiveRef(new ObjID(ObjID.REGISTRY_ID),
new TCPEndpoint(host, port, csf, null),
false);
RemoteRef ref =
(csf == null) ? new UnicastRef(liveRef) : new UnicastRef2(liveRef);
return (Registry) Util.createProxy(RegistryImpl.class, ref, false);
}
3.服务发现
如果 Server 端和 Registry 在同一端,那可以直接使用在创建 Registry 时使用的 RegistryImpl, 直接调用其相关方法,这没什么好说的。
如果Server端和 Registry 不同端,则在 Server 端或 Client 端使用 LocateRegistry.getRegistry() 方法获取注册中心时都是一样的流程:
首先在本地创建了一个包含了具体通信地址、端口的 RegistryImpl_Stub 对象
通过调用这个本地的 RegistryImpl_Stub 对象的 bind/list... 等方法,来与 Registry 端进行通信
而 RegistryImpl_Stub 的每个方法,都实际上调用了 RemoteRef 的 invoke 方法,进行了一次远程调用链接
这个过程使用 java 原生序列化及反序列化来实现
获取了注册中心后,如果是 Server 端,我们希望在注册中心上绑定(bind)我们的服务,如果是 Client 端,我们希望在注册中心遍历(list)、查找(lookup)和调用服务,查找的逻辑我们放在下一部分服务调用来说,这里主要关注绑定的过程。我们来看看RegistryImpl_Stub#bind
public void bind(String var1, Remote var2) throws AccessException, AlreadyBoundException, RemoteException {
try {
RemoteCall var3 = super.ref.newCall(this, operations, 0, 4905912898345647071L);
try {
ObjectOutput var4 = var3.getOutputStream();
var4.writeObject(var1);
var4.writeObject(var2);
} catch (IOException var5) {
throw new MarshalException("error marshalling arguments", var5);
}
super.ref.invoke(var3);
super.ref.done(var3);
} catch (RuntimeException var6) {
throw var6;
} catch (RemoteException var7) {
throw var7;
} catch (AlreadyBoundException var8) {
throw var8;
} catch (Exception var9) {
throw new UnexpectedException("undeclared checked exception", var9);
}
}
对于 Server 端向注册中心上绑定(bind)来说,无论是Registry还是 Naming 的 bind 方法,实际上都是调用 Server 端生成的本地 RegistryImpl_Stub 的bind方法。这个方法比较简单粗暴,建立连接然后向流里 writeObject 。实际通过调用 UnicastRef 的invoke方法来进行网络传输。
public Object invoke(Remote obj, Method method, Object[] params, long opnum)
throws Exception
{
if (clientRefLog.isLoggable(Log.VERBOSE)) {
clientRefLog.log(Log.VERBOSE, "method: " + method);
}
if (clientCallLog.isLoggable(Log.VERBOSE)) {
logClientCall(obj, method);
}
Connection conn = ref.getChannel().newConnection();
RemoteCall call = null;
boolean reuse = true;
boolean alreadyFreed = false;
try {
if (clientRefLog.isLoggable(Log.VERBOSE)) {
clientRefLog.log(Log.VERBOSE, "opnum = " + opnum);
}
call = new StreamRemoteCall(conn, ref.getObjID(), -1, opnum);
try {
ObjectOutput out = call.getOutputStream();
marshalCustomCallData(out);
Class<?>[] types = method.getParameterTypes();
for (int i = 0; i < types.length; i++) {
marshalValue(types[i], params[i], out);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
clientRefLog.log(Log.BRIEF, "IOException marshalling arguments: ", e);
throw new MarshalException("error marshalling arguments", e);
}
call.executeCall();
try {
Class<?> rtype = method.getReturnType();
if (rtype == void.class)
return null;
ObjectInput in = call.getInputStream();
Object returnValue = unmarshalValue(rtype, in);
alreadyFreed = true;
clientRefLog.log(Log.BRIEF, "free connection (reuse = true)");
ref.getChannel().free(conn, true);
return returnValue;
} catch (IOException e) {
clientRefLog.log(Log.BRIEF, "IOException unmarshalling return: ", e);
throw new UnmarshalException("error unmarshalling return", e);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
clientRefLog.log(Log.BRIEF, "ClassNotFoundException unmarshalling return: ", e);
throw new UnmarshalException("error unmarshalling return", e);
} finally {
try {
call.done();
} catch (IOException e) {
reuse = false;
}
}
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
if ((call == null) || (((StreamRemoteCall) call).getServerException() != e)) {
reuse = false;
}
throw e;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
reuse = false;
throw e;
} catch (Error e) {
reuse = false;
throw e;
} finally {
if (!alreadyFreed) {
if (clientRefLog.isLoggable(Log.BRIEF)) {
clientRefLog.log(Log.BRIEF, "free connection (reuse = " + reuse + ")");
}
ref.getChannel().free(conn, reuse);
}
}
}
其中的这一部分
ObjectOutput out = call.getOutputStream();
marshalCustomCallData(out);
Class<?>[] types = method.getParameterTypes();
for (int i = 0; i < types.length; i++) {
marshalValue(types[i], params[i], out);
}
他就是获取信息流,然后序列化他,marshalValue这个是用来序列化的
那在 Registry 端都做了什么呢?
在 Registry 端,由 sun.rmi.transport.tcp.TCPTransport#handleMessages 来处理请求,调用 Transport#serviceCall 方法处理。
TCPTransport#exportObject --> TCPTransport#listen() --> TCPTransport#AcceptLoop --> TCPTransport#run() -->TCPTransport#executeAcceptLoop --> TCPTransport#ConnectionHandler --> TCPTransport#run0 -->TCPTransport#handleMessages --> Transport#serviceCall
public boolean serviceCall(final RemoteCall call) {
try {
/* read object id */
final Remote impl;
ObjID id;
try {
id = ObjID.read(call.getInputStream());
} catch (java.io.IOException e) {
throw new MarshalException("unable to read objID", e);
}
/* get the remote object */
Transport transport = id.equals(dgcID) ? null : this;
Target target =
ObjectTable.getTarget(new ObjectEndpoint(id, transport));
if (target == null || (impl = target.getImpl()) == null) {
throw new NoSuchObjectException("no such object in table");
}
final Dispatcher disp = target.getDispatcher();
target.incrementCallCount();
try {
/* call the dispatcher */
transportLog.log(Log.VERBOSE, "call dispatcher");
final AccessControlContext acc =
target.getAccessControlContext();
ClassLoader ccl = target.getContextClassLoader();
ClassLoader savedCcl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
try {
setContextClassLoader(ccl);
currentTransport.set(this);
try {
java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(
new java.security.PrivilegedExceptionAction<Void>() {
public Void run() throws IOException {
checkAcceptPermission(acc);
disp.dispatch(impl, call);
return null;
}
}, acc);
} catch (java.security.PrivilegedActionException pae) {
throw (IOException) pae.getException();
}
} finally {
setContextClassLoader(savedCcl);
currentTransport.set(null);
}
} catch (IOException ex) {
transportLog.log(Log.BRIEF,
"exception thrown by dispatcher: ", ex);
return false;
} finally {
target.decrementCallCount();
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// if calls are being logged, write out exception
if (UnicastServerRef.callLog.isLoggable(Log.BRIEF)) {
// include client host name if possible
String clientHost = "";
try {
clientHost = "[" +
RemoteServer.getClientHost() + "] ";
} catch (ServerNotActiveException ex) {
}
String message = clientHost + "exception: ";
UnicastServerRef.callLog.log(Log.BRIEF, message, e);
}
/* We will get a RemoteException if either a) the objID is
* not readable, b) the target is not in the object table, or
* c) the object is in the midst of being unexported (note:
* NoSuchObjectException is thrown by the incrementCallCount
* method if the object is being unexported). Here it is
* relatively safe to marshal an exception to the client
* since the client will not have seen a return value yet.
*/
try {
ObjectOutput out = call.getResultStream(false);
UnicastServerRef.clearStackTraces(e);
out.writeObject(e);
call.releaseOutputStream();
} catch (IOException ie) {
transportLog.log(Log.BRIEF,
"exception thrown marshalling exception: ", ie);
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
serviceCall 方法中从 ObjectTable 中获取封装的 Target 对象,并获取其中的封装的UnicastServerRef以及RegistryImpl对象。然后调用 UnicastServerRef 的 dispatch 方法
public void dispatch(Remote obj, RemoteCall call) throws IOException {
// positive operation number in 1.1 stubs;
// negative version number in 1.2 stubs and beyond...
int num;
long op;
try {
// read remote call header
ObjectInput in;
try {
in = call.getInputStream();
num = in.readInt();
if (num >= 0) {
if (skel != null) {
oldDispatch(obj, call, num);
return;
} else {
throw new UnmarshalException(
"skeleton class not found but required " +
"for client version");
}
}
op = in.readLong();
} catch (Exception readEx) {
throw new UnmarshalException("error unmarshalling call header",
readEx);
}
/*
* Since only system classes (with null class loaders) will be on
* the execution stack during parameter unmarshalling for the 1.2
* stub protocol, tell the MarshalInputStream not to bother trying
* to resolve classes using its superclasses's default method of
* consulting the first non-null class loader on the stack.
*/
MarshalInputStream marshalStream = (MarshalInputStream) in;
marshalStream.skipDefaultResolveClass();
Method method = hashToMethod_Map.get(op);
if (method == null) {
throw new UnmarshalException("unrecognized method hash: " +
"method not supported by remote object");
}
// if calls are being logged, write out object id and operation
logCall(obj, method);
// unmarshal parameters
Class<?>[] types = method.getParameterTypes();
Object[] params = new Object[types.length];
try {
unmarshalCustomCallData(in);
for (int i = 0; i < types.length; i++) {
params[i] = unmarshalValue(types[i], in);
}
} catch (java.io.IOException e) {
throw new UnmarshalException(
"error unmarshalling arguments", e);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new UnmarshalException(
"error unmarshalling arguments", e);
} finally {
call.releaseInputStream();
}
// make upcall on remote object
Object result;
try {
result = method.invoke(obj, params);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
throw e.getTargetException();
}
// marshal return value
try {
ObjectOutput out = call.getResultStream(true);
Class<?> rtype = method.getReturnType();
if (rtype != void.class) {
marshalValue(rtype, result, out);
}
} catch (IOException ex) {
throw new MarshalException("error marshalling return", ex);
/*
* This throw is problematic because when it is caught below,
* we attempt to marshal it back to the client, but at this
* point, a "normal return" has already been indicated,
* so marshalling an exception will corrupt the stream.
* This was the case with skeletons as well; there is no
* immediately obvious solution without a protocol change.
*/
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
logCallException(e);
ObjectOutput out = call.getResultStream(false);
if (e instanceof Error) {
e = new ServerError(
"Error occurred in server thread", (Error) e);
} else if (e instanceof RemoteException) {
e = new ServerException(
"RemoteException occurred in server thread",
(Exception) e);
}
if (suppressStackTraces) {
clearStackTraces(e);
}
out.writeObject(e);
} finally {
call.releaseInputStream(); // in case skeleton doesn't
call.releaseOutputStream();
}
}
`UnicastServerRef` 的 `dispatch` 方法调用` oldDispatch `方法,这里判断了` this.skel` 是否为空,用来区别自己是 `Registry `还是 `Server`。注册中心必然是空的,因为他没有skel远程对象
oldDispatch 方法调用 this.skel 也就是 RegistryImpl_Skel 类的 dispatch 方法,这里再次解释客户端和服务端用的是RegistryImpl_Stub发出信息,然后注册中心用的是RegistryImpl_Skel接受来自服务端和客户端的信息
public void oldDispatch(Remote obj, RemoteCall call, int op)
throws IOException
{
long hash; // hash for matching stub with skeleton
try {
// read remote call header
ObjectInput in;
try {
in = call.getInputStream();
try {
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("sun.rmi.transport.DGCImpl_Skel");
if (clazz.isAssignableFrom(skel.getClass())) {
((MarshalInputStream)in).useCodebaseOnly();
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ignore) { }
hash = in.readLong();
} catch (Exception readEx) {
throw new UnmarshalException("error unmarshalling call header",
readEx);
}
// if calls are being logged, write out object id and operation
logCall(obj, skel.getOperations()[op]);
unmarshalCustomCallData(in);
// dispatch to skeleton for remote object
skel.dispatch(obj, call, op, hash);
} catch (Throwable e) {
logCallException(e);
ObjectOutput out = call.getResultStream(false);
if (e instanceof Error) {
e = new ServerError(
"Error occurred in server thread", (Error) e);
} else if (e instanceof RemoteException) {
e = new ServerException(
"RemoteException occurred in server thread",
(Exception) e);
}
if (suppressStackTraces) {
clearStackTraces(e);
}
out.writeObject(e);
} finally {
call.releaseInputStream(); // in case skeleton doesn't
call.releaseOutputStream();
}
}
进入RegistryImpl_Skel 的 dispatch 方法
public void dispatch(Remote var1, RemoteCall var2, int var3, long var4) throws Exception {
if (var4 != 4905912898345647071L) {
throw new SkeletonMismatchException("interface hash mismatch");
} else {
RegistryImpl var6 = (RegistryImpl)var1;
String var7;
Remote var8;
ObjectInput var10;
ObjectInput var11;
switch (var3) {
case 0:
try {
var11 = var2.getInputStream();
var7 = (String)var11.readObject();
var8 = (Remote)var11.readObject();
} catch (IOException var94) {
throw new UnmarshalException("error unmarshalling arguments", var94);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException var95) {
throw new UnmarshalException("error unmarshalling arguments", var95);
} finally {
var2.releaseInputStream();
}
var6.bind(var7, var8);
try {
var2.getResultStream(true);
break;
} catch (IOException var93) {
throw new MarshalException("error marshalling return", var93);
}
case 1:
var2.releaseInputStream();
String[] var97 = var6.list();
try {
ObjectOutput var98 = var2.getResultStream(true);
var98.writeObject(var97);
break;
} catch (IOException var92) {
throw new MarshalException("error marshalling return", var92);
}
case 2:
try {
var10 = var2.getInputStream();
var7 = (String)var10.readObject();
} catch (IOException var89) {
throw new UnmarshalException("error unmarshalling arguments", var89);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException var90) {
throw new UnmarshalException("error unmarshalling arguments", var90);
} finally {
var2.releaseInputStream();
}
var8 = var6.lookup(var7);
try {
ObjectOutput var9 = var2.getResultStream(true);
var9.writeObject(var8);
break;
} catch (IOException var88) {
throw new MarshalException("error marshalling return", var88);
}
case 3:
try {
var11 = var2.getInputStream();
var7 = (String)var11.readObject();
var8 = (Remote)var11.readObject();
} catch (IOException var85) {
throw new UnmarshalException("error unmarshalling arguments", var85);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException var86) {
throw new UnmarshalException("error unmarshalling arguments", var86);
} finally {
var2.releaseInputStream();
}
var6.rebind(var7, var8);
try {
var2.getResultStream(true);
break;
} catch (IOException var84) {
throw new MarshalException("error marshalling return", var84);
}
case 4:
try {
var10 = var2.getInputStream();
var7 = (String)var10.readObject();
} catch (IOException var81) {
throw new UnmarshalException("error unmarshalling arguments", var81);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException var82) {
throw new UnmarshalException("error unmarshalling arguments", var82);
} finally {
var2.releaseInputStream();
}
var6.unbind(var7);
try {
var2.getResultStream(true);
break;
} catch (IOException var80) {
throw new MarshalException("error marshalling return", var80);
}
default:
throw new UnmarshalException("invalid method number");
}
}
}
例如 0 代表着bind 方法,则从流中读取对应的内容,反序列化,然后调用 RegistryImpl 的bind方法进行绑定。
4.服务调用
之后就是 Client 端向 Registry 端查询和请求的过程了。客户端获取 Registry 的流程与上面分析的服务端一致,这里不再重复。还是通过调用本地创建的RegistryImpl_Stub对象。
在调用其 lookup 方法时,会向Registry端传递序列化的 name ,然后将 Registry 端回传的结果反序列化,很好理解。
public Remote lookup(String var1) throws AccessException, NotBoundException, RemoteException {
try {
RemoteCall var2 = super.ref.newCall(this, operations, 2, 4905912898345647071L);
try {
ObjectOutput var3 = var2.getOutputStream();
var3.writeObject(var1);
} catch (IOException var18) {
throw new MarshalException("error marshalling arguments", var18);
}
super.ref.invoke(var2);
Remote var23;
try {
ObjectInput var6 = var2.getInputStream();
var23 = (Remote)var6.readObject();
} catch (IOException var15) {
throw new UnmarshalException("error unmarshalling return", var15);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException var16) {
throw new UnmarshalException("error unmarshalling return", var16);
} finally {
super.ref.done(var2);
}
return var23;
} catch (RuntimeException var19) {
throw var19;
} catch (RemoteException var20) {
throw var20;
} catch (NotBoundException var21) {
throw var21;
} catch (Exception var22) {
throw new UnexpectedException("undeclared checked exception", var22);
}
}
这里还是关注Registry 端的做法,依旧是 RegistryImpl_Skel 的 dispatch 方法,lookup 方法对应的值是 2 ,调用 RegistryImpl 的 lookup 方法,然后将查询到的结果 writeObject 到流中。
case 2:
try {
var10 = var2.getInputStream();
var7 = (String)var10.readObject();
} catch (IOException var89) {
throw new UnmarshalException("error unmarshalling arguments", var89);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException var90) {
throw new UnmarshalException("error unmarshalling arguments", var90);
} finally {
var2.releaseInputStream();
}
var8 = var6.lookup(var7);
try {
ObjectOutput var9 = var2.getResultStream(true);
var9.writeObject(var8);
break;
} catch (IOException var88) {
throw new MarshalException("error marshalling return", var88);
}
Client 拿到 Registry 端返回的动态代理对象并且反序列化后,对其进行调用,这看起来是本地进行调用,但实际上是动态代理的 RemoteObjectInvocationHandler 委托RemoteRef的invoke方法进行远程通信,由于这个动态代理类中保存了真正 Server 端对此项服务监听的端口,因此 Client 端直接与 Server 端进行通信。简而言之就是看似是客户端在本地反射调用,其实是反序列化后通过远程通信,在sever端调用函数,就像是图片中的过程
Server 端由 UnicastServerRef 的 dispatch 方法来处理客户端的请求,会在hashToMethod_Map中寻找Client 端对应执行 Method 的 hash 值,如果找到了,则会反序列化Client端传来的参数,并且通过反射调用。
op = in.readLong();
Method method = hashToMethod_Map.get(op);
调用后将结果序列化给 Client 端,Client 端拿到结果反序列化,完成整个调用的过程。
最后我想说一句就是dispatch,他是用来接受信息的,也是反序列化东西的,他在RegistryImpl_Skel有,来接受客户端和服务端的信息,服务端也有来接受客户端的信息,服务端的dispatch在handless-->serviceCall-->UnicastServerRef#dispatch
DGCImpl
分布式垃圾回收
他是在生成远程对象的时候创建的,就是在发布远程对象的时候创建的
UnicastRemoteObject#exportObject-->UnicastServerRef#exportObject-->LiveRef#exportObject-->TCPEndpoint#exportObject-->TCPTransport#exportObject-->Transport#exportObject-->ObjectTable#putTarget
static void putTarget(Target target) throws ExportException {
ObjectEndpoint oe = target.getObjectEndpoint();
WeakRef weakImpl = target.getWeakImpl();
if (DGCImpl.dgcLog.isLoggable(Log.VERBOSE)) {
DGCImpl.dgcLog.log(Log.VERBOSE, "add object " + oe);
}
synchronized (tableLock) {
/**
* Do nothing if impl has already been collected (see 6597112). Check while
* holding tableLock to ensure that Reaper cannot process weakImpl in between
* null check and put/increment effects.
*/
if (target.getImpl() != null) {
if (objTable.containsKey(oe)) {
throw new ExportException(
"internal error: ObjID already in use");
} else if (implTable.containsKey(weakImpl)) {
throw new ExportException("object already exported");
}
objTable.put(oe, target);
implTable.put(weakImpl, target);
if (!target.isPermanent()) {
incrementKeepAliveCount();
}
}
}
}
注意看
if (DGCImpl.dgcLog.isLoggable(Log.VERBOSE)) {
DGCImpl.dgcLog.log(Log.VERBOSE, "add object " + oe);
}
这个里面的dgcLog是个静态变量,对静态变量调用的时候,会初始化这个类,初始化的时候会调用这个类的静态代码块
static final Log dgcLog = Log.getLog("sun.rmi.dgc", "dgc",
LogStream.parseLevel(AccessController.doPrivileged(
new GetPropertyAction("sun.rmi.dgc.logLevel"))));
上面这个是静态函数
下面这个是这个类的静态代码块
static {
/*
* "Export" the singleton DGCImpl in a context isolated from
* the arbitrary current thread context.
*/
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Void>() {
public Void run() {
ClassLoader savedCcl =
Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
try {
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(
ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader());
/*
* Put remote collector object in table by hand to prevent
* listen on port. (UnicastServerRef.exportObject would
* cause transport to listen.)
*/
try {
dgc = new DGCImpl();
ObjID dgcID = new ObjID(ObjID.DGC_ID);
LiveRef ref = new LiveRef(dgcID, 0);
UnicastServerRef disp = new UnicastServerRef(ref);
Remote stub =
Util.createProxy(DGCImpl.class,
new UnicastRef(ref), true);
disp.setSkeleton(dgc);
Permissions perms = new Permissions();
perms.add(new SocketPermission("*", "accept,resolve"));
ProtectionDomain[] pd = { new ProtectionDomain(null, perms) };
AccessControlContext acceptAcc = new AccessControlContext(pd);
Target target = AccessController.doPrivileged(
new PrivilegedAction<Target>() {
public Target run() {
return new Target(dgc, disp, stub, dgcID, true);
}
}, acceptAcc);
ObjectTable.putTarget(target);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw new Error(
"exception initializing server-side DGC", e);
}
} finally {
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(savedCcl);
}
return null;
}
});
}
在这里他就是创建了一个stub
Remote stub = Util.createProxy(DGCImpl.class, new UnicastRef(ref), true);
和之前创建过程一样,它是有DGCImpl_stub类的
我们去看一下DGCImpl_stub
public void clean(ObjID[] var1, long var2, VMID var4, boolean var5) throws RemoteException {
try {
RemoteCall var6 = super.ref.newCall(this, operations, 0, -669196253586618813L);
try {
ObjectOutput var7 = var6.getOutputStream();
var7.writeObject(var1);
var7.writeLong(var2);
var7.writeObject(var4);
var7.writeBoolean(var5);
} catch (IOException var8) {
throw new MarshalException("error marshalling arguments", var8);
}
super.ref.invoke(var6);
super.ref.done(var6);
} catch (RuntimeException var9) {
throw var9;
} catch (RemoteException var10) {
throw var10;
} catch (Exception var11) {
throw new UnexpectedException("undeclared checked exception", var11);
}
}
public Lease dirty(ObjID[] var1, long var2, Lease var4) throws RemoteException {
try {
RemoteCall var5 = super.ref.newCall(this, operations, 1, -669196253586618813L);
try {
ObjectOutput var6 = var5.getOutputStream();
var6.writeObject(var1);
var6.writeLong(var2);
var6.writeObject(var4);
} catch (IOException var20) {
throw new MarshalException("error marshalling arguments", var20);
}
super.ref.invoke(var5);
Lease var24;
try {
ObjectInput var9 = var5.getInputStream();
var24 = (Lease)var9.readObject();
} catch (IOException var17) {
throw new UnmarshalException("error unmarshalling return", var17);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException var18) {
throw new UnmarshalException("error unmarshalling return", var18);
} finally {
super.ref.done(var5);
}
return var24;
} catch (RuntimeException var21) {
throw var21;
} catch (RemoteException var22) {
throw var22;
} catch (Exception var23) {
throw new UnexpectedException("undeclared checked exception", var23);
}
}
他有两个方法都是清除,都调用了invoke,所以所有的stub都会被攻击的


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号