PYTORCH 卷积神经网络+CIFAR10数据分类+用VGG16对CIFAR10分类(代码练习)
一、卷积神经网

import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F import torch.optim as optim from torchvision import datasets, transforms import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy # 一个函数,用来计算模型中有多少参数 def get_n_params(model): np=0 for p in list(model.parameters()): np += p.nelement() return np # 使用GPU训练,可以在菜单 "代码执行工具" -> "更改运行时类型" 里进行设置 device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
深度神经网络特性:
- 很多层: compositionality
- 卷积: locality + stationarity of images
- 池化: Invariance of object class to translations
1.加载数据(MNIST)

1 input_size = 28*28 # MNIST上的图像尺寸是 28x28 2 output_size = 10 # 类别为 0 到 9 的数字,因此为十类 3 4 train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader( 5 datasets.MNIST('./data', train=True, download=True, 6 transform=transforms.Compose( 7 [transforms.ToTensor(), 8 transforms.Normalize((0.1307,), (0.3081,))])), 9 batch_size=64, shuffle=True) 10 11 test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader( 12 datasets.MNIST('./data', train=False, transform=transforms.Compose([ 13 transforms.ToTensor(), 14 transforms.Normalize((0.1307,), (0.3081,))])), 15 batch_size=1000, shuffle=True)
显示数据集中的部分图像
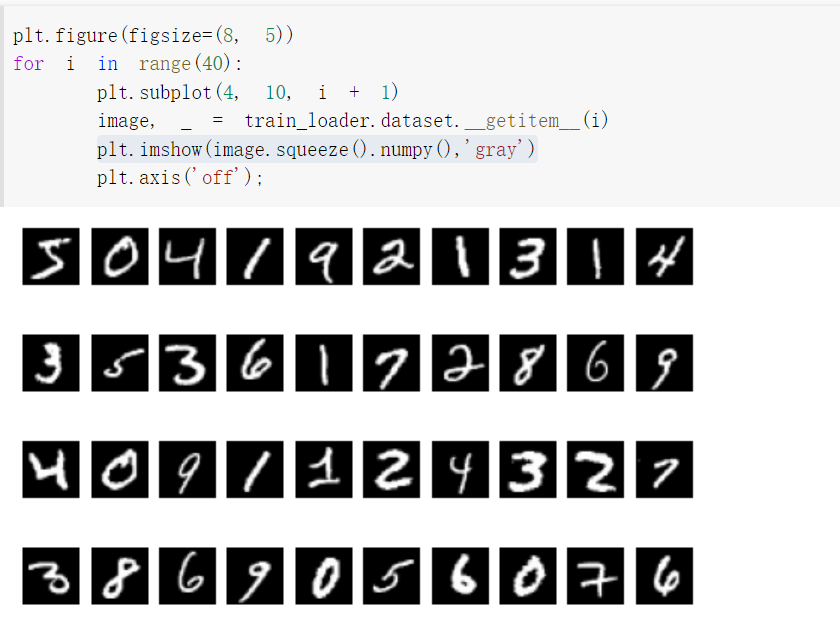
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 5))表示figure的长、宽(单位inch)
plt.imshow(image.squeeze().numpy(),'gray')gray取灰度图。

2.创建网络
定义网络时,需要继承nn.Module,并实现它的forward方法,把网络中具有可学习参数的层放在构造函数init中。
只要在nn.Module的子类中定义了forward函数,backward函数就会自动被实现(利用autograd)。

1 class FC2Layer(nn.Module): 2 def __init__(self, input_size, n_hidden, output_size): 3 # nn.Module子类的函数必须在构造函数中执行父类的构造函数 4 # 下式等价于nn.Module.__init__(self) 5 super(FC2Layer, self).__init__() 6 self.input_size = input_size 7 # 这里直接用 Sequential 就定义了网络,注意要和下面 CNN 的代码区分开 8 self.network = nn.Sequential( 9 nn.Linear(input_size, n_hidden), 10 nn.ReLU(), 11 nn.Linear(n_hidden, n_hidden), 12 nn.ReLU(), 13 nn.Linear(n_hidden, output_size), 14 nn.LogSoftmax(dim=1) 15 ) 16 def forward(self, x): 17 # view一般出现在model类的forward函数中,用于改变输入或输出的形状 18 # x.view(-1, self.input_size) 的意思是多维的数据展成二维 19 # 代码指定二维数据的列数为 input_size=784,行数 -1 表示我们不想算,电脑会自己计算对应的数字 20 # 在 DataLoader 部分,我们可以看到 batch_size 是64,所以得到 x 的行数是64 21 # 大家可以加一行代码:print(x.cpu().numpy().shape) 22 # 训练过程中,就会看到 (64, 784) 的输出,和我们的预期是一致的 23 24 # forward 函数的作用是,指定网络的运行过程,这个全连接网络可能看不啥意义, 25 # 下面的CNN网络可以看出 forward 的作用。 26 x = x.view(-1, self.input_size) 27 return self.network(x) 28 29 30 31 class CNN(nn.Module): 32 def __init__(self, input_size, n_feature, output_size): 33 # 执行父类的构造函数,所有的网络都要这么写 34 super(CNN, self).__init__() 35 # 下面是网络里典型结构的一些定义,一般就是卷积和全连接 36 # 池化、ReLU一类的不用在这里定义 37 self.n_feature = n_feature 38 self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1, out_channels=n_feature, kernel_size=5) 39 self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(n_feature, n_feature, kernel_size=5) 40 self.fc1 = nn.Linear(n_feature*4*4, 50) 41 self.fc2 = nn.Linear(50, 10) 42 43 # 下面的 forward 函数,定义了网络的结构,按照一定顺序,把上面构建的一些结构组织起来 44 # 意思就是,conv1, conv2 等等的,可以多次重用 45 def forward(self, x, verbose=False): 46 x = self.conv1(x) 47 x = F.relu(x) 48 x = F.max_pool2d(x, kernel_size=2) 49 x = self.conv2(x) 50 x = F.relu(x) 51 x = F.max_pool2d(x, kernel_size=2) 52 x = x.view(-1, self.n_feature*4*4) 53 x = self.fc1(x) 54 x = F.relu(x) 55 x = self.fc2(x) 56 x = F.log_softmax(x, dim=1) 57 return x

1 def train(model): 2 model.train() 3 # 主里从train_loader里,64个样本一个batch为单位提取样本进行训练 4 for batch_idx, (data, target) in enumerate(train_loader): 5 # 把数据送到GPU中 6 data, target = data.to(device), target.to(device) 7 8 optimizer.zero_grad() 9 output = model(data) 10 loss = F.nll_loss(output, target) 11 loss.backward() 12 optimizer.step() 13 if batch_idx % 100 == 0: 14 print('Train: [{}/{} ({:.0f}%)]\tLoss: {:.6f}'.format( 15 batch_idx * len(data), len(train_loader.dataset), 16 100. * batch_idx / len(train_loader), loss.item())) 17 18 19 def test(model): 20 model.eval() 21 test_loss = 0 22 correct = 0 23 for data, target in test_loader: 24 # 把数据送到GPU中 25 data, target = data.to(device), target.to(device) 26 # 把数据送入模型,得到预测结果 27 output = model(data) 28 # 计算本次batch的损失,并加到 test_loss 中 29 test_loss += F.nll_loss(output, target, reduction='sum').item() 30 # get the index of the max log-probability,最后一层输出10个数, 31 # 值最大的那个即对应着分类结果,然后把分类结果保存在 pred 里 32 pred = output.data.max(1, keepdim=True)[1] 33 # 将 pred 与 target 相比,得到正确预测结果的数量,并加到 correct 中 34 # 这里需要注意一下 view_as ,意思是把 target 变成维度和 pred 一样的意思 35 correct += pred.eq(target.data.view_as(pred)).cpu().sum().item() 36 37 test_loss /= len(test_loader.dataset) 38 accuracy = 100. * correct / len(test_loader.dataset) 39 print('\nTest set: Average loss: {:.4f}, Accuracy: {}/{} ({:.0f}%)\n'.format( 40 test_loss, correct, len(test_loader.dataset), 41 accuracy))
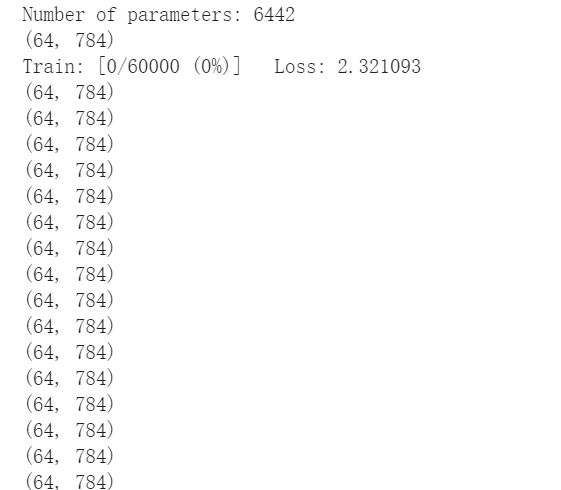
加入print(x.cpu().numpy().shape)出现(64,784)
去掉print(x.cpu().numpy().shape)后
![]()

3.在小型全连接网络上训练(Fully-connected network)
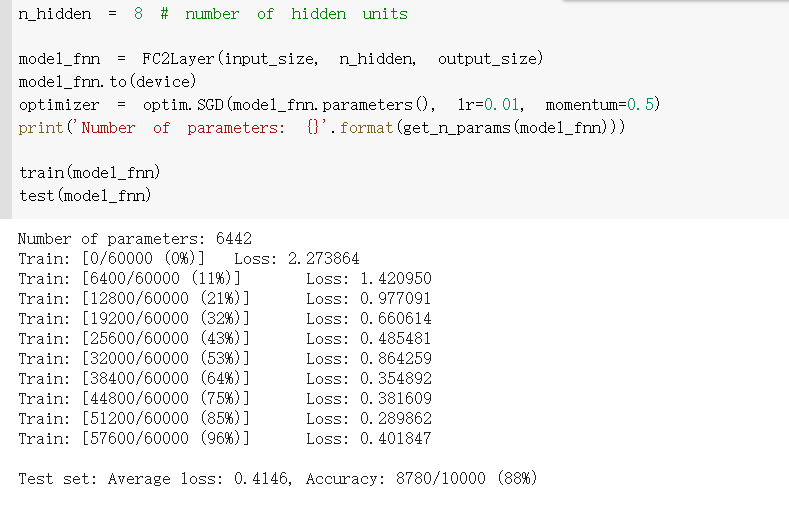
4.在卷积神经网络上训练
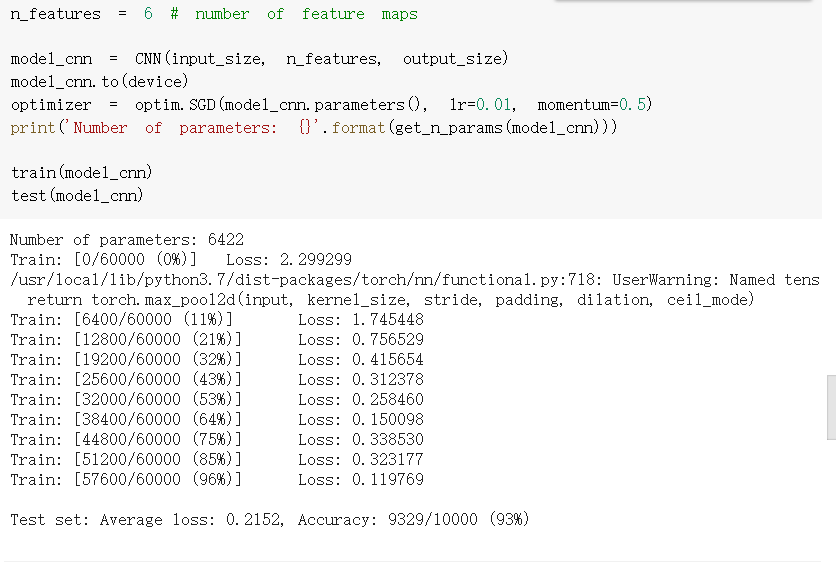
通过上面的测试结果发现,含有相同参数的 CNN 效果要明显优于简单的全连接网络,是因为 CNN 能够通过卷积和池化更好的挖掘图像中的信息
5. 打乱像素顺序再次在两个网络上训练与测试
下面代码展示随机打乱像素顺序后,图像的形态:

1 # 这里解释一下 torch.randperm 函数,给定参数n,返回一个从0到n-1的随机整数排列 2 perm = torch.randperm(784) 3 plt.figure(figsize=(8, 4)) 4 for i in range(10): 5 image, _ = train_loader.dataset.__getitem__(i) 6 # permute pixels 7 image_perm = image.view(-1, 28*28).clone() 8 image_perm = image_perm[:, perm] 9 image_perm = image_perm.view(-1, 1, 28, 28) 10 plt.subplot(4, 5, i + 1) 11 plt.imshow(image.squeeze().numpy(), 'gray') 12 plt.axis('off') 13 plt.subplot(4, 5, i + 11) 14 plt.imshow(image_perm.squeeze().numpy(), 'gray') 15 plt.axis('off')

1 # 对每个 batch 里的数据,打乱像素顺序的函数 2 def perm_pixel(data, perm): 3 # 转化为二维矩阵 4 data_new = data.view(-1, 28*28) 5 # 打乱像素顺序 6 data_new = data_new[:, perm] 7 # 恢复为原来4维的 tensor 8 data_new = data_new.view(-1, 1, 28, 28) 9 return data_new 10 11 # 训练函数 12 def train_perm(model, perm): 13 model.train() 14 for batch_idx, (data, target) in enumerate(train_loader): 15 data, target = data.to(device), target.to(device) 16 # 像素打乱顺序 17 data = perm_pixel(data, perm) 18 19 optimizer.zero_grad() 20 output = model(data) 21 loss = F.nll_loss(output, target) 22 loss.backward() 23 optimizer.step() 24 if batch_idx % 100 == 0: 25 print('Train: [{}/{} ({:.0f}%)]\tLoss: {:.6f}'.format( 26 batch_idx * len(data), len(train_loader.dataset), 27 100. * batch_idx / len(train_loader), loss.item())) 28 29 # 测试函数 30 def test_perm(model, perm): 31 model.eval() 32 test_loss = 0 33 correct = 0 34 for data, target in test_loader: 35 data, target = data.to(device), target.to(device) 36 37 # 像素打乱顺序 38 data = perm_pixel(data, perm) 39 40 output = model(data) 41 test_loss += F.nll_loss(output, target, reduction='sum').item() 42 pred = output.data.max(1, keepdim=True)[1] 43 correct += pred.eq(target.data.view_as(pred)).cpu().sum().item() 44 45 test_loss /= len(test_loader.dataset) 46 accuracy = 100. * correct / len(test_loader.dataset) 47 print('\nTest set: Average loss: {:.4f}, Accuracy: {}/{} ({:.0f}%)\n'.format( 48 test_loss, correct, len(test_loader.dataset), 49 accuracy))

1 perm = torch.randperm(784) 2 n_hidden = 8 # number of hidden units 3 4 model_fnn = FC2Layer(input_size, n_hidden, output_size) 5 model_fnn.to(device) 6 optimizer = optim.SGD(model_fnn.parameters(), lr=0.01, momentum=0.5) 7 print('Number of parameters: {}'.format(get_n_params(model_fnn))) 8 9 train_perm(model_fnn, perm) 10 test_perm(model_fnn, perm)
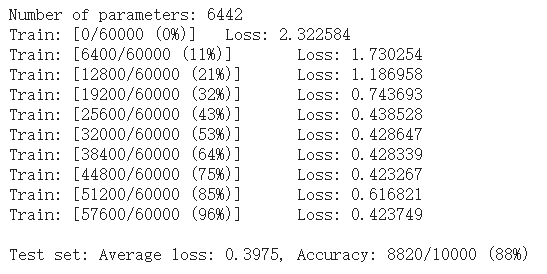

1 perm = torch.randperm(784) 2 n_features = 6 # number of feature maps 3 4 model_cnn = CNN(input_size, n_features, output_size) 5 model_cnn.to(device) 6 optimizer = optim.SGD(model_cnn.parameters(), lr=0.01, momentum=0.5) 7 print('Number of parameters: {}'.format(get_n_params(model_cnn))) 8 9 train_perm(model_cnn, perm) 10 test_perm(model_cnn, perm)
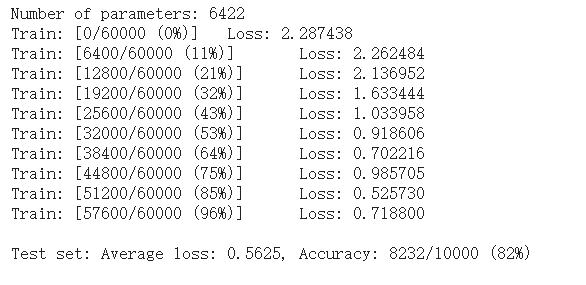
从打乱像素顺序的实验结果来看,全连接网络的性能基本上没有发生变化,但是 卷积神经网络的性能明显下降。
这是因为对于卷积神经网络,会利用像素的局部关系,但是打乱顺序以后,这些像素间的关系将无法得到利用。
二、CIFAR10数据分类
input[channel] = (input[channel] - mean[channel]) / std[channel]

1 import torch 2 import torchvision 3 import torchvision.transforms as transforms 4 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 5 import numpy as np 6 import torch.nn as nn 7 import torch.nn.functional as F 8 import torch.optim as optim 9 10 # 使用GPU训练,可以在菜单 "代码执行工具" -> "更改运行时类型" 里进行设置 11 device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu") 12 13 transform = transforms.Compose( 14 [transforms.ToTensor(), 15 transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))]) 16 17 # 注意下面代码中:训练的 shuffle 是 True,测试的 shuffle 是 false 18 # 训练时可以打乱顺序增加多样性,测试是没有必要 19 trainset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root='./data', train=True, 20 download=True, transform=transform) 21 trainloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(trainset, batch_size=64, 22 shuffle=True, num_workers=2) 23 24 testset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root='./data', train=False, 25 download=True, transform=transform) 26 testloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(testset, batch_size=8, 27 shuffle=False, num_workers=2) 28 29 classes = ('plane', 'car', 'bird', 'cat', 30 'deer', 'dog', 'frog', 'horse', 'ship', 'truck')

1 def imshow(img): 2 plt.figure(figsize=(8,8)) 3 img = img / 2 + 0.5 # 转换到 [0,1] 之间 4 npimg = img.numpy() 5 plt.imshow(np.transpose(npimg, (1, 2, 0))) 6 plt.show() 7 8 # 得到一组图像 9 images, labels = iter(trainloader).next() 10 # 展示图像 11 imshow(torchvision.utils.make_grid(images)) 12 # 展示第一行图像的标签 13 for j in range(8): 14 print(classes[labels[j]])


1 class Net(nn.Module): 2 def __init__(self): 3 super(Net, self).__init__() 4 self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 6, 5) 5 self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2) 6 self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5) 7 self.fc1 = nn.Linear(16 * 5 * 5, 120) 8 self.fc2 = nn.Linear(120, 84) 9 self.fc3 = nn.Linear(84, 10) 10 11 def forward(self, x): 12 x = self.pool(F.relu(self.conv1(x))) 13 x = self.pool(F.relu(self.conv2(x))) 14 x = x.view(-1, 16 * 5 * 5) 15 x = F.relu(self.fc1(x)) 16 x = F.relu(self.fc2(x)) 17 x = self.fc3(x) 18 return x 19 20 # 网络放到GPU上 21 net = Net().to(device) 22 criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() 23 optimizer = optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=0.001)

1 for epoch in range(10): # 重复多轮训练 2 for i, (inputs, labels) in enumerate(trainloader): 3 inputs = inputs.to(device) 4 labels = labels.to(device) 5 # 优化器梯度归零 6 optimizer.zero_grad() 7 # 正向传播 + 反向传播 + 优化 8 outputs = net(inputs) 9 loss = criterion(outputs, labels) 10 loss.backward() 11 optimizer.step() 12 # 输出统计信息 13 if i % 100 == 0: 14 print('Epoch: %d Minibatch: %5d loss: %.3f' %(epoch + 1, i + 1, loss.item())) 15 16 print('Finished Training')
测试集中取八张图
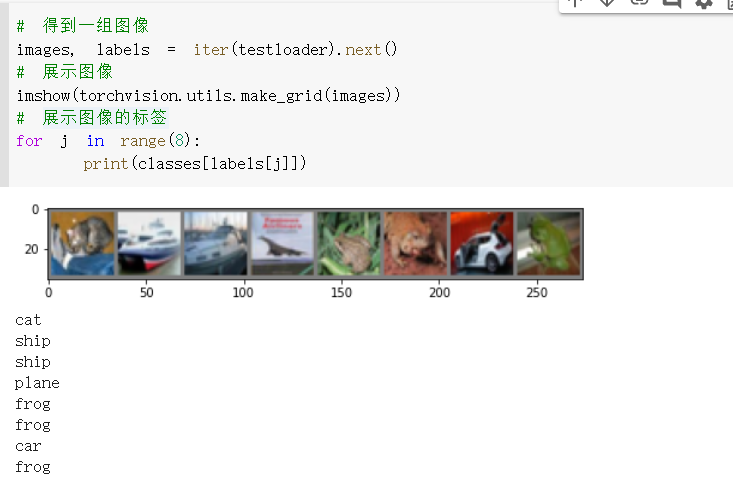

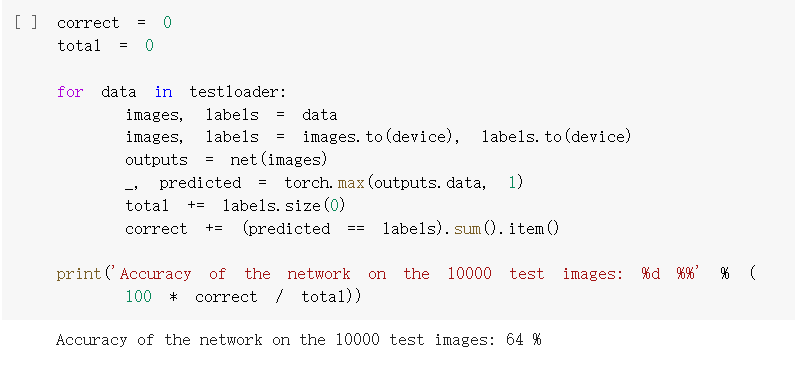
准确率64%
三、使用 VGG16 对 CIFAR10 分类

1.定义dataloader
 2.
2.
1 cfg = [64, 'M', 128, 'M', 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 'M'] 2 class VGG(nn.Module): 3 def __init__(self): 4 super(VGG, self).__init__() 5 #self.cfg = [64, 'M', 128, 'M', 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 'M'] 6 self.features = self._make_layers(cfg) 7 #self.classifier = nn.Linear(2048, 10) 8 self.classifier = nn.Linear(512, 10) 9 10 def forward(self, x): 11 out = self.features(x) 12 out = out.view(out.size(0), -1) 13 out = self.classifier(out) 14 return out 15 16 def _make_layers(self, cfg): 17 layers = [] 18 in_channels = 3 19 for x in cfg: 20 if x == 'M': 21 layers += [nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)] 22 else: 23 layers += [nn.Conv2d(in_channels, x, kernel_size=3, padding=1), 24 nn.BatchNorm2d(x), 25 nn.ReLU(inplace=True)] 26 in_channels = x 27 layers += [nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=1, stride=1)] 28 return nn.Sequential(*layers)

1 net = VGG().to(device) 2 criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() 3 optimizer = optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=0.001)
 3.
3.
1 for epoch in range(10): # 重复多轮训练 2 for i, (inputs, labels) in enumerate(trainloader): 3 inputs = inputs.to(device) 4 labels = labels.to(device) 5 # 优化器梯度归零 6 optimizer.zero_grad() 7 # 正向传播 + 反向传播 + 优化 8 outputs = net(inputs) 9 loss = criterion(outputs, labels) 10 loss.backward() 11 optimizer.step() 12 # 输出统计信息 13 if i % 100 == 0: 14 print('Epoch: %d Minibatch: %5d loss: %.3f' %(epoch + 1, i + 1, loss.item())) 15 16 print('Finished Training')
4.测试验证准确率
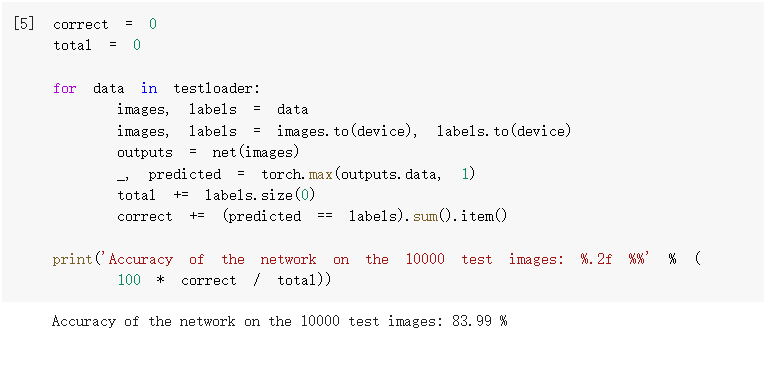
准确率为83.99%,相较之前有所提升。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号