spring 基础(四) spring jdbc
springJDBC在事务管理方面更占优势,同时处理速度也比mybatis快一点。
1.基础
- Spring JDBC是Spring框架用于处理关系型数据库的模块。
- Spring JDBC对JDBC API进行封装,极大简化开发工作量。
- JdbcTemplate是Spring JDBC核心类,提供数据CRUD方法。
- Mybatis作为orm框架,封装程度较高,适合敏捷开发。
-
Jdbc使用步骤:
Maven工程弓|入依赖spring-jdbc
applicationContext.xml配置DataSource数据源
在Dao注入JdbcTemplate对象,实现数据CRUD - CURD:查询有多种,但是删除、修改、新增都是用update
- demo:
1:首先在pom中引入以下包
<dependencies>
<!-- spring ioc-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.2.6.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!--spring jdbc-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>5.2.6.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!--mysql引入-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.22</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 单元测试-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>5.2.4.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 单元测试 框架-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2:创建一个实体

public class Employee { private Integer eno; private String ename; private Float salary; private String dname; private Date hiredate; public Integer getEno() { return eno; } public void setEno(Integer eno) { this.eno = eno; } public String getEname() { return ename; } public void setEname(String ename) { this.ename = ename; } public Float getSalary() { return salary; } public void setSalary(Float salary) { this.salary = salary; } public String getDname() { return dname; } public void setDname(String dname) { this.dname = dname; } public Date getHiredate() { return hiredate; } public void setHiredate(Date hiredate) { this.hiredate = hiredate; } @Override public String toString() { return "Employee{" + "eno=" + eno + ", ename='" + ename + '\'' + ", salary=" + salary + ", dname='" + dname + '\'' + ", hiredate=" + hiredate + '}'; }
3:创建dao
public class EmployeeDao { private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; public JdbcTemplate getJdbcTemplate() { return jdbcTemplate; } public void setJdbcTemplate(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) { this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate; } /** * 根据id查找数据 * queryForObject 返回单条数据 * * @param eno * @return */ public Employee findById(Integer eno) { String sql = "SELECT * FROM employee WHERE eno = ?"; //查询单条数据 如果有多个条件,则 new Object[]{eno,eno2,eno3} 数组中的顺序对应着sql中问好的顺序 Employee employee = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, new Object[]{eno}, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Employee>(Employee.class)); return employee; } /** * query 返回list * * @param depName * @return */ public List<Employee> findByName(String depName) { String sql = "SELECT * FROM employee WHERE dname = ?"; List<Employee> query = jdbcTemplate.query(sql, new Object[]{depName}, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Employee>(Employee.class)); return query; } /** * queryForList 返回map集合数据 ,当返回的字段名字是entity中没有的时候就使用这个 * @param depName * @return */ public List<Map<String, Object>> findMapByName(String depName) { String sql = "SELECT eno enoAs,ename enameAs,salary salaryAs,dname dnameAs FROM employee WHERE dname = ?"; List<Map<String, Object>> maps = jdbcTemplate.queryForList(sql, new Object[]{"depName"}); return maps; } public void insert(Employee employee){ String sql = "insert into employee(eno,ename,salary,dname,hiredate) values(?,?,?,?,?)"; //利用update方法实现数据写入操作 jdbcTemplate.update(sql,new Object[]{ employee.getEno() , employee.getEname(),employee.getSalary(),employee.getDname() , employee.getHiredate() }); } public int update(Employee employee){ String sql = "UPDATE employee SET ename = ?, salary = ?, dname = ?, hiredate = ? WHERE eno = ?"; int count = jdbcTemplate.update(sql, new Object[]{employee.getEname(), employee.getSalary(), employee.getDname(), employee.getHiredate(), employee.getEno()}); return count; } public int delete(Integer eno){ String sql = "delete from employee where eno = ?"; return jdbcTemplate.update(sql, new Object[]{eno}); } }
4:创建service

public class EmployeeService { private EmployeeDao employeeDao; private DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager; public EmployeeDao getEmployeeDao() { return employeeDao; } public void setEmployeeDao(EmployeeDao employeeDao) { this.employeeDao = employeeDao; } public DataSourceTransactionManager getTransactionManager() { return transactionManager; } public void setTransactionManager(DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager) { this.transactionManager = transactionManager; } //编程性事务 public void batchImport(){ //定义了事务默认的标准配置 TransactionDefinition definition = new DefaultTransactionDefinition(); //开始一个事务,返回事务状态,事务状态说明当前事务的执行阶段 TransactionStatus status = transactionManager.getTransaction(definition); try { for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) { /*if (i == 3) { throw new RuntimeException("意料之外的异常"); }*/ Employee employee = new Employee(); employee.setEno(8000 + i); employee.setEname("员工" + i); employee.setSalary(4000f); employee.setDname("市场部"); employee.setHiredate(new Date()); employeeDao.insert(employee); } transactionManager.commit(status); //提交事务 }catch (RuntimeException e){ transactionManager.rollback(status); //回滚事务 throw e; } } }
5:创建applicationContext.xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!-- 数据源--> <bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource"> <property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:33068/imooc?useSSL=false&useUnicode=true& characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true"/> <property name="username" value="root"/> <property name="password" value="Ee123"/> </bean> <!-- JdbcTemplate提供数据CRUD的api--> <bean id="JdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> </bean> <bean id="employeeDao" class="com.item.spring.jdbc.dao.EmployeeDao"> <!--为Dao注入JdbcTemplate对象--> <property name="jdbcTemplate" ref="JdbcTemplate"/> </bean> <!-- 编程性 事务管理器--> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property> </bean> <bean id="employeeService" class="com.item.spring.jdbc.service.EmployeeService"> <property name="employeeDao" ref="employeeDao"/> <property name="transactionManager" ref="transactionManager"/> </bean> </beans>
6:创建一个测试类
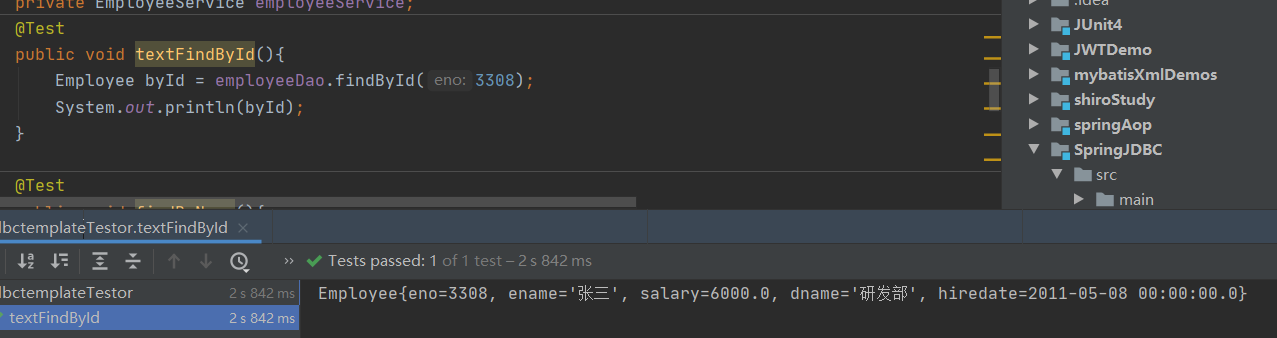
/** * @RunWith+ @ContextConfiguration作用= ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:applicationContext.xml"); * */ @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) //JUnit 控制权交给spring @ContextConfiguration(locations = {"classpath:applicationContext.xml"}) public class JdbctemplateTestor { @Resource private EmployeeDao employeeDao; @Resource private EmployeeService employeeService; @Test public void textFindById(){ Employee byId = employeeDao.findById(3308); System.out.println(byId); } @Test public void findByName(){ List<Employee> list = employeeDao.findByName("研发部"); System.out.println(list); } @Test public void findMapByName(){ List<Map<String, Object>> map = employeeDao.findMapByName("研发部"); System.out.println(map); } @Test public void testBatchImport(){ employeeService.batchImport(); System.out.println("批量导入成功"); } }
2.spring事务管理
- 事务是以一种可靠的、-致的方式,访问和操作数据库的程序单元;简单理解:要么把事情做完,要么什么都不做,不要做一半。
- 事务依赖于数据库实现,MySQL通过事务区作为数据缓冲地带。
2.1spring编程式事务
- 基础
- 编程式事务是指通过代码手动提交回滚事务的事务控制方法。
- SpringJDBC通过TransactionManager事务管理器实现事务控制。
- 事务管理器提供commit/rollback方法进行事务提交与回滚。
- 优点是程序中好控制,缺点是程序中容易人为破坏。
- 事务中执行sql始终用一条数据库连接。执行多条sql,前面sql执行完毕之后放在事务区中,等待全部执行完毕之后决定是提交还是回滚。
- demo,已经在上面展示,主要实在service中以及applicationContext.xml中配置:
2.2spring声明式事务
- 声明式事务指在不修改源码情况下通过配置形式自动实现事务控制,声明式事务本质就是AOP环绕通知。
- 当目标方法执行成功时,自动提交事务。
- 当目标方法抛出运行时异常时,自动事务回滚。
- 由于声明式事务都是再xml文件中配置,指定那些名称方法执行事务,这个命名带来规范性同时也限制住了命名规则。
- 配置过程:
- 配置TransactionManager事务管理器
- 配置事务通知与事务属性
- 为事务通知绑定PointCut切点、
- demo(基础代码和前面案例一样,就不展示。主要显示编程事务):
1:applicationContext.xml
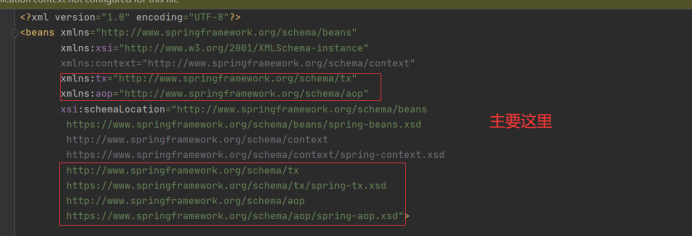
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx https://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <!-- 数据源 --> <bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource"> <property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:33068/imooc?useSSL=false&useUnicode=true& characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true"/> <property name="username" value="root"/> <property name="password" value="Ee123"/> </bean> <!--JdbcTemplate提供数据CRUD的API--> <bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> </bean> <bean id="employeeDao" class="com.item.springJdbc.dao.EmployeeDao"> <!--为Dao注入JdbcTemplate对象--> <property name="jdbcTemplate" ref="jdbcTemplate"/> </bean> <bean id="batchService" class="com.item.springJdbc.service.BatchService"> <property name="employeeDao" ref="employeeDao"/> </bean> <bean id="employeeService" class="com.item.springJdbc.service.EmployeeService"> <property name="employeeDao" ref="employeeDao"/> <property name="batchService" ref="batchService"/> </bean> <!--
此处事务的作用域是com.item下任何子子孙孙/子包,只要文件是Service结尾,的方法都将使用到事务。而具体是某些方法在<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">中配置
<tx:method name="batchImport" propagation="REQUIRED"/> 说明只要方法名是batchImport,都将使用事务
--> <!-- 1.事务管理器,用于创建事务/提交/回滚 --> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> </bean> <!--2.事务通知配置,决定哪些方法使用事务,哪些方法不使用事务 --> <tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager"> <tx:attributes> <!-- 目标方法名为batchImport时,启用声明式事务,成功提交,运行时异常回滚 --> <tx:method name="batchImport" propagation="REQUIRED"/> <tx:method name="batch*" propagation="REQUIRED"/> <!-- 设置所有findXXX方法不需要使用事务 --> <tx:method name="find*" propagation="NOT_SUPPORTED" read-only="true"/> <tx:method name="get*" propagation="NOT_SUPPORTED" read-only="true"/> <tx:method name="importJob1" propagation="REQUIRES_NEW"/> <tx:method name="importJob2" propagation="REQUIRES_NEW"/> <tx:method name="*" propagation="REQUIRED"/> </tx:attributes> </tx:advice> <!--3. 定义声明式事务的作用范围--> <aop:config> <aop:pointcut id="pointcut" expression="execution(* com.item..*Service.*(..))"/> <aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/> </aop:config> </beans>
2:service文件
public class EmployeeService { public EmployeeDao getEmployeeDao() { return employeeDao; } public void setEmployeeDao(EmployeeDao employeeDao) { this.employeeDao = employeeDao; } public BatchService getBatchService() { return batchService; } public void setBatchService(BatchService batchService) { this.batchService = batchService; } private EmployeeDao employeeDao; private BatchService batchService; public void batchImport() { for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
//此处代码为测试事务使用 // if(i==3){ // throw new RuntimeException("意料之外的异常"); // } Employee employee = new Employee(); employee.setEno(8000 + i); employee.setEname("员工" + i); employee.setSalary(4000f); employee.setDname("市场部"); employee.setHiredate(new Date()); employeeDao.insert(employee); } } public void startImportJob(){ batchService.importJob1(); if(1==1){ throw new RuntimeException("意料之外的异常"); } batchService.importJob2(); System.out.println("批量导入成功"); } }
2.3spring注解式事务
- 注解事务最大的好处是不再去xml文件中配置,哪个方法/类想使用事务就只用标记就行
- demo:

applicationContext.xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx https://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <context:component-scan base-package="com.item"/> <!--数据源--> <bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource"> <property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:33068/imooc?useSSL=false&useUnicode=true& characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true"/> <property name="username" value="root"/> <property name="password" value="Ee123"/> </bean> <!--JdbcTemplate--> <bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> </bean> <!--事务管理器--> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> </bean> <!-- 启用注解形式声明式事务 --> <tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/> </beans>
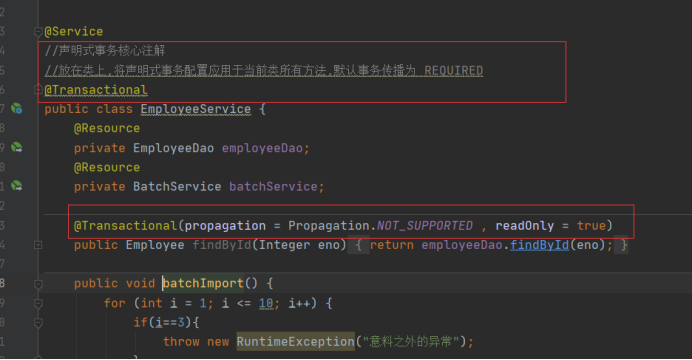
service:
@Service //声明式事务核心注解 //放在类上,将声明式事务配置应用于当前类所有方法,默认事务传播为 REQUIRED @Transactional public class EmployeeService { @Resource private EmployeeDao employeeDao; @Resource private BatchService batchService; @Transactional(propagation = Propagation.NOT_SUPPORTED , readOnly = true) public Employee findById(Integer eno){ return employeeDao.findById(eno); } public void batchImport() { for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) { if(i==3){ throw new RuntimeException("意料之外的异常"); } Employee employee = new Employee(); employee.setEno(8000 + i); employee.setEname("员工" + i); employee.setSalary(4000f); employee.setDname("市场部"); employee.setHiredate(new Date()); employeeDao.insert(employee); } } public void startImportJob(){ batchService.importJob1(); if(1==1){ throw new RuntimeException("意料之外的异常"); } batchService.importJob2(); System.out.println("批量导入成功"); } public EmployeeDao getEmployeeDao() { return employeeDao; } public void setEmployeeDao(EmployeeDao employeeDao) { this.employeeDao = employeeDao; } public BatchService getBatchService() { return batchService; } public void setBatchService(BatchService batchService) { this.batchService = batchService; } }
3.事务的传播行为
- 事务传播行为是指多个拥有事务的方法在嵌套调用时的事务控制方式
- XML: < tx:method name=”..” propagation="REQUIRED"/>
- 注解:@Transactional(propagation= Propagation.REQUIRED)
- 事务传播行为七种类型:
- PROPAGATION_REQUIRED(默认) :如果当前没有事务,就新建一个事务,如果已经存在一个事务中,加入到这个事务中。这是最常见的选择.也是系统默认。
- PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS:支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就以非事务方式执行
- PROPAGATION_MANDATORY:使用当前的事务,如果当前没有事务,就抛出异常
- PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW:新建事务,如果当前存在事务,把当前事务挂起
- PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED:以非事务方式执行操作,如果当前存在事务,就把当前事务挂起
- PROPAGATION_NEVER:以非事务方式执行,如果当前存在事务,则抛出异常
- PROPAGATION_NESTED:如果当前存在事务,则在嵌套事务内执行。如果当前没有事务,则执行与PROPAGATION_REQUIRE类似的操作
相当于只有一个事务

即便多个事务放在一起执行,也是多个事务。每个事务间互不影响





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号