POJ1942 Paths on a Grid
Imagine you are attending your math lesson at school. Once again, you are bored because your teacher tells things that you already mastered years ago (this time he's explaining that (a+b) 2=a 2+2ab+b 2). So you decide to waste your time with drawing modern art instead.
Fortunately you have a piece of squared paper and you choose a rectangle of size n*m on the paper. Let's call this rectangle together with the lines it contains a grid. Starting at the lower left corner of the grid, you move your pencil to the upper right corner, taking care that it stays on the lines and moves only to the right or up. The result is shown on the left:
![]()
Really a masterpiece, isn't it? Repeating the procedure one more time, you arrive with the picture shown on the right. Now you wonder: how many different works of art can you produce?
Fortunately you have a piece of squared paper and you choose a rectangle of size n*m on the paper. Let's call this rectangle together with the lines it contains a grid. Starting at the lower left corner of the grid, you move your pencil to the upper right corner, taking care that it stays on the lines and moves only to the right or up. The result is shown on the left:
Really a masterpiece, isn't it? Repeating the procedure one more time, you arrive with the picture shown on the right. Now you wonder: how many different works of art can you produce?
Input
The input contains several testcases. Each is specified by two unsigned 32-bit integers n and m, denoting the size of the rectangle. As you can observe, the number of lines of the corresponding grid is one more in each dimension. Input is terminated by n=m=0.
Output
For each test case output on a line the number of different art works that can be generated using the procedure described above. That is, how many paths are there on a grid where each step of the path consists of moving one unit to the right or one unit up? You may safely assume that this number fits into a 32-bit unsigned integer.
Sample Input
5 4 1 1 0 0
Sample Output
126 2
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
高中数学,就是向右走m次,向上走n次有多少种走法。
太久没写过排列组合差点忘记怎么写了,有点丢人。其实就是填坑,一共要走m+n步,相当于有m+n个坑,先选m个坑把向右走的萝卜埋进去,剩下的肯定就是向上走的了。
所以就是C(n+m,n)。然后为了避免超时,要取min(m,n)来算。
自己写的时候考虑到先阶乘再算会超,所以采用一边乘一边除的方法来做,但是发现直接除会丢余数,结果差很多。然后就用了double来写,但是实际上double也会丢精度,能过纯粹运气好数据没卡我。
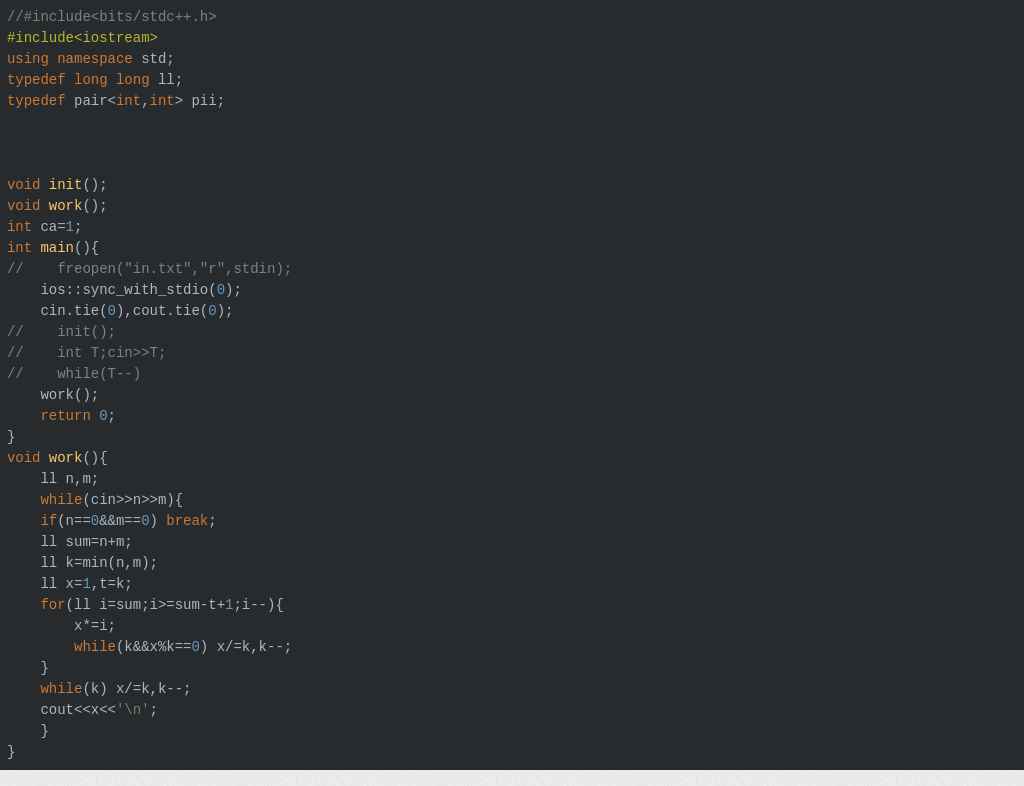
从dalao的代码那边学到了,可以先判断能不能整除,不能就先乘下一个数,乘完再除,反正最后肯定可以整除的。
自己的代码:
#include <iostream> #include <map> #include <cstdio> #include <cstdlib> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; typedef long long LL; LL m,n; int main() { while(scanf("%lld%lld",&m,&n)!=EOF) { if(m==0&&n==0)break; LL sum=m+n; double k=min(n,m); double x=1; for(LL i=0;i<min(n,m);i++) { x*=(sum/k); //printf("%lld %lld %lld\n",x,sum,k); sum--; k--; } printf("%.0lf\n",x); } return 0; }
然后放一下大佬正确的求组合数代码:




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号