题目集4~6的总结Blog
前言:
1.知识点:
- Java中的类的继承与封装
- Java中的正则表达式
- 几种排序的方法
- Java接口,以及多态的使用方法
2.题量以及难度:
- 第四次作业只有三个题,题量较少但题目难度太大题目的分值没有分配好
- 第五次作业有五个题,前几个题目难度较低,后两个题目难度较大,而且测试点不明确,错了也不知道哪里错了
- 第六次作业有六个题,题目难度依次增加,但题目内容单一,前几个只有正则表达式,且难度较低,后两个题难度适中
设计与分析:
1.题目集4(7-2)、题目集5(7-4)两种日期类聚合设计的优劣比较
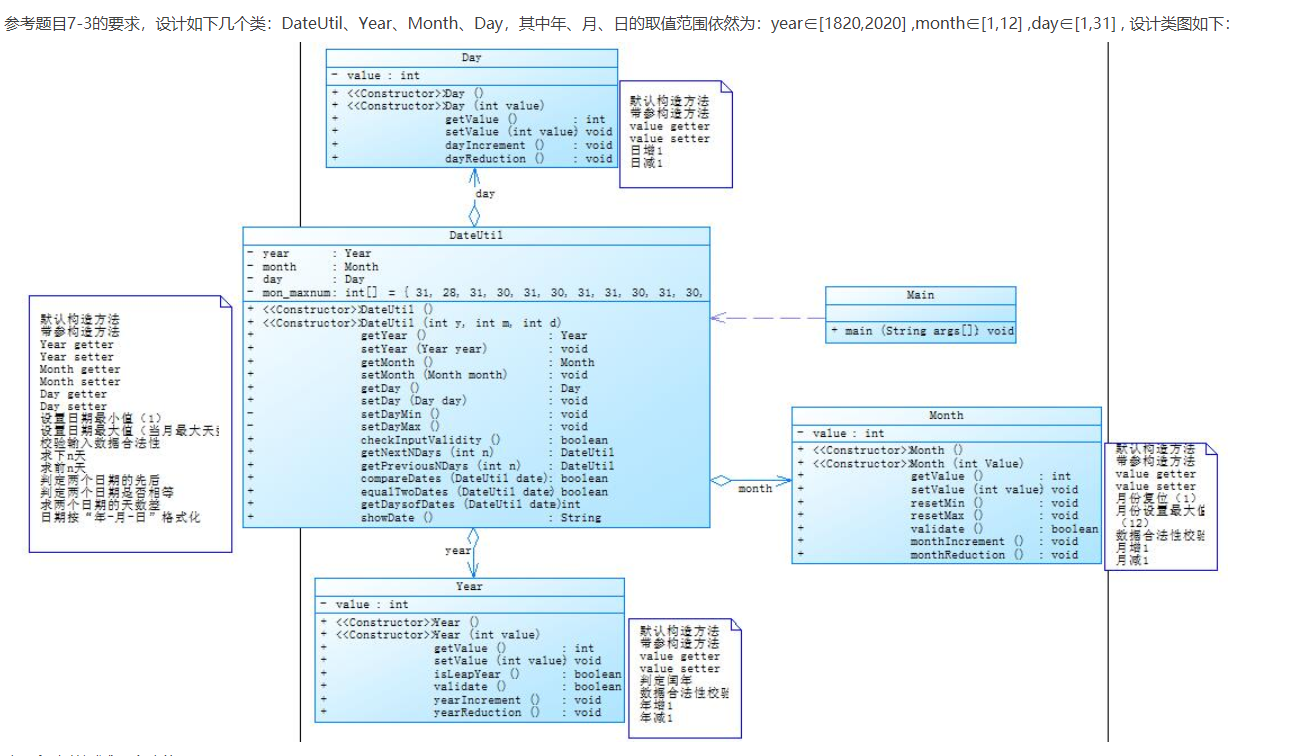
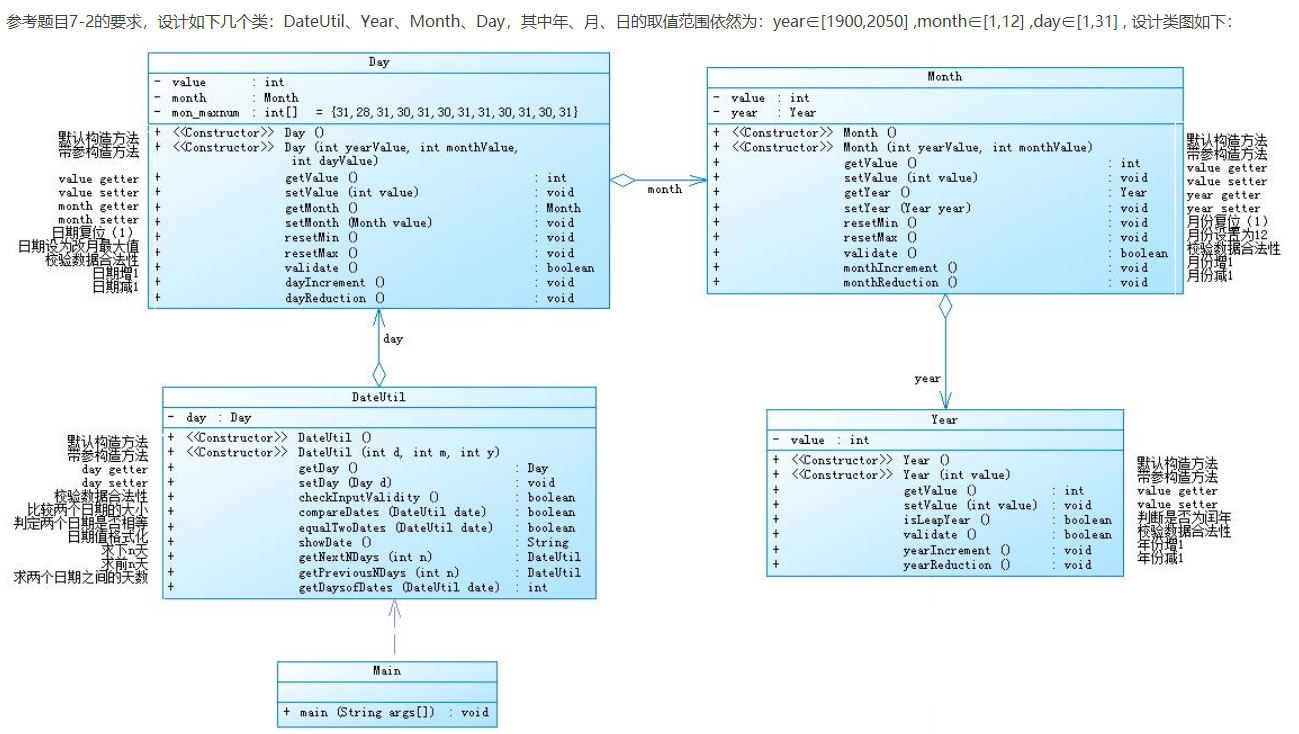
题目集4(7-2)的代码:
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input =new Scanner(System.in); int abc=input.nextInt(); if(abc<1||abc>3) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); return; } switch(abc){ case 1: int temp1=input.nextInt(); int temp2=input.nextInt(); int temp3=input.nextInt(); int temp4=input.nextInt(); if(myPrintf(temp1,temp2,temp3)==0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); return; } Date1(temp1,temp2,temp3,temp4); case 2: int sun1=input.nextInt(); int sun2=input.nextInt(); int sun3=input.nextInt(); int sun4=input.nextInt(); if(myPrintf(sun1,sun2,sun3)==0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); return; } Date2(sun1,sun2,sun3,sun4); case 3: int data1=input.nextInt(); int data2=input.nextInt(); int data3=input.nextInt(); int data4=input.nextInt(); int data5=input.nextInt(); int data6=input.nextInt(); if(myPrintf(data1,data2,data3)==0||myPrintf(data4,data5,data6)==0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); return; } int day1,day2,sun; day1=numOfDays(data1,data2,data3); day2=numOfDays(data4,data5,data6); sun=Math.abs(day2-day1); System.out.println(sun); } } public static int myPrintf(int year,int month,int day) { int[] list={31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; int x; x=isLeapYear(year); if(x==1) list[1]=29; if(year<1900||year>2050||month<1||month>12||day<1||day>31||day>list[month-1]) return 0; else return 1; } public static int isLeapYear(int year) { if(year%400==0||(year%4==0&&year%100!=0)) { return 1; } else { return 0; } } public static int numOfDays(int year,int month ,int day) { int temp=0,sum=0; for(int i=1;i<year;i++) { if(isLeapYear(i)==1) { temp=temp+366; } else { temp=temp+365; } } if(year%4==0&&year%100!=0||year%400==0) { switch(month) { case 1:sum=0;break; case 2:sum=31;break; case 3:sum=60;break; case 4:sum=91;break; case 5:sum=121;break; case 6:sum=152;break; case 7:sum=182;break; case 8:sum=213;break; case 9:sum=244;break; case 10:sum=274;break; case 11:sum=305;break; case 12:sum=335;break; } } else { switch(month) { case 1:sum=0;break; case 2:sum=31;break; case 3:sum=59;break; case 4:sum=90;break; case 5:sum=120;break; case 6:sum=151;break; case 7:sum=181;break; case 8:sum=212;break; case 9:sum=243;break; case 10:sum=273;break; case 11:sum=304;break; case 12:sum=334;break; } } temp=temp+sum+day; return temp; } public static void Date1(int year,int month,int day,int n) { int a=year,b=month,c=day; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { if(b==12&&c==31){ a++; b=1; c=1; } else if(isLeapYear(a)==1) { if((b==1||b==3||b==5||b==7||b==8||b==10||b==12)&&c==31) { b=b+1; c=1; } else if((b==4||b==6||b==9||b==11)&&c==30) { b=b+1; c=1; } else if(b==2&&c==29) { b=b+1; c=1; } else { c=c+1; } } else if(isLeapYear(a)==0) { if((b==1||b==3||b==5||b==7||b==8||b==10||b==12)&&c==31) { b=b+1; c=1; } else if((b==4||b==6||b==9||b==11)&&c==30) { b=b+1; c=1; } else if(b==2&&c==28) { b=b+1; c=1; } else { c=c+1; } } } System.out.println(a+"-"+b+"-"+c); } public static void Date2(int year,int month,int day,int n) { int a=year,b=month,c=day; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { if(b==1&&c==1){ a--; b=12; c=31; } else if(isLeapYear(a)==1) { if((b==2||b==4||b==6||b==8||b==9||b==11)&&c==1) { b--; c=31; } else if((b==5||b==7||b==10||b==12)&&c==1) { b--; c=30; } else if(b==3&&c==1) { b--; c=29; } else { c=c-1; } } else if(isLeapYear(a)==0) { if((b==1||b==2||b==4||b==6||b==8||b==9||b==11)&&c==1) { b--; c=31; } else if((b==5||b==7||b==10||b==12)&&c==1) { b--; c=30; } else if(b==3&&c==1) { b--; c=28; } else { c=c-1; } } } System.out.println(a+"-"+b+"-"+c); } }
题目集5(7-4)的代码:
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input =new Scanner(System.in); int abc=input.nextInt(); if(abc<1||abc>3) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); return; } switch(abc){ case 1: int temp1=input.nextInt(); int temp2=input.nextInt(); int temp3=input.nextInt(); long temp4=input.nextLong(); if(myPrintf(temp1,temp2,temp3)==0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); return; } System.out.print(temp1+"-"+temp2+"-"+temp3+" next "+temp4+" days is:"); Date1(temp1,temp2,temp3,temp4); case 2: int sun1=input.nextInt(); int sun2=input.nextInt(); int sun3=input.nextInt(); long sun4=input.nextLong(); if(myPrintf(sun1,sun2,sun3)==0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); return; } System.out.print(sun1+"-"+sun2+"-"+sun3+" previous "+sun4+" days is:"); Date2(sun1,sun2,sun3,sun4); case 3: int data1=input.nextInt(); int data2=input.nextInt(); int data3=input.nextInt(); int data4=input.nextInt(); int data5=input.nextInt(); int data6=input.nextInt(); if(myPrintf(data1,data2,data3)==0||myPrintf(data4,data5,data6)==0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); return; } System.out.print("The days between "+data1+"-"+data2+"-"+data3+" and "+data4+"-"+data5+"-"+data6+" are:"); int day1,day2,sun; day1=numOfDays(data1,data2,data3); day2=numOfDays(data4,data5,data6); sun=Math.abs(day2-day1); System.out.println(sun); } } public static int myPrintf(int year,int month,int day) { int[] list={31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; int x; x=isLeapYear(year); if(x==1) list[1]=29; if(year<1820||year>2020||month<1||month>12||day<1||day>31||day>list[month-1]) return 0; else return 1; } public static int isLeapYear(long year) { if(year%400==0||(year%4==0&&year%100!=0)) { return 1; } else { return 0; } } public static int numOfDays(int year,int month ,int day) { int temp=0,sum=0; for(int i=1;i<year;i++) { if(isLeapYear(i)==1) { temp=temp+366; } else { temp=temp+365; } } if(year%4==0&&year%100!=0||year%400==0) { switch(month) { case 1:sum=0;break; case 2:sum=31;break; case 3:sum=60;break; case 4:sum=91;break; case 5:sum=121;break; case 6:sum=152;break; case 7:sum=182;break; case 8:sum=213;break; case 9:sum=244;break; case 10:sum=274;break; case 11:sum=305;break; case 12:sum=335;break; } } else { switch(month) { case 1:sum=0;break; case 2:sum=31;break; case 3:sum=59;break; case 4:sum=90;break; case 5:sum=120;break; case 6:sum=151;break; case 7:sum=181;break; case 8:sum=212;break; case 9:sum=243;break; case 10:sum=273;break; case 11:sum=304;break; case 12:sum=334;break; } } temp=temp+sum+day; return temp; } public static void Date1(int year,int month,int day,long n) { long a=year,b=month,c=day; for(long i=1;i<=n;i++) { if(b==12&&c==31){ a++; b=1; c=1; } else if(isLeapYear(a)==1) { if((b==1||b==3||b==5||b==7||b==8||b==10||b==12)&&c==31) { b=b+1; c=1; } else if((b==4||b==6||b==9||b==11)&&c==30) { b=b+1; c=1; } else if(b==2&&c==29) { b=b+1; c=1; } else { c=c+1; } } else if(isLeapYear(a)==0) { if((b==1||b==3||b==5||b==7||b==8||b==10||b==12)&&c==31) { b=b+1; c=1; } else if((b==4||b==6||b==9||b==11)&&c==30) { b=b+1; c=1; } else if(b==2&&c==28) { b=b+1; c=1; } else { c=c+1; } } } System.out.println(a+"-"+b+"-"+c); } public static void Date2(int year,int month,int day,long n) { long a=year,b=month,c=day; for(long i=1;i<=n;i++) { if(b==1&&c==1){ a--; b=12; c=31; } else if(isLeapYear(a)==1) { if((b==2||b==4||b==6||b==8||b==9||b==11)&&c==1) { b--; c=31; } else if((b==5||b==7||b==10||b==12)&&c==1) { b--; c=30; } else if(b==3&&c==1) { b--; c=29; } else { c=c-1; } } else if(isLeapYear(a)==0) { if((b==1||b==2||b==4||b==6||b==8||b==9||b==11)&&c==1) { b--; c=31; } else if((b==5||b==7||b==10||b==12)&&c==1) { b--; c=30; } else if(b==3&&c==1) { b--; c=28; } else { c=c-1; } } } System.out.println(a+"-"+b+"-"+c); } }
1.题目集4(7-2)中的聚合度较低,没有体现到聚合的好处,复用性较低,不能体现这个程序的优点;
2.题目集5(7-4)中聚合度高,体现了聚合的好处,代码复用性高,各个类的联系没有那么紧密.
2.题目集4(7-3)、题目集6(7-5、7-6)三种渐进式图形继承设计的思路与技术运用(封装、继承、多态、接口等)
- 类Shape,无属,有一个返回0.0的求图形面积的公有方法
public double getArea();//求图形面积 - 类Circle,继承自Shape,有一个私有实型的属性radius(半径),重写父类继承来的求面积方法,求圆的面积
- 类Rectangle,继承自Shape,有两个私有实型属性width和length,重写父类继承来的求面积方法,求矩形的面积
- 类Ball,继承自Circle,其属性从父类继承,重写父类求面积方法,求球表面积,此外,定义一求球体积的方法
public double getVolume();//求球体积 - 类Box,继承自Rectangle,除从父类继承的属性外,再定义一个属性height,重写父类继承来的求面积方法,求立方体表面积,此外,定义一求立方体体积的方法
public double getVolume();//求立方体体积 - 注意:
- 每个类均有构造方法,且构造方法内必须输出如下内容:
Constructing 类名 - 每个类属性均为私有,且必须有getter和setter方法(可用Eclipse自动生成)
- 输出的数值均保留两位小数
主方法内,主要实现四个功能(1-4): 从键盘输入1,则定义圆类,从键盘输入圆的半径后,主要输出圆的面积; 从键盘输入2,则定义矩形类,从键盘输入矩形的宽和长后,主要输出矩形的面积; 从键盘输入3,则定义球类,从键盘输入球的半径后,主要输出球的表面积和体积; 从键盘输入4,则定义立方体类,从键盘输入立方体的宽、长和高度后,主要输出立方体的表面积和体积;
假如数据输入非法(包括圆、矩形、球及立方体对象的属性不大于0和输入选择值非1-4),系统输出Wrong Format
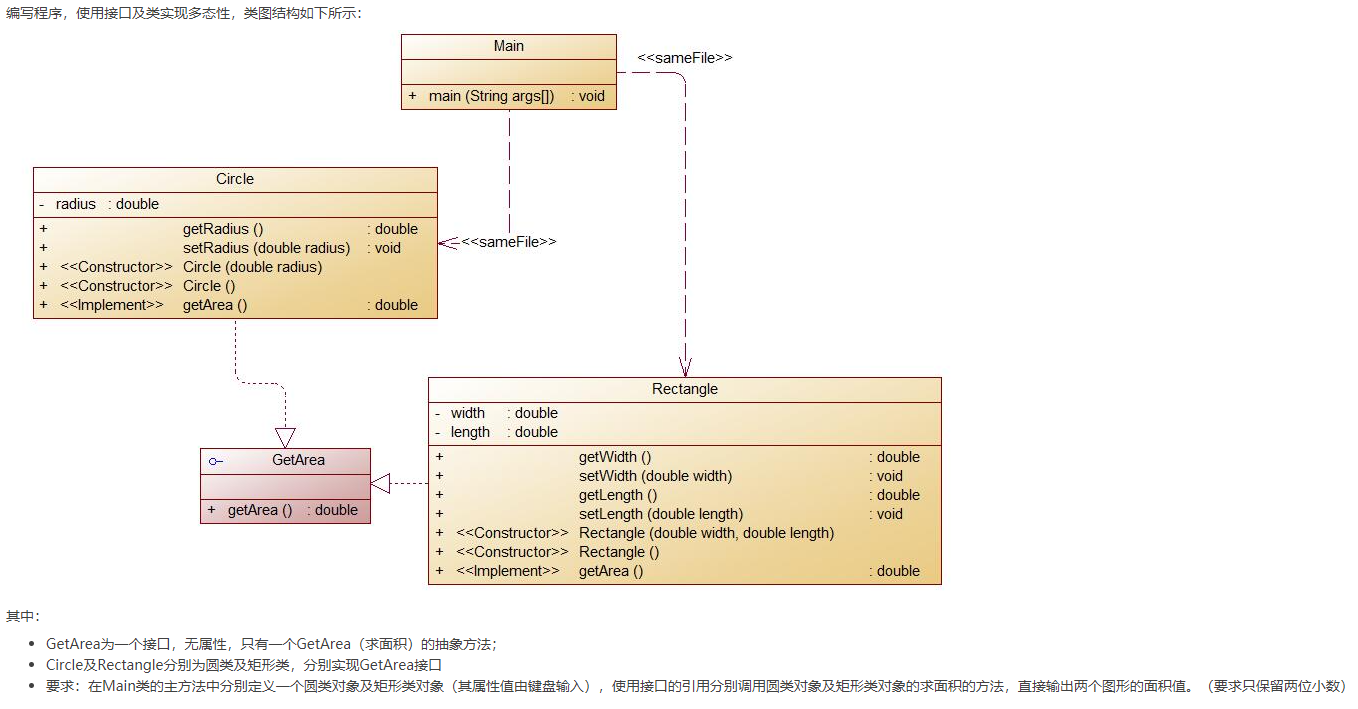
1.题目集4(7-3),这一题主要运用了封装,继承,没有使用多态和接口,题目比较简单,先定义一个父类shape,然后让另外几个类继承就行,使用了构造方法
2.题目集6(7-5、7-6)这一题主要运用了封装,继承,也要使用接口和多态,先定义一个抽象方法.
3.对三次题目集中用到的正则表达式技术的分析总结:
"[1-9][0-9]{4,14}"
"[a-zA-Z0-9]{4}"
String list1= "[2][0][2][0][1][1-7][1-3][0-9]{8}";
String list2= "[2][0][2][0][1][1-7][4][0]{8}";
String list3= "[2][0][2][0][6][1][1-3][0-9]{8}";
String list4= "[2][0][2][0][6][1][4][0]{8}";
String list5= "[2][0][2][0][7][1-3][1-3][0-9]{8}";
String list6= "[2][0][2][0][7][1-3][4][0]{8}";
String list7= "[2][0][2][0][8][1-2][1-3][0-9]{8}";
String list8= "[2][0][2][0][8][1-2][4][0]{8}";
1.正则表达式还是我不太会的地方,这几个简单的题还是写出来了,难题还是不会.
2.了解了java.util.regex是一个用正则表达式所订制的模式来对字符串进行匹配工作的类库包。它包括两个类:Pattern和Matcher Pattern 一个Pattern是一个正则表达式经编译后的表现模式。 Matcher 一个Matcher对象是一个状态机器,它依据Pattern对象做为匹配模式对字符串展开匹配检查。 首先一个Pattern实例订制了一个所用语法与PERL的类似的正则表达式经编译后的模式,然后一个Matcher实例在这个给定的Pattern实例的模式控制下进行字符串的匹配工作。
会了一些Pattern和Matcher 的用法.
3.Pattern类用于创建一个正则表达式,也可以说创建一个匹配模式,它的构造方法是私有的,不可以直接创建,但可以通过Pattern.complie(String regex)简单工厂方法创建一个正则表达式,.
当使用matches(),lookingAt(),find()执行匹配操作后,就可以利用以上三个方法得到更详细的信息.
4.start()返回匹配到的子字符串在字符串中的索引位置.
end()返回匹配到的子字符串的最后一个字符在字符串中的索引位置.
group()返回匹配到的子字符串
4.题目集5(7-4)中Java集合框架应用的分析总结
这个题目比较难,我目前还不会写,,在网上找了一些关于集合框架的东西
1.框架可以这样来理解,如建一座房子,先把房子的梁、柱子建起来,这就是一个房子的框架。至于房子内部怎样,哪里是房间,哪里是客厅,就看设计者。软件也是一样,把一个软件的大概的梁、柱子建起来,就是软件的框架。一个软件半成品,帮你做了一些基础工作,你就可以在这个基础之上,来定制适合你自己的应用。流行的框架非常灵活,以适应不同的需求。打个比方,如果你输入到屏幕上用System.out.println()如果println方法都要自己去实现,那么是不是很恐怖。所以框架在解决大规模的问题上,这些基础工作是必需的。
2.框架就是一颗松树,你只要在上边挂点装饰物和几片小雪花,装几个小电灯,它就可以变成炫目喜庆的圣诞树。
采坑心得:
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner abc=new Scanner(System.in); int a=abc.nextInt(); if(a<1||a>4){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); return; } switch(a) { case 1: double r=abc.nextDouble(); if(r<0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); return; } Circle sc1=new Circle(); System.out.println("Circle's area:"+String.format("%.2f",Circle.getArea(r))); case 2: double width=abc.nextDouble(); double length=abc.nextDouble(); if(length<0||width<0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); return; } Rectangle sc2=new Rectangle(); System.out.println("Rectangle's area:"+String.format("%.2f",Rectangle.getArea(width,length))); case 3: double data=abc.nextDouble(); if(data<0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); return; } Ball sc3=new Ball(); System.out.println("Ball's surface area:"+String.format("%.2f",Ball.getArea(data))); System.out.println("Ball's volume:"+String.format("%.2f",Ball.getVolume(data))); case 4: double data1=abc.nextDouble(); double data2=abc.nextDouble(); double data3=abc.nextDouble(); if(data1<0||data2<0||data3<0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); return; } Box sc4=new Box(); System.out.println("Box's surface area:"+String.format("%.2f",Box.getArea(data1,data2,data3))); System.out.println("Box's volume:"+String.format("%.2f",Box.getVolume(data1,data2,data3))); } } } class Shape{ public Shape(){ System.out.println("Constructing Shape"); } public static double getArea(double r){ return 0.0; } } class Circle extends Shape{ private double radius; public Circle(double r) { // TODO 自动生成的构造函数存根 this.radius =r; } public double getRadius() { return radius; } public void setRadius(double radius) { this.radius = radius; } public Circle(){ System.out.println("Constructing Circle"); } public static double getArea(double r){ return Math.PI*r*r; } } class Rectangle extends Shape{ private double width; private double length; public double getWidth() { return width; } public void setWidth(double width) { this.width = width; } public double getLength() { return length; } public void setLength(double length) { this.length = length; } public Rectangle(){ System.out.println("Constructing Rectangle"); } public Rectangle(double width,double length) { // TODO 自动生成的构造函数存根 this.width=width; this.length =length; } public static double getArea(double width,double length){ return width*length; } } class Ball extends Circle{ private double radius; public double getRadius() { return radius; } public void setRadius(double radius) { this.radius = radius; } public Ball(double data) { // TODO 自动生成的构造函数存根 this.radius=data; } public Ball(){ System.out.println("Constructing Ball"); } public static double getArea(double radius){ return 4*Math.PI*radius*radius; } public static double getVolume(double radius) { return (4*Math.PI*radius*radius*radius)/3; } } class Box extends Rectangle{ private double width; private double length; private double height; public double getWidth() { return width; } public void setWidth(double width) { this.width = width; } public double getLength() { return length; } public void setLength(double length) { this.length = length; } public double getHeight() { return height; } public void setHeight(double height) { this.height = height; } public Box(double width,double length,double height) { // TODO 自动生成的构造函数存根 this.width=width; this.length =length; this.height=height; } public Box(){ System.out.println("Constructing Box"); } public static double getArea(double width,double length,double height){ return (width*length+width*height+height*length)*2; } public static double getVolume(double width,double length,double height) { return width*length*height; } }
1.在题目集四中计算两个日期相差的天数的时候,一开始老是想不到如何去计算,一直出错,后来想起之前写过求一个日期到一月一号的天数,想到用两个日期同时减去一个日期,然后再用两个书相减,这样便解决了这个问题.
2.在使用插入排序的时候忘记了j的变化,导致一开始排序一直出错,说明自己对这几种排序方式还不熟练,还要加强.
3.在对字符串进行升序排列时不知道可以将字符串转化为数组,用Arrays.sort()来进行排序,浪费了好多时间,还写不出来.
4.在使用接口时忘记定义抽象类,导致代码不能运行,这方面还要加强.
改进建议:对相应题目的编码改进给出自己的见解,做到可持续改进
1.在写代码的时候尽量使用类的封装,养成良好的习惯.
2.多使用继承,接口等方式,增强代码的复用性,同时增加代码的安全性;
3.要及时复习之前学习过的东西,课后及时复习;
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input =new Scanner(System.in); int abc=input.nextInt(); if(abc<1||abc>3) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); return; } switch(abc){ case 1: int temp1=input.nextInt(); int temp2=input.nextInt(); int temp3=input.nextInt(); long temp4=input.nextLong(); if(myPrintf(temp1,temp2,temp3)==0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); return; } System.out.print(temp1+"-"+temp2+"-"+temp3+" next "+temp4+" days is:"); Date1(temp1,temp2,temp3,temp4); case 2: int sun1=input.nextInt(); int sun2=input.nextInt(); int sun3=input.nextInt(); long sun4=input.nextLong(); if(myPrintf(sun1,sun2,sun3)==0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); return; } System.out.print(sun1+"-"+sun2+"-"+sun3+" previous "+sun4+" days is:"); Date2(sun1,sun2,sun3,sun4); case 3: int data1=input.nextInt(); int data2=input.nextInt(); int data3=input.nextInt(); int data4=input.nextInt(); int data5=input.nextInt(); int data6=input.nextInt(); if(myPrintf(data1,data2,data3)==0||myPrintf(data4,data5,data6)==0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); return; } System.out.print("The days between "+data1+"-"+data2+"-"+data3+" and "+data4+"-"+data5+"-"+data6+" are:"); int day1,day2,sun; day1=numOfDays(data1,data2,data3); day2=numOfDays(data4,data5,data6); sun=Math.abs(day2-day1); System.out.println(sun); } } public static int myPrintf(int year,int month,int day) { int[] list={31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; int x; x=isLeapYear(year); if(x==1) list[1]=29; if(year<1820||year>2020||month<1||month>12||day<1||day>31||day>list[month-1]) return 0; else return 1; } public static int isLeapYear(long year) { if(year%400==0||(year%4==0&&year%100!=0)) { return 1; } else { return 0; } } public static int numOfDays(int year,int month ,int day) { int temp=0,sum=0; for(int i=1;i<year;i++) { if(isLeapYear(i)==1) { temp=temp+366; } else { temp=temp+365; } } if(year%4==0&&year%100!=0||year%400==0) { switch(month) { case 1:sum=0;break; case 2:sum=31;break; case 3:sum=60;break; case 4:sum=91;break; case 5:sum=121;break; case 6:sum=152;break; case 7:sum=182;break; case 8:sum=213;break; case 9:sum=244;break; case 10:sum=274;break; case 11:sum=305;break; case 12:sum=335;break; } } else { switch(month) { case 1:sum=0;break; case 2:sum=31;break; case 3:sum=59;break; case 4:sum=90;break; case 5:sum=120;break; case 6:sum=151;break; case 7:sum=181;break; case 8:sum=212;break; case 9:sum=243;break; case 10:sum=273;break; case 11:sum=304;break; case 12:sum=334;break; } } temp=temp+sum+day; return temp; } public static void Date1(int year,int month,int day,long n) { long a=year,b=month,c=day; for(long i=1;i<=n;i++) { if(b==12&&c==31){ a++; b=1; c=1; } else if(isLeapYear(a)==1) { if((b==1||b==3||b==5||b==7||b==8||b==10||b==12)&&c==31) { b=b+1; c=1; } else if((b==4||b==6||b==9||b==11)&&c==30) { b=b+1; c=1; } else if(b==2&&c==29) { b=b+1; c=1; } else { c=c+1; } } else if(isLeapYear(a)==0) { if((b==1||b==3||b==5||b==7||b==8||b==10||b==12)&&c==31) { b=b+1; c=1; } else if((b==4||b==6||b==9||b==11)&&c==30) { b=b+1; c=1; } else if(b==2&&c==28) { b=b+1; c=1; } else { c=c+1; } } } System.out.println(a+"-"+b+"-"+c); } public static void Date2(int year,int month,int day,long n) { long a=year,b=month,c=day; for(long i=1;i<=n;i++) { if(b==1&&c==1){ a--; b=12; c=31; } else if(isLeapYear(a)==1) { if((b==2||b==4||b==6||b==8||b==9||b==11)&&c==1) { b--; c=31; } else if((b==5||b==7||b==10||b==12)&&c==1) { b--; c=30; } else if(b==3&&c==1) { b--; c=29; } else { c=c-1; } } else if(isLeapYear(a)==0) { if((b==1||b==2||b==4||b==6||b==8||b==9||b==11)&&c==1) { b--; c=31; } else if((b==5||b==7||b==10||b==12)&&c==1) { b--; c=30; } else if(b==3&&c==1) { b--; c=28; } else { c=c-1; } } } System.out.println(a+"-"+b+"-"+c); } }
在这个题目中不要用这么大一串代码去写日期的变化,可以直接用一个循环去求.
总结:
1.课后多看书巩固知识点,课前复习,尽量将代码做的更好.
2.在这几次作业中,我学习了正则表达式,继承,多态,接口等新的东西,学到了很多.
3.我觉得上课的参与还是不够多,老师要多和学生交流,增强两者之间的互动.
4.我觉得pta上面的题目的难度应该要梯度增加,分值也要分配均匀一点
5.我觉得pta上面的题目的测试点应该告诉出来,不然连哪里错了都不知道.
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner abc=new Scanner(System.in);int a=abc.nextInt();if(a<1||a>4){System.out.println("Wrong Format");return;}switch(a){case 1: double r=abc.nextDouble();if(r<0) {System.out.println("Wrong Format");return;}Circle sc1=new Circle();System.out.println("Circle's area:"+String.format("%.2f",Circle.getArea(r)));case 2: double width=abc.nextDouble();double length=abc.nextDouble();if(length<0||width<0) {System.out.println("Wrong Format");return;}Rectangle sc2=new Rectangle();System.out.println("Rectangle's area:"+String.format("%.2f",Rectangle.getArea(width,length)));case 3: double data=abc.nextDouble();if(data<0) {System.out.println("Wrong Format");return;}Ball sc3=new Ball();System.out.println("Ball's surface area:"+String.format("%.2f",Ball.getArea(data)));System.out.println("Ball's volume:"+String.format("%.2f",Ball.getVolume(data)));case 4:double data1=abc.nextDouble();double data2=abc.nextDouble();double data3=abc.nextDouble();if(data1<0||data2<0||data3<0) {System.out.println("Wrong Format");return;}Box sc4=new Box();System.out.println("Box's surface area:"+String.format("%.2f",Box.getArea(data1,data2,data3)));System.out.println("Box's volume:"+String.format("%.2f",Box.getVolume(data1,data2,data3)));}}}class Shape{ public Shape(){System.out.println("Constructing Shape");}public static double getArea(double r){return 0.0;}}class Circle extends Shape{private double radius;public Circle(double r) {// TODO 自动生成的构造函数存根this.radius =r;}public double getRadius() {return radius;}public void setRadius(double radius) {this.radius = radius;}public Circle(){System.out.println("Constructing Circle");}public static double getArea(double r){return Math.PI*r*r;}}class Rectangle extends Shape{private double width;private double length;public double getWidth() {return width;}public void setWidth(double width) {this.width = width;}public double getLength() {return length;}public void setLength(double length) {this.length = length;}public Rectangle(){System.out.println("Constructing Rectangle");}public Rectangle(double width,double length) {// TODO 自动生成的构造函数存根this.width=width;this.length =length;}public static double getArea(double width,double length){return width*length;}}class Ball extends Circle{private double radius;public double getRadius() {return radius;}public void setRadius(double radius) {this.radius = radius;}public Ball(double data) {// TODO 自动生成的构造函数存根this.radius=data;}public Ball(){System.out.println("Constructing Ball");}public static double getArea(double radius){return 4*Math.PI*radius*radius;}public static double getVolume(double radius) {return (4*Math.PI*radius*radius*radius)/3;}}class Box extends Rectangle{private double width;private double length;private double height;public double getWidth() {return width;}public void setWidth(double width) {this.width = width;}public double getLength() {return length;}public void setLength(double length) {this.length = length;}public double getHeight() {return height;}public void setHeight(double height) {this.height = height;}public Box(double width,double length,double height) {// TODO 自动生成的构造函数存根this.width=width;this.length =length;this.height=height;}public Box(){System.out.println("Constructing Box");}public static double getArea(double width,double length,double height){return (width*length+width*height+height*length)*2;}public static double getVolume(double width,double length,double height) {return width*length*height;}}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号