高级语言程序设计第九次个人作业
作业内容
- 声明一个结构体类型,用来存放某个学生的姓名、学号、性别、班级、三科成绩,并且打印出来该学生信息。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
//存放学生信息的结构体
struct students{
char name[50];
unsigned num;
char sex;
unsigned classes;
float score1,score2,score3;
};
int main(void) {
students stu;
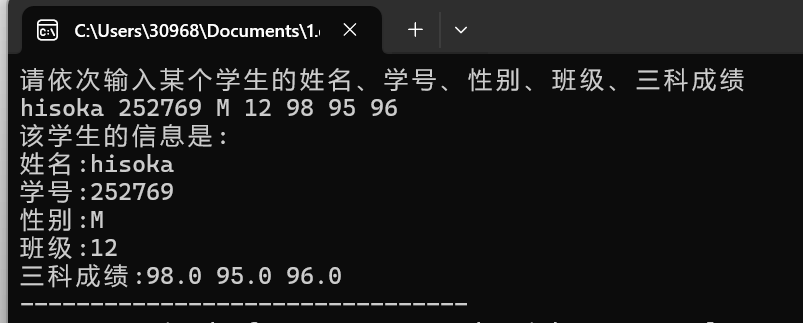
printf("请依次输入某个学生的姓名、学号、性别、班级、三科成绩\n");
scanf("%s%d %c %d%f%f%f",stu.name,&stu.num,&stu.sex,&stu.classes,&stu.score1,&stu.score2,&stu.score3);
printf("该学生的信息是:\n");
printf("姓名:%s\n学号:%d\n性别:%c\n班级:%d\n三科成绩:%.1f %.1f %.1f",stu.name,stu.num,stu.sex,stu.classes,stu.score1,stu.score2,stu.score3); //依次输出学生信息
return 0;
}
![屏幕截图 2025-12-12 183723]()
- 定义一个结构体数组,用来存放班级中N个学生以上信息,编写三个函数进行信息输入、排序和输出。分别使用数组和指针作为函数参数,完成学生信息输入、以及成绩从小到大排序、按排序顺序进行信息输出。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAX_NUM 100
struct student {
char name[50];
unsigned int num;
char gender;
unsigned int class_num;
float score;
};
// 输入学生信息
void input(int n, struct student stu[]) {
printf("请输入 %d 个学生的姓名、学号、性别、班级、成绩\n", n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
printf("学生 %d: ", i + 1);
scanf("%s %u %c %u %f",
stu[i].name,
&stu[i].num,
&stu[i].gender,
&stu[i].class_num,
&stu[i].score);
}
}
// 输出学生信息
void output(int n, struct student stu[]) {
printf("\n排序后的学生信息:\n");
printf("姓名\t学号\t性别\t班级\t成绩\n");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
printf("%s\t%u\t%c\t%u\t%.1f\n",
stu[i].name,
stu[i].num,
stu[i].gender,
stu[i].class_num,
stu[i].score);
}
}
// 按成绩从小到大排序(冒泡排序)
void sort(int n, struct student stu[]) {
struct student temp;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n - i - 1; j++) {
if (stu[j].score > stu[j + 1].score) {
// 交换
temp = stu[j];
stu[j] = stu[j + 1];
stu[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
int main() {
int n;
struct student stu[MAX_NUM];
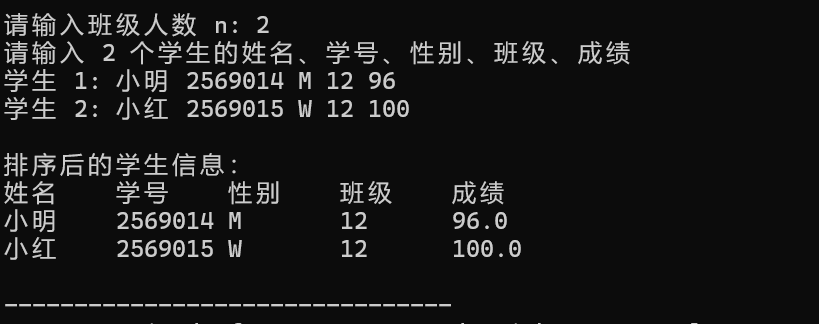
printf("请输入班级人数 n: ");
scanf("%d", &n);
if (n <= 0 || n > MAX_NUM) {
printf("人数无效,应在 1 到 %d 之间\n", MAX_NUM);
return 1;
}
input(n, stu);
sort(n, stu);
output(n, stu);
return 0;
}
![屏幕截图 2025-12-15 180237]()
- 设计一个程序以指针和结构体变量名分别访问结构体变量的成员,进行输出。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define max_num 100
struct students{
char name[50];
unsigned num;
char sex;
unsigned classes;
float score;
};
int main(void) {
students stu;
struct students *p=&stu; //定义一个指向结构体的指针
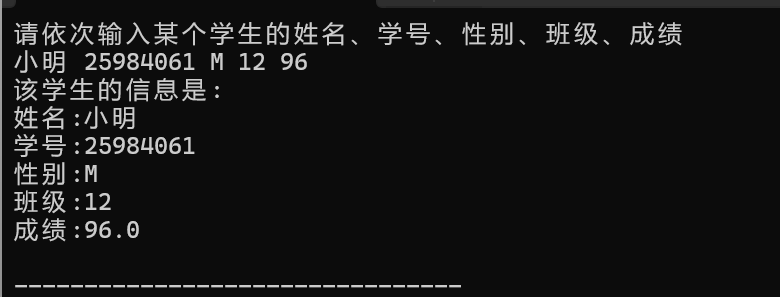
printf("请依次输入某个学生的姓名、学号、性别、班级、成绩\n");
scanf("%s%d %c %d%f",stu.name,&stu.num,&stu.sex,&stu.classes,&stu.score);
//变量名输出
printf("用变量名输出该学生的信息是:\n");
printf("姓名:%s\n学号:%d\n性别:%c\n班级:%d\n成绩:%.1f\n\n",stu.name,stu.num,stu.sex,stu.classes,stu.score);
//指针输出
printf("用指针输出该学生的信息是:\n");
printf("姓名:%s\n学号:%d\n性别:%c\n班级:%d\n成绩:%.1f",p->name,p->num,p->sex,p->classes,p->score);
return 0;
}
![屏幕截图 2025-12-14 202718]()
- 设计一个程序使用typedef定义结构体类型的别名。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define max_num 100
typedef struct { //typedef定义结构体类型的别名
char name[50];
unsigned num;
char sex;
unsigned classes;
float score;
}students;
int main(void) {
students stu;
printf("请依次输入某个学生的姓名、学号、性别、班级、成绩\n");
scanf("%s%d %c %d%f",stu.name,&stu.num,&stu.sex,&stu.classes,&stu.score);
printf("该学生的信息是:\n");
printf("姓名:%s\n学号:%d\n性别:%c\n班级:%d\n成绩:%.1f\n",stu.name,stu.num,stu.sex,stu.classes,stu.score);
return 0;
}
![image]()
- 建立一个链表,链表的节点个数为N(>5),使用从链尾到链头的建立方式和从链头到链尾的建立方式。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#define max_num 100
struct node {
int num;
struct node* next;
};
int main(void) {
int data[10]={0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
node *head,*r;
head=(node *)malloc(sizeof (node));
head->next=NULL;
r=head;
int N;
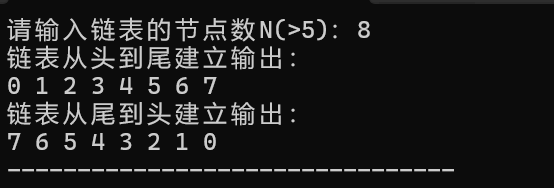
printf("请输入链表的节点数N(>5):");
scanf("%d",&N);
//链表从头到尾建立
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
node *p;
p=(node *)malloc(sizeof (node));
p->num=data[i];
r->next=p;
r=p;
}
r->next=NULL;
printf("链表从头到尾建立输出:\n");
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
head=head->next;
printf("%d ",head->num);
}
printf("\n");
//链表从尾到头建立
head->next=NULL;
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
node *p;
p=(node *)malloc(sizeof (node));
p->num=data[i];
p->next=head->next;
head->next=p;
}
printf("链表从尾到头建立输出:\n");
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
head=head->next;
printf("%d ",head->num);
}
return 0;
}
![屏幕截图 2025-12-14 214637]()
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#define max_num 100
struct node {
int num;
struct node* next;
};
int main(void) {
int data[10]={0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
int del;
node *head,*r;
head=(node *)malloc(sizeof (node));
head->next=NULL;
r=head;
int N;
printf("请输入链表的节点数N(>5):");
scanf("%d",&N);
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
node *p;
p=(node *)malloc(sizeof (node));
p->num=data[i];
r->next=p;
r=p;
}
r->next=NULL;
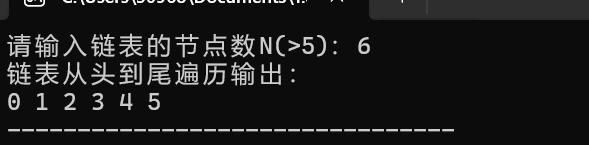
printf("链表从头到尾遍历输出:\n");
for(node* p=head->next;p!=NULL;p=p->next){ //对链表进行遍历输出
printf("%d ",p->num);
}
return 0;
}
![屏幕截图 2025-12-14 221031]()
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#define max_num 100
struct node {
int num;
struct node* next;
};
int main(void) {
int data[10]={0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
int del;
node *head,*r;
head=(node *)malloc(sizeof (node));
head->next=NULL;
r=head;
int N;
printf("请输入链表的节点数N(>5):");
scanf("%d",&N);
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
node *p;
p=(node *)malloc(sizeof (node));
p->num=data[i];
r->next=p;
r=p;
}
r->next=NULL;
printf("链表从头到尾遍历输出:\n");
for(node* p=head->next;p!=NULL;p=p->next){ //对链表进行遍历输出
printf("%d ",p->num);
}
printf("\n");
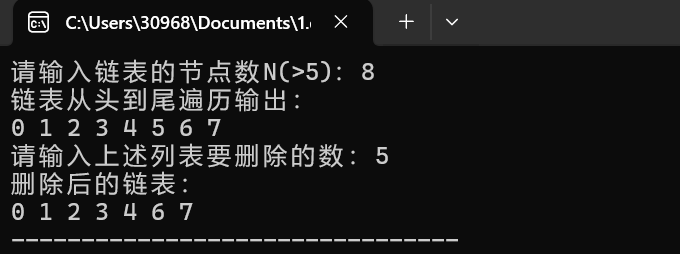
printf("请输入上述列表要删除的数:");
scanf("%d",&del);
node *pre;
node *p=head->next;
while(p->num!=del){ //找要删除的数的位置
pre=p;
p=p->next;
}
pre->next=p->next; //删除数
free(p);
printf("删除后的链表:\n");
for(node* p=head->next;p!=NULL;p=p->next){
printf("%d ",p->num);
}
return 0;
}
![屏幕截图 2025-12-14 220935]()
- 编写程序根据一定的条件,删除多个节点,该条件要在作业中写出。
//删除用户输入范围内的所有数,然后输出删除后的链表
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#define max_num 100
struct node {
int num;
struct node* next;
};
int main(void) {
int data[10]={0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
int del;
node *head,*r;
head=(node *)malloc(sizeof (node));
head->next=NULL;
r=head;
int N;
printf("请输入链表的节点数N(>5):");
scanf("%d",&N);
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){ //建立链表
node *p;
p=(node *)malloc(sizeof (node));
p->num=data[i];
r->next=p;
r=p;
}
r->next=NULL;
printf("链表从头到尾遍历输出:\n");
for(node* p=head->next;p!=NULL;p=p->next){
printf("%d ",p->num);
}
printf("\n");
int min,max;
printf("请输入上述列表要删除的数的范围:"); //删除范围在min-max之间的数
scanf("%d%d",&min,&max);
node *pre;
for(node* p=head->next;p!=NULL;p=p->next){
if(p->num>=min&&p->num<=max){
pre->next=p->next;
p=pre; //tips:返回前一个重新判断,以防漏判断p->next这个节点
}
else pre=p;
}
printf("删除后的链表:\n");
for(node* p=head->next;p!=NULL;p=p->next){
printf("%d ",p->num);
}
return 0;
}
![屏幕截图 2025-12-14 223106]()
- 编写程序根据一定的条件,插入多个节点,该条件要在作业中写出。
//插入数在用户指定位置,并由用户提供插入的数的个数和具体的值
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#define max_num 100
struct node {
int num;
struct node* next;
};
int main(void) {
int data[10]={0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
int del;
node *head,*r;
head=(node *)malloc(sizeof (node));
head->next=NULL;
r=head;
int N;
printf("请输入链表的节点数N(>5):");
scanf("%d",&N);
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
node *p;
p=(node *)malloc(sizeof (node));
p->num=data[i];
r->next=p;
r=p;
}
r->next=NULL;
printf("链表从头到尾遍历输出:\n");
for(node* p=head->next;p!=NULL;p=p->next){
printf("%d ",p->num);
}
printf("\n");
int ad,n;
int number[50];
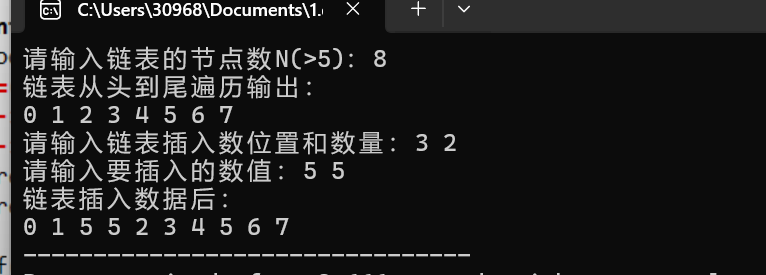
printf("请输入链表插入数位置和数量:"); //用户输入插入位置和插入个数
scanf("%d%d",&ad,&n);
printf("请输入要插入的数值:"); //用户输入插入数值
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
scanf("%d",&number[i]);
}
node *pre;
pre=head;
for(int i=1;i<ad;i++){ //找到要插入的位置
pre=pre->next;
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ //依次插入用户提供的值
node *p;
p=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
p->num=number[i];
p->next=pre->next;
pre->next=p;
pre=pre->next;
}
printf("链表插入数据后:\n");
for(node* p=head->next;p!=NULL;p=p->next){ //输出插入数后的链表
printf("%d ",p->num);
}
return 0;
}
![屏幕截图 2025-12-14 225241]()




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号